演示了创建曲面节点的函数
(1)首先设置面数据的顶点坐标,设置面数据在I和J方向的网格个数,以及网格间距,随便设置z和颜色。也可以通过读取外部数据的方式获取顶点坐标和网格上的属性值,根据需要的色标计算每个网格的rgb颜色值。
(2)每个网格一个图元,设置它的坐标索引,并设置颜色数组,通过图元绑定的方式渲染进行显示。
效果如下,下面是代码。
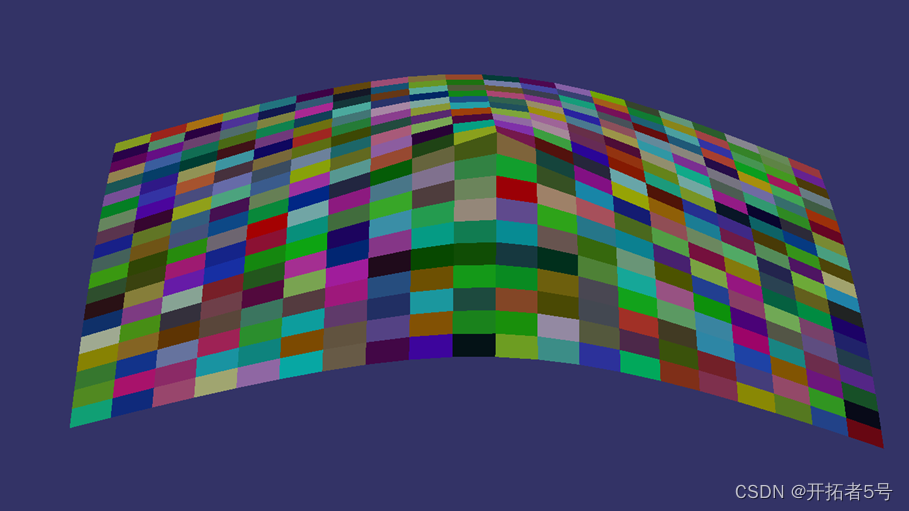
// osg_hello.cpp : This file contains the 'main' function. Program execution begins and ends there.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <random>
#ifdef _WIN32
#include <windows.h>
#endif
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osg/Node>
#include <osg/Geode>
#include <osg/Group>
#include <osgDB/ReadFile>
#include <osgDB/WriteFile>
#include <osgUtil/Optimizer>
/// <summary>
/// 创建曲面节点对象
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Node> createSurface() {
//创建一个节点对象
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geode> geode = new osg::Geode();
//创建一个集合对象
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Geometry> geom = new osg::Geometry();
//面数据网格的相关参数
int ni = 20;
int nj = 20;
float dx = 10.0f;
float dy = 5.0f;
float xMid = ni * dx / 2;
float yMid = nj * dy / 2;
//创建顶点数组
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array> vertx = new osg::Vec3Array();
for (int j = 0; j <= nj; j++) {
float y = j * dy;
for (int i = 0; i <= ni; i++) {
float x = i * dx;
float z = -0.5 * sqrt(pow(x - xMid, 2) + pow(y - yMid, 2));
vertx->push_back(osg::Vec3(x,y,z));
}
}
std::random_device dev;
std::default_random_engine rnd(dev());
std::uniform_real_distribution<float> u(0,1);
//设置顶点数据
geom->setVertexArray(vertx.get());
//创建颜色数组
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec4Array> vcolor = new osg::Vec4Array();
for (int j = 0; j < nj; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < ni; i++) {
int index = j * (ni+1) + i;
//创建四边形定点数组,指定绘图基元为四边形,注意添加顺序
osg::ref_ptr<osg::DrawElementsUInt> quad =
new osg::DrawElementsUInt(osg::PrimitiveSet::QUADS, 0);
quad->push_back(index);
quad->push_back(index + 1);
quad->push_back(index + ni + 2);
quad->push_back(index + ni + 1);
//添加到几何体
geom->addPrimitiveSet(quad.get());
//vcolor->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)); //red
vcolor->push_back(osg::Vec4(u(rnd), u(rnd), u(rnd), 1.0f)); //random color for simple
}
}
//设置颜色数组
geom->setColorArray(vcolor.get());
//设置颜色的绑定方式为单个顶点
//geom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_PER_VERTEX);
geom->setColorBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_PER_PRIMITIVE_SET);
// 创建法线数组
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Vec3Array>nc = new osg::Vec3Array();
//添加法线
nc->push_back(osg::Vec3(0.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f));
// 设置法线数组
geom->setNormalArray(nc.get());
//设置法线的绑定方式为全部顶点
geom->setNormalBinding(osg::Geometry::BIND_OVERALL);
//添加到叶节点
geode->addDrawable(geom.get());
return geode.get();
}
int main()
{
// 创建Viewer对象,场景浏览器创建一个节点。viewer->setSceneData(root.get())viewer->realize(viewer - un();
osg::ref_ptr<osgViewer::Viewer> viewer = new osgViewer::Viewer();
//创建场最组节点
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> root = new osg::Group();
//创建面对象
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Node> node = createSurface();
//添加到场景
root->addChild(node.get());
//优化场景数据
osgUtil::Optimizer optimizer;
optimizer.optimize(root.get());
//设置场景数据
viewer->setSceneData(root.get());
//设置渲染的窗口
//viewer->setUpViewAcrossAllScreens(); //default on all screens
viewer->setUpViewOnSingleScreen(0);
//开始渣染
viewer->run();
return 0;
}
标签:get,三维,geom,曲面,include,ref,ptr,osg From: https://www.cnblogs.com/oliver2022/p/16609419.html