数论
1.快速幂
解决次数很高的幂取模问题
快速幂问题:
求ab %p
做法:(核心思想合并基数modp)
利用while循环,循环条件是指数b不为0
指数和1做&运算相当于将指数转为二进制再与1做&
例如指数为6:就化成110&1为0
每次&1会得到化成二进制后当前位数是1还是0
还要设置一个基数base,每次base就平方
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long int qmi(long long int a,long long int b,long long int p){
long long int base =a;//当前底数
long long int ans=1;//答案
while(b){
if(b&1)ans=ans*base%p;
b>>=1;
base=base*base%p;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
long long int a,b,p;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b>>p;
cout<<qmi(a,b,p)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}2.逆元
解决问题:ax除以m为1,则称x为b的逆元。
费马定理:
ap-1除以p余数为1
可推出(a*ap-2)除以p余数为1
所以a的逆元是ap-2 对p取余数
求逆元题目:(核心思想利用快速幂求ap-2 对p取余数)
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
ll qmi(ll a,ll b ,ll p){
ll ans=1;
ll base=a;
while(b){
if(b&1)ans=ans*base%p;
base=base*base%p;
b>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int main(){
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll a,p;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>p;
if(a%p==0)cout<<"impossible"<<endl;
else cout<<qmi(a,p-2,p)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}3.求最大公约数:gcd(欧几里得算法)
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long int gcd(long long int a,long long int b){
if(!b){
return a;
}
else{
gcd(b,a%b);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
long long int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<gcd(a,b)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}//欧几里得算法求最大公因数
gcd(a,b)来求a,b的最大公约数
当b==0,返回a --->gcd(a,0)返回a,因为a和0的最大公约数是a
当b!=0时,递归gcd(b,a%b)
4.扩展欧几里得算法:
给定 n 对正整数 ai,bi,对于每对数,求出一组 xi,yi,使其满足 ai×xi+bi×yi=gcd(ai,bi)。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n行,每行包含两个整数 ai,bi。
输出格式
输出共 n行,对于每组 ai,bi,求出一组满足条件的 xi,yi,每组结果占一行。
本题答案不唯一,输出任意满足条件的 xi,yi 均可。
数据范围
1≤n≤105
1≤ai,bi≤2×109
输入样例:
2
4 6
8 18输出样例:
-1 1
-2 1查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int exgcd(int a,int b,int&x,int&y){
if(!b){
//exgcd(a,0)
x=1;
y=0;
return a;
}
int d=exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=a/b*x;
return d;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
int a,b;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b;
int x,y;
exgcd(a,b,x,y);
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
}
return 0;
}扩展欧几里得算法:
exgcd(a,b,x,y)
适用于ai×xi+bi×yi=gcd(ai,bi)求xi,yi满足ai×xi+bi×yi等于ai,bi的最大公因数
求法:
b相等于0:
x=1,y=0;
a*1+0*b=(a,0)
exgcd(a,0)--->返回a,因为a和0的最大公约数是a。
返回a
b不想等于0:
就递归--->exgcd(b,a%b,y,x)
y-=a/b*x;

exgcd(b,a%b,y,x)的接下来的思路:设最大公因数d
b*y+(a%b)*x=d
--->b*y+(a-⌊a/b⌋*b)*x=d;
--->a*x+b*(y-⌊a/b⌋*x)=d;
所以b的系数y变为y-⌊a/b⌋*x
5.线性同余方程
给定 n 组数据 ai,bi,mi,对于每组数求出一个 xi,使其满足 ai×xi≡bi(modmi),如果无解则输出 impossible。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n 行,每行包含一组数据 ai,bi,mi。
输出格式
输出共 n行,每组数据输出一个整数表示一个满足条件的 xi,如果无解则输出 impossible。
每组数据结果占一行,结果可能不唯一,输出任意一个满足条件的结果均可。
输出答案必须在 int范围之内。
数据范围
1≤n≤105,
1≤ai,bi,mi≤2×109
输入样例:
2
2 3 6
4 3 5输出样例:
impossible
-3
查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll& y ){
//exgcd(a,0)
if(!b) {
x=1;
y=0;
return a;
}
ll d= exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=(a/b)*x;
return d;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
ll a,b,m;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b>>m;//
ll x,y;
ll d= exgcd(a,m,x,y);
if(b%d!=0)cout<<"impossible"<<endl;
else cout<<(((b/d)*x)%m)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}分析思路:
ai×xi≡bi(modmi);
--->ax=my+b;
ax-my=b
化成扩展欧几里德方程:
另-y为t,设等号右边为d
--->ax+mt=d
所以所要的xi为((b/d)*x)%m,
有无解的条件是:
(1)无解:b%d不为0
(2)有解:b%d为0
利用扩展欧几里德算法:(照搬欧几里德算法)
ll exgcd(ll a,ll b,ll &x,ll& y ){
//exgcd(a,0)
if(!b) {
x=1;
y=0;
return a;
}
ll d= exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=(a/b)*x;
return d;
}
//x,y要用引用才能修改
6.高斯消元
输入一个包含 n个方程 ,n个未知数的线性方程组。
方程组中的系数为实数。
求解这个方程组。
下图为一个包含 m 个方程 n 个未知数的线性方程组示例:
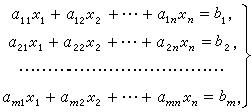
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 n+1个实数,表示一个方程的 n 个系数以及等号右侧的常数。
输出格式
如果给定线性方程组存在唯一解,则输出共 n行,其中第 i 行输出第 i 个未知数的解,结果保留两位小数。
注意:本题有 SPJ,当输出结果为 0.00 时,输出 -0.00 也会判对。在数学中,一般没有正零或负零的概念,所以严格来说应当输出 0.00,但是考虑到本题作为一道模板题,考察点并不在于此,在此处卡住大多同学的代码没有太大意义,故增加 SPJ,对输出 -0.00 的代码也予以判对。
如果给定线性方程组存在无数解,则输出 Infinite group solutions。
如果给定线性方程组无解,则输出 No solution。
数据范围
1≤n≤100
所有输入系数以及常数均保留两位小数,绝对值均不超过 100。
输入样例:
3
1.00 2.00 -1.00 -6.00
2.00 1.00 -3.00 -9.00
-1.00 -1.00 2.00 7.00输出样例:
1.00
-2.00
3.00查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
const double eps = 1e-8;
int n;
double a[N][N];//增广矩阵
int gauss() // 高斯消元,答案存于a[i][n]中,0 <= i < n
{
int c, r;
for (c = 0, r = 0; c < n; c ++ )
{
int t = r;//r为当前起始行数 ,t默认这是当前列中绝对值最大元素对应的行下标 每次从r开始
for (int i = r; i < n; i ++ ) // 找当前列中绝对值最大的行
if (fabs(a[i][c]) > fabs(a[t][c]))
t = i;
if (fabs(a[t][c]) < eps) continue;//这一列全为0跳过
for (int i = c; i <= n; i ++ ) swap(a[t][i], a[r][i]); // 将绝对值最大的行换到最顶端
// 将当前行的首位变成1,这一行除以这一行第一个非零元素,从这一行第n个元素往前
for (int i = n; i >= c; i -- ) a[r][i] /= a[r][c];
// 用当前行将下面所有的列消成0
for (int i = r + 1; i < n; i ++ )//从把当前行往下所有行的当前列化为0
if (fabs(a[i][c]) > eps)
for (int j = n; j >= c; j -- )
a[i][j] -= a[r][j] * a[i][c];
r ++ ;
}
if (r < n)
{
for (int i = r; i < n; i ++ )
if (fabs(a[i][n]) > eps)
return 2; // 无解
return 1; // 有无穷多组解
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i -- )
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j ++ )
a[i][n] -= a[i][j] * a[j][n];
return 0; // 有唯一解
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
//增广矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < n + 1; j ++ )
scanf("%lf", &a[i][j]);
//gauss定理返回值表示解的类型(0唯一解,1无穷多解,2无解)
int t = gauss();
if (t == 2) puts("No solution");
else if (t == 1) puts("Infinite group solutions");
else
{
//x0~xn
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
printf("%.2lf\n", a[i][n]);//保留两位小数
}
return 0;
}
// 对于浮点数保留位数用printf的写法:
printf("%.保留位数lf",变量名称);
//代码分析
首先是main函数:
输入增广矩阵
然后调用高斯消元函数(高斯消元算法)
高斯消元函数的返回值:
返回值为2:无解
返回值为1:无穷解
返回值为0:唯一解
然后是高斯消元函数
int r,c;
for(r=0,c=0;c<n;c++){
//fabs()//浮点数绝对值
//t从当前行开始,然后用来记录当前列最大元素的行下标,找当前列最大元素的行标
int t =r;
for(int i=r;i<n;i++){
if(fabs(a[i][c])>fabs(a[t][c])){
t=i;
}
}
//如果当前列元素最大值为0就跳过,因为是浮点数有精度问题所以设个p对p赋个很小的值1e-8
if(fabs(a[t][c])<p)continue;//绝对值接近0
//是对增广矩阵的变化,下标从0~n
for(int i=r;i<=n;i++)swap(a[t][i],a[r][i]);//t行是当前列绝对值最大的行标,t行与当前行r一 一交换,从列下标r开始,因为这行前r列都为0
for(int i=n;i>=r;i--){
a[r][i]/=a[r][c];
}//从右往左目的是让该行首元素为1
// //对r+1行开始,用第r行处理目的是消除第r+1列开始向下所有列的首非零元素
for(int i=r+1;i<n;i++){
if(fabs(a[i][c])>p){
for(int j=n;j>=c;j--){
a[i][j]-=a[r][j]*a[i][c];
}
}
}
//唯一解--->n-1行往上求解
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
//只改变每一行最后一列
a[i][n]-=a[i][j]*a[j][n];//这一行的每一列乘上对称行上的尾元素
}
}
return 0;//唯一解
}
组合数:
<题型一>
给定 n 组询问,每组询问给定两个整数 a,b,请你输出 Cabmod(109+7)的值。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n行,每行包含一组 a和 b。
输出格式
共 n行,每行输出一个询问的解。
数据范围
1≤n≤10000
1≤b≤a≤2000
输入样例:
3
3 1
5 3
2 2输出样例:
3
10
1查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=2010;
const long long int p=1e9+7;
int c[N][N];
void init(){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
if(!j)c[i][j]=1;
else{
c[i][j]=(c[i-1][j]+c[i-1][j-1])%p;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
init();
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<c[a][b]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}<题型二>
给定 n 组询问,每组询问给定两个整数 a,b,请你输出 Cabmod(109+7) 的值。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n 行,每行包含一组 a 和 b。
输出格式
共 n 行,每行输出一个询问的解。
数据范围
1≤n≤10000
1≤b≤a≤105
输入样例:
3
3 1
5 3
2 2输出样例:
3
10
1查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e5+6;
long long int mod=1e9+7;
int fact[N];
int infact[N];
int qmi(int a,int b,int c){
int res=1;
//快速幂 a 的b次方模c
while(b){
if(b&1)res=(long long int)res*a%c;
a=(long long int)a*a%c;
b>>=1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
//初始化:
fact[0]=infact[0]=1;
int n;
cin>>n;
int a,b;
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
fact[i]=(long long int)fact[i-1]*i%mod;
infact[i]=(long long int)infact[i-1]*qmi(i,mod-2,mod)%mod;
}
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<(long long int)fact[a]*infact[a-b]%mod*infact[b]%mod<<endl;
}
return 0;
}利用逆元思想
fact数组存放阶乘结果,infact数组存放逆元阶乘结果即infact[p]表示1/p!
Cab=a!/((a-b)!*b!);
<题型四>利用质因子分解+高精度乘法解决组合
输入 a,b,求 Cab 的值。
注意结果可能很大,需要使用高精度计算。
输入格式
共一行,包含两个整数 a 和 b。
输出格式
共一行,输出 Ca b 的值。
数据范围
1≤b≤a≤5000
输入样例:
5 3输出样例:
10查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5010;
int primes[N], cnt;
int sum[N];
bool st[N];
void get_primes(int n)
{
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i ++ )
{
if (!st[i]) primes[cnt ++ ] = i;
for (int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j ++ )
{
st[primes[j] * i] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}
int get(int n, int p)
{
int res = 0;
while (n)
{
res += n / p;
n /= p;
}
return res;
}
vector<int> mul(vector<int> a, int b)
{
vector<int> c;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i ++ )
{
t += a[i] * b;
c.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
while (t)
{
c.push_back(t % 10);
t /= 10;
}
return c;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
get_primes(a);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++ )
{
int p = primes[i];
sum[i] = get(a, p) - get(a - b, p) - get(b, p);
}
vector<int> res;
res.push_back(1);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++ )
for (int j = 0; j < sum[i]; j ++ )
res = mul(res, primes[i]);
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i -- ) printf("%d", res[i]);
puts("");
return 0;
}
代码思路分析:
全局变量:
const int N=5010;
int cnt;
int prime[N];//存放的质数
bool st[N];//是否被筛掉,默认没删除,删除改完true
int sum[N];//该质数出现次数
先用质数筛,再计算每个范围内质数在C a b 中出现次数,最后采取高精度乘法。
利用高精度算法求得的是个数组,然后需要倒着输出。
本题需要用四个函数,
(1)线性筛素数
//线性筛素数
void get_primes(int a){
for(int i=2;i<=a;i++){
if(!st[i])prime[cnt++]=i;//没被删,说明是素数
for(int j=0;prime[j]<=n/i;j++){
st[i*prime[j]]=true;
if(i%prime[j]==0)break;
}
}
}
核心代码:
st[i*prime[j]]=true;//筛掉就变为true
if(i%prime[j]==0)break;//i是prime[j]的倍数就break
(2)求数字n中p出现的次数
//get函数
int get(int a,int p){
int ans=0;
while(a){
ans+=a/p;
a/=p;
}
return res;
}
用ans来存放p出现的个数,先p,p2 ,p3 ...
(3)高精度乘低精度模板
//高精度乘低精度
vector<int>mul(vector<int>res,int b){
vector<int>a;
int t=0;
//逐位相乘
for(int i=0;i<res.size();i++){
t+=res[i]*b;
a.push_back(t%10);
t/=10;
}
//如果t还有剩
while(t){
a.push_back(t%10);
t/=10;
}
return a;
}
(4)main函数
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
get_primes(a);//a中所有质数
//质因数出现的次数(一共有cnt个素数)
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
int p=prime[i];//得到当前素数
//利用公式C a b=a!/((a-b)!*b!)
sum[i]=get(a,p)-get(a-b,p)-get(b,p);//得到Cab这个组合数中该素数出现的次数 }
//高精度乘法
vector<int>res;
res.push_back(1);
//让结果乘上素数,每个素数出现次数
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++){
for(int j=0;j<sum[i];j++){
res=mul(res,prime[i]);
}
}
//倒着输出答案用数组存,动态数组vector
for(int i=res.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
cout<<res[i];
}
<题型三>用卢卡斯定理求组合数
给定 n组询问,每组询问给定三个整数 a,b,p,其中 p 是质数,请你输出 Cabmodp 的值。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n行,每行包含一组 a,b,p。
输出格式
共 n 行,每行输出一个询问的解。
数据范围
1≤n≤20
1≤b≤a≤1018
1≤p≤105
输入样例:
3
5 3 7
3 1 5
6 4 13输出样例:
3
3
2查看代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int ll;
//快速幂
ll qmi(int a,int b,int c){
ll res=1%c;//返回值
while(b){
if(b&1){
res=(ll)res*a%c;
}
b>>=1;
a=(ll)a*a%c;
}
return res;
}
//求组合数
ll C(ll a,ll b,ll p){
if(a<b)return 0;
int i,j;
int x=1;//分子
int y=1;//分母
for( i=a,j=1;j<=b;i--,j++){
x=(ll)x*i%p;
y=(ll)y*j%p;
}
return (ll)x*qmi(y,p-2,p)%p;
}
ll lucass(ll a,ll b,ll p){
if(a<p&&b<p)return C(a,b,p);
return (ll)lucass(a/p,b/p,p)*C(a%p,b%p,p)%p;//递归lucass用除,组合数用%
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
ll a,b,p;
cin>>a>>b>>p;
cout<<lucass(a,b,p)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}利用lucass定理求组合数
一共有四个函数
(1)主函数main
调用lucass定理,返回组合数值。
子函数
(2)快速幂模版
(3)组合数
Ca b=(a-b+1)!/b!
利用循环求阶乘,分别计算组合数结果的分子(a-b+1)!,分母b!
然后得到分子分母
返回值是分子*分母的逆元%p
除法都用乘逆元,所以分母的逆元为qmi(分母,p-2,p)
(4)lucass定理函数(核心)
if(a<p&&b<p)return C(a,b,p);
//用lucass定理递推用除p,再乘以取余组合数,最后%p.
return (ll)lucass(a/p,b/p,p)*C(a%p,b%p,p)%p;
容斥原理
查看代码
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 20;
int p[N], n, m;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) cin >> p[i];
int res = 0;//res表示满足条件的整数有多少个
//枚举从1 到 1111...(m个1)的每一个集合状态, (至少选中一个集合)
for(int i = 1; i < 1 << m; i++) {
int t = 1; //选中集合对应质数的乘积
int s = 0; //选中的集合数量
//枚举当前状态的每一位
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
//选中一个集合
if(i >> j & 1){
//乘积大于n, 则n/t = 0, 跳出这轮循环
if((LL)t * p[j] > n){
t = -1;
break;
}
s++; //有一个1,集合数量+1
t *= p[j];
}
}
if(t == -1) continue;
if(s %2) res += n / t; //选中奇数个集合, 则系数应该是1, n/t为当前这种状态的集合数量
else res -= n / t; //反之则为 -1
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}//对于m个质数搭配的集合有2m -1种,因为不包括一个质数不含的情况
核心代码
利用位运算,2m 用1<<m
//集合搭配有2 m 种
for(int i=1;i<1<<m;i++){
int t=1;//记录当前所取集合乘积的值
int s=0;//记录取了多少个集合
//有m个质数
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
//i>>j&1表示i向右j位i>>j,表示从右往左第j位是否为0
if(i>>j&1){
//n仅仅用来限制范围
if(t*p[j]>n){
t=-1;//表示这种情况不符合
break;
}
s++;
t*=p[j];}
if(t==-1)continue;//不满足条件
//利用容斥原理,奇数次的符号为正,偶数次的符号为负。
if(s%2){//奇数
res=res+n/t;
}
else{
res=res-n/t;
}
}
标签:输出,return,数论,res,ll,long,int From: https://www.cnblogs.com/luckyhappyyaoyao/p/17984904