栈与队列
前言
栈与队列作为线性表结构的代表,在计算机领域应用广泛。我们耳熟能详的系统栈,进程处理等计算机操作系统底层实现原理都是间接或者直接使用了相关数据结构或其思想,下面让我们来介绍这两种数据结构。
栈
结构定义
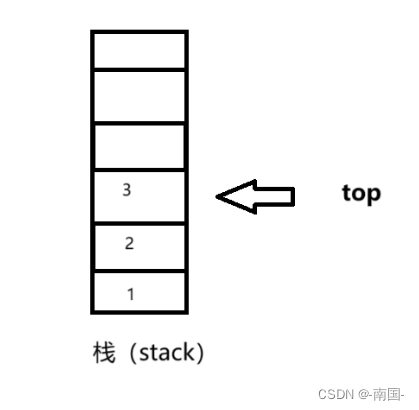
栈(stack)是限定仅在表尾进行插入或者删除的线性表。对于栈来说,表尾端称为栈顶(top),表头端称为栈低(bottom)。不含元素的空表称为空栈。因为栈限定在表尾进行插入或者删除,所以栈又被称为后进先出的线性表(简称LIFO:Last in, First out.结构)。
- 定义结构体
typedef struct Stack {
int *data;
int top, size;
}Stack;
结构操作
- 初始化(init)
//初始化
Stack *init(int n) {
Stack *s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 10));
s->top = -1;
s->size = n;
return s;
}
- 压栈、入栈(push)
//入栈
int push(Stack *s, int val) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (s->top + 1 == s->size) {
if (!expand(s)) return 0;
printf("expand Stack->size is successful!\n");
}
s->data[++s->top] = val;
return 1;
}
- 获取栈顶元素(top/front)
//获取队首元素
int top(Stack *s) {
if (empty(s)) return -1;
return s->data[s->top];
}
- 扩容操作(expand)
//扩容
int expand(Stack *s) {
int exp_size = s->size;
int *p;
while (exp_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(s->data, (s->size + exp_size));
if (p) break;
exp_size /= 2;
}
if (p == NULL) return 0;
s->data = p;
s->size += exp_size;
return 1;
}
- 销毁(clear)
//销毁
void clear(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return ;
free(s->data);
free(s);
return ;
}
- 判空(empty)
//判空操作
int empty(Stack *s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
- 出栈、弹栈(pop)
//出栈
int pop(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (empty(s)) return 0;
s->data[s->top--];
return 1;
}
完整代码(栈)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
//顺序栈:初始化、销毁、获取队首元素、判空操作、入栈、出栈
typedef struct Stack {
int *data;
int top, size;
}Stack;
//初始化
Stack *init(int n) {
Stack *s = (Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
s->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 10));
s->top = -1;
s->size = n;
return s;
}
//判空操作
int empty(Stack *s) {
return s->top == -1;
}
//获取队首元素
int top(Stack *s) {
if (empty(s)) return -1;
return s->data[s->top];
}
//扩容
int expand(Stack *s) {
int exp_size = s->size;
int *p;
while (exp_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(s->data, (s->size + exp_size));
if (p) break;
exp_size /= 2;
}
if (p == NULL) return 0;
s->data = p;
s->size += exp_size;
return 1;
}
//入栈
int push(Stack *s, int val) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (s->top + 1 == s->size) {
if (!expand(s)) return 0;
printf("expand Stack->size is successful!\n");
}
s->data[++s->top] = val;
return 1;
}
//出栈
int pop(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return 0;
if (empty(s)) return 0;
s->data[s->top--];
return 1;
}
//销毁
void output(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL || empty(s)) return ;
printf("[");
for (int i = 0; i <= s->top; i++) {
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", s->data[i]);
}
printf("] <== Stack[%d]\n", s->top + 1);
return ;
}
//销毁
void clear(Stack *s) {
if (s == NULL) return ;
free(s->data);
free(s);
return ;
}
int main () {
#define max_op 20
int op, val;
srand(time(0));
Stack *s = init(10);//测试
for (int i = 0; i < max_op; i++) {
op = rand() % 4;
val = rand() % 100 + 1;
switch (op) {
case 0:
case 1:
case 2: {
printf("push val(%d) to the Stack is %s!\n", val, push(s, val) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
case 3: {
val = top(s);
printf("pop val(%d) from the Stack is %s!\n", val, pop(s) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
}
output(s);
}
clear(s);
#undef max_op
return 0;
}
队列
结构定义
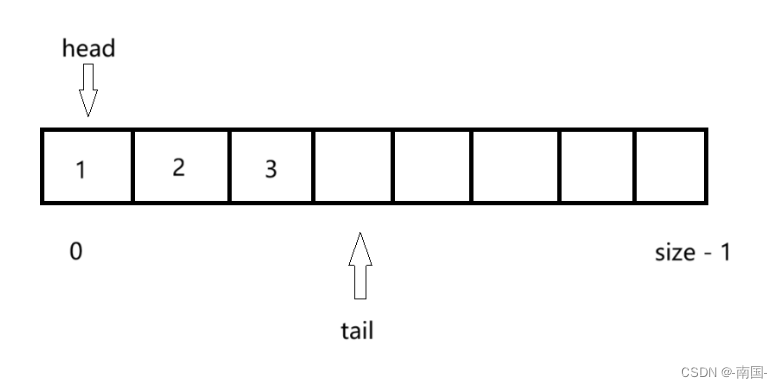
相比于栈结构而言,队列是队首出队,队尾入队的受限线性表结构。特点是先入先出(LILO)
- 定义结构体
typedef struct Queue {
int *data;
int head, tail, size;
}Queue;
结构操作
- 初始化(init)
//初始化队列
Queue *init(int n) {
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 10));
q->head = q->tail = 0;
q->size = n;
return q;
}
- 销毁(clear)
//销毁
void clear(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return ;
free(q->data);
free(q);
return ;
}
- 判空(empty)
//判空操作
int empty(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return 1;
return q->head == q->tail;
}
- 获取队首元素(front)
//获取队首元素
int front(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || empty(q)) return -1;
return q->data[q->head];
}
- 入队(push)
//入队操作
int push(Queue *q, int val) {
if (q == NULL) return 0;
if (q->tail + 1 == q->size) {
if (!expand(q)) return 0;
printf("expand the Queue size is successful!\n");
}
q->data[q->tail++] = val;
return 1;
}
- 出队(pop)
//出队操作
int pop(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || empty(q)) return 0;
q->head++;
return 1;
}
循环队列
- 循环队列实现思路?
- 队列再结构体的属性中定义一个cnt变量,即q→cnt 。
- 当head == q→size 时 使得head -= q→size;tail 亦然。
- 当需要遍历队列时,(0 → q→cnt) ⇒ q→data[(q→head + i)% q→size];即可
完整代码(队列、循环队列)
- 队列
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
//顺序表队列:初始化、销毁、扩容、获取队首元素、判空、入队、出队
typedef struct Queue {
int *data;
int head, tail, size;
}Queue;
//初始化队列
Queue *init(int n) {
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 10));
q->head = q->tail = 0;
q->size = n;
return q;
}
//判空操作
int empty(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return 1;
return q->head == q->tail;
}
//获取队首元素
int front(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || empty(q)) return -1;
return q->data[q->head];
}
int expand(Queue *q) {
int exp_size = q->size;
int *p;
while (exp_size) {
p = (int *)realloc(q->data, (exp_size + q->size));
if (p) break;
exp_size /= 2;
}
if (p == NULL) return 0;
q->data = p;
q->size += exp_size;
return 1;
}
//入队操作
int push(Queue *q, int val) {
if (q == NULL) return 0;
if (q->tail + 1 == q->size) {
if (!expand(q)) return 0;
printf("expand the Queue size is successful!\n");
}
q->data[q->tail++] = val;
return 1;
}
//出队操作
int pop(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || empty(q)) return 0;
q->head++;
return 1;
}
//遍历
void output(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || empty(q)) return ;
printf("[");
for (int i = q->head; i < q->tail; i++) {
i != q->head && printf(",");
printf("%d", q->data[i]);
}
printf("] <== Queue[%d]\n", q->tail - q->head);
return ;
}
//销毁
void clear(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return ;
free(q->data);
free(q);
return ;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
int op, val;
#define max_op 20
Queue *q = init(10);
for (int i = 0; i < max_op; i++) {
op = rand() % 4;
val = rand() % 100 + 1;
switch(op) {
case 0:
case 1:
case 2: {
printf("push val(%d) to the Queue is %s!\n", val, push(q, val) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
case 3: {
val = front(q);
printf("pop front(%d) from the Queue is %s!\n", val, pop(q) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
}
output(q);
}
clear(q);
#undef max_op
return 0;
}
- 循环队列
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
//循环队列:初始化、销毁、获取队首元素、判空操作、出队、入队、遍历
typedef struct Queue{
int *data;
int head, tail, size, cnt;
}Queue;
//初始化
Queue *init(int n) {
Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
q->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (n + 5));
q->head = q->tail = q->cnt = 0;
q->size = n;
return q;
}
//判空
int empty(Queue *q) {
return q->cnt;
}
//获取队首元素
int front(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || !empty(q)) return -1;
return q->data[q->head];
}
//入队
int push(Queue *q, int val) {
if (q == NULL) return 0;
if (q->cnt == q->size) return 0;//队列满了
q->data[q->tail++] = val;
if (q->tail == q->size) q->tail -= q->size;
q->cnt++;
return 1;
}
//出队
int pop(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL || !empty(q)) return 0;
q->head++;
if (q->head == q->size) q->head -= q->size;
q->cnt--;
return 1;
}
//遍历
void output(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return ;
printf("[");
for (int i = 0; i < q->cnt; i++) {
i && printf(", ");
printf("%d", q->data[(q->head + i) % q->size]);
}
printf("] <== Queue[%d]\n", q->cnt);
}
//销毁
void clear(Queue *q) {
if (q == NULL) return ;
free(q->data);
free(q);
return ;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
#define max_op 30
Queue *q = init(10);
int op, val;
for (int i = 0; i < max_op; i++) {
op = rand() % 4;
val = rand() % 100 + 1;
switch (op) {
case 0:
case 1:
case 2: {
printf("Push val(%d) to the Queue is %s!\n", val, push(q, val) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
case 3: {
val = front(q);
printf("Pop val(%d) from the Queue is %s!\n", val, pop(q) ? "YES" : "NO");
} break;
}
output(q);
}
#undef max_op
clear(q);
return 0;
}