火烧赤壁
题目背景
曹操平定北方以后,公元 208 年,率领大军南下,进攻刘表。他的人马还没有到荆州,刘表已经病死。他的儿子刘琮听到曹军声势浩大,吓破了胆,先派人求降了。
孙权任命周瑜为都督,拨给他三万水军,叫他同刘备协力抵抗曹操。
隆冬的十一月,天气突然回暖,刮起了东南风。
没想到东吴船队离开北岸大约二里距离,前面十条大船突然同时起火。火借风势,风助火威。十条火船,好比十条火龙一样,闯进曹军水寨。那里的船舰,都挤在一起,又躲不开,很快地都烧起来。一眨眼工夫,已经烧成一片火海。
曹操气急败坏的把你找来,要你钻入火海把连环线上着火的船只的长度统计出来!
题目描述
给定每个起火部分的起点和终点,请你求出燃烧位置的长度之和。
输入格式
第一行一个整数,表示起火的信息条数 \(n\)。
接下来 \(n\) 行,每行两个整数 \(a, b\),表示一个着火位置的起点和终点(注意:左闭右开)。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数表示答案。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
3
-1 1
5 11
2 9
样例输出 #1
11
提示
数据规模与约定
对于全部的测试点,保证 \(1 \leq n \leq 2 \times 10^4\),\(-2^{31} \leq a < b \lt 2^{31}\),且答案小于 \(2^{31}\)。
AC code:
- 首先看到\(a ,b\)的范围高达\(-2^{31} \leq a < b \lt 2^{31}\),然后在题目的题目要求来看,自然想到用离散化的做法来解决这道题目.
虽然这道题目我用贪心加上模拟也能做,而且效率还更高一点,但是这只是我用来离散化的一个练习题,练习离散化才是重点- 这里特别要注意这个题目有坑,n的数据范围不止是\(2 \cdot 10^4\) 我这里用了 \(2\cdot 10^5\)才能够完全AC
- 离散化的本质就是建立一个数组映射来节约空间(特别是这种按一般思维上需要进行一步一步覆盖的题目)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
const int MAXN= 200009;
#define int long long
int a[MAXN],b[MAXN],c[MAXN];
bool mmm[MAXN];
using namespace std;
signed main()
{
int n,ctop=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
c[++ctop]=a[i];
c[++ctop]=b[i];
}
sort(c+1,c+ctop+1);
int t=unique(c+1,c+ctop+1)-c;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
a[i]=lower_bound(c+1,c+t,a[i])-c;
b[i]=lower_bound(c+1,c+t,b[i])-c-1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=a[i];j<=b[i];j++)
{
mmm[j]=1;
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=t;i++)
{
if(mmm[i]){
ans+=c[i+1]-c[i];
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
[USACO12FEB] Overplanting S
题目描述
Farmer John has purchased a new machine that is capable of planting grass within any rectangular region of his farm that is "axially aligned" (i.e., with vertical and horizontal sides). Unfortunately, the machine malfunctions one day and plants grass in not one, but N (1 <= N <= 1000) different rectangular regions, some of which may even overlap.
Given the rectangular regions planted with grass, please help FJ compute the total area in his farm that is now covered with grass.
在一个笛卡尔平面坐标系里(则 \(X\) 轴向右是正方向,\(Y\) 轴向上是正方向),有 \(N\ (1 \le N \le 1000)\) 个矩形,第 \(i\) 个矩形的左上角坐标是 \((x_1,y_1)\),右下角坐标是 \((x_2,y_2)\)。问这 \(N\) 个矩形所覆盖的面积是多少?
注意:被重复覆盖的区域的面积只算一次。
输入格式
第一行,一个整数 \(N\ (1 \le N \le 1000)\)。
接下来有 \(N\) 行,每行描述一个矩形的信息,分别是矩形的 \(x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2(-10^8 \le x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2 \le 10^8)\)。
输出格式
一个整数,被 \(N\) 个矩形覆盖的区域的面积。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2
0 5 4 1
2 4 6 2
样例输出 #1
20
AC code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
const int MAXN=1009;
#define int long long
long long a[MAXN][4],c[MAXN*4],f[MAXN*4][MAXN*4],ctop;
using namespace std;
using i64 = long long;
signed main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)cin>>a[i][j];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
c[++ctop]=a[i][j];
}
}
sort(c+1,c+1+ctop);
ctop=unique(c+1,c+ctop+1)-c;
map<int,int>mmm;
for(int i=1;i<ctop;i++)
{
mmm[c[i]]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
a[i][j]=mmm[a[i][j]];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=a[i][0];j<a[i][2];j++)
{
f[j][a[i][1]]--,f[j][a[i][3]]++;
// cout<<"a[i][1]="<<a[i][1]<<endl;
// cout<<"a[i][3]="<<a[i][3]<<endl;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<ctop;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<ctop;j++)
{
f[i][j]=f[i][j-1]+f[i][j];
}
}
long long ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<ctop-1;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<ctop-1;j++)
{
if(f[i][j]>0)
{
ans+=(long long)(c[j+1]-c[j])*(c[i+1]-c[i]);
// cout<<c[j+1]<<" "<<c[j]<<endl;
// cout<<c[j+1]-c[j]<<' '<<c[i+1]-c[i]<<endl;
}
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
注意的细节:
-
ctop=unique(c+1,c+ctop+1)-c;这一步unique 会把所有重复元素放到数组尾端,然后返回值是一个地址,指向第一个重复元素的位置.就像这样
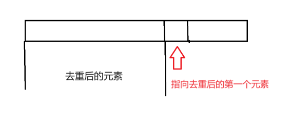
-
注意这里\(xOy\)的坐标的方向是右上为正的,所以左上角的y坐标大于右下角的y坐标.所以有:
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { for(int j=a[i][0];j<a[i][2];j++) { f[j][a[i][1]]--,f[j][a[i][3]]++; // cout<<"a[i][1]="<<a[i][1]<<endl; // cout<<"a[i][3]="<<a[i][3]<<endl; } } -
最后矩形覆盖的方式是右减左,所以要注意控制计算过程为左闭右开,因为我们计算的相当于是线段的长度.

-
还有一个细节要记住,因为离散化的过程中每个点存在4个数据,所以
f数组的边长应该是4*MAXN,我在这里吃了一发WA