1.splay
普通权值平衡树
【模板】普通平衡树
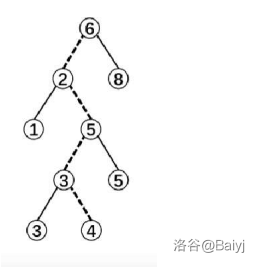
二叉查找树:
又:二叉搜索树、二叉排序树。它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;它的左、右子树也分别是二叉排序树。
splay树或伸展树,是一种平衡二叉查找树,它通过splay伸展操作不断将某个节点旋转到根节点,使得整棵树仍然满足二叉查找树的性质,能够在均摊\(O(log N)\)的时间内完成插入、查找和删除操作,并且保持平衡而不至于退化成链。
1.节点
对于每个节点,我们需要存储以下信息:
struct Splay {
int fa; //父节点
int ch[2]; //子节点
int val; //权值
int cnt; //权值的出现次数
int size; //所在子树的大小
} t[N];
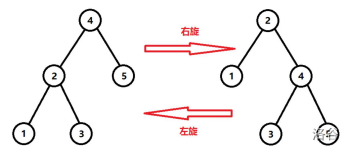
2.旋转(rotate操作)
为了使Splay保持平衡而进行旋转操作,旋转的本质是将某个节点上移一个位置。
旋转rotate需要保证:
1.整棵Splay的中序遍历不变(不能破坏二叉查找树的性质)。
2.受影响的节点维护的信息依然正确有效。
3.root必须指向旋转后的根节点。
在Splay中旋转分为两种:左旋和右旋。
inline void rotate(int x) { //x是要旋转的点
rg int y = t[x].fa;
rg int z = t[y].fa; //x的祖父
rg int k = t[y].ch[1] == x; //x是y的哪一个儿子 0是左儿子,1是右儿子
t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1] == y] = x; //z的原来在y的位置变为x
t[x].fa = z; //x的父亲变成z
t[y].ch[k] = t[x].ch[k ^ 1]; //x的与x原来在y的相对的那个儿子变成y的儿子
t[t[x].ch[k ^ 1]].fa = y; //更新父节点
t[x].ch[k ^ 1] = y; //x的与x原来相对位置的儿子变成y
t[y].fa = x; //更新父节点
update(y); //更新y的子树大小
update(x); //更新x的子树大小
}
3.伸展(Splay操作)
这个操作是基于rotate的。
令p为x的父亲,g为x的祖父。
Splay步骤有三种:
1.g是k:
直接\(rotate(x)\)即可。
2.g不是k且x,p,g共线:
此时\(rotate(x)\)两次即可。
3.p不是k且x,p,g不共线:
此时先\(rotate(p)\)再\(rotate(x)\)即可。
\(Splay(x,k)\),作用是把x转到k节点的左儿子或右儿子位置上。
inline void splay(int x, int k) { //将x旋转为k的儿子,如果k是0则旋转到根
while (t[x].fa != k) { //一直旋转到x成为king的儿子
rg int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa;
if (z != k) { //第2、3种情况
(t[z].ch[0] == y) ^ (t[y].ch[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y); //判断共线还是不共线
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x; //如果k是0,则将根节点更新为x
}
4.查找(Find操作)
从根节点开始,左侧都比它小,右侧都比它大,所以只需要相应的往左/往右递归。
如果当前位置的val已经是要查找的数,那么直接把它Splay到根节点,方便接下来的操作。
如果找不到,u的值就是和x值挨着的点。并把它旋转到根。(找一个不存在的点的前驱后继值时就用上了)
inline void Find(int x) { //查找x的位置,并将其旋转到根节点
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return ; //树空
while (t[u].ch[x > t[u].val] && x != t[u].val) { //当存在儿子并且当前位置的值不等于x
u = t[u].ch[x > t[u].val]; //跳转到儿子,查找x的父节点
}
splay(u, 0); //把当前位置旋转到根节点
}
5.插入(insert操作)
功能:插入x。
往Splay中插入一个数,类似于find操作,只是如果是已存在的数,就可以直接在查找到的节点进行计数;
如果不存在,在递归的查找过程中,会找到它的父节点的位置,然后就会发现底下没有了,所以新建一个节点就可以了。
inline void insert(int x) { //插入x
rg int u = root, fa = 0; //当前位置u,u的父节点fa
while (u && t[u].val != x) { //当u存在并且没有移动到当前的值
fa = u; //向下u的儿子,父节点变为u
u = t[u].ch[x > t[u].val]; //大于当前位置则向右侧找,否则向左找
}
if (u) { //存在这个位置
t[u].cnt++;
} else { //不存在则要新建一个节点来存放
u = ++tot; //新节点位置
if (fa) { //如果父节点非根
t[fa].ch[x > t[fa].val] = u;
}
t[u].ch[0] = t[u].ch[1] = 0; //不存在儿子
t[tot].fa = fa; //父节点
t[tot].val = x; //值
t[tot].cnt = 1; //数量
t[tot].size = 1; //大小
}
splay(u, 0); //把当前位置移到根
}
6.找x节点的前驱节点next(x,0),后继节点next(x,1)
首先要执行find操作,把要查找的数弄到根节点。
然后,以前驱为例,先确定前驱比它小,在左子树上,然后它的前驱是左子树中最大的值,所以一直跳右节点就行了。
对于后继反过来就行了。
inline int Next(int x, int f) { //查找x的前驱(0)或者后继(1)
find(x); //找到x并且把它伸展到根节点
rg int u = root; //此时x的父节点(存在的话)就是根节点
if (t[u].val > x && f) return u; //如果当前节点的值大于x并且要找的是后继
if (t[u].val < x && !f) return u; //如果当前节点的值小于x并且要查找的是前驱
u = t[u].ch[f]; //查找后继的话在左儿子上找,前驱在右儿子上找
while (t[u].ch[f ^ 1]) u = t[u].ch[f ^ 1]; //要反着跳转
return u;
}
7.删除操作
首先找到这个数的前驱,把它Splay到根节点;然后找到这个数的后继,把它旋转到前驱的底下。
比前驱大的是后继,在右子树,比后继小且比前驱大的有且仅有当前数在后继的左子树上面。
因此直接把当前根节点的右儿子的左儿子删掉就可以了。
inline void Delete(int x) { //删除x
rg int last = Next(x, 0); //查找x的前驱
rg int next = Next(x, 1); //查找x的后继
splay(last, 0); //将前驱旋转到根节点
splay(next, last); //将后继旋转到前驱的下面
//显然此时后继是前驱的右儿子,x是后继的左儿子
rg int del = t[next].ch[0]; //后继的左儿子,即x
if (t[del].cnt > 1) { //如果超过一个
t[del].cnt--; //直接减少一个
splay(del, 0);
} else t[next].ch[0] = 0; //这个节点直接丢掉
}
8.第k大
从当前节点开始,检查左子树大小,因为所有比当前位置小的数都在左侧。
如果左侧的数的个数多余k,则证明第k大在左子树中;否则向右子树找,找k-左子树大小-当前位置的数的个数。
记住特判k恰好在当前位置。
inline int kth(int x) { //查找排名为x的数
rg int u = root;
if (t[u].size < x) { //如果当前树上没有这么多数
return qwq;
}
while (true) {
rg int y = t[u].ch[0]; //左儿子
if (x > t[y].size + t[u].cnt) { //如果排名比左儿子的大小和当前节点的数量要大
x -= t[y].size + t[u].cnt; //数量减少
u = t[u].ch[1]; //那么当前排名的数一定在右儿子上找
} else { //否则在当前节点或左子树上找
if (t[y].size >= x) { //左儿子的节点数足够
u = y; //在左儿子上继续找
} else {
return t[u].val;
}
}
}
}
总代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 201000;
struct splay_tree {
int fa, cnt, ch[2], val, size;
} t[N];
int root, tot;
inline void update(int x) { //更新子树大小
t[x].size = t[t[x].ch[0]].size + t[t[x].ch[1]].size + t[x].cnt; //左子树+右子树+本身多少个,cnt记录重复个数
}
inline void rotate(int x) { //x是要旋转的点
rg int y = t[x].fa;
rg int z = t[y].fa; //x的祖父
rg int k = t[y].ch[1] == x; //x是y的哪一个儿子 0是左儿子,1是右儿子
t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1] == y] = x; //z的原来在y的位置变为x
t[x].fa = z; //x的父亲变成z
t[y].ch[k] = t[x].ch[k ^ 1]; //x的与x原来在y的相对的那个儿子变成y的儿子
t[t[x].ch[k ^ 1]].fa = y; //更新父节点
t[x].ch[k ^ 1] = y; //x的与x原来相对位置的儿子变成y
t[y].fa = x; //更新父节点
update(y); //更新y的子树大小
update(x); //更新x的子树大小
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) { //将x旋转为king的儿子,如果king是0则旋转到根
while (t[x].fa != k) { //一直旋转到x成为king的儿子
rg int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa;
if (z != k) { //第2、3种情况
(t[z].ch[0] == y) ^ (t[y].ch[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y); //判断共线还是不共线
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x; //如果king是0,则将根节点更新为x
}
inline void find(int x) { //查找x的位置,并将其旋转到根节点
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return ; //树空
while (t[u].ch[x > t[u].val] && x != t[u].val) { //当存在儿子并且当前位置的值不等于x
u = t[u].ch[x > t[u].val]; //跳转到儿子,查找x的父节点
}
splay(u, 0); //把当前位置旋转到根节点
}
inline void insert(int x) { //插入x
rg int u = root, fa = 0; //当前位置u,u的父节点fa
while (u && t[u].val != x) { //当u存在并且没有移动到当前的值
fa = u; //向下u的儿子,父节点变为u
u = t[u].ch[x > t[u].val]; //大于当前位置则向右侧找,否则向左找
}
if (u) { //存在这个位置
t[u].cnt++;
} else { //不存在则要新建一个节点来存放
u = ++tot; //新节点位置
if (fa) { //如果父节点非根
t[fa].ch[x > t[fa].val] = u;
}
t[u].ch[0] = t[u].ch[1] = 0; //不存在儿子
t[tot].fa = fa; //父节点
t[tot].val = x; //值
t[tot].cnt = 1; //数量
t[tot].size = 1; //大小
}
splay(u, 0); //把当前位置移到根
}
inline int Next(int x, int f) { //查找x的前驱(0)或者后继(1)
find(x); //找到x并且把它伸展到根节点
rg int u = root; //此时x的父节点(存在的话)就是根节点
if (t[u].val > x && f) return u; //如果当前节点的值大于x并且要找的是后继
if (t[u].val < x && !f) return u; //如果当前节点的值小于x并且要查找的是前驱
u = t[u].ch[f]; //查找后继的话在左儿子上找,前驱在右儿子上找
while (t[u].ch[f ^ 1]) u = t[u].ch[f ^ 1]; //要反着跳转
return u;
}
inline void Delete(int x) { //删除x
rg int last = Next(x, 0); //查找x的前驱
rg int next = Next(x, 1); //查找x的后继
splay(last, 0); //将前驱旋转到根节点
splay(next, last); //将后继旋转到前驱的下面
//显然此时后继是前驱的右儿子,x是后继的左儿子
rg int del = t[next].ch[0]; //后继的左儿子,即x
if (t[del].cnt > 1) { //如果超过一个
t[del].cnt--; //直接减少一个
splay(del, 0);
} else t[next].ch[0] = 0; //这个节点直接丢掉
}
inline int kth(int x) { //查找排名为x的数
rg int u = root;
if (t[u].size < x) { //如果当前树上没有这么多数
return qwq;
}
while (true) {
rg int y = t[u].ch[0]; //左儿子
if (x > t[y].size + t[u].cnt) { //如果排名比左儿子的大小和当前节点的数量要大
x -= t[y].size + t[u].cnt; //数量减少
u = t[u].ch[1]; //那么当前排名的数一定在右儿子上找
} else { //否则在当前节点或左子树上找
if (t[y].size >= x) { //左儿子的节点数足够
u = y; //在左儿子上继续找
} else {
return t[u].val;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
insert(1e9); //插入极限大小两值,否则找前驱和后继会出现问题
insert(-1e9);
while (n--) {
rg int opt, x;
scanf("%d%d", &opt, &x);
if (opt == 1) insert(x);
if (opt == 2) Delete(x);
if (opt == 3) {
find(x);
printf("%d\n", t[t[root].ch[0]].size);
}
if (opt == 4) printf("%d\n", kth(x + 1));
if (opt == 5) printf("%d\n", t[Next(x, 0)].val);
if (opt == 6) printf("%d\n", t[Next(x, 1)].val);
}
return qwq;
}
区间Splay的基本性质
首先,我们类比之前二叉搜索树以及权值Splay的性质,可以构造出如下的一棵树:
1.对于树中的每个节点,如果它有左子树,那么它的左子树中的每一个节点在原序列中的位置都比这个节点靠前;
2.对于树中的每个节点,如果它有右子树,那么它的右子树中的每一个节点在原序列中的位置都比这个节点靠后。
例:对1,5,4,2,3建立区间Splay。
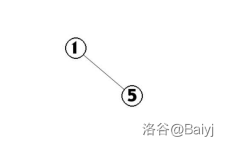
1.插入1

2.插入5,由于5的位置比2靠后,因此5插入到2的右儿子处
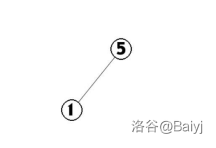
3.为了维护树的平衡,我们将5Splay到根节点
4.插入4,4的位置在5之后
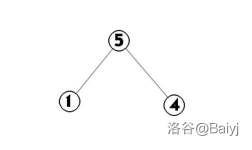
5.同样,将4Splay到根
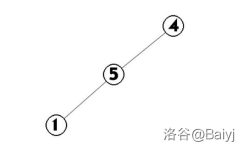
\(\dots\)
最后这棵树可能是这样的:
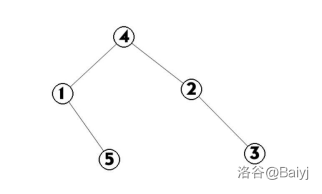
我们会发现一个重要的性质:对这棵Splay树进行中序遍历后得到的恰好是原序列。
那么,如果我们把元素在序列中的位置当作权值,区间Splay其实就是一棵每个点的权值都可能动态变化的权值Splay。至于为什么权值会变化,是因为这个数在序列中的位置可能发生了变化(比如翻转)。
区间Splay中,每个节点在存储它本身的信息外,还存储着它子树这段连续区间的信息,比如说上图中标号为1的节点可能除了存自己的value、size外还存着1,5的value之和,4节点可能存着所有节点value的总和,通过这种信息合并可以像线段树一样大大缩短查询的复杂度。
可以这样认为:区间Splay中每个节点代表的不只是它本身,还可以代表它的整棵子树。
具体操作:
kth
区间Splay中查找目前序列中第k位置上的数和二叉搜索树查找第k小是一摸一样的。
inline int kth(int x) {
rg int u = root;
while (true) {
if (t[u].tag) pushdown(u);
if (x <= t[t[u].ch[0]].siz) u = t[u].ch[0];
else if (t[t[u].ch[0]].siz + 1 == x) return u;
else {
x -= (t[t[u].ch[0]].siz + 1);
u = t[u].ch[1];
}
}
}
pushup
将子树信息向上合并(以维护子树和为例)
inline void pushup(int x) {
rg int l = t[x].ch[0], r = t[x].ch[1];
t[x].sum = t[l.sum] + t[r].sum + t[x].value;
t[x].siz = t[l].siz + t[r].siz + 1;
}
Split
区间Splay的核心操作,就是提取一段区间[l,r],具体操作就是先将kth(l-1)旋转到根,再把kth(r+1)旋转到根的右儿子,那么由于区间Splay的中序遍历为原序列,现在kth(r+1)的左子树就正好是[l,r]这段区间。
inline int split(int l, int r) {
rg int x = kth(l), y = kth(r + 2); //因为前后各加了哨兵,所以是l-1和r+1
splay(x, 0);
splay(y, x);
return t[y].ch[0]; //返回代表区间[l,r]的节点编号
}
Insert
假设我们要将数k插入到第x个数后面,那么先splay(kth(x),kth(x+1)),后将x作为现在kth(x+1)的左儿子就可以了。
Delete
和Insert一样,只不过是将kth(x+2)(因为加了哨兵)的左儿子删去。
Pushdown
首先,如果我们要将区间[l,r]每个数加上k,那么肯定先要split(l,r),将这段区间提取出来,之后打懒标记,由于我们统计答案是自上而下的,所以可以在所有复合操作所共有的kth操作中访问下传标记,这样就能保证解的正确性。
inline void pushdown(int x) {
rg int l = t[x].ch[0], r = t[x].ch[1];
if (t[x].tag) { //是否有统一赋值的标记
t[x].tag = 0;
if (l) {
t[l].tag = 1;
t[l].value = t[x].value;
t[l].sum = t[x].value * t[l].siz;
}
if (r) {
t[r].tag = 1;
t[r].value = t[x].value;
t[r].sum = t[x].value * t[r].siz;
}
}
}
其实你会发现区间Splay对于区间加,区间乘,区间赋值,区间Rmq问题的处理和线段树是一摸一样的,大多数线段树都可以用区间Splay代替,而区间Splay能处理的问题会更多。
区间Splay的rotate,Splay和权值Splay并没有什么区别。
【模板】文艺平衡树
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 100003;
int n, m;
struct node {
int ch[2], fa, val;
int siz, tag;
inline void init(int _fa, int _val) {
fa = _fa;
val = _val;
siz = 1;
}
} t[N];
int root, idx;
inline void pushup(int x) {
rg int l = t[x].ch[0], r = t[x].ch[1];
t[x].siz = t[l].siz + t[r].siz + 1;
}
inline void pushdown(int x) {
if (t[x].tag) { //是否有统一赋值的标记
swap(t[x].ch[0], t[x].ch[1]);
t[t[x].ch[0]].tag ^= 1;
t[t[x].ch[1]].tag ^= 1;
t[x].tag = 0;
}
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa;
rg int k = t[y].ch[1] == x;
t[z].ch[t[z].ch[1] == y] = x;
t[x].fa = z;
t[y].ch[k] = t[x].ch[k ^ 1];
t[t[x].ch[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
t[x].ch[k ^ 1] = y;
t[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) {
while (t[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = t[x].fa, z = t[y].fa;
if (z != k) {
(t[y].ch[0] == x) ^ (t[z].ch[0] == y) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline void insert(int x) {
rg int u = root, fa = 0;
while (u) {
fa = u;
u = t[u].ch[x > t[u].val];
}
u = ++idx;
t[fa].ch[x > t[fa].val] = u;
t[u].init(fa, x);
splay(u, 0);
}
inline int kth(int x) { //返回第k个节点编号
rg int u = root;
while (true) {
pushdown(u);
if (x <= t[t[u].ch[0]].siz) u = t[u].ch[0];
else if (t[t[u].ch[0]].siz + 1 == x) return u;
else {
x -= (t[t[u].ch[0]].siz + 1);
u = t[u].ch[1];
}
}
}
inline void output(int x) { //中序遍历输出
pushdown(x); //先传标记,因为有的节点的旋转没有下传到儿子节点
if (t[x].ch[0]) output(t[x].ch[0]); //中序遍历输出左儿子
if (t[x].val >= 1 && t[x].val <= n) { //这个判断的作用是过滤掉两个哨兵
printf("%d ", t[x].val);
}
if (t[x].ch[1]) output(t[x].ch[1]); //中序遍历输出右儿子
}
int main() {
insert(1e9);
insert(-1e9);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
insert(i);
}
while (m--) {
rg int l, r;
scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);
l = kth(l);
r = kth(r + 2);
splay(l, 0);
splay(r, l);
t[t[r].ch[0]].tag ^= 1;
}
output(root);
return qwq;
}
fhq-tread(无旋treap)
主要思想:
顾名思义,无旋意味着它没有旋转操作。
事实上,无旋treap只有两种操作,一种是split(分裂),一种是merge(合并)。
与splay相比,基本上可以代替splay的所有功能,但是在处理LCT问题上没有splay优秀。
函数解释:
split(分裂)
split要把一棵平衡树拆成两棵树,左边的树上节点的值都小于等于v,右边的树上节点的值都大于等于v。
p:当前子树根节点,
v:以v为分界线分割树,
x,y:分裂之后两棵子树的根,左边子树根是x,右边子树根是y,这里要传地址,方便写。
注意:当根为0时,一定要清空x,y,不然会死循环。
按值分裂:根据给的值v把一棵树分裂成两棵树,一棵树的值\(val \le v\),另一棵树的值\(val > v\)。
情况1:
如果当前节点p的\(val \le v\),说明p以及其左子树都属于分裂后的左treap,p的右子树也可能部分\(\le v\),因此需要继续递归分裂右子树,把\(\le v\)的那部分作为p的右子树。把x指向左treap的根。
情况2:
如果当前节点p的\(val > v\),说明p以及其右子树都属于分裂后的右treap,p的左子树也可能部分\(> v\),因此需要继续递归分裂左子树,把\(> v\)的那部分作为p的左子树。把y指向右treap的根。
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
//这里的x和y都取地址了,也就是说所有的split函数,
//都可以更改这个内存地址的值,只要指向这个地址的这俩参数就都等于这个数
if (!p) {
x = y = 0; //清空
return ;
}
if (tr[p].val <= v) {
x = p; //左子树已经分裂出去了,直接x=p
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y); //在右子树上查找,把拆下来右子树上节点值<=v的点放回到x的右子树上
pushup(x);
} else {
y = p; //去左子树里面找值大于v的节点,并且把它并到y的左子树上
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
}
}
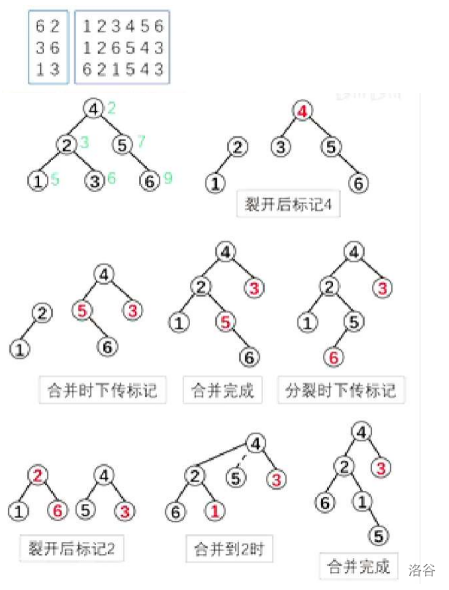
模拟过程:
注意:p=6中的6是点的编号,不是权值。
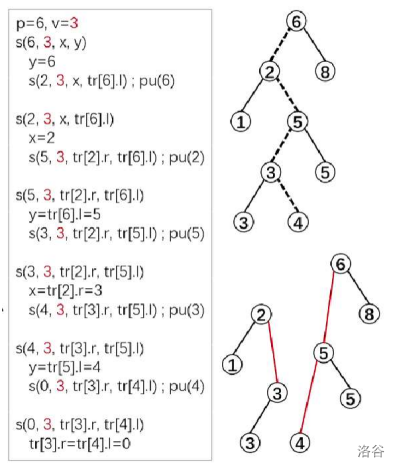
merge(合并)
merge函数要实现把两个分开的树再合并到一起,并返回合并后的根节点。
x,y:两棵树的根。
这个操作类似于线段树合并。
注意:合并时只能是两个相邻的子树合并,不能跳着合并。例如:
树rt-->子树a和子树b
子树b-->子树c和子树d(-->表示拆成两棵树)
那么我们合并时,只能\(merge(a, merge(c, d))\)或\(merge(merge(a, c), d)\),而不能\(merge(merge(a,d), c)\)。
合并函数两个参数:左treap的根指针x、右treap的根指针y。必须满足x中所有节点的val值小于等于y中所有节点的val值。
因为两个treap已经有序,所以在合并的时候只需要考虑把哪个树放在上面,把哪个树放在下面,也就是需要判断将哪个树作为子树,根据堆的性质,我们把随机数key值小的放在上面。
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
模拟过程:
圆圈里面是节点权值,绿色数字表示随机数。
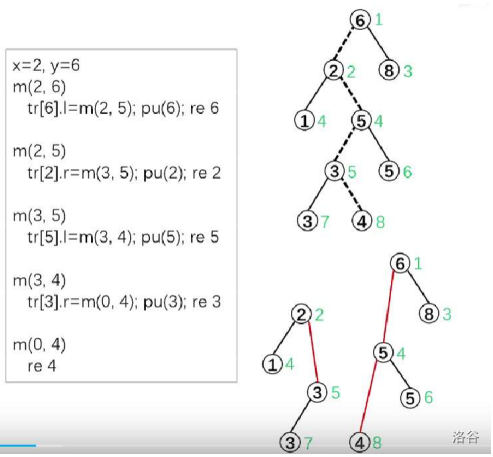
insert(插入)
假设insert(3)
1.先把原图按着3分裂,\(split(root, 3, x, y)\)分裂成两个treap。\(x=2\)的这个子树上都是\(\le 3\)的,\(y=6\)这个子树上都是\(>3\)的。
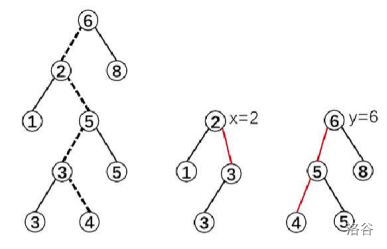
2.新建z子树,只有一个根节点,以3为权值的根。
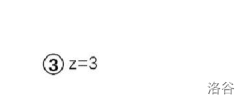
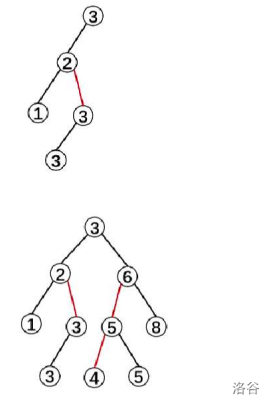
3.先合并x和y两棵树,再合并y(假设x点的随机值大于z的随机值,y的随机值大于z的随机值)
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
nownode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
Delete(删除)
令\(Delete(3)\)表示如果存在多个权值为3的点,删除一个。
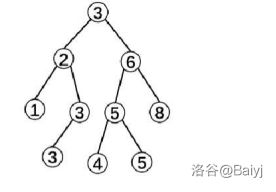
1.先把原图按着3分裂成两棵树x和z。
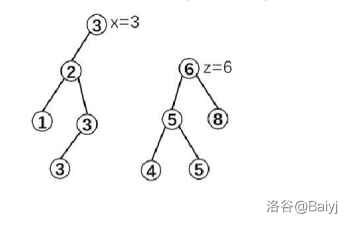
2.把\(x=3\)这棵树再按着3-1分裂成两棵,即把\(<3\)的节点放到x上,等于3的节点砍成y。
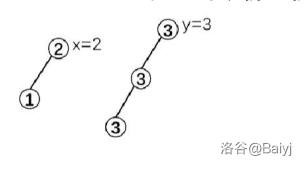
3.最关键的删点:
\(y=merge(tr[y].l,tr[y].r)\),删点之后变成:
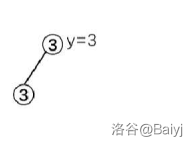
这句话的解释:
合并y的左、右子树,y是等于3的那棵树的树根,对于图中而言,\(merge(tr[y].l, tr[y].r)\)相当于是\(y=3\)那棵子树的左子树中那两个3,与右子树(空),也就是0合并,其实还算是左子树,把合并后的结果重新赋值给y,就相当于删除了原来那个3的根。
4.合并\(x=2\)和删除之后的\(y=3\),合并结果为(假设\(x=2\)的随机值小于\(y=3\)的随机值):
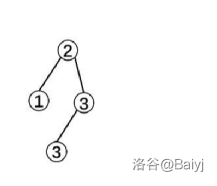
5.再去和\(z=6\)那棵树合并(假设\(z=6\)的点随机值最小)
inline void del(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, z);
split(x, v - 1, x, y);
y = merge(tr[y].l, tr[y].r);
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
查询以root为根的子树排名为v的数权值是多少
inline int getval(int root, int v) {
if (v == tr[tr[root].l].size + 1) return tr[root].val;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].l].size) return getval(tr[root].l, v);
else return getval(tr[root].r, v - tr[tr[root].l].size - 1);
}
前驱
inline int gerpre(int v) {
rg int x, y, siz, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
siz = tr[x].size;
ans = getval(x, siz);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
后继
inline int getnxt(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v, x, y);
ans = getval(y, 1);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
排名
inline int rank(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = tr[x].size + 1;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
【模板】普通平衡树
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val;
int rnd;
int size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
int n;
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
//这里的x和y都取地址了,也就是说所有的split函数,
//都可以更改这个内存地址的值,只要指向这个地址的这俩参数就都等于这个数
if (!p) {
x = y = 0; //清空
return ;
}
if (tr[p].val <= v) {
x = p; //左子树已经分裂出去了,直接x=p
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y); //在右子树上查找,把拆下来右子树上节点值<=v的点放回到x的右子树上
} else {
y = p; //去左子树里面找值大于v的节点,并且把它并到y的左子树上
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
inline void del(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, z);
split(x, v - 1, x, y);
y = merge(tr[y].l, tr[y].r);
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
inline int getrank(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = tr[x].size + 1;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline int getval(int root, int v) {
if (v == tr[tr[root].l].size + 1) return tr[root].val;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].l].size) return getval(tr[root].l, v);
else return getval(tr[root].r, v - tr[tr[root].l].size - 1);
}
inline int getpre(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = getval(x, tr[x].size);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline int getnxt(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v, x, y);
ans = getval(y, 1);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
int main() {
int opt, v;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &opt, &v);
if (opt == 1) insert(v);
if (opt == 2) del(v);
if (opt == 3) printf("%d\n", getrank(v));
if (opt == 4) printf("%d\n", getval(root, v));
if (opt == 5) printf("%d\n", getpre(v));
if (opt == 6) printf("%d\n", getnxt(v));
}
return qwq;
}
【模板】文艺平衡树
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val;
int rnd;
int size;
int tag;
} tr[N];
int n, m, root, idx;
inline int newnode(int v) {
idx++;
tr[idx].val = v;
tr[idx].rnd = rand();
tr[idx].size = 1;
return idx;
}
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
}
inline void pushdown(int p) {
if (!p) return ;
if (tr[p].tag) {
swap(tr[p].l, tr[p].r);
tr[tr[p].l].tag ^= 1;
tr[tr[p].r].tag ^= 1;
tr[p].tag = 0;
}
}
inline void split(int p, int k, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return;
}
pushdown(p);
if (k > tr[tr[p].l].size) {
k -= tr[tr[p].l].size + 1;
x = p;
split(tr[p].r, k, tr[p].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[p].l, k, x, tr[p].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
pushdown(x);
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
pushdown(y);
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void reverse(int l, int r) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, r, x, z);
split(x, l - 1, x, y);
//此时y子树就对应[l,r]区间
tr[y].tag ^= 1;
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
inline void output(int p) {
if (!p) return ;
pushdown(p);
output(tr[p].l);
printf("%d ", tr[p].val);
output(tr[p].r);
}
int main() {
srand(time(NULL));
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
root = merge(root, newnode(i));
}
rg int x, y;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
reverse(x, y);
}
output(root);
return qwq;
}
例题1:[NOI2005] 维护数列
建一棵splay。
一个个insert显然很慢,所以写一个build来建一段序列。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 3, inf = 2e9;
int n, m, root, idx;
struct node {
//lx表示从区间左端点l开始的连续的前缀最大子序列,
//rx表示从区间右端点r开始的连续的后缀最大子序列
//maxx表示这个区间中的最大子序列
int lx, rx, maxx;
int fa, c[2], sum, size, val;
bool tag, rev;
} tr[N];
int a[N], id[N];
queue<int> q;
inline void pushup(int x) {
rg int l = tr[x].c[0], r = tr[x].c[1];
tr[x].sum = tr[l].sum + tr[r].sum + tr[x].val;
tr[x].size = tr[l].size + tr[r].size + 1;
tr[x].maxx = max(tr[l].maxx, max(tr[r].maxx, tr[l].rx + tr[x].val + tr[r].lx));
tr[x].lx = max(tr[l].lx, tr[l].sum + tr[x].val + tr[r].lx);
tr[x].rx = max(tr[r].rx, tr[r].sum + tr[x].val + tr[l].rx);
}
inline void pushdown(int x) {
rg int l = tr[x].c[0], r = tr[x].c[1];
if (tr[x].tag) {
tr[x].rev = tr[x].tag = 0; //有了一个统一修改的标记,再翻转就没有什么意义了
if (l) {
tr[l].tag = 1;
tr[l].val = tr[x].val;
tr[l].sum = tr[x].val * tr[l].size;
}
if (r) {
tr[r].tag = 1;
tr[r].val = tr[x].val;
tr[r].sum = tr[x].val * tr[r].size;
}
if (tr[x].val >= 0) {
if (l) tr[l].lx = tr[l].rx = tr[l].maxx = tr[l].sum;
if (r) tr[r].lx = tr[r].rx = tr[r].maxx = tr[r].sum;
} else {
if (l) {
tr[l].lx = tr[l].rx = 0;
tr[l].maxx = tr[x].val;
}
if (r) {
tr[r].lx = tr[r].rx = 0;
tr[r].maxx = tr[x].val;
}
}
}
if (tr[x].rev) {
tr[x].rev = 0;
tr[l].rev ^= 1;
tr[r].rev ^= 1;
swap(tr[l].lx, tr[l].rx);
swap(tr[r].lx, tr[r].rx);
//注意,在翻转操作中,前后缀的最长上升子序列都反过来了,很容易错
swap(tr[l].c[0], tr[l].c[1]);
swap(tr[r].c[0], tr[r].c[1]);
}
}
inline void rotate(int x, int &k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int l = (tr[y].c[1] == x), r = l ^ 1;
if (y == k) k = x;
else tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[tr[x].c[r]].fa = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[l] = tr[x].c[r];
tr[x].c[r] = y;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int &k) {
while (x != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (y != k) {
(tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x, k) : rotate(y, k);
}
rotate(x, k);
}
}
inline int find(int x, int rk) {
pushdown(x);
rg int l = tr[x].c[0], r = tr[x].c[1];
if (tr[l].size + 1 == rk) return x;
if (tr[l].size >= rk) return find(l, rk);
else return find(r, rk - tr[l].size - 1);
}
inline void recycle(int x) { //回收冗余编号
rg int &l = tr[x].c[0], &r = tr[x].c[1];
if (l) recycle(l);
if (r) recycle(r);
q.push(x);
tr[x].fa = l = r = tr[x].tag = tr[x].rev = 0;
}
//找到[k+1,k+tot],并把k和k+tot+1移到根和右儿子的位置,
//然后返回这个右儿子的左儿子,这就是我们需要操作的区间
inline int split(int k, int tot) {
rg int x = find(root, k), y = find(root, k + tot + 1);
splay(x, root);
splay(y, tr[x].c[1]);
return tr[y].c[0];
}
inline void query(int k, int tot) {
rg int x = split(k, tot);
printf("%d\n", tr[x].sum);
}
inline void modify(int k, int tot, int val) {
rg int x = split(k, tot), y = tr[x].fa;
tr[x].val = val;
tr[x].tag = 1;
tr[x].sum = tr[x].size * val;
if (val >= 0) tr[x].lx = tr[x].rx = tr[x].maxx = tr[x].sum;
else {
tr[x].lx = tr[x].rx = 0;
tr[x].maxx = val;
}
pushup(y);
pushup(tr[y].fa);
}
inline void rever(int k, int tot) {
rg int x = split(k, tot), y = tr[x].fa;
if (!tr[x].tag) {
tr[x].rev ^= 1;
swap(tr[x].c[0], tr[x].c[1]);
swap(tr[x].lx, tr[x].rx);
pushup(y);
pushup(tr[y].fa);
}
}
inline void erase(int k, int tot) {
rg int x = split(k, tot), y = tr[x].fa;
recycle(x);
tr[y].c[0] = 0;
pushup(y);
pushup(tr[y].fa);
}
inline void build(int l, int r, int f) {
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1, now = id[mid], pre = id[f];
if (l == r) {
tr[now].maxx = tr[now].sum = a[l];
tr[now].tag = tr[now].rev = 0; //这里清0是必要,因为这个编号之前可能冗余了
tr[now].lx = tr[now].rx = max(a[l], 0);
tr[now].size = 1;
}
if (l < mid) build(l, mid - 1, mid);
if (mid < r) build(mid + 1, r, mid);
tr[now].val = a[mid];
tr[now].fa = pre;
pushup(now);
tr[pre].c[mid >= f] = now; //当mid>=f时,now是插入到右区间取了,所以tr[pre].c[1]=now,当mid<f时同理
}
inline void insert(int k, int tot) {
for (rg int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) {
if (!q.empty()) {
id[i] = q.front();
q.pop();
} else id[i] = ++idx;
}
build(1, tot, 0);
rg int z = id[(1 + tot) >> 1]; //取中点为根
rg int x = find(root, k + 1), y = find(root, k + 2); //首先根据中序遍历找到我们需要操作的区间的实际编号
splay(x, root);
splay(y, tr[x].c[1]); //把k+1和(k+1)+1移到根和右儿子
tr[z].fa = y;
tr[y].c[0] = z; //直接把需要输入的这个平衡树挂到右儿子的左儿子上就好了
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
tr[0].maxx = a[1] = a[n + 2] = -inf;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i + 1]);
}
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n + 2; i++) {
id[i] = i; //虚拟了两个节点1和n+2,然后把需要操作的区间整体右移一个单位
}
build(1, n + 2, 0);
root = (n + 3) >> 1; //取最中间的为根
idx = n + 2;
rg int k, tot, val;
rg char ch[10];
while (m--) {
scanf("%s", ch);
if (ch[0] != 'M' || ch[2] != 'X') scanf("%d%d", &k, &tot);
if (ch[0] == 'I') insert(k, tot);
if (ch[0] == 'D') erase(k, tot);
if (ch[0] == 'M') {
if (ch[2] == 'X') printf("%d\n", tr[root].maxx);
else {
scanf("%d", &val);
modify(k, tot, val);
}
}
if (ch[0] == 'R') rever(k, tot);
if (ch[0] == 'G') query(k, tot);
}
return qwq;
}
例题2:[HNOI2002] 营业额统计
对于\(a[i]\),insert后找到它的前驱和后继,区差较小的加入ans即可。
splay
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 33003;
struct node {
int fa, c[2], val, cnt, size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].size = tr[tr[x].c[0]].size + tr[tr[x].c[1]].size + tr[x].cnt;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int k = tr[y].c[1] == x;
tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[k] = tr[x].c[k ^ 1];
tr[tr[x].c[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
tr[x].c[k ^ 1] = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) {
while (tr[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (z != k) {
(tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline void Find(int x) {
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return ;
while (tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val] && x != tr[u].val) {
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline void insert(int x) {
rg int u = root, fa = 0;
while (u && tr[u].val != x) {
fa = u;
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
if (u) {
tr[u].cnt++;
} else {
u = ++idx;
if (fa) tr[fa].c[x > tr[fa].val] = u;
tr[u].c[0] = tr[u].c[1] = 0;
tr[idx].fa = fa;
tr[idx].val = x;
tr[idx].cnt = tr[idx].size = 1;
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline int next(int x, int f) {
Find(x);
rg int u = root;
if (tr[u].val >= x && f) return u;
if (tr[u].val <= x && !f) return u;
u = tr[u].c[f];
while (tr[u].c[f ^ 1]) u = tr[u].c[f ^ 1];
return u;
}
int n, a, ans;
int main() {
insert(-1e9);
insert(1e9);
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &a);
ans = a;
insert(a);
for (rg int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a);
ans += min(abs(a - tr[next(a, 0)].val), abs(a - tr[next(a, 1)].val));
insert(a);
}
printf("%d", ans);
return qwq;
}
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 33003;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val, rnd, size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[p].val <= v) {
x = p;
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
inline int getval(int root, int v) {
if (v == tr[tr[root].l].size + 1) return tr[root].val;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].l].size) return getval(tr[root].l, v);
else return getval(tr[root].r, v - tr[tr[root].l].size - 1);
}
inline int getpre(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v, x, y);
ans = getval(x, tr[x].size);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline int getnxt(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = getval(y, 1);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
int n, a, ans;
int main() {
srand(time(NULL));
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &a);
insert(-1e9);
insert(1e9);
ans = a;
insert(a);
for (rg int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a);
ans += min(abs(a - getpre(a)), abs(a - getnxt(a)));
insert(a);
}
printf("%d", ans);
return qwq;
}
例题3:[HNOI2004] 宠物收养场
对于不满意度,即求当前特点值与其前驱与后继的最小差值。
乍一看要开两棵平衡树分别维护宠物与领养者,但我们发现,任意时刻,当前的平衡树上都只有宠物或只有领养者,所以维护一颗平衡树即可。
splay
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 8e4 + 3, mod = 1e6;
struct node {
int fa, c[2], val, size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].size = tr[tr[x].c[0]].size + tr[tr[x].c[1]].size + 1;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int k = tr[y].c[1] == x;
tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[k] = tr[x].c[k ^ 1];
tr[tr[x].c[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
tr[x].c[k ^ 1] = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) {
while (tr[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (z != k) {
(tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline void find(int x) {
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return ;
while (tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val] && x != tr[u].val) {
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline void insert(int x) {
rg int u = root, fa = 0;
while (u && tr[u].val != x) {
fa = u;
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
if (u) {
//tr[u].cnt++;
} else {
u = ++idx;
if (fa) tr[fa].c[x > tr[fa].val] = u;
tr[u].c[0] = tr[u].c[1] = 0;
tr[idx].fa = fa;
tr[idx].val = x;
tr[idx].size = 1;
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline int Next1(int x, int f) {
find(x);
rg int u = root;
if (tr[u].val > x && f) return u;
if (tr[u].val < x && !f) return u;
u = tr[u].c[f];
while (tr[u].c[f ^ 1]) u = tr[u].c[f ^ 1];
return u;
}
inline int Next2(int x, int f) {
find(x);
rg int u = root;
if (tr[u].val >= x && f) return u;
if (tr[u].val <= x && !f) return u;
u = tr[u].c[f];
while (tr[u].c[f ^ 1]) u = tr[u].c[f ^ 1];
return u;
}
inline void Delete(int x) {
rg int last = Next1(x, 0);
rg int next = Next1(x, 1);
splay(last, 0);
splay(next, last);
rg int del = tr[next].c[0];
tr[next].c[0] = 0;
}
int n, ans, opt, x;
int cnt[2];
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
insert(-1e9);
insert(1e9);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &opt, &x);
cnt[opt]++;
if (cnt[opt] > cnt[opt ^ 1]) {
insert(x);
} else {
rg int a1 = tr[Next2(x, 0)].val, a2 = tr[Next2(x, 1)].val;
if (x - a1 <= a2 - x) {
ans = (ans + x - a1) % mod;
Delete(a1);
} else {
ans = (ans + a2 - x) % mod;
Delete(a2);
}
}
}
printf("%d", ans % mod);
return qwq;
}
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 8e4 + 3, mod = 1e6;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val, rnd, size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[p].val <= v) {
x = p;
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
inline int getval(int root, int v) {
if (v == tr[tr[root].l].size + 1) return tr[root].val;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].l].size) return getval(tr[root].l, v);
else return getval(tr[root].r, v - tr[tr[root].l].size - 1);
}
inline int getpre(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v, x, y);
ans = getval(x, tr[x].size);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline int getnxt(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = getval(y, 1);
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline void Delete(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, z);
split(x, v - 1, x, y);
y = merge(tr[y].l, tr[y].r);
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
int n, ans, opt, x;
int cnt[2];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
srand(time(NULL));
cin >> n;
insert(-1e9);
insert(1e9);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> opt >> x;
cnt[opt]++;
if (cnt[opt] > cnt[opt ^ 1]) {
insert(x);
} else {
rg int a1 = getpre(x), a2 = getnxt(x);
if (x - a1 <= a2 - x) {
ans = (ans + x - a1) % mod;
Delete(a1);
} else {
ans = (ans + a2 - x) % mod;
Delete(a2);
}
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
return qwq;
}
例题4:[NOI2004] 郁闷的出纳员
对于删除操作,我们将\(<min+k\)的所有数旋转到根的右子树的左子树,一举消灭。
splay
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
struct node {
int fa, val, c[2], cnt, size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx, tag;
int n, minn, cnt;
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].size = tr[tr[x].c[0]].size + tr[tr[x].c[1]].size + tr[x].cnt;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int k = tr[y].c[1] == x;
tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[k] = tr[x].c[k ^ 1];
tr[tr[x].c[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
tr[x].c[k ^ 1] = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) {
while (tr[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (z != k) {
(tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline void find(int x) {
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return ;
while (tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val] && x != tr[u].val) {
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline void insert(int x) {
rg int u = root, fa = 0;
while (u && tr[u].val != x) {
fa = u;
u = tr[u].c[x > tr[u].val];
}
if (u) {
tr[u].cnt++;
} else {
u = ++idx;
if (fa) {
tr[fa].c[x > tr[fa].val] = u;
}
tr[u].c[0] = tr[u].c[1] = 0;
tr[idx].fa = fa;
tr[idx].val = x;
tr[idx].cnt = 1;
tr[idx].size = 1;
}
splay(u, 0);
}
inline int Next(int x, int f) {
find(x);
rg int u = root;
if (tr[u].val >= x && f) return u;
if (tr[u].val < x && !f) return u;
u = tr[u].c[f];
while (tr[u].c[f ^ 1]) u = tr[u].c[f ^ 1];
return u;
}
inline void Delete() {
rg int next = Next(minn + tag, 1);
splay(1, 0);
splay(next, 1);
cnt += tr[tr[tr[root].c[1]].c[0]].size;
tr[tr[root].c[1]].c[0] = 0;
tr[tr[tr[root].c[1]].c[0]].size = 0;
pushup(tr[root].c[1]);
pushup(root);
}
inline int kth(int x) {
rg int u = root;
if (tr[u].size - 1 < x) return -1;
while (true) {
rg int r = tr[u].c[1];
if (x > tr[r].size + tr[u].cnt) {
x -= tr[r].size + tr[u].cnt;
u = tr[u].c[0];
} else {
if (tr[r].size >= x) u = r;
else return tr[u].val;
}
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
insert(-1e9);
insert(1e9);
cin >> n >> minn;
rg char opt;
rg int k;
while (n--) {
cin >> opt >> k;
if (opt == 'I') {
if (k >= minn) insert(k + tag);
}
if (opt == 'A') {
tag -= k;
}
if (opt == 'S') {
tag += k;
Delete();
}
if (opt == 'F') {
rg int res = kth(k + 1);
if (res == -1) cout << -1 << "\n";
else cout << res - tag << "\n";
}
}
cout << cnt << "\n";
return qwq;
}
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val;
int rnd;
int size;
} tr[N];
int root, idx, tag;
int n, minn, cnt;
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[p].val <= v) {
x = p;
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
inline void del(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
cnt += tr[x].size;
root = y;
}
inline int getval(int root, int v) {
if (tr[root].size < v) return -1;
if (v == tr[tr[root].r].size + 1) return tr[root].val;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].r].size) return getval(tr[root].r, v);
else return getval(tr[root].l, v - tr[tr[root].r].size - 1);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> minn;
rg char opt;
rg int k;
while (n--) {
cin >> opt >> k;
if (opt == 'I') {
if (k >= minn) insert(k + tag);
}
if (opt == 'A') {
tag -= k;
}
if (opt == 'S') {
tag += k;
del(minn + tag);
}
if (opt == 'F') {
rg int res = getval(root, k);
if (res == -1) cout << -1 << "\n";
else cout << res - tag << "\n";
}
}
cout << cnt << "\n";
return qwq;
}
例题5:[TJOI2013] 最长上升子序列
设\(dp[i]\)表示以第i个元素结尾的LIS长度。
考虑在\(pos\)位置后插入元素x(由题意,x是当前序列中的最大元素)
对序列LIS的影响分三段:
- 左半段\([1,pos]\):事实上完全没有影响。
- 右半段\([pos+1,n]\):(n是还没有加入这个元素时的序列长度)由于x是当前序列中的最大元素,因此也无法影响它们。
- 新的这个位置(设为\(pos'\)):由于x是当前序列中的最大元素,因此左半段都能转移过来,即:
\(dp[pos] = \displaystyle\max_{i=1}^{pos'}dp[i]+1\)
接下来暴力把\([pos+1,n]\)右移一格,加入\(dp[pos']\)即可。
而两个关键部分:求\(dp[pos']\)和把\([pos+1,n]\)右移一格都是可以优化的。
求\(dp[pos']\)用线段树很直观。
把\([pos+1,n]\)右移一格这种维护序列的经典操作,完全可以使用平衡树,并且线段树也不需要了,可以顺带统计掉。
具体做法是:每个节点(假设维护\([l,r]\)这个区间,节点本身是位置\(pos\))维护两个额外信息\(val=dp[pos],maxv=\displaystyle\max_{k=l}^{r}dp[k]\)。插入时,将序列分割,左半段和右半段不变,新建一个节点表示\(pos'\),令\(val=maxv=\text{左半段的maxv+1}\)。
splay
调不出来,不放了……
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
struct node {
int l, r;
int val, rnd, size, maxv;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
int n;
inline void pushup(int p) {
tr[p].size = tr[tr[p].l].size + tr[tr[p].r].size + 1;
tr[p].maxv = max(tr[p].val, max(tr[tr[p].l].maxv, tr[tr[p].r].maxv));
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].val = tr[x].maxv = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[tr[p].l].size < v) {
x = p;
split(tr[x].r, v - tr[tr[p].l].size - 1, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, tr[x].maxv + 1);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for (rg int i = 1, pos; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> pos;
insert(pos);
cout << tr[root].maxv << "\n";
}
return qwq;
}
例题6:[JSOI2008] 火星人
做法:平衡树维护哈希值。
观察插入操作,插入的实际上是一个下标,比如在下标2和3之间插入一个字母a,相当于插入了一个位于2.5的a。对于此类问题,平衡树上的关键字设为下标,而它的值则为它表示的字母。 所以对于一个节点,它的左子树上的节点都是在下标比它小的字符,右子树上的节点都是下标比它大的字符。
对于查询操作:
比较明显,我们可以二分公共前缀的长度。而对于区间Hash,我们可以得到:
\(hash[x]=hash[lc]\times base^{size[rc]+1}+val[x]^{size[rc]}+hash[rc]\)
splay
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 3;
struct node {
int val, fa, c[2], siz;
ull hash;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
int n;
ull p[N], base = 131;
inline void pushup(int x) {
if (!x) return ;
tr[x].siz = tr[tr[x].c[0]].siz + tr[tr[x].c[1]].siz + 1;
tr[x].hash = tr[tr[x].c[0]].hash * p[tr[tr[x].c[1]].siz + 1] + (ull)tr[x].val * p[tr[tr[x].c[1]].siz] + tr[tr[x].c[1]].hash;
}
inline void build(int l, int r, int x) {
if (l > r) return ;
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (mid >= x) tr[x].c[1] = mid;
else tr[x].c[0] = mid;
tr[mid].fa = x;
tr[mid].siz = 1;
if (l == r) return ;
build(l, mid - 1, mid);
build(mid + 1, r, mid);
pushup(mid);
return ;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int k = tr[y].c[1] == x;
tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[k] = tr[x].c[k ^ 1];
tr[tr[x].c[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
tr[x].c[k ^ 1] = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k) {
while (tr[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (z != k) {
(tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline int find(int x) {
rg int u = root;
if (!u) return qwq;
while (true) {
if (tr[tr[u].c[0]].siz + 1 == x) return u;
if (tr[tr[u].c[0]].siz + 1 < x) {
x -= tr[tr[u].c[0]].siz + 1;
u = tr[u].c[1];
} else {
u = tr[u].c[0];
}
}
}
inline int get_hash(int l, int r) {
rg int x = find(l);
rg int y = find(r + 2);
splay(x, 0);
splay(y, x);
return tr[tr[tr[root].c[1]].c[0]].hash;
}
inline void update(int x, char c) {
splay(find(x + 1), 0);
tr[root].val = c - 'a';
pushup(root);
}
inline void insert(int p, int c) {
rg int x = find(p + 1);
rg int y = find(p + 2);
splay(x, 0);
splay(y, x);
tr[tr[root].c[1]].c[0] = ++idx;
tr[idx].fa = tr[root].c[1];
tr[idx].val = tr[idx].siz = c - 'a';
splay(idx, 0);
}
char ch[N];
int t;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> ch + 1;
n = strlen(ch + 1);
p[0] = 1;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= (n << 1); i++) {
p[i] = p[i - 1] * base;
}
for (rg int i = 2; i <= n + 1; i++) {
tr[i].val = tr[i].hash = ch[i - 1] - 'a';
}
build(1, n + 2, root);
root = (n + 3) >> 1; //取中点为根
idx = n + 2;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
rg char opt, c;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 'Q') {
rg int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x > y) swap(x, y);
rg int l = 0, r = idx - y - 1, mid;
while (l < r) { //二分公共前缀的长度
mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (get_hash(x, x + mid - 1) == get_hash(y, y + mid - 1)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l << "\n";
}
if (opt == 'R') {
rg int x;
cin >> x >> c;
update(x, c);
}
if (opt == 'I') {
rg int u;
cin >> u >> c;
insert(u, c);
}
}
return qwq;
}
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
#define ull unsigned long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 3;
struct node {
int l, r;
int siz, val, rnd;
ull hash;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
int n;
ull p[N];
int base = 131;
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].siz = tr[tr[x].l].siz + tr[tr[x].r].siz + 1;
tr[x].hash = tr[tr[x].l].hash * p[tr[tr[x].r].siz + 1] + (ull)tr[x].val * p[tr[tr[x].r].siz] + tr[tr[x].r].hash;
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].siz = 1;
tr[x].val = tr[x].hash = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
}
inline void split(int u, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!u) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[tr[u].l].siz + 1 <= v) {
x = u;
split(tr[x].r, v - tr[tr[u].l].siz - 1, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = u;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(u);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline ull get_hash(int l, int r) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, r, x, z);
split(x, l - 1, x, y);
rg ull res = tr[y].hash;
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
return res;
}
inline void update(int u, char c) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, u, x, z);
split(x, u - 1, x, y);
tr[y].hash = tr[y].val = c - 'a';
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
inline void insert(int u, char c) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, u, x, y);
newnode(z, c - 'a');
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
char ch[N];
int t;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> ch + 1;
n = strlen(ch + 1);
p[0] = 1;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= (n << 1); i++) {
p[i] = p[i - 1] * base;
}
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
rg int x;
newnode(x, ch[i] - 'a');
root = merge(root, x);
}
cin >> t;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {
char opt, c;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 'Q') {
rg int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x > y) swap(x, y);
rg int l = 0, r = tr[root].siz - y + 1, mid;
while (l < r) {
mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if (get_hash(x, x + mid - 1) == get_hash(y, y + mid - 1)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
cout << l << "\n";
}
if (opt == 'R') {
rg int x;
cin >> x >> c;
update(x, c);
}
if (opt == 'I') {
rg int x;
cin >> x >> c;
insert(x, c);
}
}
return qwq;
}
例题7:星系探索
由于树是动态的,又需要维护路径信息和子树信息,不妨考虑欧拉序。设进栈为\(l_x\),出栈为\(r_x\)。进栈时把值设为\(a_x\),出栈时设为\(-a_x\),那么根据欧拉序的性质有:
- x到根路径查询:直接查询\([1,l_x]\)的和即可
- x子树加v:区间\([l_x,r_x]\)加v,注意由于区间的点符号可能为正或负,要记录所有符号的和t,那么综合增加的值就是\(v\times t\)
- 将x父亲换为fa:相当于把区间\([l_x,r_x]\)接到新的父亲的入栈序\(l_{fa}\)后面
这个算法也被称为欧拉环游树(Euler Tour Tree,ETT)。
splay
打不动了……
treap
需要注意换父亲操作导致欧拉序中节点顺序改变,split时不能直接\(split(l[x])\),要在树上先求\(l_x\)现在排在序列的位置(即到根路径上左子树大小+1的和),然后再按这个排名slpit。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 3;
int n, m;
vector<int> e[N << 1];
int tim;
int lb[N], rb[N], a[N];
struct node {
int l, r, fa, rnd, siz, tval;
ll tsum; //差分标记和
ll tag, val, sum;
} tr[N];
int root, idx;
inline void newnode(int &x, int v, int type) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].siz = 1;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].tsum = tr[x].tval = type;
tr[x].sum = tr[x].val = v * type;
}
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].siz = tr[tr[x].l].siz + tr[tr[x].r].siz + 1;
tr[x].tsum = tr[x].tval + tr[tr[x].l].tsum + tr[tr[x].r].tsum;
tr[x].sum = tr[x].val + tr[tr[x].l].sum + tr[tr[x].r].sum;
if (tr[x].l) tr[tr[x].l].fa = x;
if (tr[x].r) tr[tr[x].r].fa = x;
}
inline void add_tag(int x, ll tag) {
tr[x].val += tr[x].tval * tag;
tr[x].sum += tr[x].tsum * tag;
tr[x].tag += tag;
}
inline void pushdown(int x) {
if (tr[x].tag) {
add_tag(tr[x].l, tr[x].tag);
add_tag(tr[x].r, tr[x].tag);
tr[x].tag = 0;
}
}
inline void split(int u, int k, int &x, int &y) {
if (!u) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
pushdown(u);
if (k <= tr[tr[u].l].siz) {
y = u;
split(tr[u].l, k, x, tr[y].l);
} else {
x = u;
split(tr[u].r, k - tr[tr[u].l].siz - 1, tr[x].r, y);
}
pushup(u);
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
pushdown(x);
pushdown(y);
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
} else {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
}
}
inline int get_rank(int x) {
rg int ans = tr[tr[x].l].siz + 1;
while (tr[x].fa) {
if (tr[tr[x].fa].r == x) {
ans += tr[tr[tr[x].fa].l].siz + 1;
}
x = tr[x].fa;
}
return ans;
}
inline void add(int id, int val) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, get_rank(rb[id]), y, z);
tr[y].fa = tr[z].fa = 0;
split(y, get_rank(lb[id]) - 1, x, y); //分出id子树对应的区间
tr[x].fa = tr[y].fa = 0;
add_tag(y, val);
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
tr[root].fa = 0;
}
inline ll query(int id) {
rg int x, y;
split(root, get_rank(lb[id]), x, y);
rg ll ans = tr[x].sum;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline void change_fa(int id, int fa_id) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, get_rank(rb[id]), y, z);
tr[y].fa = tr[z].fa = 0;
split(y, get_rank(lb[id]) - 1, x, y); //提取出原来的子树
tr[x].fa = tr[y].fa = 0;
root = merge(x, z);
tr[root].fa = 0;
split(root, get_rank(lb[fa_id]), x, z); //把子树插入到新的父亲后面
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
tr[root].fa = 0;
}
inline void build(int x, int f) {
rg int z;
newnode(z, a[x], 1);
lb[x] = z;
root = merge(root, z);
for (rg int i = 0; i < e[x].size(); i++) {
rg int v = e[x][i];
if (v != f) build(v, x);
}
newnode(z, a[x], -1);
rb[x] = z;
root = merge(root, z);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
rg int u, v;
rg char opt;
cin >> n;
for (rg int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> u;
e[u].push_back(i);
e[i].push_back(u);
}
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
build(1, 0);
cin >> m;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 'Q') {
cin >> u;
cout << query(u) << "\n";
}
if (opt == 'C') {
cin >> u >> v;
change_fa(u, v);
}
if (opt == 'F') {
cin >> u >> v;
add(u, v);
}
}
return qwq;
}
例题8:树套树:二逼平衡树
关于树套树的构建,我们对于外层线段树正常建树,对于线段树上的某一个节点,建立一颗平衡树,包含该节点所覆盖的序列。具体操作时我们可以将序列元素一个个插入,每经过一个线段树节点,就将该元素加入到该节点的平衡树中。
操作一,求某区间中某值的排名:在线段树上找到区间对应的节点,然后每个节点的平衡树内查询对应数的排名并求和。
操作二,求某区间中排名为k的值:由于这项操作在线段树上不可加,所以我们考虑转换为判定一个数是不是区间内排名为k的。那么我们考虑二分答案。
操作三,单点修改:我们在线段树上找到所有覆盖这个点的区间,然后再所有区间对应的平衡树中删除原数,加入新数即可。
操作四,求某区间中某值的前驱、后继:我们只需要对于所有区间分别查询,然后答案取相应的max,min即可。
splay
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 3, M = 1200003, inf = 2147483647;
int w[N];
//平衡树
struct Splay {
int c[2], fa, v, size;
void init(int _fa, int _v) {
c[0] = c[1] = 0;
fa = _fa;
v = _v;
size = 1;
}
} tr[M];
queue<int> nodes; //可用节点下标
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].size = tr[tr[x].c[0]].size + tr[tr[x].c[1]].size + 1;
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
rg int k = tr[y].c[1] == x;
tr[z].c[tr[z].c[1] == y] = x;
tr[x].fa = z;
tr[y].c[k] = tr[x].c[k ^ 1];
tr[tr[x].c[k ^ 1]].fa = y;
tr[x].c[k ^ 1] = y;
tr[y].fa = x;
pushup(y);
pushup(x);
}
inline void splay(int x, int k, int &root) {
while (tr[x].fa != k) {
rg int y = tr[x].fa, z = tr[y].fa;
if (z != k) (tr[z].c[0] == y) ^ (tr[y].c[0] == x) ? rotate(x) : rotate(y);
rotate(x);
}
if (k == 0) root = x;
}
inline void insert(int k, int &root) {
rg int x = root, fa = 0;
while (x) {
fa = x;
x = tr[x].c[k > tr[x].v];
}
tr[fa].c[k > tr[fa].v] = x = nodes.front();
nodes.pop();
tr[x].init(fa, k);
splay(x, 0, root);
}
inline int find_val(int k, int root) {
rg int x = root;
while (x) {
if (tr[x].v == k) return x;
x = tr[x].c[k > tr[x].v];
}
assert(0); //找不到的情况
}
inline void modify(int val, int k, int &root) {
rg int x = find_val(val, root);
splay(x, 0, root);
rg int l = tr[x].c[0], r = tr[x].c[1];
while (tr[l].c[1]) l = tr[l].c[1];
while (tr[r].c[0]) r = tr[r].c[0];
splay(l, 0, root);
splay(r, l, root);
nodes.push(tr[r].c[0]);
tr[r].c[0] = 0;
pushup(r);
pushup(l);
insert(k, root);
}
inline int get_sum(int k, int root) {
rg int x = root, res = 0;
while (x) {
if (tr[x].v < k) {
res += tr[tr[x].c[0]].size + 1;
x = tr[x].c[1];
} else x = tr[x].c[0];
}
return res - 1; //需要减去哨兵-inf
}
inline int get_pre(int k, int root) {
rg int x = root, res = 0;
while (x) {
if (tr[x].v < k) {
res = x;
x = tr[x].c[1];
} else x = tr[x].c[0];
}
return tr[res].v;
}
inline int get_nxt(int k, int root) {
rg int x = root, res = 0;
while (x) {
if (tr[x].v > k) {
res = x;
x = tr[x].c[0];
} else x = tr[x].c[1];
}
return tr[res].v;
}
//线段树
#define ls rt << 1
#define rs rt << 1 | 1
struct segment_tree {
int l, r, root;
} t[N << 2];
inline void build(int rt, int l, int r) {
t[rt].l = l;
t[rt].r = r;
insert(-inf, t[rt].root);
insert(inf, t[rt].root);
for (rg int i = l; i <= r; i++) insert(w[i], t[rt].root);
if (l == r) return ;
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(ls, l, mid);
build(rs, mid + 1, r);
}
inline void update(int rt, int a, int k) {
modify(w[a], k, t[rt].root); //把w[a]删掉,插入k
if (t[rt].l == t[rt].r) return ;
rg int mid = (t[rt].l + t[rt].r) >> 1;
update(ls | (a > mid), a, k);
}
inline int query(int rt, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l <= t[rt].l && t[rt].r <= r) return get_sum(k, t[rt].root);
rg int mid = (t[rt].l + t[rt].r) >> 1;
rg int res = 0;
if (l <= mid) res += query(ls, l, r, k);
if (r > mid) res += query(rs, l, r, k);
return res;
}
inline int query_pre(int rt, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l <= t[rt].l && t[rt].r <= r) return get_pre(k, t[rt].root);
rg int mid = (t[rt].l + t[rt].r) >> 1;
rg int res = -inf;
if (l <= mid) res = max(res, query_pre(ls, l, r, k));
if (r > mid) res = max(res, query_pre(rs, l, r, k));
return res;
}
inline int query_nxt(int rt, int l, int r, int k) {
if (l <= t[rt].l && t[rt].r <= r) return get_nxt(k, t[rt].root);
rg int mid = (t[rt].l + t[rt].r) >> 1;
rg int res = inf;
if (l <= mid) res = min(res, query_nxt(ls, l, r, k));
if (r > mid) res = min(res, query_nxt(rs, l, r, k));
return res;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= M - 5; i++) nodes.push(i);
rg int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> w[i];
}
build(1, 1, n);
while (m--) {
rg int opt;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 1) {
rg int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << query(1, l, r, k) + 1 << "\n";
}
if (opt == 2) {
rg int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
rg int ql = 0, qr = 0x3f3f3f3f;
while (ql < qr) {
rg int mid = (ql + qr + 1) >> 1;
if (query(1, l, r, mid) + 1 <= k) ql = mid;
else qr = mid - 1;
}
cout << ql << "\n";
}
if (opt == 3) {
rg int a, k;
cin >> a >> k;
update(1, a, k);
w[a] = k; //记录原序列的修改情况,防止重复修改a位置,导致平衡树删除错误值
}
if (opt == 4) {
rg int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << query_pre(1, l, r, k) << "\n";
}
if (opt == 5) {
rg int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << query_nxt(1, l, r, k) << "\n";
}
}
return qwq;
}
treap
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rg register
#define qwq 0
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 3, M = 2000003, inf = 2147483647;
int a[M];
int n, m;
struct node {
int v, size, rnd, l, r;
} tr[M];
int idx;
struct FHQ_Treap {
int root;
inline void pushup(int x) {
tr[x].size = tr[tr[x].l].size + tr[tr[x].r].size + 1;
}
inline int merge(int x, int y) {
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (tr[x].rnd < tr[y].rnd) {
tr[x].r = merge(tr[x].r, y);
pushup(x);
return x;
} else {
tr[y].l = merge(x, tr[y].l);
pushup(y);
return y;
}
}
inline void split(int p, int v, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) {
x = y = 0;
return ;
}
if (tr[p].v <= v) {
x = p;
split(tr[x].r, v, tr[x].r, y);
} else {
y = p;
split(tr[y].l, v, x, tr[y].l);
}
pushup(p);
}
inline void newnode(int &x, int v) {
x = ++idx;
tr[x].v = v;
tr[x].rnd = rand();
tr[x].size = 1;
}
inline void insert(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, y);
newnode(z, v);
root = merge(merge(x, z), y);
}
inline void del(int v) {
rg int x, y, z;
split(root, v, x, z);
split(x, v - 1, x, y);
y = merge(tr[y].l, tr[y].r);
root = merge(merge(x, y), z);
}
inline int get_rank(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
ans = tr[x].size + 1;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline void build(int l, int r) {
for (rg int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
insert(a[i]);
}
}
inline int get_val(int root, int v) {
if (v == tr[tr[root].l].size + 1) return tr[root].v;
else if (v <= tr[tr[root].l].size) return get_val(tr[root].l, v);
else return get_val(tr[root].r, v - tr[tr[root].l].size - 1);
}
inline int get_pre(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v - 1, x, y);
if (tr[x].size) ans = get_val(x, tr[x].size);
else ans = -inf;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
inline int get_nxt(int v) {
rg int x, y, ans;
split(root, v, x, y);
if (tr[y].size) ans = get_val(y, 1);
else ans = inf;
root = merge(x, y);
return ans;
}
} FT[M];
#define ls rt << 1
#define rs rt << 1 | 1
struct SegmentTree {
inline void Build(int rt, int l, int r) {
FT[rt].build(l, r);
if (l == r) return ;
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
Build(ls, l, mid);
Build(rs, mid + 1, r);
}
inline int query_rank(int rt, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int k) {
if (r < ql || l > qr) return qwq;
if (ql <= l && r <= qr) {
return FT[rt].get_rank(k) - 1;
}
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return query_rank(ls, l, mid, ql, qr, k) + query_rank(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, k);
}
inline int query_k(int rt, int l, int r) {
rg int L = 0, R = 0x3f3f3f3f, ans = -1;
while (L <= R) {
rg int mid = (L + R) >> 1;
if (query_rank(1, 1, n, l, r, mid) + 1 <= rt) {
ans = mid;
L = mid + 1;
} else R = mid - 1;
}
return ans;
}
inline void update(int rt, int l, int r, int pos, int k) {
FT[rt].del(a[pos]);
FT[rt].insert(k);
if (l == r) return ;
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (pos <= mid) update(ls, l, mid, pos, k);
else update(rs, mid + 1, r, pos, k);
}
inline int pre(int rt, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int k) {
if (r < ql || l > qr) return -inf;
if (ql <= l && r <= qr) return FT[rt].get_pre(k);
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return max(pre(ls, l, mid, ql, qr, k), pre(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, k));
}
inline int nxt(int rt, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int k) {
if (r < ql || l > qr) return inf;
if (ql <= l && r <= qr) return FT[rt].get_nxt(k);
rg int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
return min(nxt(ls, l, mid, ql, qr, k), nxt(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, k));
}
} ST;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (rg int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
ST.Build(1, 1, n);
for (rg int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
rg int opt, l, r, k, pos;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 1) {
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << ST.query_rank(1, 1, n, l, r, k) + 1 << "\n";
}
if (opt == 2) {
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << ST.query_k(k, l, r) << "\n";
}
if (opt == 3) {
cin >> pos >> k;
ST.update(1, 1, n, pos, k);
a[pos] = k;
}
if (opt == 4) {
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << ST.pre(1, 1, n, l, r, k) << "\n";
}
if (opt == 5) {
cin >> l >> r >> k;
cout << ST.nxt(1, 1, n, l, r, k) << "\n";
}
}
return qwq;
}


