# Back to MLP: A Simple Baseline for Human Motion Prediction #paper
1. paper-info
1.1 Metadata
- Author:: [[Wen Guo]], [[Yuming Du]], [[Xi Shen]], [[Vincent Lepetit]], [[Xavier Alameda-Pineda]], [[Francesc Moreno-Noguer]]
- 作者机构::
- Keywords:: #HMP , #FC , #LayerNormalization
- Journal::
- Date:: [[2022-08-25]]
- 状态:: #Done
1.2 Abstract
This paper tackles the problem of human motion prediction, consisting in forecasting future body poses from historically observed sequences. State-of-the-art approaches provide good results, however, they rely on deep learning architectures of arbitrary complexity, such as Recurrent Neural Networks(RNN), Transformers or Graph Convolutional Networks(GCN), typically requiring multiple training stages and more than 2 million parameters. In this paper, we show that, after combining with a series of standard practices, such as applying Discrete Cosine Transform(DCT), predicting residual displacement of joints and optimizing velocity as an auxiliary loss, a light-weight network based on multi-layer perceptrons(MLPs) with only 0.14 million parameters can surpass the state-of-the-art performance. An exhaustive evaluation on the Human3.6M, AMASS, and 3DPW datasets shows that our method, named siMLPe, consistently outperforms all other approaches. We hope that our simple method could serve as a strong baseline for the community and allow re-thinking of the human motion prediction problem. The code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/dulucas/siMLPe}.
1.3 Introduction
traditional approaches:
- Hidden Markov models
- Gaussian process latent variable models
Deeplearning methods - RNN-based
- GCN-based
- Transformer-based
之前的深度模型可以达到很好地效果,但是模型太复杂;模型参数太多;训练时间长。
本篇论文的contribution: - 用一种很简单的模型达到了很好地效果,仅仅用到了全连接层
- 提出了一种新模型
SIMLPE由三部分组成fully connected layerslayer normalizationtranspose operation
3. SIMLPE
3.1 Network architecture
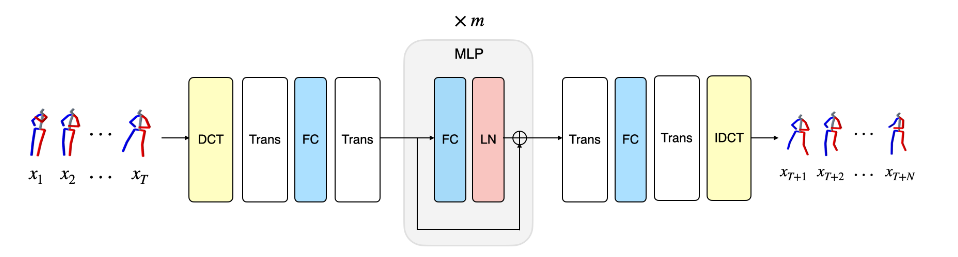
图 3-1 网络结构图
DCT: Discrete Cosine Transform 离散余弦变换, 可以将图片信息压缩加工成序列.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q2aEzeMDHMA
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/85299446
DCT matrix D为
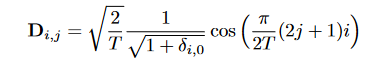
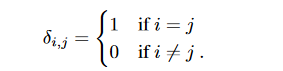
图 3-2 DCT matrix
IDCT:Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform
FC: 全连接层
Trans:transpose operation 转置操作
LN: layer normalization
Jimmy Lei Ba, Jamie Ryan Kiros, and Geoffrey E. Hinton. Layer Normalization. In arXiv Preprint, 2016.
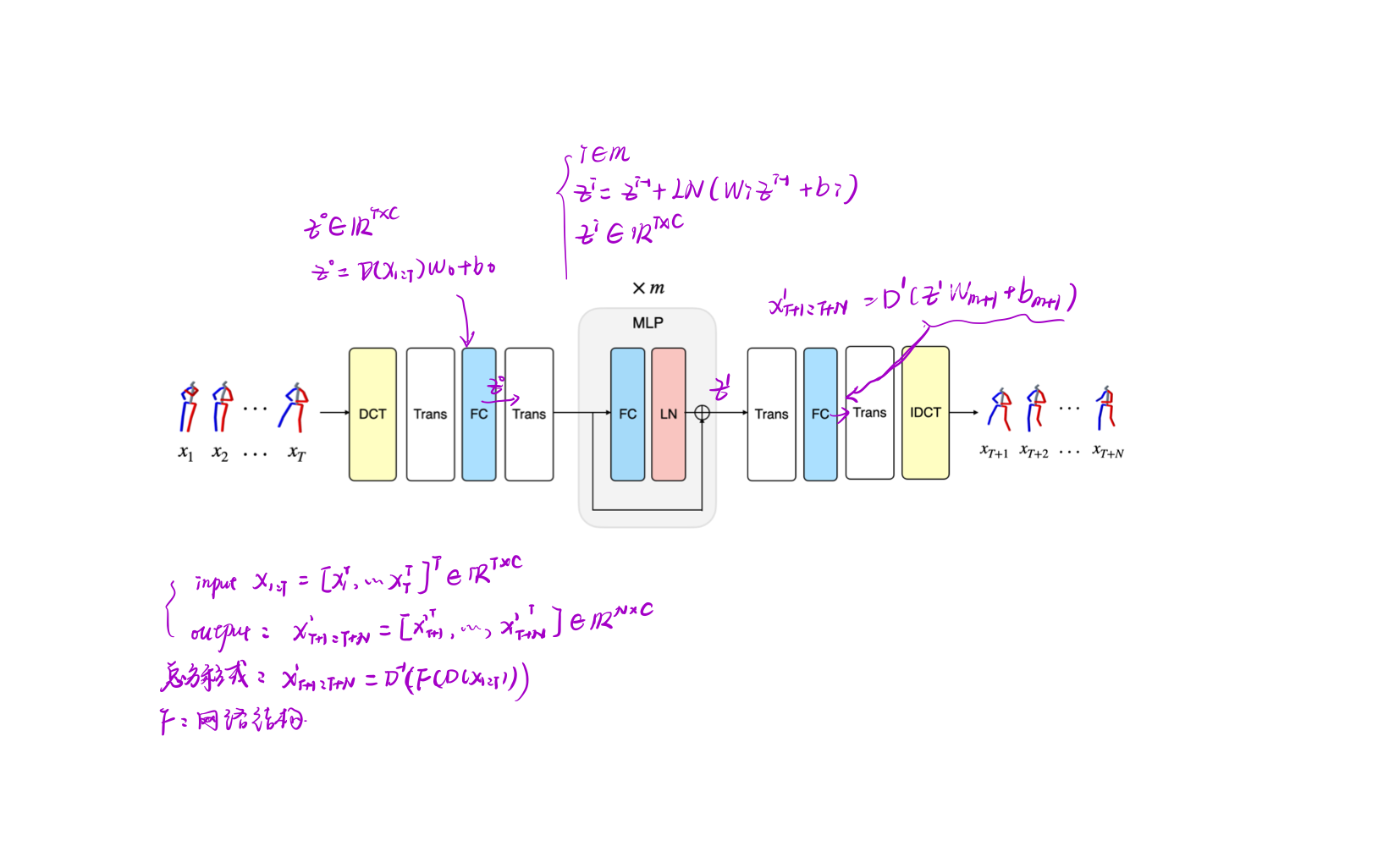
图 3-3 数学解释
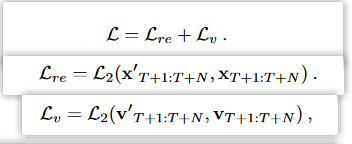
图 3-4 损失函数
损失函数由两部分组成,一部分是预测序列与真实序列的误差,一部分是在t时刻的速度误差。
优化策略: Adam optimizer
Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. In arXiv Preprint, 2014.
4. Experiments
4.1 Dataset and evaluation metric
数据集
Human3.6M dataset
Catalin Ionescu, Dragos Papava, Vlad Olaru, and Cristian Sminchisescu. Human3. 6m: Large Scale Datasets and Predictive Methods for 3D Human Sensing in Natural Environments. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013.
AMASS dataset
Naureen Mahmood, Nima Ghorbani, Nikolaus F. Troje, Gerard Pons-Moll, and Michael J. Black. AMASS: Archive of Motion Capture as Surface Shapes. In International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019.
3DPW dataset
Timo Von Marcard, Roberto Henschel, Michael J. Black, Bodo Rosenhahn, and Gerard Pons-Moll. Recovering Accurate 3D Human Pose in the Wild Using IMUs and a Moving Camera. In European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018.
4.2 结果
Human3.6m
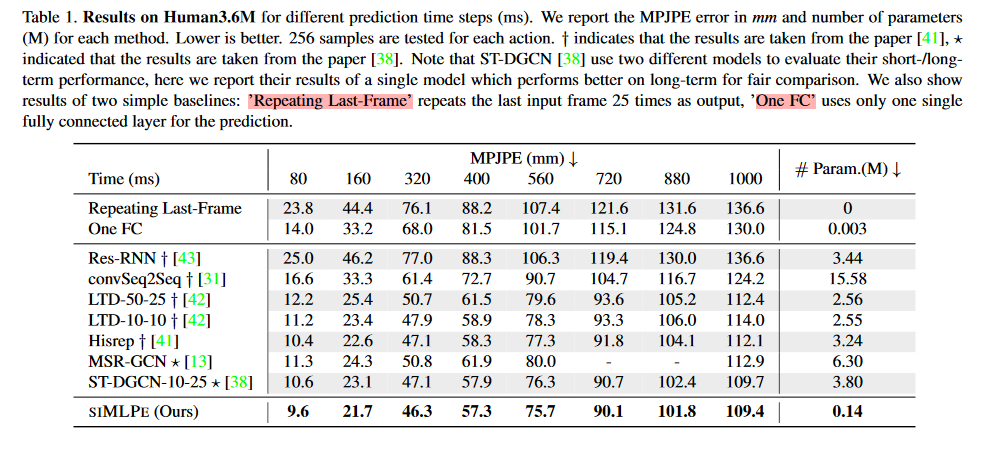
图 4-1 Human3.6m结果
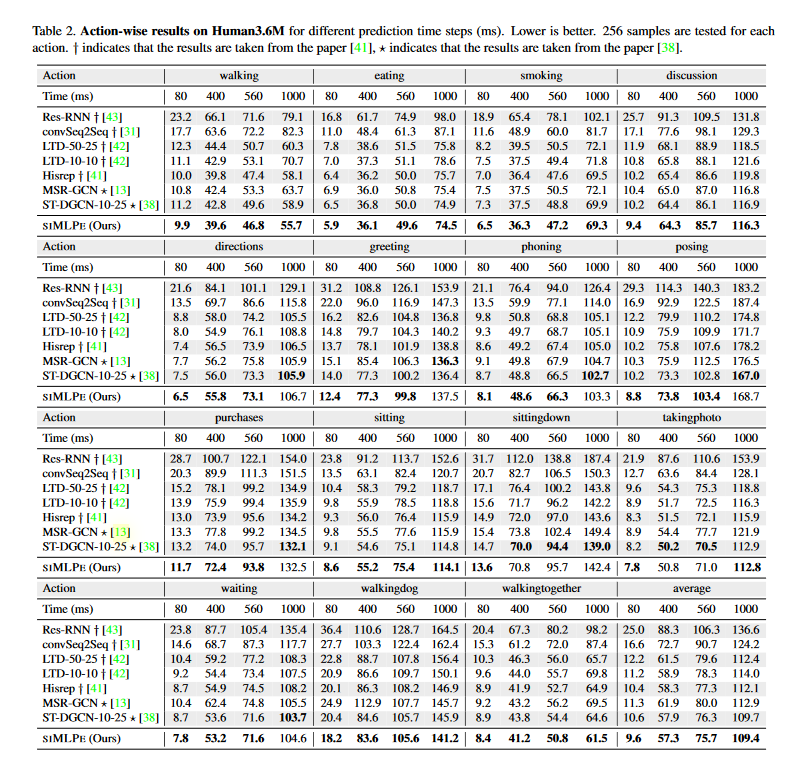
图 4-2 各种姿势结果
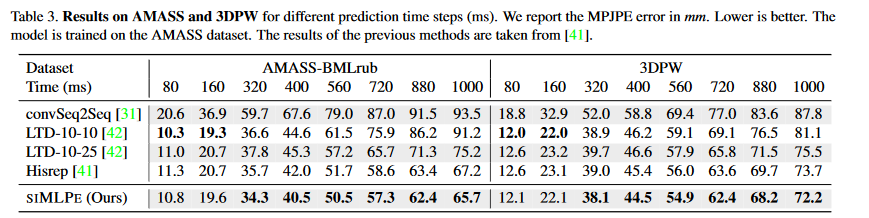
图 4-3
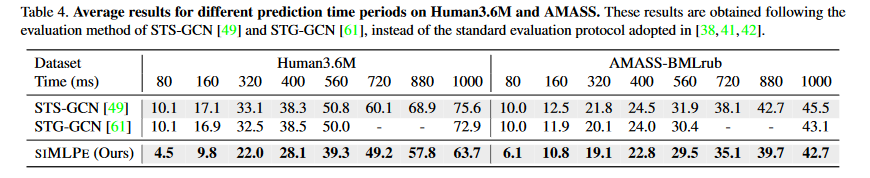
图 4-4 平均误差
4.3 Ablation study
- Number of MLP blocks
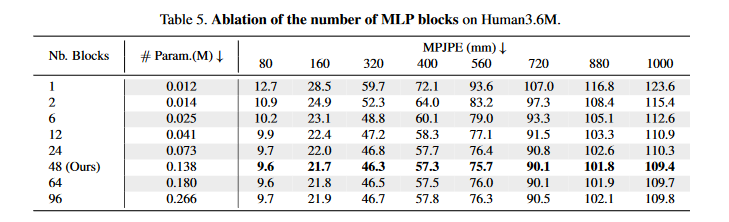
图 4-5 不同的层数比较
48层的效果最好
- Network architecture
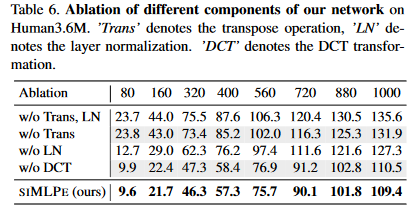
图 4-6 各层结构的重要性
transpose operation和Layer normalization 十分重要
- Data augmentation
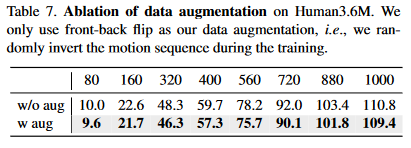
图 4-7 数据增强结果
仅仅使用了front-back flip的数据增强方法,发现实验性能显著提高。
- Loss:
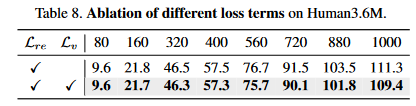
图 4-8 速度Loss的重要性
结果发现,在损失函数中加入速度损失函数可以在保证短序列预测的性能的同时,提高长序列预测的能力。
- Learning residual displacement: 比较在使用不同结构残差网络的性能
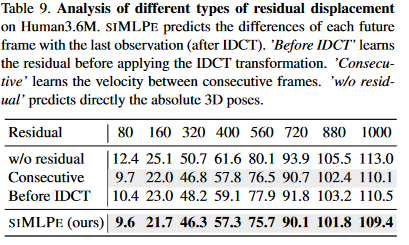
图 4-9 残差结构
通过比较不同残差位置,发现本paper的方法的性能最好。
5. 总结
该网络结构仅仅使用了简单的架构,就可以达到很好的效果,值得思考,影响人体动作预测的因素是什么,如何训练。
标签:based,Baseline,Simple,Back,Motion,MLP,paper,Human,DCT From: https://www.cnblogs.com/guixu/p/16739489.html