在生成 BEV feature 时的 scatter:
nx = int((point_cloud_range[3]-point_cloud_range[0])/voxel_size[0])
# Create the canvas for this sample
canvas = torch.zeros(
self.in_channels,
self.nx * self.ny,
dtype=voxel_features.dtype,
device=voxel_features.device)
# coors[:,2] 体素y坐标
# coors[:,3] 体素x坐标
indices = coors[:, 2] * self.nx + coors[:, 3]
indices = indices.long()
voxels = voxel_features.t()
# Now scatter the blob back to the canvas.
canvas[:, indices] = voxels
# Undo the column stacking to final 4-dim tensor
canvas = canvas.view(1, self.in_channels, self.ny, self.nx)
示例:
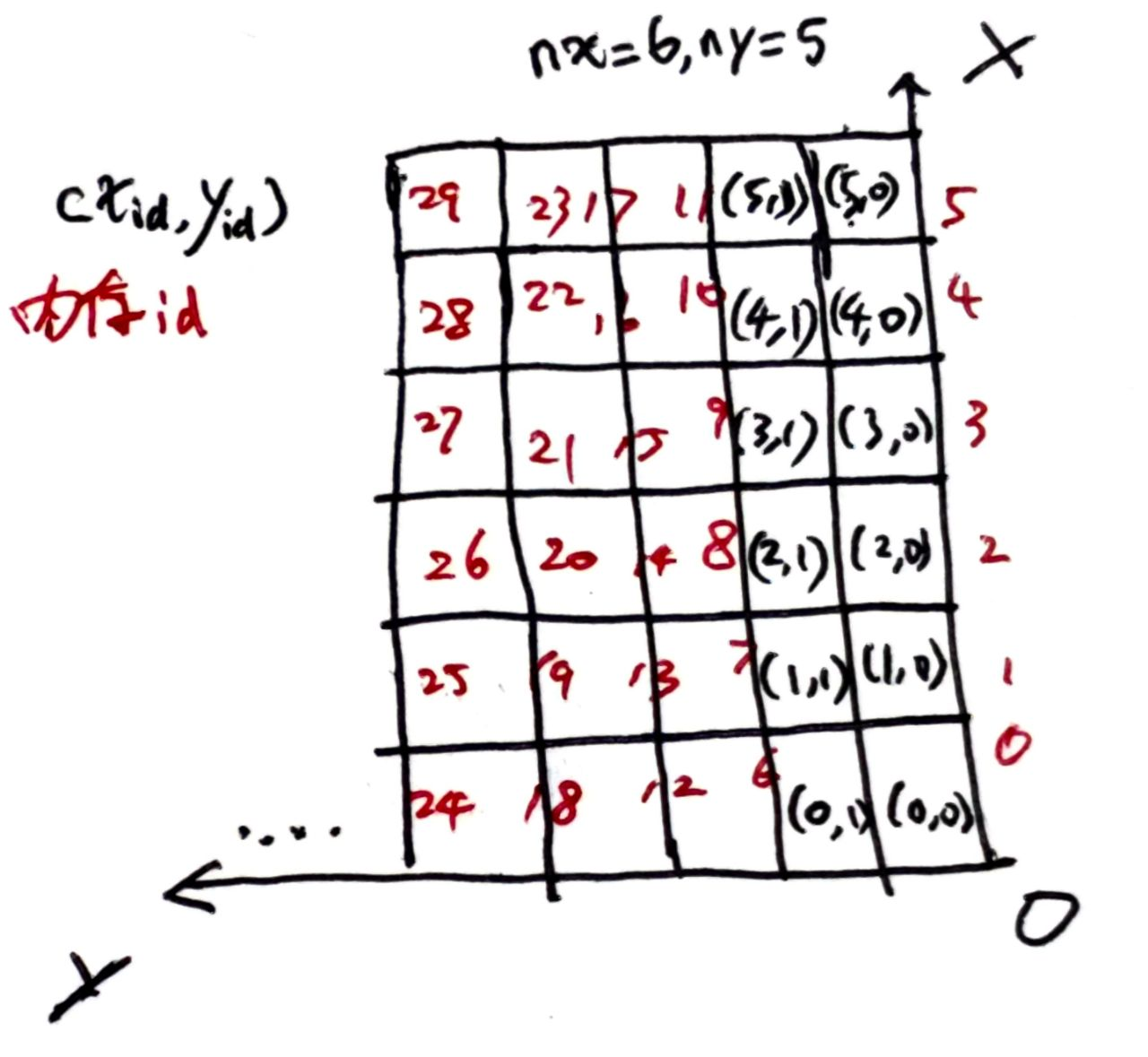
nx = 8
ny = 4
indices = []
for y in range(ny):
for x in range(nx):
idx = x + y*nx
indices.append(idx)
indices_tensor = torch.from_numpy(np.array([indices]))
print(indices_tensor)
indices_tensor = indices_tensor.view(ny, nx)
print(indices_tensor)
indices_tensor = indices_tensor.permute(1, 0)
print(indices_tensor)
result:
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17,
18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]])
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]])
tensor([[ 0, 8, 16, 24],
[ 1, 9, 17, 25],
[ 2, 10, 18, 26],
[ 3, 11, 19, 27],
[ 4, 12, 20, 28],
[ 5, 13, 21, 29],
[ 6, 14, 22, 30],
[ 7, 15, 23, 31]])
可以看到是按照 x 轴方向,行优先排列的,模型后面所有的操作都是基于这个形状的 feature 做的
occupancy 的输出格式为 1,X,Y,C
# bev_feature: (B, C_i, Dy, Dx)
# (B, C_i, Dy, Dx) -> (B, C_o, Dy, Dx) -> (B, Dx, Dy, C_o)
occ_pred = self.final_conv(bev_feats).permute(0,3,2,1)
bs, Dx, Dy = occ_pred.shape[:3]
# (B, Dx, Dy, C_o) -> (B, Dx, Dy, 2*C_o) ->(B, Dx, Dy, n_cls*Dz)
if self.use_predictor:
occ_pred = self.predictor(occ_pred)
# (B, Dx, Dy, n_cls*Dz) -> (B, Dx, Dy, Dz, n_cls)
occ_pred = occ_pred.view(bs, Dx, Dy, self.Dz, self.num_classes)
occ_score = occ_pred.softmax(-1)
# (B, Dx, Dy, Dz)
occ_res = occ_score.argmax(-1).float().contiguous()
cuda 得到 point 结果:
int y = coor_idx % occupancy_dim_size.y;
int x = coor_idx / occupancy_dim_size.y;
int occupied_idx = 0;
float lidar_x, lidar_y, lidar_z;
for (int z = 0; z < occupancy_dim_size.z; ++z) {
int semantic = round(occ_out_deveice[coor_idx * occupancy_dim_size.z + z]);
if(semantic > 0 && semantic != 2) {
occupied_idx = atomicAdd(occupied_num_device, 1);
lidar_x = (x + 0.5) * occupancy_voxel_size.x + range.min_x;
lidar_y = (y + 0.5) * occupancy_voxel_size.y + range.min_y;
lidar_z = (z + 0.5) * occupancy_voxel_size.z + range.min_z;
occupied_out_device[4 * occupied_idx] = lidar_x;
occupied_out_device[4 * occupied_idx + 1] = lidar_y;
occupied_out_device[4 * occupied_idx + 2] = lidar_z;
occupied_out_device[4 * occupied_idx + 3] = semantic;
}
}
根据 Core Concepts — NVIDIA cuDNN v9.2.1 documentation 的解释
data:
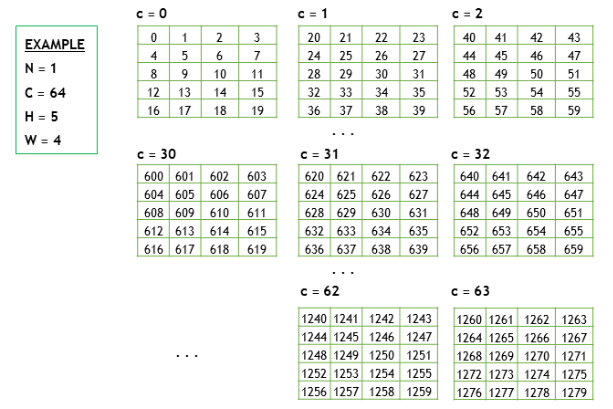
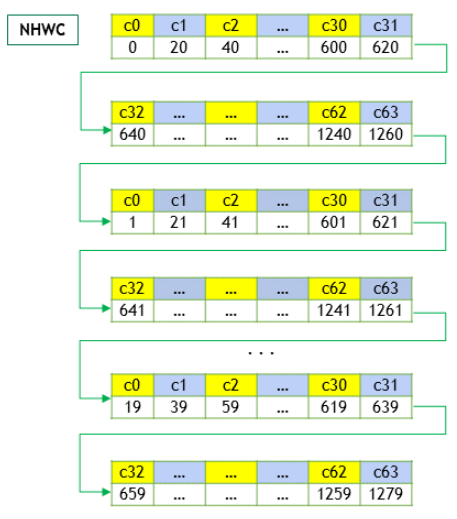
NHWC 排布的数据在内存中的顺序:
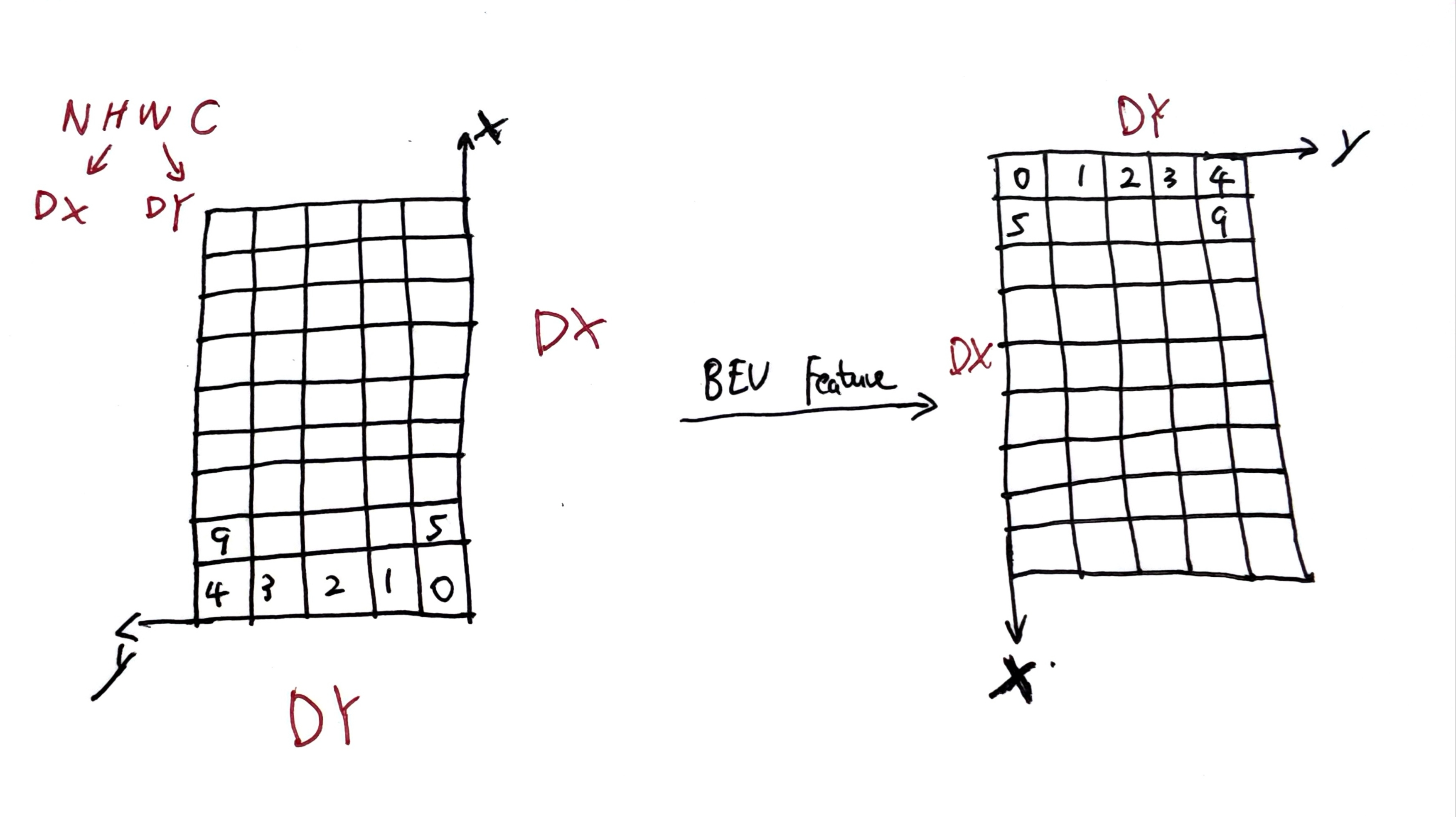
回到 BEV feature map,在 permute(0,3,2,1) 后,2,3 维度是 X, Y 内存是行排列的
int y = coor_idx % occupancy_dim_size.y;
int x = coor_idx / occupancy_dim_size.y;
图示:
occ 中的 feature:
这里得到的 BEV feature 与上述一致:
# 真实坐标id
tensor([[ 0, 8, 16, 24], # 第一列在原始BEV中的索引, 映射为内存中的 0,1,2,3
[ 1, 9, 17, 25],
[ 2, 10, 18, 26],
[ 3, 11, 19, 27],
[ 4, 12, 20, 28],
[ 5, 13, 21, 29],
[ 6, 14, 22, 30],
[ 7, 15, 23, 31]])
# 映射到内存中的id:
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27],
[28, 29, 30, 31]])
在目标检测中,centerhead 导出的onnx 最后输出的 feature map 顺序是 1,X,Y,C, 与 occ 是翻转关系:
reg_res = reg_res.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
height_res = height_res.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
dim_res = dim_res.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
rot_res = rot_res.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
数据排布:
tensor([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31]])
int x = coor_idx % occupancy_dim_size.x;
int y = coor_idx / occupancy_dim_size.x;