# BeLFusion: Latent Diffusion for Behavior-Driven Human Motion Prediction #paper
1. paper-info
1.1 Metadata
- Author:: [[German Barquero]], [[Sergio Escalera]], [[Cristina Palmero]]
- 作者机构:: Universitat de Barcelona
- Keywords:: #HMP #Diffusion
- Journal:: 预印本
- Date:: [[2022-11-25]]
- 状态:: #Done
- 链接:: http://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14304
- 修改时间:: 2022.12.07
1.2. Abstract
Stochastic human motion prediction (HMP) has generally been tackled with generative adversarial networks and variational autoencoders. Most prior works aim at predicting highly diverse movements in terms of the skeleton joints' dispersion. This has led to methods predicting fast and motion-divergent movements, which are often unrealistic and incoherent with past motion. Such methods also neglect contexts that need to anticipate diverse low-range behaviors, or actions, with subtle joint displacements. To address these issues, we present BeLFusion, a model that, for the first time, leverages latent diffusion models in HMP to sample from a latent space where behavior is disentangled from pose and motion. As a result, diversity is encouraged from a behavioral perspective. Thanks to our behavior coupler's ability to transfer sampled behavior to ongoing motion, BeLFusion's predictions display a variety of behaviors that are significantly more realistic than the state of the art. To support it, we introduce two metrics, the Area of the Cumulative Motion Distribution, and the Average Pairwise Distance Error, which are correlated to our definition of realism according to a qualitative study with 126 participants. Finally, we prove BeLFusion's generalization power in a new cross-dataset scenario for stochastic HMP.
2. Introduction
- 领域:Stochastic human motion prediction
- 针对什么问题:
- 传统方法生成的动作序列会造成姿势不真实。见Fig.1
- 作者的方法:
- 为解决预测序列与历史序列的速度和方向连贯性,将这部分信息和动作行为信息解耦出来,通过diffusion model编码到潜空间中。由于解耦之后,通过潜变量生成的动作会更加真实。
- Contributions
- BeLFusion model
- diversity motion prediction
- cross-dataset evaluation
- new metrics
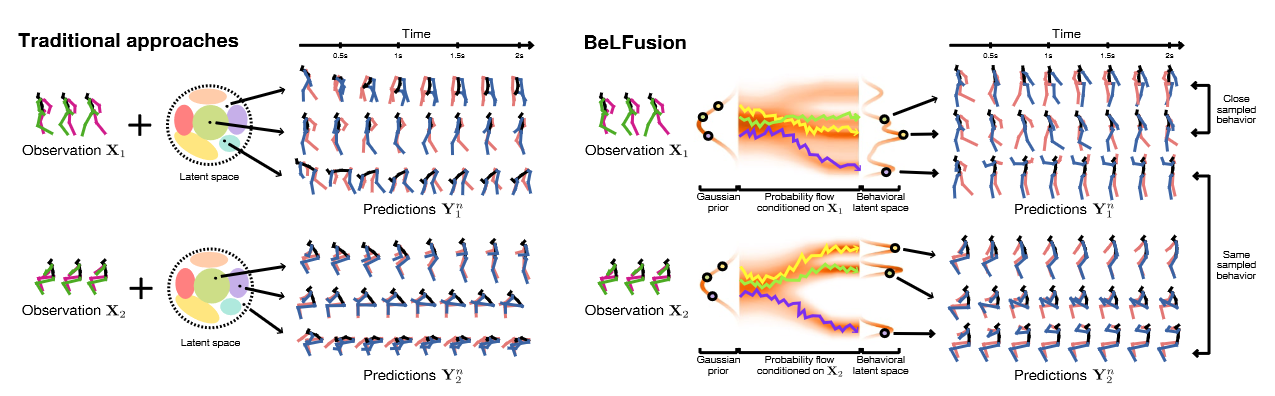
Fig.1 Tradition approaches and BeLFusion
Source:
3. Methodology
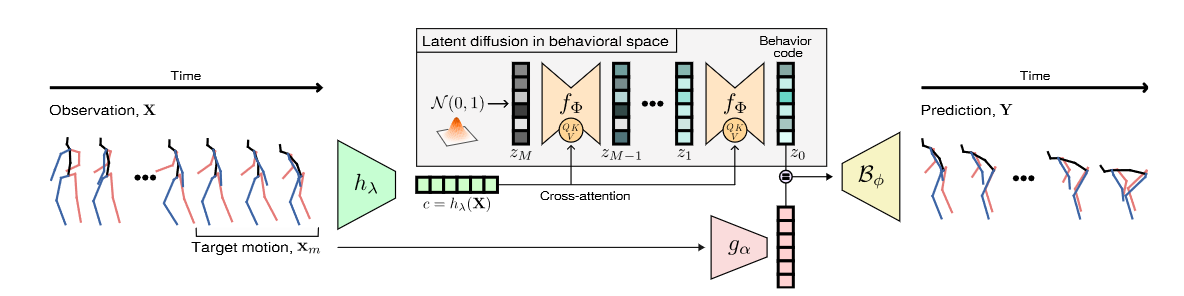
Fig. 2. BeLFusion architecture
Source:
3.1. Problem definition
给定一个历史序列\(X=\{p_{t-B},...,p_{t-2},p_{t-1}\}\)去预测未来序列\(Y^i=\{p_t^i,p_{t+1}^i,..,p_{t+T+1}^i\}\)
3.2. Motion latent diffusion
利用潜在扩散模型(Latent diffusion models--LDM)扩散采样出从动作序列解耦出的潜在变量\(z=\varepsilon(Y)\in V^3\) ,加入\(z\)后,原始问题课通过(1)表示:
同DDPM[1] ,也是去预测噪音\(\epsilon _t = f_\Phi (z_t,t,X)\)。 LDM 的损失函数为:
\[\mathcal{L}_{\text {lat }}(\mathbf{X}, \mathbf{Y})=\sum_{t=1}^{T} \underset{q\left(z_{t} \mid z_{0}\right)}{\mathbb{E}}\|f_{\Phi}\left(z_{t}, t, \mathbf{X}\right)-\underbrace{\mathcal{E}(\mathbf{Y})}_{z}\|_{1} \tag{2} \]3.3. Behavioral latent diffusion
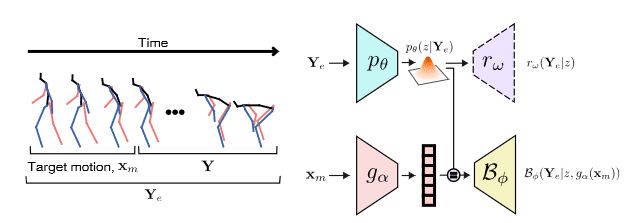
Fig. 3. 整体框架
Source:
整体模型图如Fig3所示,图像的上半部分也就是3.2部分,产生行为潜在变量\(z\)。下半部分属于真正的生成模型部分,结构类似于encoder-decoder模型。
\(\mathcal{B}_{\phi}\):行为耦合器(behavior counpler)
\(\mathcal{r}_w\):辅助decoder,用于帮助训练\(z\)。
\(\mathcal{B}_{\phi}\)和\(\mathcal{r}_w\)交替训练(类似于对抗训练), \(\mathcal{r}_w\)对应的损失函数为(3),\(\mathcal{B}_{\phi}\)对应的损失函数为(4)
4. Expereiment
- database
- Human3.6M
- AMASS
- Evaluation metrics
- Average and the Final Displacement Error metrics(ADE,FDE)
- MMADE
- MMFDE
- Average Pairwise Distance(APD):衡量多样性
- Frechet Inception Distance(FID)
总结
对行为标签进行扩散模型建模,和我预想的结构差不多,加入行为标签,对应的多样性会体现在同一种行为标签的动作序列当中。