There is a 3 lane road of length n that consists of n + 1 points labeled from 0 to n. A frog starts at point 0 in the second lane and wants to jump to point n. However, there could be obstacles along the way.
You are given an array obstacles of length n + 1 where each obstacles[i] (ranging from 0 to 3) describes an obstacle on the lane obstacles[i] at point i. If obstacles[i] == 0, there are no obstacles at point i. There will be at most one obstacle in the 3 lanes at each point.
- For example, if
obstacles[2] == 1, then there is an obstacle on lane 1 at point 2.
The frog can only travel from point i to point i + 1 on the same lane if there is not an obstacle on the lane at point i + 1. To avoid obstacles, the frog can also perform a side jump to jump to another lane (even if they are not adjacent) at the same point if there is no obstacle on the new lane.
- For example, the frog can jump from lane 3 at point 3 to lane 1 at point 3.
Return the minimum number of side jumps the frog needs to reach any lane at point n starting from lane 2 at point 0.
Note: There will be no obstacles on points 0 and n.
Example 1:
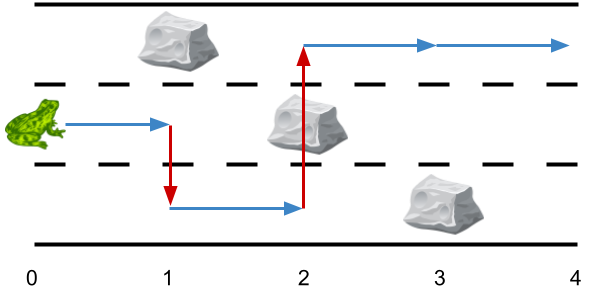
Input: obstacles = [0,1,2,3,0] Output: 2 Explanation: The optimal solution is shown by the arrows above. There are 2 side jumps (red arrows). Note that the frog can jump over obstacles only when making side jumps (as shown at point 2).
Example 2:
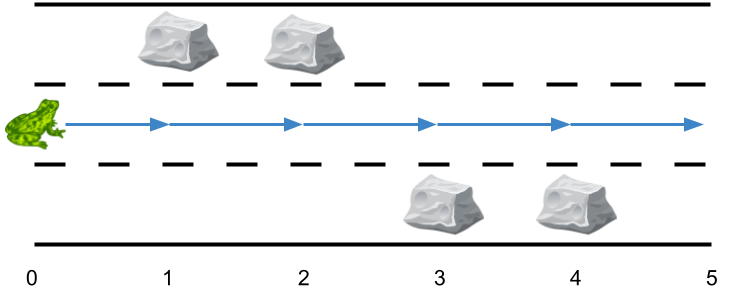
Input: obstacles = [0,1,1,3,3,0] Output: 0 Explanation: There are no obstacles on lane 2. No side jumps are required.
Example 3:
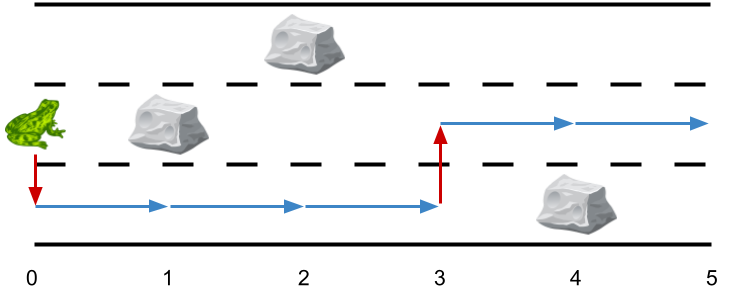
Input: obstacles = [0,2,1,0,3,0] Output: 2 Explanation: The optimal solution is shown by the arrows above. There are 2 side jumps.
Constraints:
obstacles.length == n + 11 <= n <= 5 * 1050 <= obstacles[i] <= 3obstacles[0] == obstacles[n] == 0
最少侧跳次数。
给你一个长度为 n 的 3 跑道道路 ,它总共包含 n + 1 个 点 ,编号为 0 到 n 。一只青蛙从 0 号点第二条跑道 出发 ,它想要跳到点 n 处。然而道路上可能有一些障碍。
给你一个长度为 n + 1 的数组 obstacles ,其中 obstacles[i] (取值范围从 0 到 3)表示在点 i 处的 obstacles[i] 跑道上有一个障碍。如果 obstacles[i] == 0 ,那么点 i 处没有障碍。任何一个点的三条跑道中 最多有一个 障碍。
比方说,如果 obstacles[2] == 1 ,那么说明在点 2 处跑道 1 有障碍。
这只青蛙从点 i 跳到点 i + 1 且跑道不变的前提是点 i + 1 的同一跑道上没有障碍。为了躲避障碍,这只青蛙也可以在 同一个 点处 侧跳 到 另外一条 跑道(这两条跑道可以不相邻),但前提是跳过去的跑道该点处没有障碍。比方说,这只青蛙可以从点 3 处的跑道 3 跳到点 3 处的跑道 1 。
这只青蛙从点 0 处跑道 2 出发,并想到达点 n 处的 任一跑道 ,请你返回 最少侧跳次数 。注意:点 0 处和点 n 处的任一跑道都不会有障碍。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-sideway-jumps
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路是动态规划。我们需要一个长度为 3 的数组,分别表示三条跑道,记录到达 dp[i][j] 位置的时候,最小花费是多少。i 表示走到哪一个点了,j 表示在哪一条赛道上。由于走到当前位置只和上一个位置有关,我们可以精简为一维数组。
初始化的时候,因为青蛙是在第二条跑道,跳到隔壁的跑道是有花费的,所以 dp[0] = dp[2] = 1,dp[1] = 0。开始走了之后,看一下当前赛道是否有障碍物,如果没有,则走到当前 i 位置的花费跟上一个位置 i - 1 相同;如果当前位置有障碍,则看一下是否从别的赛道跳过来的花费会更小。
时间O(n)
空间O(1) - 长度只有3的数组
Java实现
1 class Solution {
2 public int minSideJumps(int[] obstacles) {
3 int n = obstacles.length;
4 int[] dp = new int[3];
5 // 初始化的时候,0和2位置都是1,因为跳过去会有花费
6 dp[0] = dp[2] = 1;
7 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
8 int object = obstacles[i];
9 int pre0 = dp[0];
10 int pre1 = dp[1];
11 int pre2 = dp[2];
12 // 注意这里如果填Integer.MAX_VALUE,后面取更小值的时候就不对了
13 Arrays.fill(dp, (int) 2e9);
14
15 // 如果当前位置无障碍物,那么花费跟上一个位置一样
16 if (object != 1)
17 dp[0] = pre0;
18 if (object != 2)
19 dp[1] = pre1;
20 if (object != 3)
21 dp[2] = pre2;
22
23 // 看看从隔壁位置跳过来,最小花费是多少
24 if (object != 1)
25 dp[0] = Math.min(dp[0], Math.min(dp[1], dp[2]) + 1);
26 if (object != 2)
27 dp[1] = Math.min(dp[1], Math.min(dp[0], dp[2]) + 1);
28 if (object != 3)
29 dp[2] = Math.min(dp[2], Math.min(dp[0], dp[1]) + 1);
30 }
31 return Math.min(dp[0], Math.min(dp[1], dp[2]));
32 }
33 }
标签:跑道,point,int,1824,Jumps,obstacles,lane,Minimum,dp From: https://www.cnblogs.com/cnoodle/p/17063624.html