树链剖分的用处
使用树剖将整棵树剖分为若干条链,组成线性结构,可以方便用其他的数据结构维护信息。
一些定义
重儿子:该节点的所有子节点中子树大小最大的点。
轻儿子:该节点的所有除重儿子外的子节点。
重边:连接重儿子与父节点的边。
轻边:除重边外的边。
重链:由一串重边组成的链。
轻链:由一串轻边组成的链。
一些性质
- 树上的每个节点都属于且仅属于一条重链。
- 树链剖分后,一棵子树中的所有节点是连续的。
- 树链剖分后,一条链上的所有节点是连续的。
- 所有轻儿子的子树大小不超过父节点树大小的一半。
- 从根到某点的路径上,不超过 \(O(log_N)\) 条重链。
实现方法
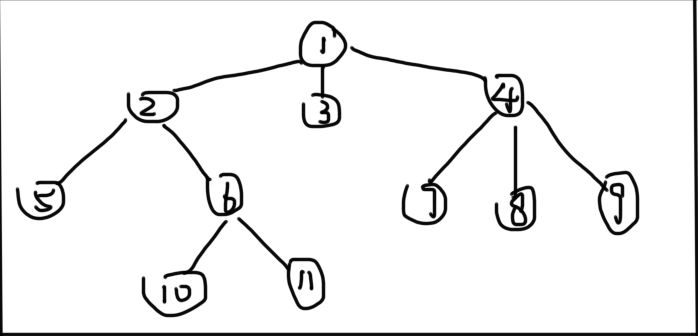
现在有一棵树:
1、一个dfs记录每个点的父亲、子树大小、重儿子编号
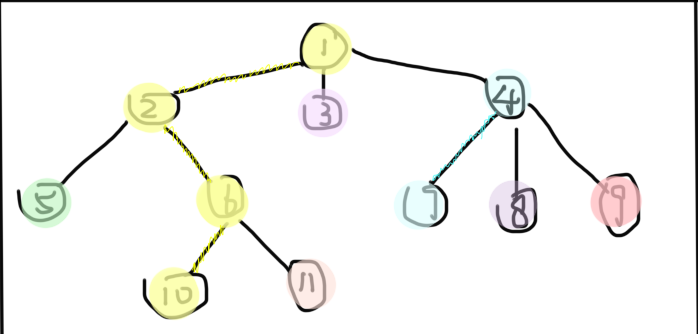
图中同一种颜色的点属于一条链,有颜色的边为重链。
int dep[N], sz[N], son[N], p[N]; //深度 子树大小 重儿子编号 父亲
void dfs1(int x, int fa) {
p[x] = fa;
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
sz[x] = 1;
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs1(v, x);
sz[x] += sz[v];
if (sz[v] > sz[son[x]]) son[x] = v;
}
}
2、优先遍历重儿子,重新编号,使一条链上的点的编号连续
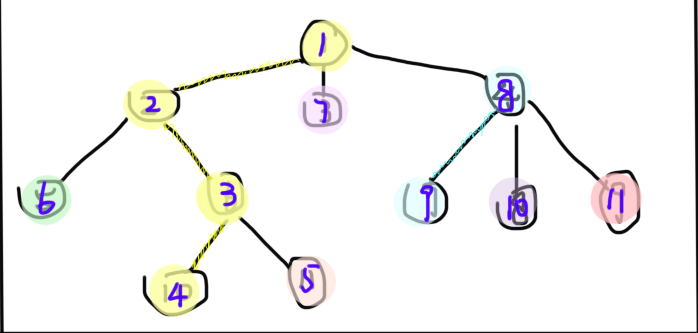
图中紫色数字即为重新编号后的结果。
int idx[N], top[N], idcnt; //节点新编号 节点所在重链顶端编号
ll nnum[N];
void dfs2(int x, int rt) {
idx[x] = ++idcnt;
nnum[idx[x]] = num[x];
top[x] = rt;
if (!son[x]) return ;
dfs2(son[x], rt);
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if (v == p[x] || v == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(v, v);
}
}
3、建一棵线段树用于维护链的信息
本题需要实现一棵求区间和的线段树。
完整代码
const int N = 100010;
int n, m, s;
ll mod; //节点个数 操作个数 根节点编号 模数
ll num[N]; //节点初值
int last[N], cnt;
struct edge {
int to, next;
} e[N << 1];
void addedge(int x, int y) {
e[++cnt].to = y;
e[cnt].next = last[x];
last[x] = cnt;
}
int dep[N], sz[N], son[N], p[N]; //深度 子树大小 重儿子编号 父亲
void dfs1(int x, int fa) {
p[x] = fa;
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
sz[x] = 1;
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs1(v, x);
sz[x] += sz[v];
if (sz[v] > sz[son[x]]) son[x] = v;
}
}
int idx[N], top[N], idcnt; //节点新编号 节点所在重链顶端编号
ll nnum[N];
void dfs2(int x, int rt) {
idx[x] = ++idcnt;
nnum[idx[x]] = num[x];
top[x] = rt;
if (!son[x]) return ;
dfs2(son[x], rt);
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].to;
if (v == p[x] || v == son[x]) continue;
dfs2(v, v);
}
}
struct SegmentTree {
ll l[N << 2], r[N << 2], sum[N << 2], add[N << 2];
void build(int rt, int L, int R) {
l[rt] = L, r[rt] = R;
if (L == R) {sum[rt] = nnum[L]; return ;}
int mid = L + R >> 1;
build(rt << 1, L, mid), build(rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, R);
update(rt);
}
void update(int rt) {
sum[rt] = (sum[rt << 1] + sum[rt << 1 | 1]) % mod;
}
void pushdown(int rt) {
add[rt << 1] = (add[rt << 1] + add[rt]) % mod, add[rt << 1 | 1] = (add[rt << 1 | 1] + add[rt]) % mod;
sum[rt << 1] = (sum[rt << 1] + (r[rt << 1] - l[rt << 1] + 1) * add[rt] % mod) % mod;
sum[rt << 1 | 1] = (sum[rt << 1 | 1] + (r[rt << 1 | 1] - l[rt << 1 | 1] + 1) * add[rt] % mod) % mod;
add[rt] = 0;
}
void change(int rt, int L, int R, ll c) {
if (R < l[rt] || r[rt] < L) return ;
if (L <= l[rt] && r[rt] <= R) {
add[rt] = (add[rt] + c) % mod;
sum[rt] = (sum[rt] + (r[rt] - l[rt] + 1) * c % mod) % mod;
return ;
}
pushdown(rt);
if (L <= r[rt << 1]) change(rt << 1, L, R, c);
if (l[rt << 1 | 1] <= R) change(rt << 1 | 1, L, R, c);
update(rt);
}
ll query(int rt, int L, int R) {
if (R < l[rt] || r[rt] < L) return 0;
if (L <= l[rt] && r[rt] <= R) return sum[rt];
pushdown(rt);
ll res = 0;
if (L <= r[rt << 1]) res = (res + query(rt << 1, L, R)) % mod;
if (l[rt << 1 | 1] <= R) res = (res + query(rt << 1 | 1, L, R)) % mod;
update(rt);
return res;
}
} tree;
void treeadd(int x, int y, ll c) {
while(top[x] != top[y]) {
if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
tree.change(1, idx[top[x]], idx[x], c);
x = p[top[x]];
}
if (dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x, y);
tree.change(1, idx[x], idx[y], c);
}
ll treequery(int x, int y) {
ll res = 0;
while (top[x] != top[y]) {
if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]]) swap(x, y);
res = (res + tree.query(1, idx[top[x]], idx[x])) % mod;
x = p[top[x]];
}
if (dep[x] > dep[y]) swap(x, y);
res = (res + tree.query(1, idx[x], idx[y])) % mod;
return res;
}
int main() {
n = read(), m = read(), s = read(), mod = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) num[i] = read() % mod;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x = read(), y = read();
addedge(x, y), addedge(y, x);
}
dep[s] = 1;
dfs1(s, s), dfs2(s, s);
tree.build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int op = read();
if (op == 1) {
int x = read(), y = read(), c = read() % mod;
treeadd(x, y, c);
}
if (op == 2) {
int x = read(), y = read();
printf("%lld\n", treequery(x, y));
}
if (op == 3) {
int x = read(), c = read() % mod;
tree.change(1, idx[x], idx[x] + sz[x] - 1, c);
}
if (op == 4) {
int x = read();
printf("%lld\n", tree.query(1, idx[x], idx[x] + sz[x] - 1));
}
}
return 0;
}