NOI2003 逃学的小孩 题解
题目简述
给定一棵树 \(T\),需要选择三个点 \(A,B,C\),需要从 \(C\) 走到 \(A,B\) 的最远距离。
(第一段题目是在讲剧情吗。。)
前置知识
- 图
- 树
- 树的直径
思路简述
这题在蓝题(提高+ / 省选-)中还是比较水的 ^_^
来看看样例吧
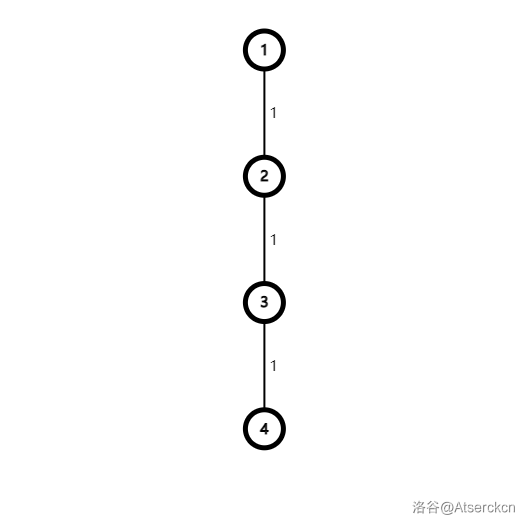
用瞪眼法(——数学老师) 看看,发现 \(A,B\) 可以设在 \(1\) 和 \(4\),然后 \(C\) 在 \(2\) 或 \(3\) 都无所谓。
那么 \(4\) 是咋来的呢?
(设 \(C\) 在 \(2\))
\(2\rightarrow 1 \rightarrow4\)。
由于是最远距离,那么——
树的直径!
而刚好,树的直径就是有两个端点,刚刚好可以一个作为 \(A\),一个作为 \(B\)。
然后 \(C\) 就是在除了 \(A,B\) 的节点,距离 \(A,B\) 的最短路径。
那么,直接枚举所有 \(C\),取最大值再加上 \(A\rightarrow B\) 的距离(直径距离)即可。
代码实现
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll N=2e5+5;
ll n,m,head[N],cnt_e,u,v,w,top,dis_start[N],dis_stop[N],start,stop,ans,ans2;
struct E{
ll from,to,w,pre;
}e[N<<1];
inline void add(ll from,ll to,ll w)//链式前向星
{
e[++cnt_e].from=from;
e[cnt_e].to=to;
e[cnt_e].w=w;
e[cnt_e].pre=head[from];
head[from]=cnt_e;
return;
}
void dfs_d(ll u/*当前节点*/,ll fa/*他爹*/,ll sum/*目前的最长路径*/)//求树的直径
{
if(sum>ans)
ans=sum,top=u;
for(ll i=head[u];i;i=e[i].pre)
{
ll v=e[i].to;
if(v==fa) continue;
dfs_d(v,u,sum+e[i].w);
}
return;
}
void dfs_dis_start(int u,int fa)//所有点到某个端点的距离
{
for(ll i=head[u];i;i=e[i].pre)
{
ll v=e[i].to;
if(v==fa) continue;
dis_start[v]=dis_start[u]+e[i].w;
dfs_dis_start(v,u);
}
return;
}
void dfs_dis_stop(int u,int fa)//所有点到另一个端点的距离
{
for(ll i=head[u];i;i=e[i].pre)
{
ll v=e[i].to;
if(v==fa) continue;
dis_stop[v]=dis_stop[u]+e[i].w;
dfs_dis_stop(v,u);
}
return;
}
signed main(){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
for(ll i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&u,&v,&w);
add(u,v,w);add(v,u,w);
}
dfs_d(1,0,0);
start=top;ans=0;
dfs_d(start,0,0);
stop=top;
dfs_dis_start(start,0);
dfs_dis_stop(stop,0);
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)//枚举所有可能的C
ans2=max(ans2,min(dis_start[i],dis_stop[i]));
printf("%lld\n",ans+ans2);
//ans:直径距离
//ans2:某个点到两个端点的最短距离
return 0;
}
小彩蛋
我:不对劲,有问题:
\(1\le T_i \le 10^9\)
十亿分钟。。。先不说你能不能活到那时候,就算能考试貌似就已经结束了吧。。
标签:fa,题解,ll,stop,逃学,dfs,start,NOI2003,dis From: https://www.cnblogs.com/Atserckcn/p/18369995