你会得到一个字符串 s (索引从 0 开始),你必须对它执行 k 个替换操作。替换操作以三个长度均为 k 的并行数组给出:indices, sources, targets。
要完成第 i 个替换操作:
- 检查 子字符串
sources[i]是否出现在 原字符串s的索引indices[i]处。 - 如果没有出现, 什么也不做 。
- 如果出现,则用
targets[i]替换 该子字符串。
例如,如果 s = "abcd" , indices[i] = 0 , sources[i] = "ab", targets[i] = "eee" ,那么替换的结果将是 "eeecd" 。
所有替换操作必须 同时 发生,这意味着替换操作不应该影响彼此的索引。测试用例保证元素间不会重叠 。
- 例如,一个
s = "abc",indices = [0,1],sources = ["ab","bc"]的测试用例将不会生成,因为"ab"和"bc"替换重叠。
在对 s 执行所有替换操作后返回 结果字符串 。
子字符串 是字符串中连续的字符序列。
示例 1:

输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["a","cd"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeebffff" 解释: "a" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "cd" 从 s 中的索引 2 开始,所以它被替换为 "ffff"。
示例 2: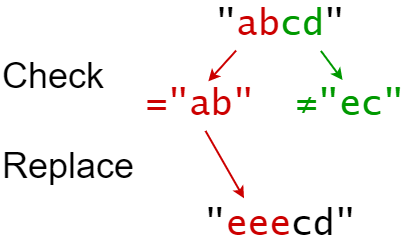
输入:s = "abcd", indices = [0,2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeecd" 解释: "ab" 从 s 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "ec" 没有从原始的 S 中的索引 2 开始,所以它没有被替换。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indices[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50s仅由小写英文字母组成sources[i]和targets[i]仅由小写英文字母组成
题目明确说明不会发生重复冲突,所以可以直接将字符串 s 从前往后遍历,不断将遍历到的字符加入答案,或者将满足条件的字符替换成新的字符,然后加入答案。
所以重要点就是:如何得知遍历到某个位置后是否需要进行置换。
两种思路:
1. 将 indices 进行排序,由于题目明确说了不会重复,所以用一个变量存储当前遍历 indices 数组的位置,如果遍历 s 的下标等于该位置,那么不论是否匹配成功,该位置都向后移一位。(匹配不成功的话,也不可能再次出现)。
2. 利用哈希表,将 indices 中的数据进行存储,准确来说,就是代替了排序和遍历 indices 的步骤,其他步骤不变。
方法1:
class Solution {
public String findReplaceString(String s, int[] indices, String[] sources, String[] targets) {
int[][] arr = new int[indices.length][];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = new int[]{indices[i], i};
}
Arrays.sort(arr, (a, b) -> (a[0] - b[0]));
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (index < arr.length && i == arr[index][0]) {
int j = arr[index][1];
if (s.startsWith(sources[j], i)) {
str.append(targets[j]);
i += sources[j].length() - 1;
} else {
str.append(s.charAt(i));
}
index++;
} else {
str.append(s.charAt(i));
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}

方法二:
class Solution {
public String findReplaceString(String s, int[] indices, String[] sources, String[] targets) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < indices.length; i++) {
map.put(indices[i], i);
}
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
// 遍历字符串 s
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (map.containsKey(i)) {
int j = map.get(i);
if (s.startsWith(sources[j], i)) {
str.append(targets[j]);
i += sources[j].length() - 1;
} else {
str.append(s.charAt(i));
}
} else {
str.append(s.charAt(i));
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}

标签:833,sources,int,---,力扣,length,str,indices,targets From: https://www.cnblogs.com/allWu/p/17632496.html