给你四个正整数 \(a,\,b,\,c,\,d\) ,求一个最简分数 \(\frac{p}{q}\) 满足 \(\frac{a}{b} < \frac{p}{q} < \frac{c}{d}\)。
若有多组解,输出 \(q\) 最小的一组,若仍有多组解,输出 \(p\) 最小的一组。
Stern-Brocot 树
首先引入分数逼近。这里的分数逼近是指用用一个分数来逼近另一个分数,使得误差趋于零。例如,假设需要逼近的分数为 \(\dfrac{r}{s}\),有分数 \(\dfrac{u}{v} > \dfrac{r}{s}\)。那么有以下结论:
\[\dfrac{r}{s} \leq \dfrac{r + u}{s + v} \leq \dfrac{u}{v} \]具体等号能不能取到记不清了,不过不影响。结论很好证明,下面证一下。
将 \(\dfrac{r + u}{s + v}\) 与 \(\dfrac{r}{s}\) 做减法,得到 \(\dfrac{r + u}{s + v} - \dfrac{r}{s} = \dfrac{(r + u)s - r(s + v)}{s(s + v)} = \dfrac{us- vr}{s(s + v)}\)。
因为 \(\dfrac{r}{s} < \dfrac{u}{v}\),两边同时乘以 \(sv\),得 \(vr < us\),即 \(us - vr > 0\)。
又因为 \(s(s + v) > 0\),所以 \(\dfrac{us - vr}{s(s + v)} > 0\)。证毕。
注意上面结论和证明成立的条件是 \(u, v, s, r > 0\)。
接下来引入 Stern-Brocot 树这个概念。
Stern-Brocot 树可以维护所有的正分数。这一点可以被我们用来解决这道题目。
首先介绍一下 Stern-Brocot 树。这个树由 \(\dfrac{0}{1}\) 和 \(\dfrac{1}{0}\) 两个分数开始。\(\dfrac{1}{0}\) 不大好定义,暂且把它当做 \(+ \infty\)。将这两个分数作为源节点。
接下来,像我们刚才讨论的分数逼近,将 \(\dfrac{0}{1}\) 和 \(\dfrac{1}{0}\) 的分子分母分别相加,得到另外一个分数 \(\dfrac{1}{1}\)。这个分数确实在 \(\dfrac{0}{1}\) 与 \(\dfrac{1}{0}\) 之间。\(\dfrac{1}{1}\) 被成为第 \(1\) 层迭代后的节点。
同样的,将 \(\dfrac{1}{1}\) 与 \(\dfrac{0}{1}, \dfrac{1}{0}\) 分别进行操作,得到两个分数,称为第二次迭代。
所以我们得到了 Stern-Brocot 树的构建基础:将 \(\dfrac{a}{b}\) 与 \(\dfrac{c}{d}\) 分子分母分别相加,得到 \(\dfrac{a + c}{b + d}\) 作为下一轮迭代的节点。
例如,进行三次操作后,这棵树就会变成这样:
\[\begin{array}{c} \dfrac{0}{1}, \dfrac{1}{1}, \dfrac{1}{0} \\\\ \dfrac{0}{1}, \dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{1}{1}, \dfrac{2}{1}, \dfrac{1}{0} \\\\ \dfrac{0}{1}, \dfrac{1}{3}, \dfrac{1}{2}, \dfrac{2}{3}, \dfrac{1}{1}, \dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{2}{1}, \dfrac{3}{1}, \dfrac{1}{0} \end{array} \]注意,某些节点(就是第 \(i\) 层存在,第 \(i + 1\) 层也存在的节点),实际上在第 \(i + 1\) 层是不会出现的。只是为了方便比较加了上去。
可以看到,第三层的第二个分数 \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) 就是左右两边两个数分子分母分别相加的和。第四个,第六个和第八个以此类推。
下面是来自 OI-wiki 的一张图。
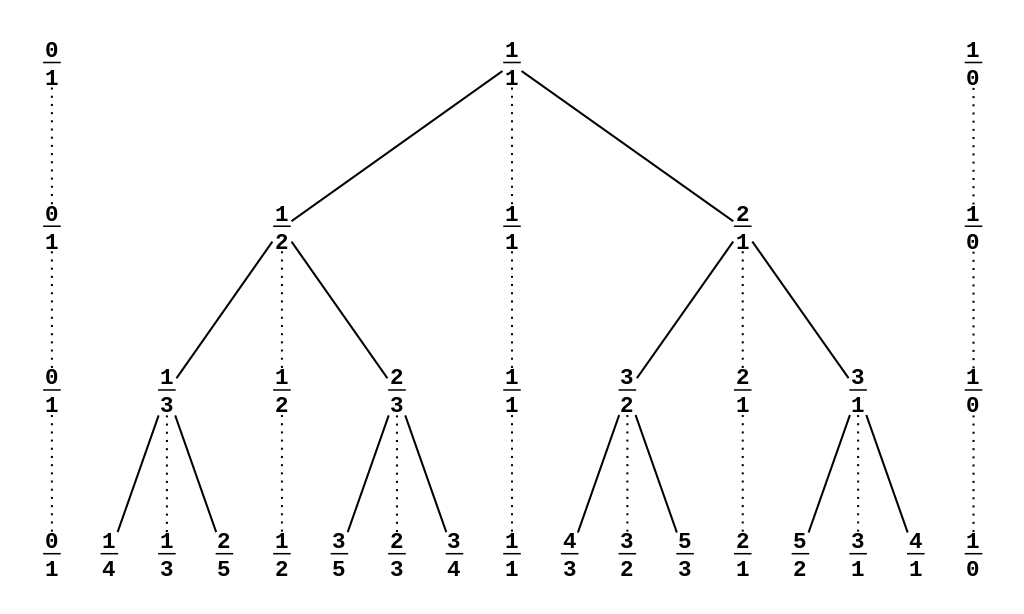
刚才所提到的不存在的节点就是虚线相连的那些节点。可以看到,这棵树具有二叉结构。因此在这棵树上搜索只需要花费 \(O(\log_2 n)\) 的时间。非常优秀。
关于最简性的证明可以看 OI-wiki 上的解释。这里不再赘述。
对于这道题,显然可以在 Stern-Brocot 树上二分来求解。具体的,如果当前结果 \(\dfrac{x}{y}\) 在左端点 \(\dfrac{A}{B}\) 的左边,则向右递归,反之亦然。于是可以写出这样的代码:
void solve(int a = 0, int b = 1, int c = 1, int d = 0) {
int x = a + c, y = b + d;
long double now = (long double)x / y;
long double L = (long double)A / B, R = (long double)C / D;
if (now > L && now < R) {
ans = {x, y}; return;
}
if (now <= L) solve(x, y, c, d);
else solve(a, b, x, y);
}
交上去以后发现只有 \(60\) 分。说明我们需要继续优化算法。
如果把递归时的路径打印出来,我们发现可能会连续地向左(向右)递归很多次。这很不好,因为浪费了许多时间。那么是否可以用较短的复杂度计算出接下来需要连续向左(向右)递归多少次呢?
答案是可以的。假设当前的递归函数是 \((a, b, c, d)\),当前分数 \(\dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{a + c}{b + d}\)。假设 \(\dfrac{A}{B} < \dfrac{x}{y} < \dfrac{C}{D}\),这是最好的,可以直接输出了。但是如果 \(\dfrac{x}{y} \le \dfrac{A}{B}\),显然需要向右递归。假设向右递归的次数为 \(t\),那么 \(\dfrac{x + ct}{y + dt} \ge \dfrac{A}{B}\)。解一下这个不等式:
\[\begin{array}{c} \dfrac{x + ct}{y + dt} \ge \dfrac{A}{B} \\\\ (x + ct)B \ge (y + dt)A \\\\ xB + cBt \ge yA + dAt \\\\ t \ge \dfrac{yA - xB}{cB - dA} \end{array} \]同理,如果 \(\dfrac{x}{y} \ge \dfrac{C}{D}\),那么需要连续向左递归的次数 \(t \ge \dfrac{yC - xD}{aD - bC}\)。
如此,我们用 \(O(1)\) 的时间求出了连续向左(向右)递归的次数。
代码
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using PII = pair<int, int>;
PII ans;
int A, B, C, D;
void solve(int a = 0, int b = 1, int c = 1, int d = 0) {
int x = a + c, y = b + d;
long double now = (long double)x / y;
long double L = (long double)A / B, R = (long double)C / D;
if (now > L && now < R) {
ans = {x, y}; return;
}
if (now <= L) {
int t = (int)(y * A - x * B) / (c * B - d * A);
solve(x + c * t, y + d * t, c, d);
}
else {
int t = (int)(y * C - x * D) / (a * D - b * C);
solve(a, b, x + a * t, y + b * t);
}
}
signed main() {
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &A, &B, &C, &D) != EOF) {
solve();
printf("%d/%d\n", ans.first, ans.second);
}
return 0;
}
简短精炼的代码后面有个小坑:别忘了用 long double。
最后留个 Stern-Brocot 树的练习题:P1298 最接近的分数。
标签:分数,int,dfrac,long,double,Brocot,笔记,Stern From: https://www.cnblogs.com/Link-Cut-Y/p/18575232