目录
Why
We need a set of tools and technologies designed to efficiently deploy, manage, and orchestrate containerized applications in a container runtime environment.
What
Synopsis
K8s, short for Kubernetes, is an open-source container orchestration platform originally developed by Google and now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It is one of the most popular and widely used tools for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
Design Goals
The main goals of Kubernetes are to simplify and automate the management of containerized workloads, provide a consistent and reliable platform for deploying applications, and enable seamless scaling and integration in modern cloud-native environments.
Architecture
image1

Image from: https://devopscube.com/kubernetes-architecture-explained/
image2
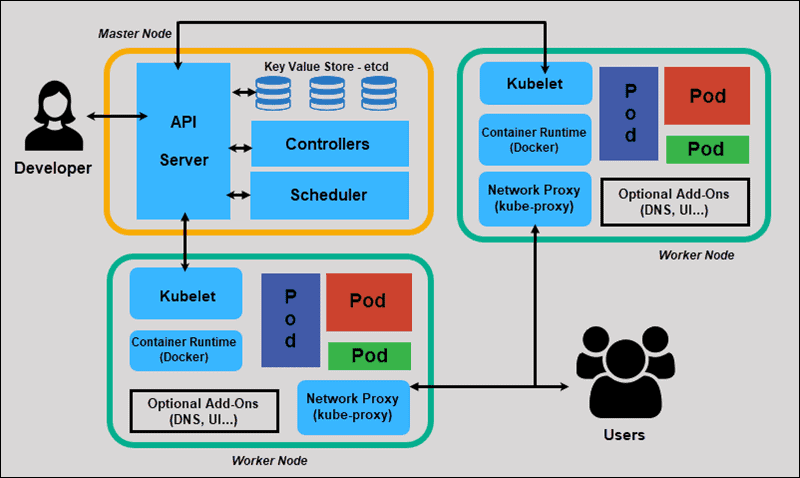
Image from: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/understanding-kubernetes-architecture-diagrams
image3
Image from: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
Main Componets
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Control Plane Components | |
| API Server | Exposes the Kubernetes API and processes API requests to maintain the desired state of the cluster. |
| etcd | A distributed key-value store that stores the cluster's configuration data, ensuring data consistency. |
| Scheduler | Responsible for making decisions about where to place newly created pods based on resource requirements. |
| Controller Manager | A collection of controllers that monitor the cluster's state and perform actions to maintain the desired state. |
| Cloud Controller Manager | Provides an interface to interact with cloud provider APIs for managing cloud-specific resources. |
| Node Components | |
| Kubelet | Runs on each node and ensures that containers are running and healthy. It communicates with the API server. |
| Container Runtime | The software responsible for running containers, such as Docker or containerd. |
| Kube-Proxy | Handles network routing for services and maintains network rules on nodes. |
| Additional Components | |
| Ingress Controller | Manages external access to services within the cluster by routing incoming traffic. |
| Dashboard | A web-based user interface for managing and monitoring the cluster. |
| DNS | Provides DNS-based service discovery for pods and services within the cluster. |
Core Resouces
some core resouces
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Pods | The smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. A pod is a group of one or more tightly coupled containers that share the same network namespace and can be scheduled and deployed together on the same host. |
| ReplicaSets | A higher-level abstraction that ensures a specified number of identical pods are running at all times. It can be used to scale the number of pods up or down based on defined rules. |
| Deployments | A higher-level resource that manages ReplicaSets and provides declarative updates for Pods and ReplicaSets. Deployments allow you to specify the desired state of the application, and Kubernetes handles the actual state reconciliation. |
| Services | An abstraction that exposes a set of pods to other services within the cluster or externally. Services provide load balancing and a stable endpoint for connecting to the pods. |
| Namespaces | A way to logically divide and isolate resources within a cluster. Namespaces are used to avoid naming collisions and to organize resources into manageable groups. |
| ConfigMaps and Secrets | Resources to store configuration data and sensitive information, respectively, outside of the container images. They can be mounted as volumes or passed as environment variables to containers. |
| Persistent Volumes | Resources that allow decoupling of storage from pods. Persistent Volumes (PVs) represent physical storage, and Persistent Volume Claims (PVCs) are requests for that storage. |
| StatefulSets | A higher-level abstraction for managing stateful applications. It ensures that pods are created and scaled in a specific order, and each pod gets a stable hostname. |
| DaemonSets | Ensures that a specific pod runs on each node in the cluster, ensuring that certain background tasks, logging agents, or monitoring agents are present on every node. |
| Jobs and CronJobs | Resources to run batch or one-time tasks (Jobs) or scheduled tasks (CronJobs) within the cluster. |
| Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) | A resource that automatically scales the number of pods in a deployment based on CPU utilization or custom metrics. |
| Network Policies | These define how pods are allowed to communicate with each other within the cluster, providing a level of network segmentation and security. |
| Ingress | A resource that manages external access to services within the cluster by exposing HTTP and HTTPS routes to the services. |
related cmds
# show all the k8s resource types
kubectl api-resources
# get detailed information of a resource type
kubectl explain pods
kubectl explain pods.metadata
How
Implementation Mechanism
Kubernetes works based on a combination of declarative configuration, control loops, and API interactions. Its implementation mechanism involves several components collaborating to manage containerized applications efficiently. Here's a high-level overview of how Kubernetes works:
-
Declarative Configuration: Users define the desired state of the cluster and applications using YAML or JSON manifests.
-
API Server: The central component that exposes the Kubernetes API, handling requests from clients.
-
etcd: A distributed key-value store that stores the desired state of the cluster.
-
Controllers and Control Loops: Controllers monitor the cluster's state and take corrective actions to ensure it matches the desired state.
-
Scheduler: Determines the best node to place new pods based on resource requirements and constraints.
-
Kubelet and Data Plane: Kubelet on each node executes and manages containers. Data plane components handle container execution and networking.
-
Client Tools: Tools like
kubectland the Kubernetes Dashboard interact with the API server to manage the cluster.
In summary, Kubernetes works by maintaining a desired state specified through declarative configuration. It employs control loops, controllers, and API interactions to continuously monitor and reconcile the actual state with the desired state. This ensures that the cluster remains in the desired state, even as workloads and conditions change over time. The data plane components on each node execute and manage containers, while the control plane components orchestrate and manage the overall state of the cluster.
Data Flow
Example: create a pod.

Image from: https://devopscube.com/kubernetes-architecture-explained/
标签:Kubernetes,desired,介绍,cluster,state,API,英文版,k8s,pods From: https://www.cnblogs.com/fireyun/p/18377048