虚树
用途
- 一棵树上进行 m 次不同的操作, 每次用到 k 个节点( $\sum k $ $ O(n) 级别$ )
- 用于于树上 DP
原理
- 将原树里的一部分用到的节点抠出来, 建一棵新树(虚树), 在上面进行 DP
- 优点: 降低每次操作的复杂度
构建
- 将要用到的节点(设为 s)按照 dfn 序排序
- dfn 序相近的在原树上的位置一定是相邻的
- 把树分成几条链来构建
- 链的终点是当前链最深的 s 节点
- 比如下图中 1, 9, 8 是 s 节点, 那么就会有(1, 5, 7, 8)(1, 9)两条链
- 链的终点是当前链最深的 s 节点
- 还要多加一些节点(相邻两点的 lca)
-

- 比如 1, 6, 10 节点是我要用到的 s 节点
- 但是 6 和 10 不在同一条链上, 把他们直接连在 1 上是不合理的, 所以引入他们的 lca 也就是 1 节点
-
- 类似于笛卡尔树, 我们用栈来维护链
过程
-
栈叫 st, 栈顶元素的下标为 top
-
初始时将第一个 s 节点入栈
-
当前节点为 now , 他和 st[top] 的 lca 叫 Lca
-
考虑 now, st[top], st[top - 1] 的关系
-
Lca == st[top]
-
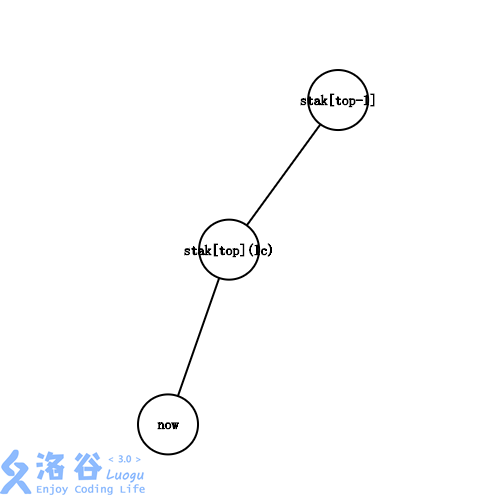
-
now 和 st[top] 在同一条链上, 说明这条链还没处理完, 将 now 入栈即可
-
-
Lca 在 st[top], st[top - 1] 之间
-
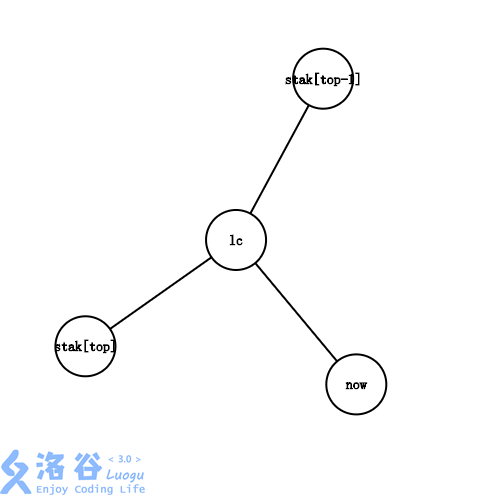
- 说明 st[top] 这条链处理完了, 将 st[top] 和 Lca 连边, 然后出栈
- 将 Lca, now 入栈
-
-
Lca == st[top - 1]
-
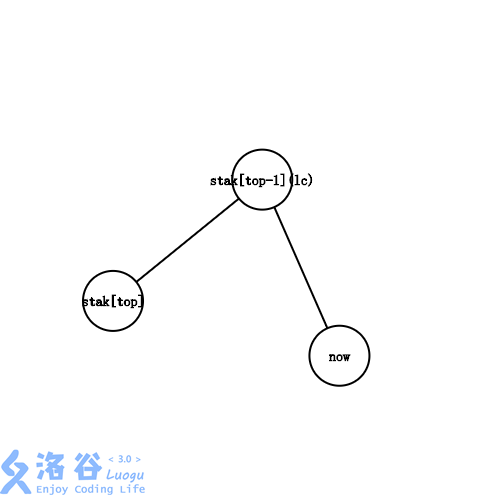
- 与情况 2 类似, 只是不必再把 Lca 入栈一次
-
-
Lca 在 st[top - 1] 上面
-
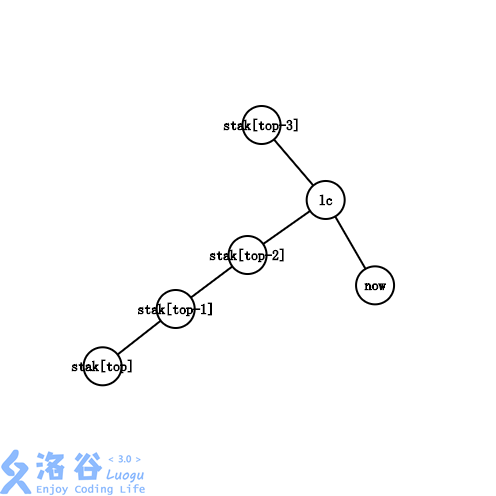
-
同样是 st[top] 这条链处理完了, 只不过往上返回的层数多了点
-
st[top], st[top - 1] 连边, While 循环往上跳, 重复操作, 直到遇到 1, 2, 3 的情况然后退出即可
-
复杂度
- \(\sum k * log n(LCA) + nlogn(排序)\)
例题
P2495 [SDOI2011] 消耗战
-
每次对这 k 个岛建虚树即可
-
关于 Dp
- 考虑断开 x 子树内所有关键节点的代价
- 如果 x 是关键点
- 当前的断开的代价是他到根节点路径上的最小边权
- 没必要加上 x 子树里关键点断开的代价(断开 x 时整棵子树都掉下来了)
- 否则
- 代价为 $ min(他到根节点路径上的最小边权, x 子树里关键点断开的代价) $
-
代码
-
# include <bits/stdc++.h> # define int long long using namespace std; const int M = 1e6 + 10; const int N = 3e5 + 10; int n, m; int u, v, w; int k, h[N]; int mini[N], tag[N]; int dfn[N], si[N], son[N], tp[N], fa[N], dep[N], cdfn; int st[N], top; struct Add_edge{ struct Edge1{ int to, val, nxt; }e[M]; int hd[N], cnt; void Insert(int u, int v, int w){ e[++cnt].to = v; e[cnt].val = w; e[cnt].nxt = hd[u]; hd[u] = cnt; } }a, b; bool cmp(int x, int y){ return dfn[x] < dfn[y]; } void Dfs1(int x, int y){ fa[x] = y; si[x] = 1; dep[x] = dep[y] + 1; dfn[x] = ++cdfn; for(int i = a.hd[x]; i; i = a.e[i].nxt){ int to = a.e[i].to; if(to == y){ continue; } mini[to] = min(mini[x], a.e[i].val); Dfs1(to, x); si[x] += si[to]; if(si[son[x]] < si[to]){ son[x] = to; } } } void Dfs2(int x, int top){ tp[x] = top; if(son[x]){ Dfs2(son[x], top); } for(int i = a.hd[x]; i; i = a.e[i].nxt){ int to = a.e[i].to; if(tp[to]){ continue; } Dfs2(to, to); } } int Lca(int x, int y){ while(tp[x] != tp[y]){ if(dep[tp[x]] < dep[tp[y]]){ swap(x, y); } x = fa[tp[x]]; } if(dep[x] > dep[y]){ swap(x, y); } return x; } int Dp(int x, int y){ int sum = 0; for(int i = b.hd[x]; i; i = b.e[i].nxt){ int to = b.e[i].to; if(to == y){ continue; } sum += Dp(to, x); } int ret = 0; if(tag[x]){ ret = mini[x]; }else{ ret = min(mini[x], sum); } tag[x] = 0; b.hd[x] = 0; return ret; } signed main(){ // freopen("1.in", "r", stdin); ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ cin >> u >> v >> w; a.Insert(u, v, w); a.Insert(v, u, w); } mini[1] = (int)1e18; Dfs1(1, 0); Dfs2(1, 1); cin >> m; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){ cin >> k; for(int j = 1; j <= k; j++){ cin >> h[j]; tag[h[j]] = 1; } sort(h + 1, h + 1 + k, cmp); b.cnt = 0; top = 1; st[1] = h[1]; for(int j = 2; j <= k; j++){ int lca = Lca(st[top], h[j]); while(true){ if(dep[lca] >= dep[st[top - 1]]){ b.Insert(lca, st[top], 0); if(lca != st[top - 1]){ st[top] = lca; }else{ top--; } break; }else{ b.Insert(st[top - 1], st[top], 0); top--; } } st[++top] = h[j]; } while(--top){ b.Insert(st[top], st[top + 1], 0); } cout << Dp(st[1], 0) << "\n"; } }
-
P4103 [HEOI2014] 大工程
-
还是虚树, 不详写了吧
-
代码
-
特判一下, 如果 st[top] == Lca 那就别连边了
-
# include <bits/stdc++.h> # define int long long # define double long double using namespace std; const int N = (int)1e6 + 10; int n, q; int u, v; int k, id[N], tag[N]; int fa[N], dep[N], si[N], son[N], dfn[N], top[N], cdfn; int st[N], tp; int f[N], g[N], aa, bb, cc, siz[N]; struct Add_edge{ struct Edge{ int to, val, nxt; }e[2 * N]; int hd[N], cnt; void Insert(int u, int v, int w){ e[++cnt].to = v; e[cnt].val = w; e[cnt].nxt = hd[u]; hd[u] = cnt; } }a, b; bool cmp(int x, int y){ return dfn[x] < dfn[y]; } void Dfs1(int x, int y){ fa[x] = y; si[x] = 1; dfn[x] = ++cdfn; dep[x] = dep[y] + 1; for(int i = a.hd[x]; i; i = a.e[i].nxt){ int to = a.e[i].to; if(to == y){ continue; } Dfs1(to, x); si[x] += si[to]; if(si[son[x]] < si[to]){ son[x] = to; } } } void Dfs2(int x, int tp){ top[x] = tp; if(son[x]){ Dfs2(son[x], tp); } for(int i = a.hd[x]; i; i = a.e[i].nxt){ int to = a.e[i].to; if(top[to]){ continue; } Dfs2(to, to); } } int Lca(int x, int y){ while(top[x] != top[y]){ if(dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]){ swap(x, y); } x = fa[top[x]]; } if(dep[x] > dep[y]){ swap(x, y); } return x; } void Dp(int x, int y){ siz[x] = tag[x]; f[x] = 0, g[x] = (tag[x] ? 0 : (int)1e18); for(int i = b.hd[x]; i; i = b.e[i].nxt){ int to = b.e[i].to; if(to == y){ continue; } Dp(to, x); aa += (k - siz[to]) * siz[to] * b.e[i].val; if(siz[x]){ bb = max(bb, f[x] + f[to] + b.e[i].val); cc = min(cc, g[x] + g[to] + b.e[i].val); } f[x] = max(f[x], f[to] + b.e[i].val); g[x] = min(g[x], g[to] + b.e[i].val); siz[x] += siz[to]; } tag[x] = 0; b.hd[x] = 0; } signed main(){ // freopen("1.in", "r", stdin); cin >> n; for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){ cin >> u >> v; a.Insert(u, v, 1ll); a.Insert(v, u, 1ll); } Dfs1(1, 0); Dfs2(1, 1); cin >> q; for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++){ cin >> k; for(int j = 1; j <= k; j++){ cin >> id[j]; tag[id[j]] = 1; } sort(id + 1, id + 1 + k, cmp); b.cnt = 0; tp = 1; st[1] = id[1]; for(int j = 2; j <= k; j++){ int now = id[j]; int lca = Lca(st[tp], now); while(true){ if(dep[lca] >= dep[st[tp - 1]]){ if(lca != st[tp]) b.Insert(lca, st[tp], dep[st[tp]] - dep[lca]); if(st[tp - 1] == lca){ tp--; }else{ st[tp] = lca; } break; }else{ b.Insert(st[tp - 1], st[tp], dep[st[tp]] - dep[st[tp - 1]]); tp--; } } st[++tp] = now; } while(--tp){ b.Insert(st[tp], st[tp + 1], dep[st[tp + 1]] - dep[st[tp]]); } aa = 0, bb = 0, cc = (int)1e18; Dp(st[1], 0); cout << aa << " " << cc << " " << bb << "\n"; } }
-