学习笔记4
@
目录课程:《Linux》
班级:2111
姓名:杨博川
学号:20211121
日期:2023年9月30日
一、第七章学习笔记及操作截图
1.五个级别
(1)硬件级别
硬件级别的文件操作包括:
fdisk:将硬盘、U盘或SDC盘分区。
mkfs:格式化磁盘分区,为系统做好准备。
fsck:检查和维修系统。
碎片整理:压缩文件系统中的文件。
(2)操作系统内核中的文件系统函数
kmount(), kumount() (mount/umount file systems)
kmkdir(), krmdir() (make/remove directory)
kchdir(), kgetcwd() (change directory, get CWD pathname)
klink(), kunlink() (hard link/unlink files)
kchmod(), kchown(), kutime() (change r|w|x permissions,owner,time)
kcreat(), kopen() (create/open file for R,W,RW,APPEND)
kread(), kwrite() (read/write opened files)
klseek(), kclose() (lseek/close file descriptors)
ksymlink(), kreadlink() (create/read symbolic link files)
kstat(), kfstat(), klstat() (get file status/information)
kopendir(), kreaddir() (open/read directories)
(3)系统调用
#include<fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *agrv[])
{
int fd, n;
char buf[1024];
if((fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY))<0)
exit(1);
lseek(fd, 1024, SEEK_SET);
n = read(fd, buf, 1024);
close(fd);
}
(4)I/O库函数
FILE mode I/0: fopen(),fread(); fwrite(),fseek(),fclose(),fflush()
char mode I/0: getc(), getchar(),ugetc(); putc(),putchar()
line mode I/0: gets(), fgets(); puts(), fputs()
formatted I/0: acanf(),fscanf(),sscanf(); printf(),fprintf(),sprintf()
(5)用户命令
mkdir, rmdir, cd, pwd, ls, link, unlink, rm, cat, cp, mv, chmod, etc.
(6)sh脚本
2.文件I/O操作
涉及fread() fwrite()等函数(详见后文)
3.低级别文件操作
- 分区
Command (m for help): m ---输出帮助信息
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag ---设置启动分区
b edit bsd disklabel ---编辑分区标签
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition --删除一个分区
l list known partition types --列出分区类型
m print this menu --帮助
n add a new partition --建立一个新的分区
o create a new empty DOS partition table --创建一个新的空白DOS分区表
p print the partition table ---打印分区表
q quit without saving changes ---退出不保存设置
s create a new empty Sun disklabel ---
t change a partition's system id ---改变分区的ID
u change display/entry units ---改变显示的单位
v verify the partition table ---检查验证分区表
w write table to disk and exit ---保存分区表
x extra functionality (experts only)
- 格式化分区
- 挂载分区
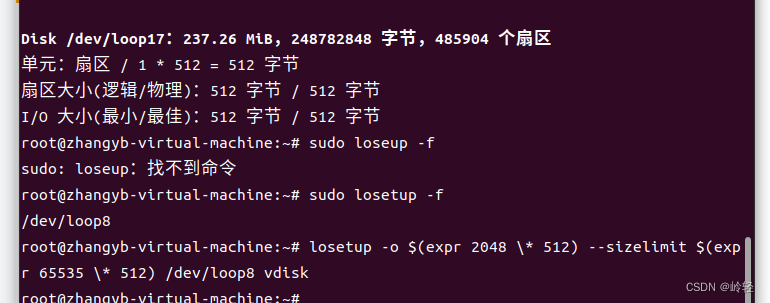
#(1)用dd命令创建一个虚拟磁盘映像
dd if=/dev/zero of=mydisk bs=1024 count=32768
#(2)在vdisk上运行fdisk来创建一个分区P1
fdisk vdisk
#(3)使用以下扇区数在vdisk的分区1上创建一个循环设备
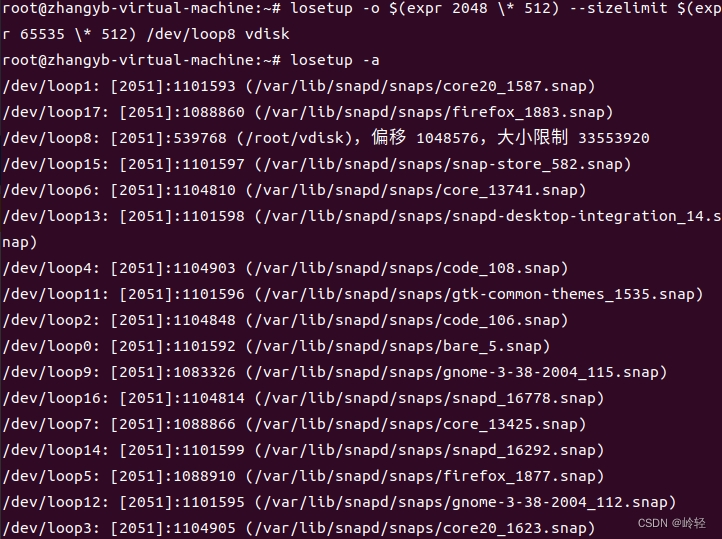
losetup -o $(expr 2048 \* 512) --sizelimit $(expr 65535 \* 512) /dev/loop1
vdisk
losetup -a
#(4)格式化/dev/loop1,它是一个EXT2文件系统
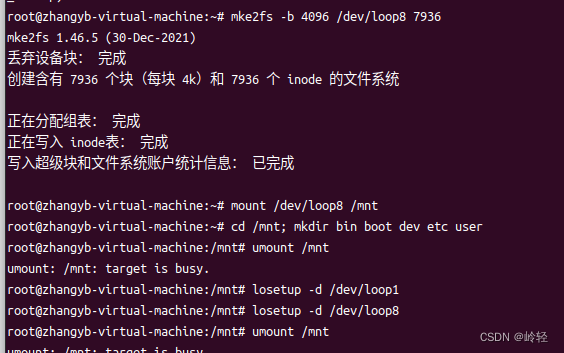
mke2fs -b 4096 /dev/loop1 7936
#(5)挂载循环设备
mount /dev/loop1 /mnt
#(6)访问作为文件系统一部分的挂载系统
(cd /mnt; mkdir bin boot dev etc user)
#(7)设备使用完毕后,将其卸载
umount /mnt
#(8)循环设备使用完毕后,通过以下命令将其断开
losetup -d /dev/loop1
4.EXT2文件系统
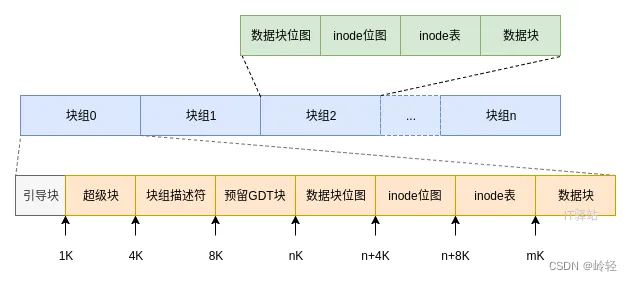
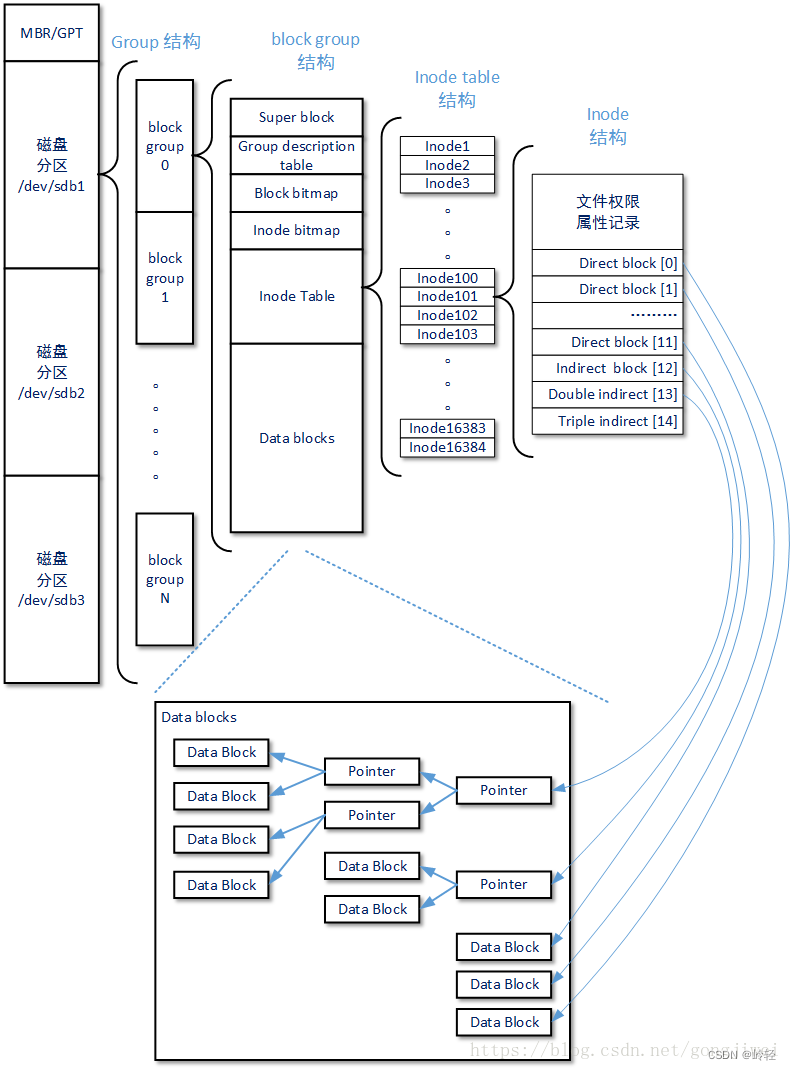 lock#0:引导块 容纳从磁盘引导操作系统的引导程序
lock#0:引导块 容纳从磁盘引导操作系统的引导程序
超级块
Block#1 超级块
*拓展:超级块记录的信息有:
1、block 与 inode 的总量(分区内所有Block Group的block和inode总量);
2、未使用与已使用的 inode / block 数量;
3、block 与 inode 的大小 (block 为 1, 2, 4K,inode 为 128 bytes);
4、filesystem 的挂载时间、最近一次写入数据的时间、最近一次检验磁盘 (fsck) 的时间等文件系统的相关信息;
5、一个 valid bit 数值,若此文件系统已被挂载,则 valid bit 为 0 ,若未被挂载,则 valid bit 为 1 。
以上引用:ext2文件系统详解
- 块组描述符
Block#2 每组用一个块描述符结构体描述 - 位图
Block#8 块位图 0位表示对应项处于FREE状态,1位表示对应项处于IN_USE状态
Block#9 索引节点位图 - 索引节点
Block#10
struct ext2_inode {
__u16i_mode;/* 文件类型和访问权限 */
__u16i_uid;/* 文件拥有者标识号*/
__u32i_size;/* 以字节计的文件大小 */
__u32i_atime;/* 文件的最后一次访问时间 */
__u32i_ctime;/* 该节点最后被修改时间 */
__u32i_mtime;/* 文件内容的最后修改时间 */
__u32i_dtime;/* 文件删除时间 */
__u16i_gid;/* 文件的用户组标志符 */
__u16i_links_count;/* 文件的硬链接计数 */
__u32i_blocks;/* 文件所占块数(每块以512字节计)*/
__u32i_flags;/* 打开文件的方式 */
union/*特定操作系统的信息*/
__u32i_block[Ext2_N_BLOCKS];/* 指向数据块的指针数组 */
__u32i_version;/* 文件的版本号(用于 NFS) */
__u32i_file_acl;/*文件访问控制表(已不再使用) */
__u32i_dir_acl;/*目录 访问控制表(已不再使用)*/
__u8l_i_frag;/* 每块中的片数 */
__u32 i_faddr;/* 片的地址 */
union/*特定操作系统信息*/
}
i_block[15]包含着指向文件磁盘块的指针
直接块
间接块
双重间接块
三重间接块
二.第七章部分代码/操作截图
- 目录条目
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/io.h>
#include <ext2fs/ext2_fs.h>
typedef unsigned char u8;
typedef struct ext2_super_block SUPER;
typedef struct ext2_group_desc GD;
#define BLKSIZE 1024
SUPER *sp;
GD *gp;
char buf[BLKSIZE];
int fd;
// get_block() reads a disk block into a buf[]?
int get_block(int fd, int blk, char *buf)
{
lseek(fd, (long)blk*BLKSIZE, SEEK_SET);
return read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE);
}
int imap(char *device)
{
int i, ninodes, blksize, imapblk;
fd = open(device, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s failedn", device);
exit(1);
}
get_block(fd, 1, buf); // get superblock
sp = (SUPER *)buf;
// check magic number to ensure itz s an EXT2 FS ninodes = sp->s_inodes_count //
ninodes = sp->s_inodes_count;
printf("ninodes = %dn", ninodes);
get_block(fd, 2, buf); //
gp = (GD *)buf;
imapblk = gp->bg_inode_bitmap;
printf("imapblk = %dn", imapblk);
get_block(fd, imapblk, buf);
for ( i = 0; i <= ninodes/8; i++)
{
printf("%02x ", (u8)buf[i]);
}
printf("n");
}
char *dev = "vdisk";
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
if(argc>1) dev = argv[1];
imap(dev);
}
- 显示位图
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/io.h>
#include <ext2fs/ext2_fs.h>
#define BLKSIZE 1024
typedef struct ext2_group_desc GD;
typedef struct ext2_super_block SUPER;
typedef struct ext2_dir_entry_2 DIR;
typedef struct ext2_inode INODE;
SUPER *sp;
GD *gp;
INODE *ip;
DIR *dp;
char buf[BLKSIZE];
int fd,firstdata, inodesize ,blksize, iblock;
char *dev = "vdisk";
int get_block(int fd, int blk, char *buf)
{
lseek(fd, blk*BLKSIZE, SEEK_SET);
return read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE);
}
int inode (char *dev)
{
int i;
fd = open(dev, O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open faildn");
exit(1);
}
get_block(fd, 2, buf);
gp = (GD *)buf;
printf("bmap_block=%d imap_block=%d inodes_table=%d n",
gp->bg_block_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_table);
iblock = gp->bg_inode_table;
printf("----root inode information----n");
get_block(fd, iblock, buf);
ip = (INODE *)buf;
ip++;
printf("mode = %4x ",ip->i_mode);
printf("uid = %d gid = %dn", ip->i_uid, ip->i_gid);
printf("size = %dn", ip->i_size);
//unsigned int tmp = ip->i_ctime;
printf("ctime = %s",ctime((const time_t *)&ip->i_ctime));
printf("links = %dn", ip->i_links_count);
for ( i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
if(ip->i_block[i])
{
printf("i_block[%d] = %dn", i, ip->i_block[i]);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc>1) dev = argv[1];
inode(dev);
}
- 显示根索引节点
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/io.h>
#include <ext2fs/ext2_fs.h>
#define BLKSIZE 1024
typedef struct ext2_group_desc GD;
typedef struct ext2_super_block SUPER;
typedef struct ext2_dir_entry_2 DIR;
typedef struct ext2_inode INODE;
SUPER *sp;
GD *gp;
INODE *ip;
DIR *dp;
char buf[BLKSIZE];
int fd,firstdata, inodesize ,blksize, iblock;
char *dev = "mydisk";
int get_block(int fd, int blk, char *buf)
{
lseek(fd, blk*BLKSIZE, SEEK_SET);
return read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE);
}
int inode (char *dev)
{
int i;
fd = open(dev, O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
printf("open faildn");
exit(1);
}
get_block(fd, 2, buf);
gp = (GD *)buf;
printf("bmap_block=%d imap_block=%d inodes_table=%d n",
gp->bg_block_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_bitmap,
gp->bg_inode_table);
iblock = gp->bg_inode_table;
printf("----root inode information----n");
get_block(fd, iblock, buf);
ip = (INODE *)buf;
ip++;
printf("mode = %4x ",ip->i_mode);
printf("uid = %d gid = %dn", ip->i_uid, ip->i_gid);
printf("size = %dn", ip->i_size);
//unsigned int tmp = ip->i_ctime;
printf("ctime = %s",ctime((const time_t *)&ip->i_ctime));
printf("links = %dn", ip->i_links_count);
for ( i = 0; i < 15; i++)
{
if(ip->i_block[i])
{
printf("i_block[%d] = %dn", i, ip->i_block[i]);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc>1) dev = argv[1];
inode(dev);
}
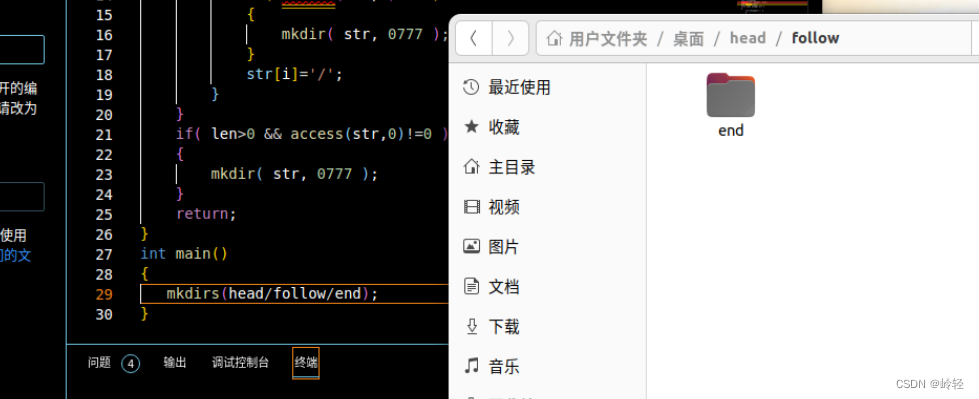
- 创造多级目录
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
void mkdirs(char *muldir)
{
int i,len;
char str[512];
strcpy(str, muldir, 512);
len=strlen(str);
for( i=0; i<len; i++ )
{
if( str[i]=='/' )
{
str[i] = '\0';
if( access(str,0)!=0 )
{
mkdir( str, 0777 );
}
str[i]='/';
}
}
if( len>0 && access(str,0)!=0 )
{
mkdir( str, 0777 );
}
return;
}
int main()
{
mkdirs(head/follow/end);
}
三.第八章学习笔记及操作截图
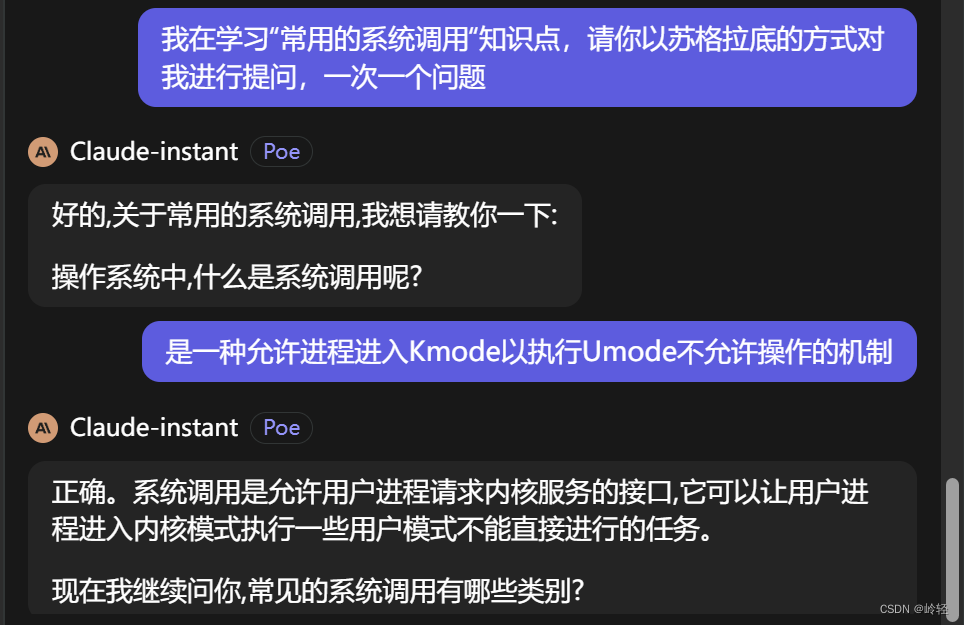
1.系统调用
两种模式:内核模式 | 用户模式
系统调用是一种允许进程进入Kmode以执行Umode不允许操作的机制
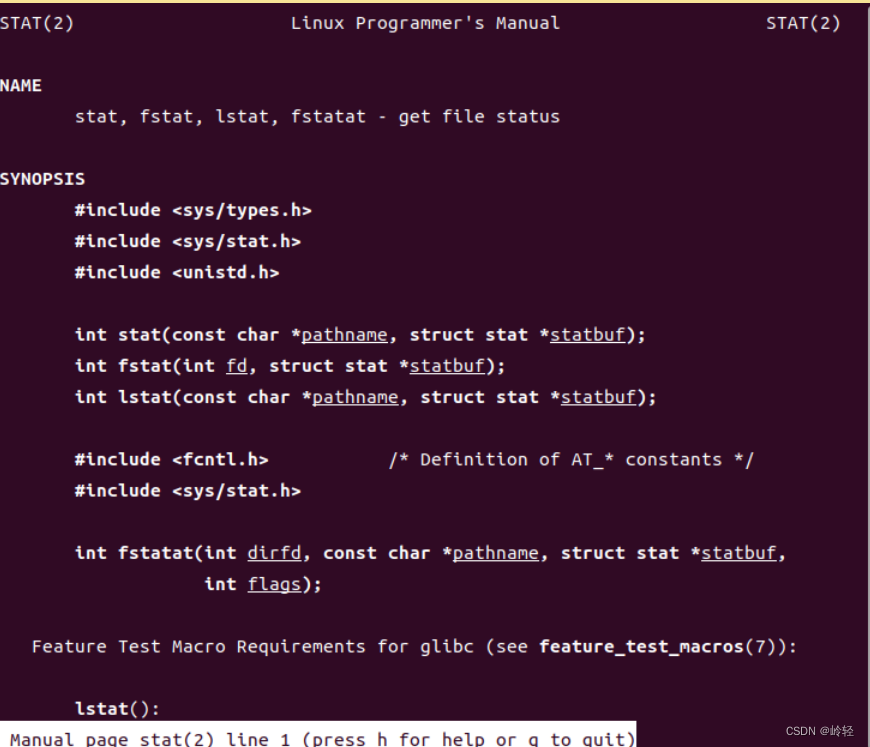
- 系统调用手册页
使用man 2+XXX即可调用
示例:man 2 stat
-
使用系统调用进行文件操作
示例:使用mkdir创建新目录
-
创造多级目录
-
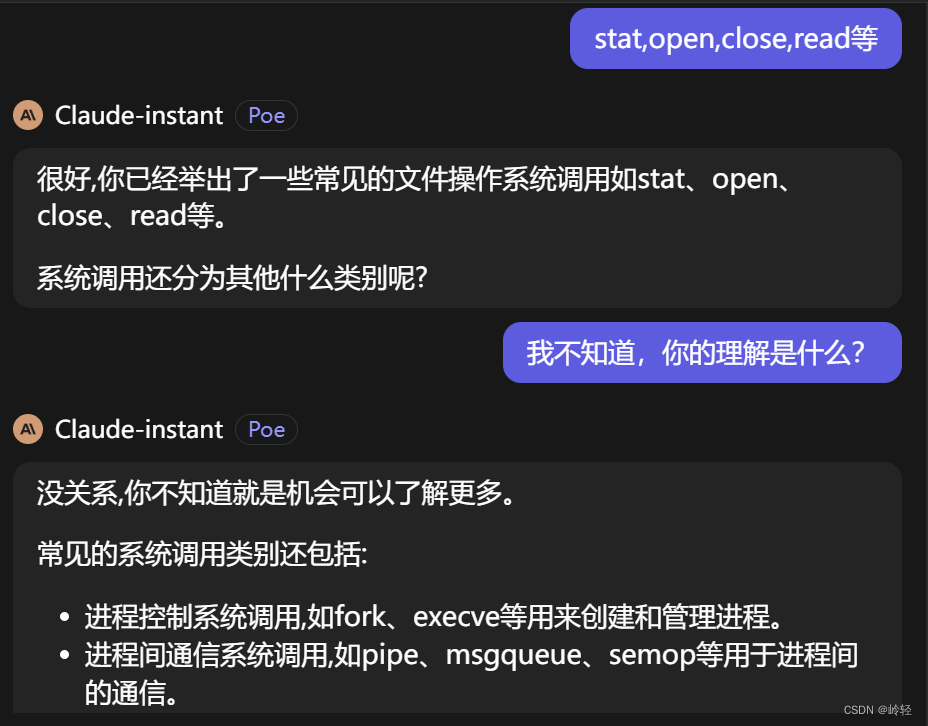
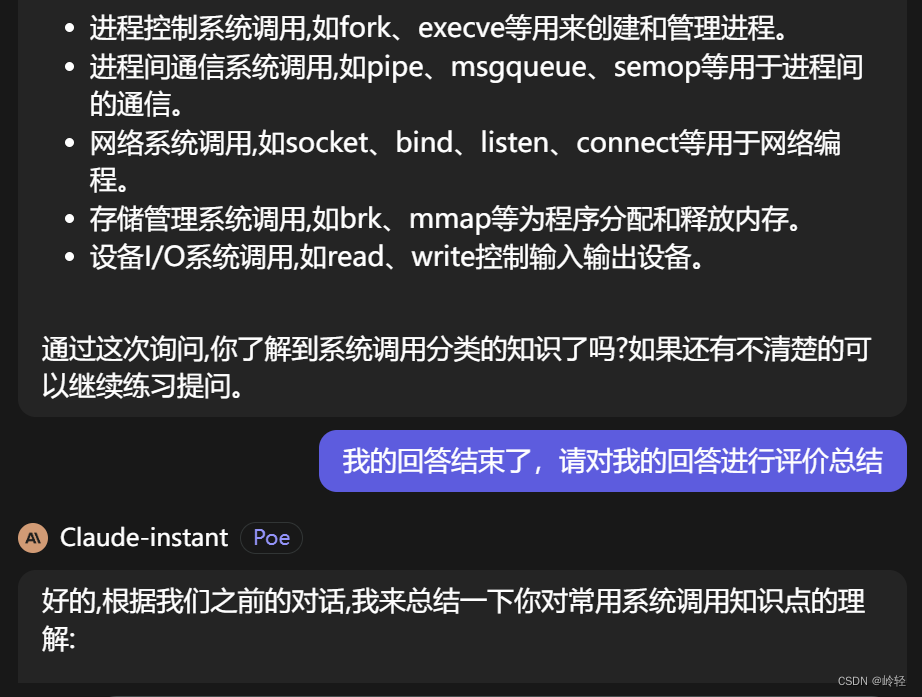
常用系统调用
open:打开一个文件进行读、写、追加
int open(char *file, int flags, int mode);
close:关闭打开的文件描述符
int close(int fd);
read:读取打开的文件描述符
int read(int fd, char buf[], int count);
write:写入打开的文件描述符
int write(int fd, char buf[], int count);
dup:将文件描述符复制到可用的最小描述符编号中
int dup(int oldfd);
dup2:将oldfd复制到newfd中,如果文件链接数为0,则删除文件
int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd);
link:将新文件硬链接到旧文件
int link(char *oldPath, char *newPath);
unlink:取消某个文件的链接;如果文件链接数为0,则删除文件
int unlink(char *pathname);
symlink:创建一个符号链接
int symlink(char *target, char *newpath);
readlink:读取符号链接文件的内容
int readlink(char *path, char *buf, int bufsize);
umask:设置文件创建掩码;文件权限为(mask & ~umask)
int umask(int umask);
mknod:创建特殊文件
int mknod(char *path,int mode,int device)
2.链接文件
- 硬链接
ln oldpath newpath
对应系统调用:link(char *oldpath,char *newpath)
减少文件链接数:unlink(char *pathname)
链接数变成0,文件被完全删除
- 软链接(符号链接)
ln -s oldpath newpath
创建符号链接或软链接
symlink(char *oldpath,char *newpath)
软连接在以下情况很好用:
通过一个较短名称访问一个较长路径
e.g x->aVeryLongPathnameFile
将标准动态库名称链接到实际版本的动态库
e.g libc.so.6->libc.2.7.so
硬链接和软链接的区别
硬链接和原来的文件没有什么区别,而且共享一个 inode 号(文件在文件系统上的唯一标识);而软链接不共享 inode,也可以说是个特殊的 inode,所以和原来的 inode 有区别。
若原文件删除了,则该软连接则不可以访问,而硬连接则是可以的。
由于符号链接的特性,导致其可以跨越磁盘分区,但硬链接不具备这个特性。
3.stat系统调用
- stat结构体
所有的stat系统调用都以stat结构体形式返回信息 - stat与文件索引节点
每个索引节点在存储设备上都有唯一的索引节点编号(ino)。每个设备都由一对设备号标识,例如0x0302表示/dev/hda2等 - 文件的类型和权限
st_mode:第一个字母表示文件类型,后面9个字符基于权限位,如果位是1,每个字符打印为r|w|x;如果位是0,则打印-。x位表示是否允许访问目录。 - opendir-readdir函数
头文件:#include<dirent.h> - readlink函数
int readlink(char *pathname,char buf[],int bufsize);
将符号链接文件的内容复制到bufsize的buf[]中,并将实际复制的字节数返回。 - ls程序
实例:打印编译地址的所有文件信息
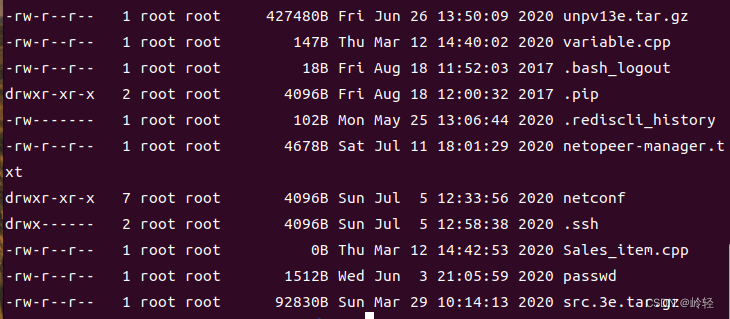
- read()系统调用
将n个字节从打开的文件描述符读入用户空间中的buf[] 返回值是实际读取的字节数,read失败返回-1 - write()系统调用
将n个字节从用户空间中的buf[]写入文件描述符,必须打开该文件描述符进行写,读写或追加
四.第八章部分代码/操作截图
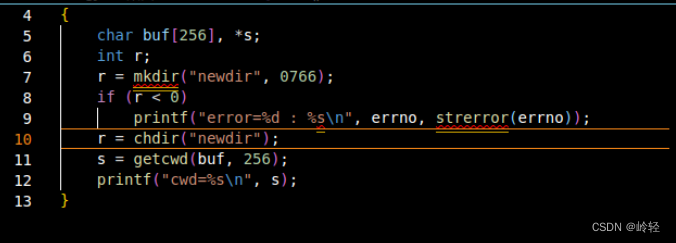
- 使用mkdir创建新目录
#include<stdio.h>
#include<errno.h>
int main()
{
char buf[256],*s;
int r;
r=mkdir("newdir",0766);//mkdir syscall
if(r<0)
printf("errno=%d : %s\n",errno,strerror(errno));
r=chdir("newdir");//cd into newdir
s=getcwd(buf,256);//get CWD string into buf[]
printf("CWD = %s\n",s);
}
- 创建多级目录
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
void mkdirs(char *muldir)
{
int i,len;
char str[512];
strcpy(str, muldir, 512);
len=strlen(str);
for( i=0; i<len; i++ )
{
if( str[i]=='/' )
{
str[i] = '\0';
if( access(str,0)!=0 )
{
mkdir( str, 0777 );
}
str[i]='/';
}
}
if( len>0 && access(str,0)!=0 )
{
mkdir( str, 0777 );
}
return;
}
int main()
{
mkdirs(head/follow/end);
}
- opendir-readdir函数
struct dirent
{
long d_ino; /* inode number 索引节点号 */
off_t d_off; /* offset to this dirent 在目录文件中的偏移 */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this d_name 文件名长 */
unsigned char d_type; /* the type of d_name 文件类型 */
char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; /* file name (null-terminated) 文件名,最长255字符 */
}
- ls程序部分
void printDir(const char* d_name)
{
struct stat statBuf;
char mode[11];
char uidName[10];
char gidName[10];
char lastChgStatTime[30];
memset(mode, 0, 11);
memset(uidName, 0, 10);
memset(gidName, 0, 10);
memset(lastChgStatTime, 0, 30);
if(printall != 1){
if((strcmp(d_name, ".") == 0) || (strcmp(d_name, "..") == 0)){
return;
}
if(d_name[0] == '.'){
return;
}
}
if(0 == lstat(d_name, &statBuf)){
if(printdetail != 1){
printf("%-s\n", d_name);
}else{
/*获取rwxrwxrwx形式的访问权限表示*/
mode2string(statBuf.st_mode, mode);
/*获取uid,gid对应的名称*/
strncpy(uidName, uid2name(statBuf.st_uid), strlen(uid2name(statBuf.st_uid)));
strncpy(gidName, gid2name(statBuf.st_gid), strlen(gid2name(statBuf.st_gid)));
/*time_t转为可读字符串*/
strncpy(lastChgStatTime, time2string(statBuf.st_ctime), strlen(time2string(statBuf.st_ctime)));
/*文件信息打印,没有把struct stat中的信息全部打印*/
printf("%-10s ", mode);
printf("%3d ", statBuf.st_nlink);
printf("%s ", uidName);
printf("%s ", gidName);
printf("%10dB ", statBuf.st_size);
printf("%s ", lastChgStatTime);
printf("%-s\n", d_name);
}
}else{
err_sys("cant't get attribute");
}
}
- 使用系统调用递归复制文件
int copy(char *read_dir_path, char *write_dir_path)
{
DIR * p_dir;
struct dirent * p_dirent;
char read_buf[256];
char write_buf[256];
sprintf(read_buf,"%s/", read_dir_path);
sprintf(write_buf,"%s/",write_dir_path);
strcat(read_dir_path,"/");
if( Is_dir(read_buf) )
{
//mkdir
if(mkdir(write_buf, 0755) < 0)
{
printf("mkdir fall:%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//opendir and readdir
if((p_dir = opendir(read_buf)) == NULL )
{
printf("Usage:cp -r <src_dir> <dat_dir> error:%s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
while((p_dirent=readdir(p_dir)) != NULL)
{
char read_buffer[256];
char write_buffer[256];
sprintf(read_buffer,"%s%s", read_buf, p_dirent->d_name);
sprintf(write_buffer,"%s%s", write_buf, p_dirent->d_name);
printf("%s\n%s\n",read_buffer,write_buffer);
//it is a directory
if( Is_dir(read_buffer) && 0 != strcmp(p_dirent->d_name, ".") && 0 != strcmp(p_dirent->d_name, "..") )
{
copy_r(read_buffer, write_buffer);
}
else if(0 != strcmp(p_dirent->d_name, ".") && 0 != strcmp(p_dirent->d_name, ".."))
{
//copy file
if( file_copy_line(read_buffer, write_buffer) < 0 )
return 0;
}
}
closedir(p_dir);
}
}
- 显示文件内容(cat)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define BLKSIZE 4096
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, i, m, n;
char buf[BLKSIZE], dummy;
if(argc>1)
{
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
exit(1);
}
while(n = read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE))
{
m = write(1, buf, n);
}
}
- 复制文件(cp sec dest 命令)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#define BLKSIZE 4096
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd, gd, n, total=0;
char buf[BLKSIZE];
if(argc<3)
exit(1);
if((fd = (open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) < 0))
exit(2);
if((gd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT)) < 0)
exit(3);
while(n = read(fd, buf, BLKSIZE))
{
write(gd, buf, n);
total += n;
}
printf("total bytes copied=%d\n", total);
close(fd);
close(gd);
}
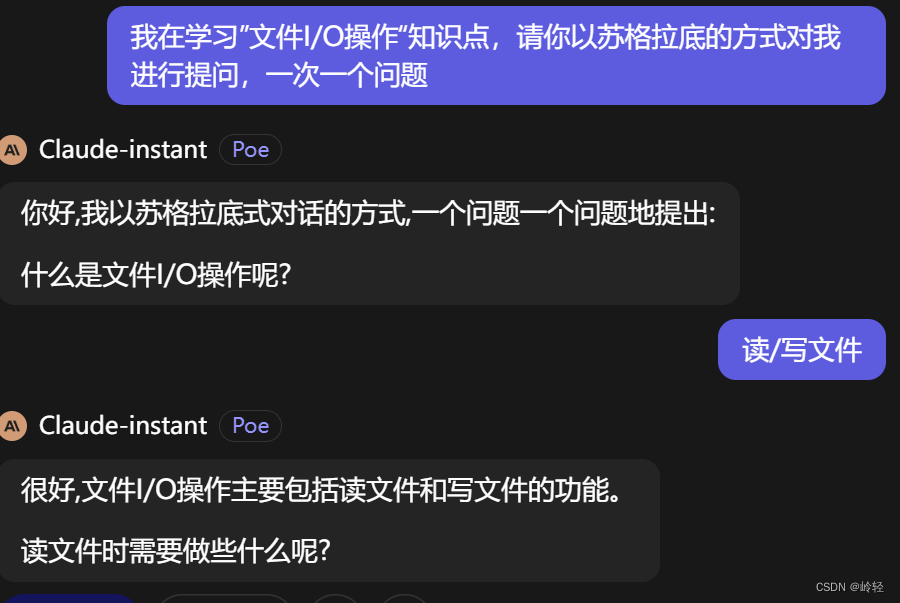
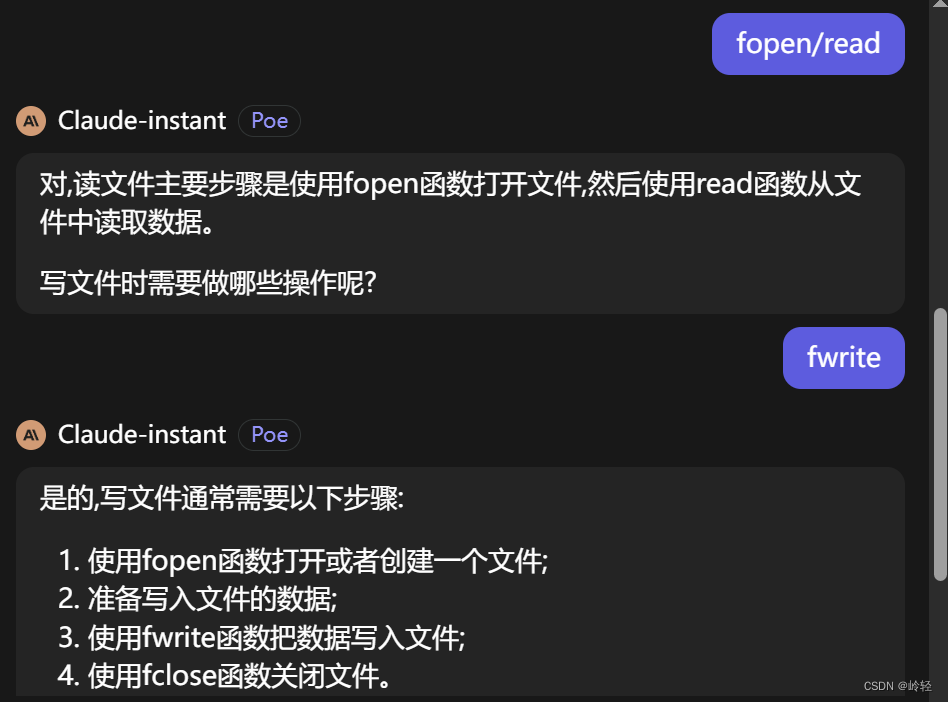
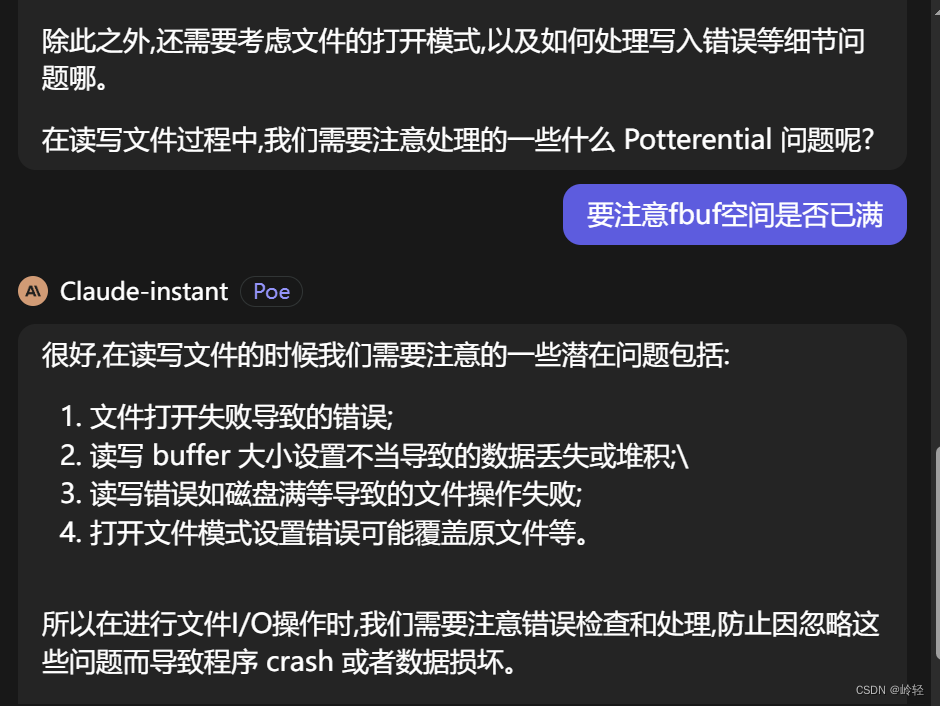
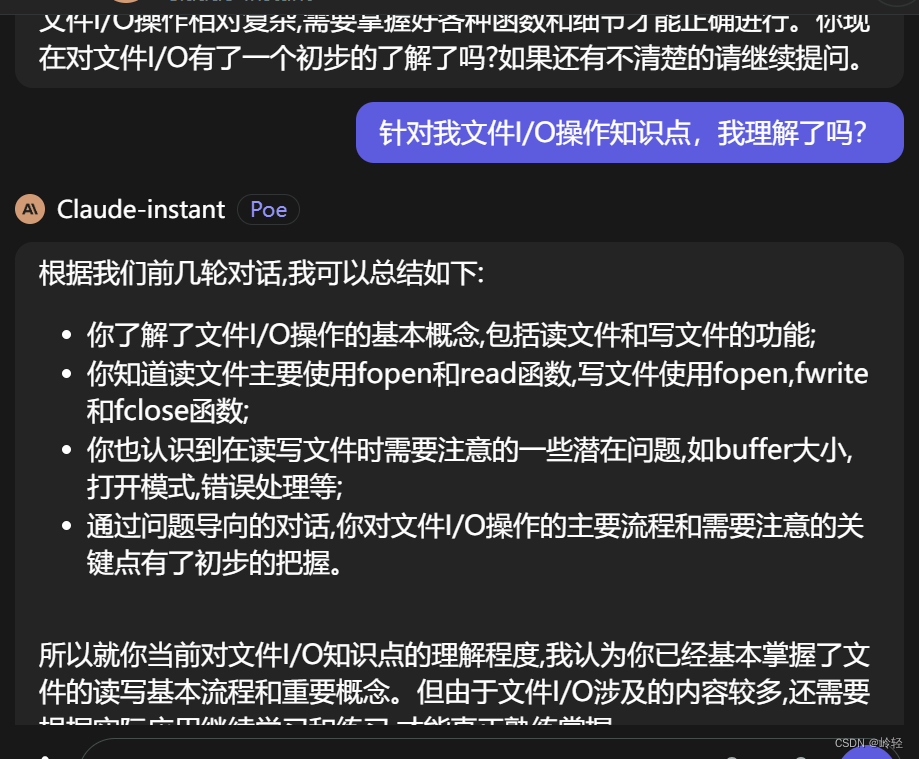
二、苏格拉底检验
问题一
问题二