牛客网FPGA题库刷题之快速入门题库(一)1~8题
第一题
题目链接:
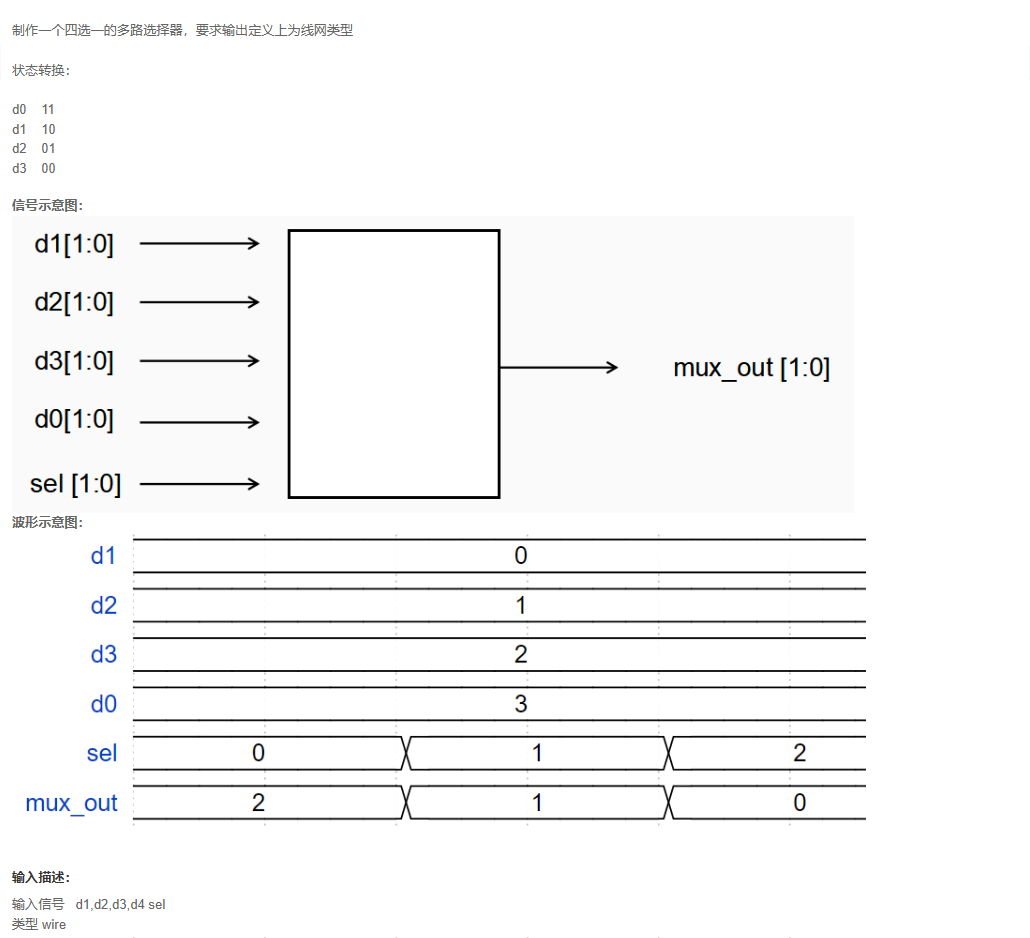
代码:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module mux4_1(
input [1:0]d1,d2,d3,d0,
input [1:0]sel,
output[1:0]mux_out
);
//*************code***********//
reg [1:0] mux_out_tmp;
always@(*)begin
case(sel)
2'b00:mux_out_tmp = d3;
2'b01:mux_out_tmp = d2;
2'b10:mux_out_tmp = d1;
2'b11:mux_out_tmp = d0;
endcase
end
assign mux_out = mux_out_tmp;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
题目解析:
用case语句实现简单的四路选择,always语句里面需要用reg,所以新建一个reg的temp变量即可
第二题
题目链接
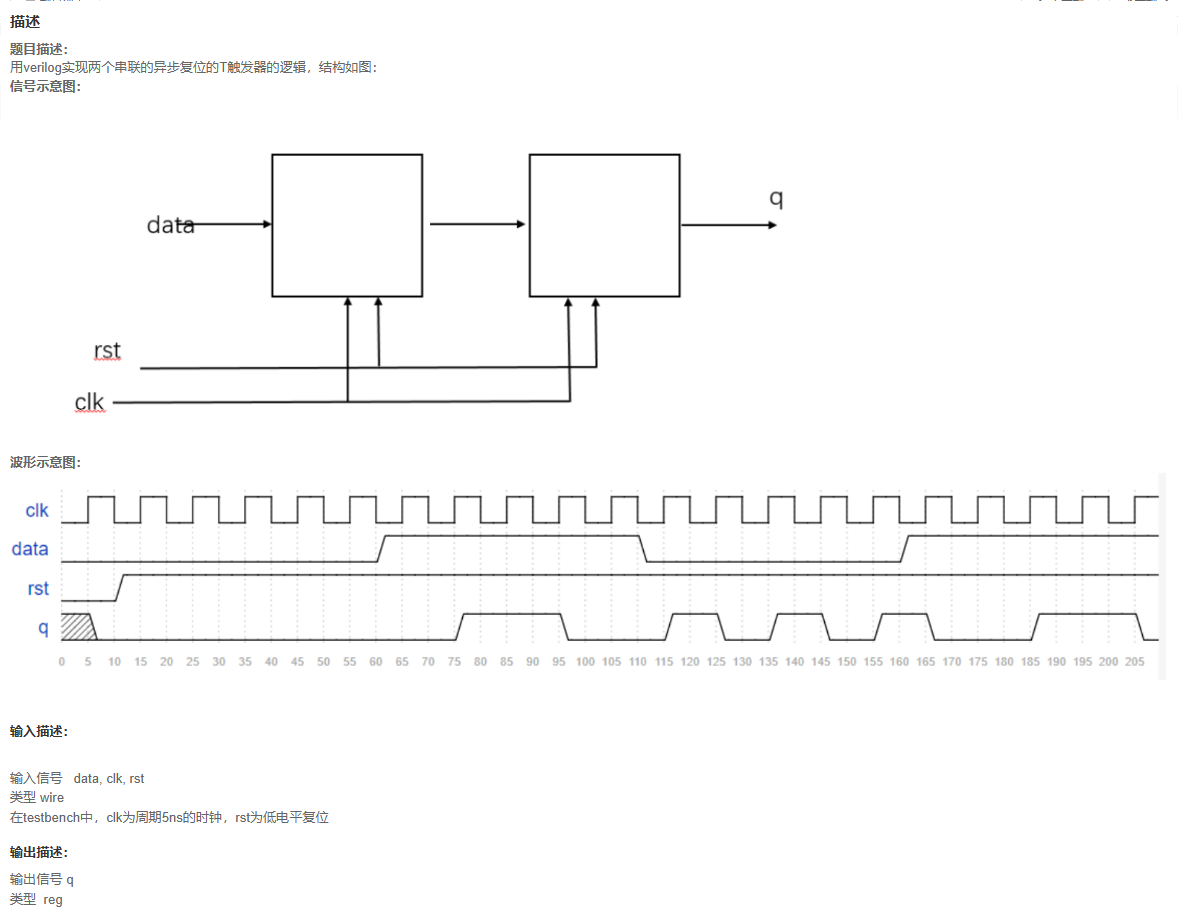
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module Tff_2 (
input wire data, clk, rst,
output reg q
);
//*************code***********//
reg tmp;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst == 1'b0)begin
tmp <= 0 ;
end
else begin
tmp <= tmp ^ data;
end
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst == 1'b0)begin
q <= 0 ;
end
else begin
q <=tmp ^q;
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
题目解析
首先了解T触发器的特性方程
Qn+1 = T Qn ' +T ' Qn = T⊕Qn (其中Qn为现态,Qn+1为次态) 也就是异或
然后题目是两个T触发器,所以第一个的输出是第二个的输入
网友的解析:
1、T触发器是进入的值为1的时候,寄存的值发生翻转
2、注意异步复位
3、需要注意寄存器翻转的逻辑,第二寄存器是否翻转取决于第一个寄存器是否为1,前者输出情况有三种:在data输入控制为1下从0到1到0不断翻转,data为0锁在1,data为0锁在0
ps: 考虑rst为1且完成了初始化,rst 低电平复位高电平有效
第三题:
题目链接
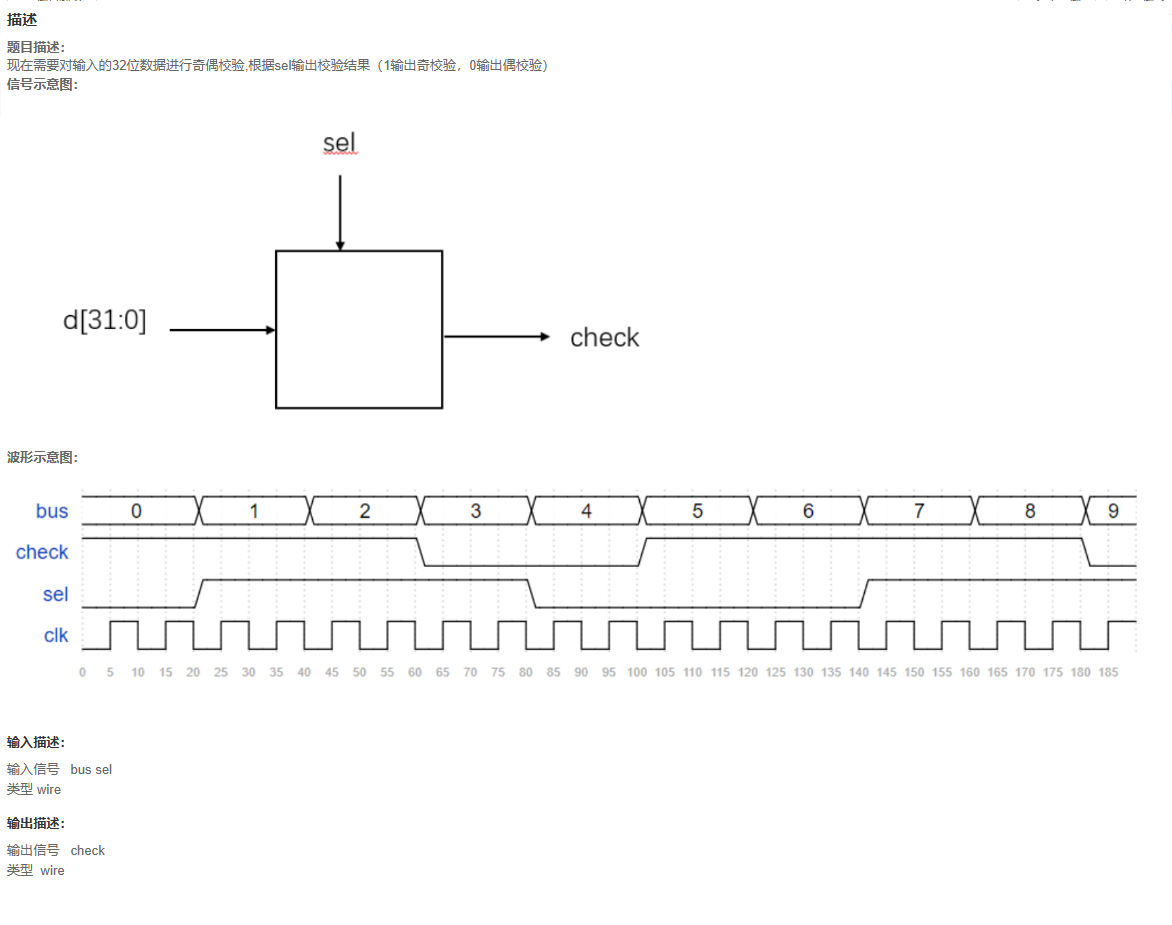
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module odd_sel(
input [31:0] bus,
input sel,
output check
);
//*************code***********//
reg tmp;
always@(*)begin
case(sel)
1'b1:tmp = ^bus;
1'b0:tmp = ~(^bus);
endcase
end
assign check =tmp;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
题目解析
需要了解什么是奇偶校验
奇校验:对输入数据添加1位0或者1,使得添加后的数包含奇数个1;
比如100,有奇数个1,那么奇校验结果就是0,这样补完0以后还是奇数个1;
偶校验:对输入数据添加1位0或者1,使得添加后的数包含偶数个1;
对bus进行异或,如果有奇数个1,输出就是1。如果有偶数个1,输出就是0
这个题目,应该是出题人搞反了,按照出题的意思,应该不能叫奇偶校验,应该是叫奇偶检测:
奇检测:输入的数据里有奇数个1就输出1;
偶检测:输入的数据里有偶数个1就输出1;
第四题
题目链接
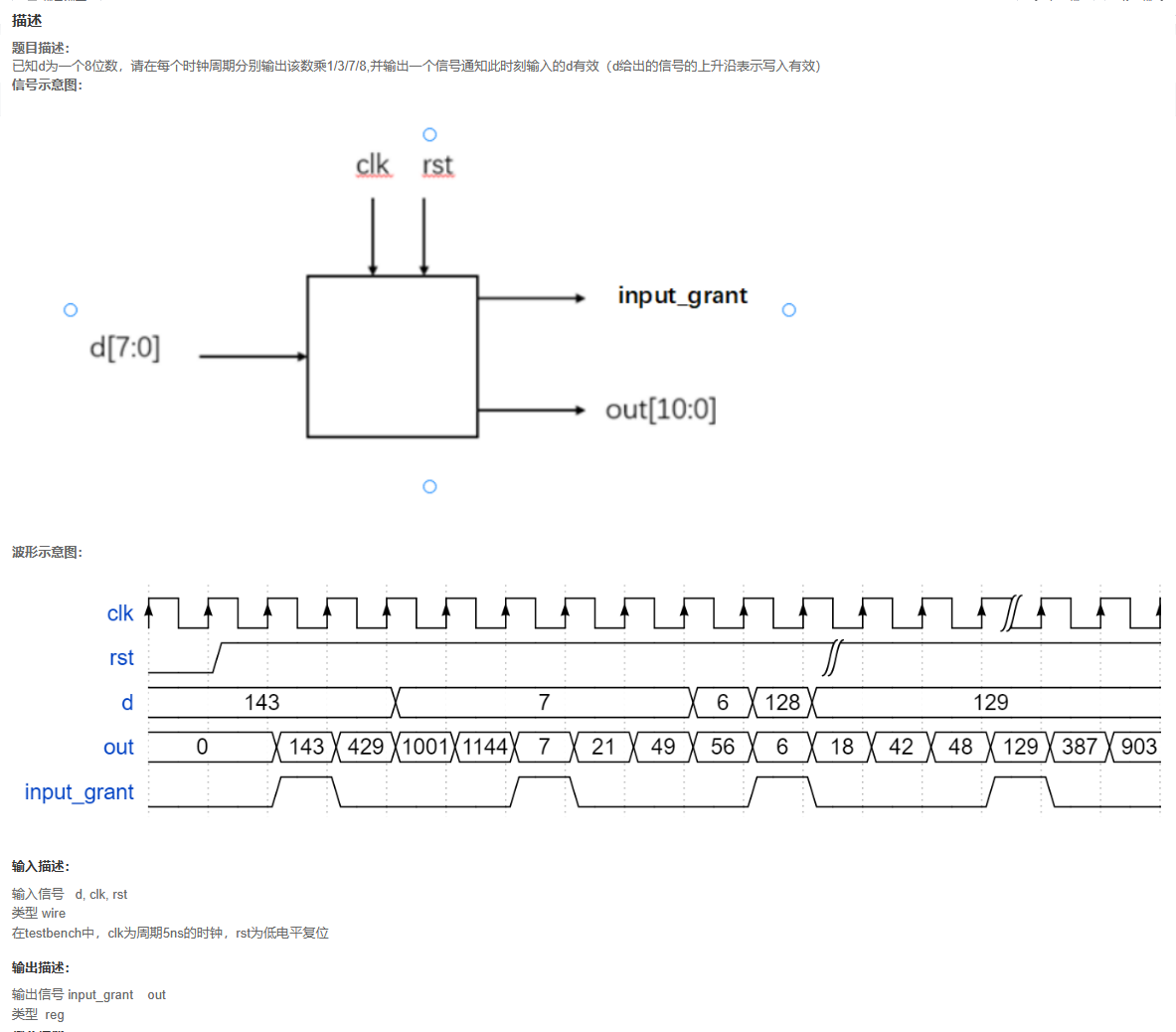
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module multi_sel(
input [7:0]d ,
input clk,
input rst,
output reg input_grant,
output reg [10:0]out
);
//*************code***********//
//wire Declaration
wire add_cnt;
wire end_cnt;
//reg Declaration
reg [1:0] cnt;
reg [7:0] tmp;
//计数器
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(!rst)begin
cnt <= 0;
end
else if(add_cnt)begin
if(end_cnt)
cnt <= 0;
else
cnt <= cnt + 1;
end
end
assign add_cnt = 1 ;
assign end_cnt = add_cnt && cnt==3 ;
//输出信号
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
input_grant <=0;
end
else if(cnt==0)begin
input_grant <=1;
end
else begin
input_grant <=0;
end
end
//数据缓存
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
tmp <= 0;
end
else if(cnt==0) begin
tmp <= d;
end
end
//信号输出
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
out <= 0;
end
else begin
case(cnt)
2'b00:out <= d;
2'b01:out <= (tmp<<1)+tmp;
2'b10:out <= (tmp<<3)-tmp;
2'b11:out <= (tmp<<3);
default:out <=0;
endcase
end
end
//*************code***********//
endmodule
题目解析
因为每个时钟周期分别输出该数乘1/3/7/8,所以需要一个计数器计算4个周期来输出数据。输出信号在计数器为0时候有效。观察波形示意图发现输出信号并不是立即跳变而是4个为一个周期来进行跳变,所以需要缓存数据。输出信号的乘法利用移位来做,可以有效增加时序性能(直接乘综合出来的加法器含有过多组合逻辑,时序性能很差)
第五题
题目链接
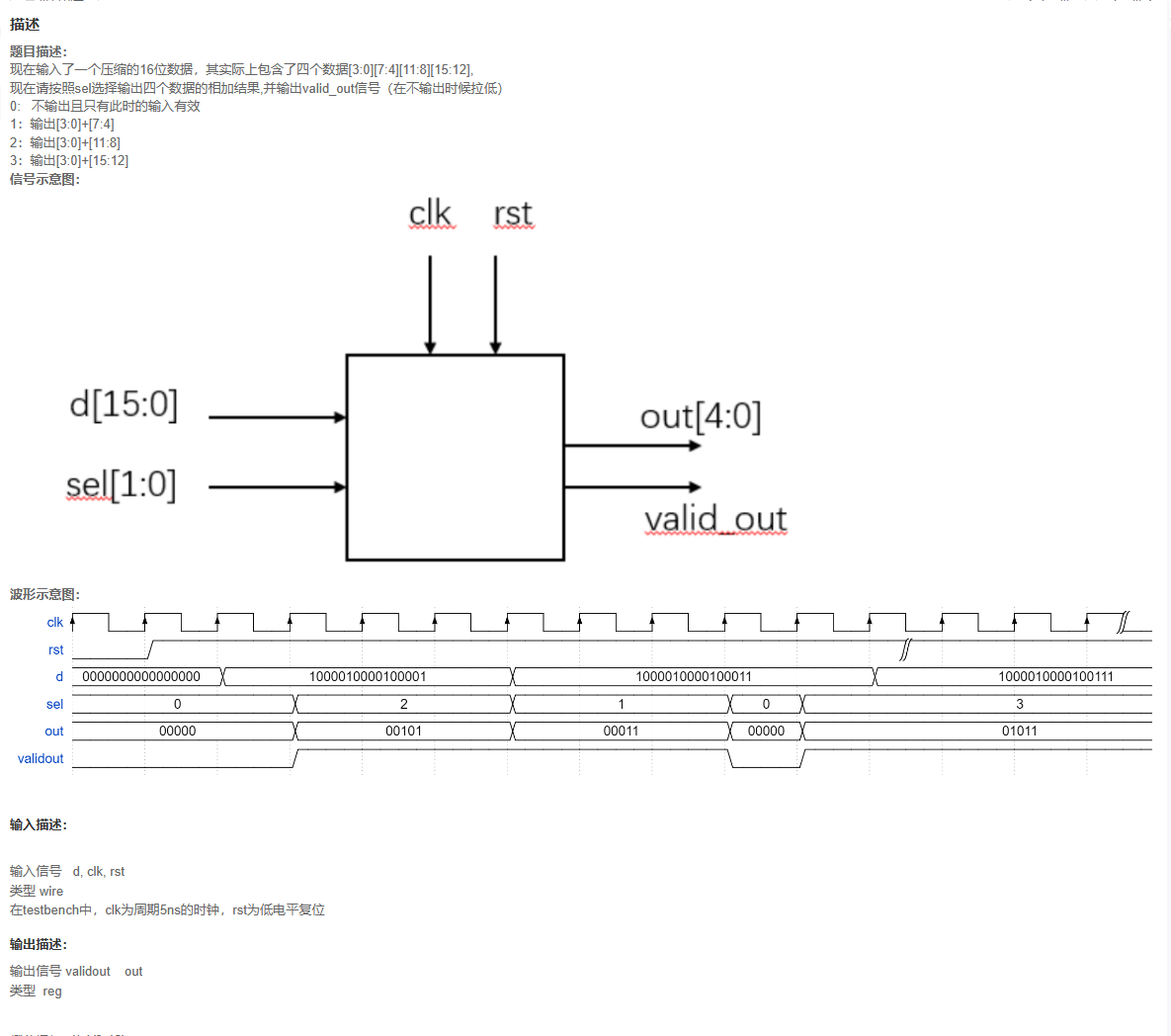
代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_cal(
input clk,
input rst,
input [15:0]d,
input [1:0]sel,
output [4:0]out,
output validout
);
//*************code***********//
//wire declaration
//reg declaration
reg [15:0] tmp;
reg valid;
reg [4:0] signal_out;
//有效信号
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
valid <= 0;
end
else if(0==sel) begin
valid <= 0;
end
else begin
valid <= 1;
end
end
assign validout = valid;
//数据缓存
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
tmp <= 0;
end
else if(0==sel) begin
tmp <= d;
end
end
//信号输出
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst)begin
if(rst==1'b0)begin
signal_out <= 0;
end
else begin
case(sel)
2'd0: signal_out <= 0;
2'd1: signal_out <= tmp[3:0] + tmp[7:4];
2'd2: signal_out <= tmp[3:0] + tmp[11:8];
2'd3: signal_out <= tmp[3:0] + tmp[15:12];
endcase
end
end
assign out =signal_out;
//*************code***********//
endmodule
题目解析
有效信号是输出时候,也就是sel不为1的时候是高电平。sel为0的时候是数据输入,所以缓存进来。信号输出就是根据题目的意思来就ok了。注意给的都是输入输出wire,不能直接在always块里面。需要声明寄存器。
第六题
题目链接

代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_select(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input signed[7:0]a,
input signed[7:0]b,
input [1:0]select,
output reg signed [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
c <= 9'd0;
else case(select)
2'b00: c <= a;
2'b01: c <= b;
2'b10: c <= a+b;
2'b11: c <= a-b;
default: c <= 9'd0;
endcase
endmodule
题目解析
没啥解析的地方,多路选择器,直接根据题意写就好了。有兴趣可以拓展一下有符号数和无符号数的区别
第七题:
题目链接

代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module data_minus(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input [7:0]a,
input [7:0]b,
output reg [8:0]c
);
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if(!rst_n)
c <= 0;
else if(a > b)
c <= a-b;
else
c <= b-a;
endmodule
题目解析
两个判断语句输出就好了
第八题
题目链接

代码
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module gen_for_module(
input [7:0] data_in,
output [7:0] data_out
);
generate
genvar i;
for(i = 0; i <8; i=i+1)
begin:assign_test//名字随便起,但是必须有
assign data_out[i] = data_in[7 - i];
end
endgenerate
endmodule
题目解析
注意考察generate语句的使用,需要注意两点,第一个需要genval产生数i,第二个就是for循环的begin必须有一个名字。
参考资料
探索者的刷题视频就很好
标签:tmp,题目,1ns,牛客,网刷题,rst,input,reg From: https://www.cnblogs.com/doincli/p/17461897.html