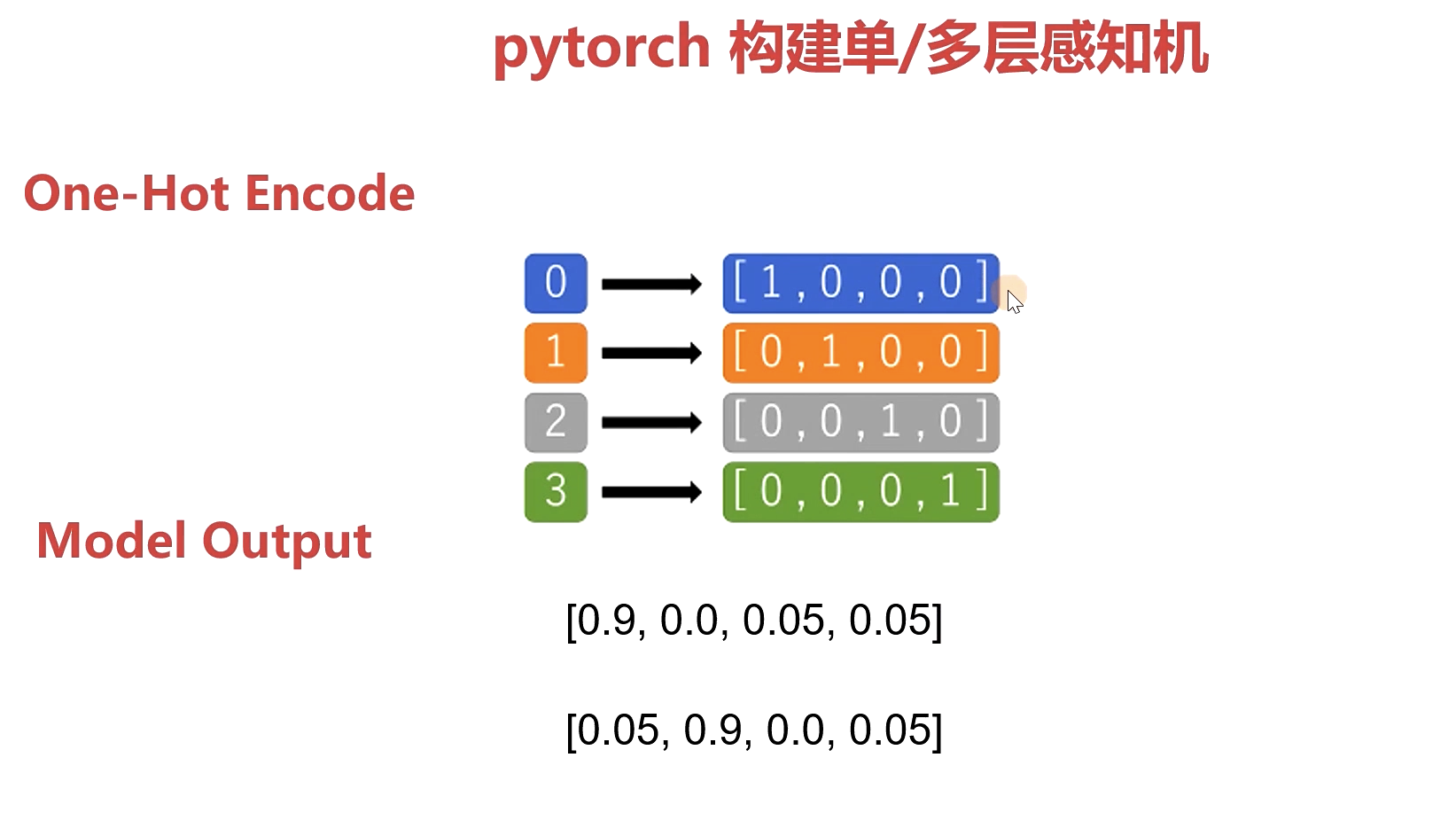
One -Hot Encode 编码:
主要用于解决神经网络用于分类的构建loss编码的方式
super()
super() 函数是用于调用父类(超类)的一个方法。
super() 是用来解决多重继承问题的,直接用类名调用父类方法在使用单继承的时候没问题,但是如果使用多继承,会涉及到查找顺序(MRO)、重复调用(钻石继承)等种种问题。
MRO 就是类的方法解析顺序表, 其实也就是继承父类方法时的顺序表。
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
class FooParent(object):
def __init__(self):
self.parent = 'I\'m the parent.'
print ('Parent')
def bar(self,message):
print ("%s from Parent" % message)
class FooChild(FooParent):
def __init__(self):
# super(FooChild,self) 首先找到 FooChild 的父类(就是类 FooParent),然后把类 FooChild 的对象转换为类 FooParent 的对象
super(FooChild,self).__init__()
print ('Child')
def bar(self,message):
super(FooChild, self).bar(message)
print ('Child bar fuction')
print (self.parent)
if __name__ == '__main__':
fooChild = FooChild()
fooChild.bar('HelloWorld')
torch.unsuqeeze()和torch.squeeze():
- torch.squeeze(input, dim = None, out = None): 返回一个tensor
- 当dim不设值时,去掉输入的tensor的所有维度为1的维度;
- 当dim为某一整数(0<=dim<input.dim())时,判断dim维的维度是否为1,若是则去掉,否则不变。
- 另外,当input是一维的时候,squeeze不变
>>> x = torch.zeros(1,1,2,1,3)
>>> x.dim()
5
>>> torch.squeeze(x).size() # 去掉dim=1的维度
torch.Size([2, 3])
>>> torch.squeeze(x,0).size() # dim=0表示第一维,且第一维的维度为1,所以去掉
torch.Size([1, 2, 1, 3])
>>> torch.squeeze(x,3).size()
torch.Size([1, 1, 2, 3])
>>> torch.squeeze(x,2).size() # dim=2,第三维的维度为2!=1,所以不变
torch.Size([1, 1, 2, 1, 3])
torch.unqueeze(input, dim, out=None): 和squeeze作用相反,unsqueeze()在dim维插入一个维度为1的维,例如原来x是n×m维的,torch.unqueeze(x,0)这返回1×n×m的tensor
>>> x = torch.tensor([1,2,3]) # dim=1,即(3)
>>> torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) # 变为(3,1)的矩阵
tensor([[ 1],
[ 2],
[ 3]])

from calendar import day_abbr
from imp import init_frozen
from operator import mod
# from selectors import EpollSelector
from turtle import back, forward
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
n_item = 1000 #数目条目
n_feature = 2 #特征维度
learning_rate = 0.001 #损失函数,学习率
epochs = 100 #训练论数
# fake data :数据
torch.manual_seed(123)
data_x = torch.randn(size=(n_item,n_feature)).float() #构造一个1000条维度为2的随机数据
data_y = torch.where(torch.subtract(data_x[:,0]*0.5, data_x[:,1]*1.5) > 0.02,0,1.).long()
data_y = F.one_hot(data_y) #one_hot encode
# shape :[n_item,2]
'''
tensor([[1,0],
[0,1],
...,
[0,1]])
'''
#构造模型
class BinaryClassificationMode(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_feature):
super(BinaryClassificationMode,self).__init__()
# super()继承父类nn.module 并把类nn.module转换为BinaryClassificationMode的对象
# ''' 单层感知机'''
# self.layer_1 = nn.Linear(in_features=in_feature,out_features=2,bias=True)
# # Linear()对输入数据应用线性变化,in_features:样本大小 in_features:输出样本大小 bias:偏置
#多层感知机 比单层感知机多了个隐藏层
self.layer_1 = nn.Linear(in_features=in_feature,out_features=128,bias=True)
self.layer_2 = nn.Linear(in_features=128,out_features=512,bias=True)
#可以定义很多层
self.layer_final = nn.Linear(in_features=512,out_features=2,bias=True) #最后一层样本输入是倒数第二层,样本输入是2 (因为是2分类问题)
#前向
def forward(self,x):
##单层感知机
# return F.sigmoid(self.layer_1(x))
#多层
layer_1_output = F.sigmoid(self.layer_1(x))
layer_2_output = F.sigmoid(self.layer_2(layer_1_output))
output = F.sigmoid(self.layer_final(layer_2_output))
return output
# 超参数
learning_rate = 0.01
epochs =100
#模型的实例
model = BinaryClassificationMode(n_feature)
#模型传入优化器
opt = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr = learning_rate)
#构造损失函数 交叉商loss(二分类问题中)
criteria = nn.BCELoss()
#训练
for epoch in range(1000):
for step in range(n_item):
x = data_x[step]
y = data_y[step]
#梯度归零 放在方向求导backward之前
opt.zero_grad()
y_hat = model(x.unsqueeze(0)) #[1,2] 增加了一个维度,在维度0的位置 从m变成了 1*m
#[1,2]:[[0.9 , 0.1]]
loss = criteria(y_hat,y.unsqueeze(0).float())
loss.backward()
#更新模型参数
opt.step()
print('Epoch: %03d, loss: %.3f' % (epoch,loss.item()))