129B. Students and Shoelaces
题意:一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的无向图,每一轮删去所有度数为 \(1\) 的点,问删几轮停止。
暴力模拟每一轮即可,每次删点更新邻居度数。
{% note success code %}
By exod40
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n , m;
int cnt[128];
int a[128][128];
int main() {
int ans = 0;
int q , w;
scanf ( "%d%d" , &n , &m );
while ( m -- ) {
scanf ( "%d%d" , &q , &w );
a[q][w] = a[w][q] = 1;
++ cnt[q]; ++ cnt[w];
}
while ( 1 ) {
int i;
vector < int > c;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if ( cnt[i] == 1 ) {
c.push_back ( i );
}
}
if ( !(int)c.size() ) break;
++ ans;
for (i = 0; i < (int)c.size(); i++) {
cnt[ c[i] ] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if ( a[ c[i] ][j] == 1 ) {
-- cnt[j];
a[ c[i] ][j] = a[j][ c[i] ] = 0;
}
}
}
}
printf ( "%d\n" , ans );
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
902B. Coloring a Tree
题意:一棵有根树,根结点为 \(1\),初始每个节点的颜色为 \(0\),每次操作可以将一个子树全部涂上一种颜色,问达到目标颜色状态的最小操作数。
做法 1
显然要从上往下涂色,dfs 时参数里传入子树目前的颜色,判断要不要更改。
{% note success code %}
By MForest
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#define pb emplace_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
#define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define in(x); { for (auto &qwertyuiop : x) cin >> qwertyuiop; }
#define out(x); { for (auto qwertyuiop : x) cout << qwertyuiop << ' '; cout << endl; }
//#define int long long
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef tree <int, null_type, less <int>, rb_tree_tag, tree_order_statistics_node_update> ordered_set;
vector <int> g[20000];
int c[20000];
int dfs(int v, int p, int uc) {
int ans = 0;
if (c[v] != uc) {
uc = c[v];
ans++;
}
for (int i : g[v]) {
if (i != p) {
ans += dfs(i, v, uc);
}
}
return ans;
}
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int x; cin >> x;
g[x].pb(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> c[i];
}
cout << dfs(1, 0, 0);
}
signed main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
solve();
}
{% endnote %}
做法 2
可以直接判断一个节点和其父亲的目标颜色是否相同,如果不同则一定需要一次操作。
{% note success code %}
By bhargav_0085
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,a[10010],fa[10100];
int main()
{
int x,s=0;
cin>>n;
for (int i=2;i<=n;++i) cin>>x,fa[i]=x;
for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) cin>>a[i],a[i]!=a[fa[i]]?++s:0;
cout<<s;
}
{% endnote %}
893C. Rumor
题意:有一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的无向图,第 \(i\) 个点有点权 \(a_i\)。每次可以花费 \(a_i\) 的代价来将 \(i\) 所在的连通块染色,求将整个图染色的最小代价。
显然对于每个连通块只需要 dfs 找到权值最小的点染色即可。
{% note success code %}
By Golovanov399
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int nxt() {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
return x;
}
int main() {
int n = nxt(), m = nxt();
vector<int> c(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
c[i] = nxt();
}
vector<vector<int>> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int u = nxt() - 1, v = nxt() - 1;
a[u].push_back(v);
a[v].push_back(u);
}
int mn;
long long ans = 0;
vector<char> used(n);
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int v) {
if (used[v]) {
return;
}
used[v] = 1;
mn = min(mn, c[v]);
for (int x : a[v]) {
dfs(x);
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (!used[i]) {
mn = 1e9 + 10;
dfs(i);
ans += mn;
}
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
1661B. Getting Zero
题意:每次操作可以将一个数 \(\times 2\% 32768\) 或 \((+1)\%32768\),不能出现非正数,问把 \(n\) 变成 \(0\) 的最小操作次数。
从 \(32768\) 开始 BFS 即可。
{% note success code %}
By SSRS_
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<int> d(32768, -1);
d[0] = 0;
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(0);
while (!Q.empty()){
int x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
int p1 = (x + 32768 - 1) % 32768;
if (d[p1] == -1){
d[p1] = d[x] + 1;
Q.push(p1);
}
if (x % 2 == 0){
int p2 = x / 2;
if (d[p2] == -1){
d[p2] = d[x] + 1;
Q.push(p2);
}
p2 += 32768 / 2;
if (d[p2] == -1){
d[p2] = d[x] + 1;
Q.push(p2);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << d[a[i]];
if (i < n - 1){
cout << ' ';
}
}
cout << endl;
}
{% endnote %}
862B. Mahmoud and Ehab and the bipartiteness
题意:给你一棵树(显然是二分图),问最多能添加多少条边使得仍然保持二分图性质。
直接二分图染色,奇数层在一边,偶数层在另一边。得到两边的点数,相乘即为最多有多少条边,减去 \(n-1\) 即可。
{% note success code %}
By Shik
const int N=1e5+10;
int n;
VI e[N];
LL c[2];
void dfs( int p, int f, int d ) {
c[d]++;
for ( int i:e[p] ) if ( i!=f ) dfs(i,p,d^1);
}
int main() {
R(n);
REP(i,n-1) {
int a,b;
R(a,b);
e[a].PB(b);
e[b].PB(a);
}
dfs(1,0,0);
LL ans=c[0]*c[1]-(n-1);
W(ans);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
755C. PolandBall and Forest
题意:一个森林,给你每个点能到达的最远节点(如有相同则选编号最小的),判断森林有几棵树。
做法 1
显然一个点与到达的最远节点在同一棵树上,可以用并查集维护,因为一棵树的直径两端自然互为最远节点,而树上其他点的最远节点一定是直径的一端,所以在这颗树上当且仅当在同一并查集内。
{% note success code %}
By Izanagi
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const long long mod=1000000007;
const long long inf=mod*mod;
int b[11000];
int UF[11000];
int FIND(int a){
if(UF[a]<0)return a;
return UF[a]=FIND(UF[a]);
}
void UNION(int a,int b){
a=FIND(a);b=FIND(b);if(a==b)return;UF[a]+=UF[b];UF[b]=a;
}
int main(){
int a;scanf("%d",&a);
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
scanf("%d",b+i);b[i]--;
}
for(int i=0;i<a;i++)UF[i]=-1;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++){
UNION(b[i],i);
}
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<a;i++)if(UF[i]<0)ret++;
printf("%d\n",ret);
}
{% endnote %}
做法 2
可以直接开 \(set\) 记录那些点被当作了最远节点。显然每棵树要么只有一个点、要么恰好有两个点被当作最远节点。对于第一种情况,该点的最远节点就是自己,否则一定为第二种情况。
{% note success code %}
By tourist
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
set <int> s;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int foo;
scanf("%d", &foo);
if (foo == i) {
ans++;
} else {
s.insert(foo);
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans + (int) s.size() / 2);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
1676G. White-Black Balanced Subtrees
题意:有根树上每个节点非黑即白,问有多少棵子树满足黑节点数量等于白节点数量。
DFS 即可,返回子树内黑白节点数量,递归往上合并。
{% note success code %}
By Joshc
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define mp make_pair
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define f first
#define s second
const int MOD = 1000000007;
vector<int> edges[4005];
char c[4005];
int ans = 0;
int dfs(int v) {
int cur = (c[v] == 'B' ? 1 : -1);
for (int i : edges[v]) cur += dfs(i);
ans += cur == 0;
return cur;
}
void solve() {
int n, x;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) edges[i].clear();
for (int i=2; i<=n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
edges[x].push_back(i);
}
for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) scanf(" %c", &c[i]);
ans = 0;
dfs(1);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
int main() {
int tests = 1;
scanf("%d", &tests);
while (tests--) solve();
}
{% endnote %}
520B. Two Buttons
题意:每次操作可以将一个数 \(\times 2\) 或 \(-1\),不能出现非正数,问将 \(n\) 变成 \(m\) 的最小操作次数。
从 \(m\) 开始 BFS 即可。
{% note success code %}
By ZSH_ZSH
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i,a,b) for (register int i=(a);i<=(b);i++)
#define drep(i,a,b) for (register int i=(a);i>=(b);i--)
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
inline ll read()
{
ll sum=0,f=0;char c=getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) f|=(c=='-'),c=getchar();
while (isdigit(c)) sum=(sum<<1)+(sum<<3)+(c^48),c=getchar();
return f?-sum:sum;
}
const int N=1000010;
int s,t,dis[N];
queue<int>q;
signed main()
{
s=read(),t=read(); dis[s]=1; q.push(s);
while (q.size())
{
int u=q.front(); q.pop();
int a=u<<1; if (a<=N-10&&a>0&&!dis[a]) dis[a]=dis[u]+1,q.push(a);
int b=u-1; if (b<=N-10&&b>0&&!dis[b]) dis[b]=dis[u]+1,q.push(b);
}
cout<<dis[t]-1<<endl;
}
{% endnote %}
1167C. News Distribution
题意:有 \(n\) 个点和 \(m\) 个点集,每个点集中的点互相连边,对于每个点输出所在连通块大小。
每个点集建立一个虚点(或使用集合中第一个节点当根),并查集维护即可。
{% note success code %}
By bhargav_0085
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 500001
int n,m,fa[N],k,x,y,s[N];
int Find(int x)
{
return fa[x]==x?x:fa[x]=Find(fa[x]);
}
void Union(int x,int y)
{
fa[Find(x)]=Find(y);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d",&k);
if(!k)
continue;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(int i=2;i<=k;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&y);
Union(x,y);
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
s[Find(i)]++;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<s[fa[i]]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
1263D. Secret Passwords
题意:有 \(n\) 个小写字母字符串,若有字母同时在两个字符串中出现,那么这两个字符串被认为是等价的。等价关系可以在这 \(n\) 个字符串中传递。问有多少个本质不同的字符串。
所有包含 \(\texttt{a}\) 的字符串都等价、所有包含 \(\texttt{b}\) 的字符串都等价,以此类推,由于可以传递,并查集维护即可。
{% note success code %}
By wucstdio
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int n,pa[500005],last[26];
char s[105];
int find(int x)
{
return x==pa[x]?x:pa[x]=find(pa[x]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)pa[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",s+1);
int m=(int)strlen(s+1);
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(last[s[j]-'a'])
{
int u=find(i);
int v=find(last[s[j]-'a']);
pa[u]=v;
}
last[s[j]-'a']=i;
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(find(i)==i)ans++;
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
164A. Variable, or There and Back Again
题意:一个有向图由 0、1、2 三种点组成,对于每个点判断是否存在一条经过该点的路径(不一定是简单路径),满足起点为 1 型点、终点为 2 型点且中间没有 1 型点(可以有 2 型点)。
做法 1(正解)
转换一下题目要求:对于每个点判断是否存在一个 1 型点能到达此点且能“在不经过 1 型点的情况下”到达一个 2 型点。
对于前者,可以直接从每个 1 型点 DFS,将能到达的点打上标记;对于后者,再转换一下限制:存在一个 2 型点,能在不经过 1 型点的情况下到达该点。于是对于后者,在反向图上从每个 2 型点开始 DFS 打标记,遇到 1 型点时直接 return 即可。
{% note success code %}
By dzhulgakov
#define N 111000
int n,m,f[N];
bool mark[N],bmark[N];
VI adj[N],badj[N];
void dfs1(int v)
{
if (mark[v]) return;
mark[v] = true;
REP(i,SZ(adj[v])) dfs1(adj[v][i]);
}
void dfs2(int v)
{
if (bmark[v]) return;
bmark[v] = true;
if (f[v] == 1) return;
REP(i,SZ(badj[v])) dfs2(badj[v][i]);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
REP(i,n)
scanf("%d",f+i);
REP(i,m)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
--x;--y;
adj[x].pb(y);
badj[y].pb(x);
}
CLEAR(mark);
CLEAR(bmark);
REP(i,n) if (!mark[i] && f[i]==1) dfs1(i);
REP(i,n) if (!bmark[i] && f[i]==2) dfs2(i);
REP(i,n)
printf(" %d"+(i==0),mark[i]&&bmark[i] ? 1 : 0);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
做法 2(错解)
直接从每个 1 型点 DFS,碰到新的 1 型点时直接 return,如果有 2 型点则回溯的时候打上标记。
{% note danger code %}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int c[100010];
vector<int> a[100010];
bool vis[100010],ans[100010];
int root;
bool dfs(int now) {
if(now!=root&&c[now]==1) return 0;
if(vis[now]) return ans[now];
vis[now]=1;
if(c[now]==2) ans[now]=1;
for(int v:a[now])
ans[now]|=dfs(v);
return ans[now];
}
signed main() {
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>c[i];
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
a[u].push_back(v);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(c[i]==1)
root=i,dfs(i);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<ans[i]<<endl;
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
这样的做法错在哪里呢?
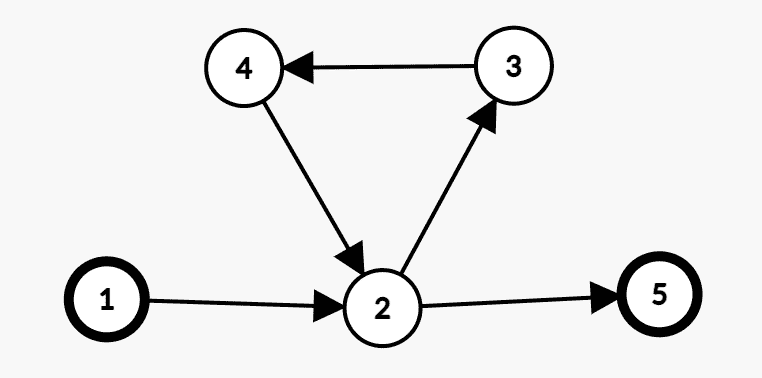
在上图的情况中,1 为 1 型点,5 为 2 型点,则显然的一条路径为 \(1\to 2\to 3\to 4\to 5\)。然而在 DFS 时,我们先搜到 2,打上了 \(vis\) 标记,走完 3、4 再次到 2 时,由于已经有了 \(vis\) 标记,程序认为它已经搜完了,于是直接返回了 0,认为 2 没法到达 2 型点。但实际上并不是没法到达,而是还没搜到。当我们回溯到 2 时,再向 5 搜,虽然可以找到 \(1\to 2\to 5\) 这条路径,但 3 和 4 的答案就定在了“无法到达”上。做法 1 就完全不会遇到这种问题。
698B. Fix a Tree
题意:一棵树可以用一个序列 \(p\) 表示。具体地,任选一个根 \(x\),当 \(i\ne x\) 时 \(p_i\) 为 \(i\) 节点的父亲,当 \(i=x\) 时 \(p_i=i\)。一棵树转换成序列的方式并不唯一。定义一个序列是合法的,当且仅当存在一棵树可以表示成该序列。给定初始序列 \(a\),问至少修改多少个元素使得该序列合法,并输出修改后的序列。
注意到,初始的 \(a\) 序列如果按照 \(i\to a_i\) 连边,会形成一个基环树森林。对于每个基环树,必然要选择环上一个点断掉一条环上的边,最后连接起来。如果存在一棵基环树的环为一个点的自环,则该点可以为树的根,无需修改。找环的操作可以用 DFS 完成,对于自环特判一下即可。
{% note success code %}
By MiracleFaFa
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <cassert>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=n-1;i>=a;i--)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define all(x) (x).begin(),(x).end()
#define fi first
#define se second
#define SZ(x) ((int)(x).size())
typedef vector<int> VI;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const ll mod=1000000007;
ll powmod(ll a,ll b) {ll res=1;a%=mod; assert(b>=0); for(;b;b>>=1){if(b&1)res=res*a%mod;a=a*a%mod;}return res;}
// head
const int N=201000;
int n,p[N],vis[N],rt,cnt,T;
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
rep(i,1,n+1) {
scanf("%d",p+i);
if (p[i]==i) rt=i;
}
rep(i,1,n+1) if (!vis[i]) {
T++;
int x=i;
while (!vis[x]) {
vis[x]=T;
x=p[x];
}
if (vis[x]==T) {
if (!rt) {
rt=x; p[x]=x;
cnt++;
}
if (x!=rt) {
p[x]=rt;
cnt++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",cnt);
rep(i,1,n+1) printf("%d ",p[i]);
}
{% endnote %}
代码细节:使用循环代替了 DFS 找环的过程。
216B. Forming Teams
题意:有一个无向图(不一定连通),每个点的度数不超过 \(2\),问最少删除多少个点,才能使得该图成为二分图且两边的点数相同。
由于每个点的度数不超过 \(2\),图一定有若干个环和若干条链组成。对于长度为偶数的环和长度为偶数的链,本身满足条件,可以不用考虑。对于奇数环,必须删掉一个点转换成偶数链,此时直接 ans++。对于奇数链,本身是二分图但两侧节点数差 \(1\),所以两个奇数链的差可以抵消。如果有奇数条奇数链,ans++,否则 ans 不变。环和链的判断可以 DFS 完成。
{% note success code %}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define pb push_back
using namespace std;
vector<int>e[111];
int used[111],cnt,cnt2;
void dfs(int x){
used[x]=1;
cnt+=e[x].size();
cnt2++;
for(int i=0;i<e[x].size();i++)
if(used[e[x][i]]==0)dfs(e[x][i]);
}
int main(){
int i,j,k,n,m,stop=0;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
e[x].pb(y);
e[y].pb(x);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!used[i]){
cnt=0;
cnt2=0;
dfs(i);
if(cnt2%2==1&&cnt2*2==cnt){
stop++;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",stop+(n-stop)%2);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
代码细节:通过 \(cnt\) 和 \(cnt2\) 的记录巧妙地判断是环还是链。
1714G. Path Prefixes
题意:一棵以 \(1\) 为根的有根树,每个边 \(i\) 有两个边权 \(a_i\) 和 \(b_i\)。对于每个点 \(i\),令 \(p_1\sim p_k\) 表示从根节点到 \(i\) 的边的序列,求最长的 \(r_i\) 使得 \(\sum\limits_{j=1}^{r_i} b_{p_j}\le\sum\limits_{j=1}^k a_{p_j}\)。
DFS 是维护根到当前点的 \(a\) 边权总和以及 \(b\) 边权前缀和 \(s\),每次在 \(s\) 中查找即可。
{% note success code %}
By tourist
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#include "algo/debug.h"
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int tt;
cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<array<int, 3>>> g(n);
for (int y = 1; y < n; y++) {
int x, w0, w1;
cin >> x >> w0 >> w1;
--x;
g[x].push_back({y, w0, w1});
g[y].push_back({x, w0, w1});
}
vector<long long> seq(1, 0);
vector<int> res(n);
function<void(int, int, long long)> Dfs = [&](int v, int pr, long long s) {
if (v > 0) {
res[v] = (int) (lower_bound(seq.begin(), seq.end(), s + 1) - seq.begin()) - 1;
}
for (auto& p : g[v]) {
int u = p[0];
if (u == pr) {
continue;
}
seq.push_back(seq.back() + p[2]);
Dfs(u, v, s + p[1]);
seq.pop_back();
}
};
Dfs(0, -1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
cout << res[i] << " \n"[i == n - 1];
}
}
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
813C. The Tag Game
题意:Alice 和 Bob 在一棵树上博弈,初始时 Alice 在 \(1\) 节点(根节点),Bob 在 \(x\) 节点。二人轮流沿边走,Bob 先走,每回合可以不走。Alice 希望尽快抓到 Bob 而 Bob 相反。问最终的回合数。
显然 Alice 可以只由浅向深走而保证抓到 Bob,此时回合最少。所以 Bob 的任务为在保证不被抓到的前提下前往尽可能深的点待着不动。
做法 1
可以先跑两遍 DFS 得出每个点与 Alice 和 Bob 的距离(与 Alice 的距离即为深度)。每个与 Bob 距离比与 Alice 距离近的点都是 Bob 能够安全到达的,所以取这些点中深度最深的即可。
{% note success code %}
By Avason
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
vector <int> e[200005];
int depa[200005],depb[200005];
inline void dfsa(int u,int f)
{
for(auto v:e[u])
if(v!=f) depa[v]=depa[u]+1,dfsa(v,u);
}
inline void dfsb(int u,int f)
{
for(auto v:e[u])
if(v!=f) depb[v]=depb[u]+1,dfsb(v,u);
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,B;
cin >> n >> B;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v;
cin >> u >> v;
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfsa(1,0);
dfsb(B,0);
int mx=0,ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(depa[i]>depb[i])
{
ans=max(ans,depa[i]*2);
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
做法 2
如果 Bob 在一个点没被抓到,那么他往下走也不会被抓到,所以在不被抓到的前提下,Bob 可以先尽可能地往上走获得后续的更多选择。找到能到达的最上面的点时,再找该子树下深度最深的点即可。
{% note success code %}
By fqw
vector<VI> es;
VI d, f, fat;
int n;
void dfs(int x, int fa, int dep) {
d[x] = dep, f[x] = dep;
fat[x] = fa;
for(int y : es[x]) {
if(y != fa) {
dfs(y, x, dep + 1);
setmax(f[x], f[y]);
}
}
}
int main() {
int x;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &x);
--x;
es.resize(n);
d.resize(n);
f.resize(n);
fat.resize(n);
repn(i, n - 1) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
--a, --b;
es[a].pb(b), es[b].pb(a);
}
dfs(0, -1, 0);
int dt = d[x] / 2 + 1;
while(d[x] > dt) x = fat[x];
printf("%d\n", f[x] * 2);
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
691D. Swaps in Permutation
题意:有一个排列和 \(m\) 个操作,每个操作 \((a_i,b_i)\) 表示交换排列的第 \(a_i\) 个元素和第 \(b_i\) 个元素。你可以以任意顺序进行操作任意多次,问操作后的最大字典序。
显然交换具有传递性,即若 \(a_1,a_2\) 可以交换、\(a_2,a_3\) 可以交换,则 \(a_1,a_2,a_3\) 可以任意排列。于是将每个 \((a_i,b_i)\) 连边,每个连通块内都可以任意排列,显然从大到小排列输出即可。
{% note success code %}
int n, k, ar[N];
vector<int> vec[N];
int w[N];
int get(int x)
{
if (w[x] == x)
return x;
return w[x] = get(w[x]);
}
void merge(int a, int b)
{
a = get(a);
b = get(b);
w[a] = b;
}
int ans[N];
int main(){
//freopen("fabro.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("fabro.out","w",stdout);
//freopen("F:/in.txt", "r", stdin);
//freopen("F:/output.txt", "w", stdout);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
//cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> ar[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
w[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
merge(a, b);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int id = get(i);
vec[id].push_back(ar[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
sort(vec[i].begin(), vec[i].end());
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int id = get(i);
int val = vec[id].back();
vec[id].pop_back();
ans[i] = val;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (i > 1)
cout << " ";
cout << ans[i];
}
cout << endl;
cin.get(); cin.get();
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
1722F. L-shapes
题意:一个 \(L\) 形如下所示
*. .* ** ** ** ** *. .*给你一个 \(n\times m\) 的矩阵,问能否由若干个 \(L\) 形拼成且每个 \(L\) 形不相交、不共边、不共定点。
可以搜索得到八连通的连通块,如果块的大小不为 \(3\) 则直接输出 No,如果为 \(3\) 则判断是否为 \(L\) 形。
{% note success code %}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int n,m;
bool good(int x, int y){
if(1<=x&&x<=n&&y>=1&&m>=y)return true;
return false;
}
signed main(){
cin.tie(nullptr)->sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<char>>mp(n+1,vector<char>(m+1));
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++){
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int j = 1; j<=m; j++){
mp[i][j] = s[j-1];
}
}
vector<int>dx = {-1,0,1,0,1,1,-1,-1};
vector<int>dy = {0,1,0,-1,-1,1,1,-1};
bool f = true;
vector<vector<bool>>vis(n+1,vector<bool>(m+1));
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j<=m; j++){
queue<pair<int,int>>q;
if(vis[i][j])continue;
if(mp[i][j]!='*')continue;
q.push({i,j});
vis[i][j] = true;
set<int>sx;
set<int>sy;
sx.insert(i);
sy.insert(j);
int cnt = 1;
while(q.size()){
pair<int,int>cur = q.front(); q.pop();
int x = cur.first; int y = cur.second;
for(int d = 0; d<8; d++){
int nx = x+dx[d];
int ny = y+dy[d];
if(!good(nx,ny))continue;
if(vis[nx][ny])continue;
if(mp[nx][ny]=='.')continue;
q.push({nx,ny});
sx.insert(nx); sy.insert(ny);
vis[nx][ny] = true;
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt==3&&sx.size()==2&&sy.size()==2)continue;
f = false;
}
}
if(f)cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
return 0;
}
{% endnote %}
29C. Mail Stamps
题意:有一个 \(n\) 个点的链,给你 \(n-1\) 条边,按顺序输出链上的点。点的下标在 \([1,10^9]\) 内。
离散化,暴力循环输出即可。
{% note success code %}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define sc scanf
#define pr printf
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fin(s) freopen( s, "r", stdin );
#define fout(s) freopen( s, "w", stdout );
const int N = 100100;
using namespace std;
int n;
vector < int > v[N], ans;
map < int, int > rv, us;
void dfs(int x, int p)
{
ans.pb(x);
for(int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i++)
if(v[x][i] != p)
dfs(v[x][i], x);
}
int main()
{
//fin("input.txt");
//fout("output.txt");
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin >> n;
int g = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if(us.find(x) == us.end()){
us[x] = ++g;
rv[g] = x;
}
if(us.find(y) == us.end()){
us[y] = ++g;
rv[g] = y;
}
x = us[x];
y = us[y];
v[x].pb(y);
v[y].pb(x);
}
int root = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= g; i++)
if(v[i].size() == 1)
root = i;
dfs(root, -1);
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
cout << rv[ans[i]] << " ";
}
{% endnote %}
213A. Game
题意:有三个电脑和 \(n\) 个游戏,第 \(i\) 个游戏需要在第 \(c_i\) 个电脑上完成,游戏之间有依赖关系但保证没有环。完成每个游戏需要一小时,在电脑之间移动 \(1\to 2,2\to 3,3\to 1\) 需要一小时,\(3\to 2,2\to 1,1\to 3\) 需要两小时。初始可以选择在任意电脑前,问完成全部游戏的最少时间。
注意到在电脑之间移动时,\(+1 \mod 3\) 花费 \(1\) 而 \(-1 \mod 3\) 花费 \(2\),所以一定不会出现 \(-1 \mod 3\)(最差也可以用两次 \(+1 \mod 3\) 代替)。所以只需要每次贪心地将当前电脑能玩的全部玩完再到下一个电脑即可。需要分类讨论初始位置。
{% note success code %}
By eddy1021
int n , c[ N ] , ind[ N ];
vector< int > v[ N ];
void init(){
n = getint();
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
c[ i ] = getint() - 1;
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ){
ind[ i ] = getint();
for( int j = 0 ; j < ind[ i ] ; j ++ ){
int fr = getint();
v[ fr ].push_back( i );
}
}
}
vector<int> q[ 3 ];
int tind[ N ];
int go( int st , int nxt ){
for( int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ )
q[ i ].clear();
for( int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ){
tind[ i ] = ind[ i ];
if( ind[ i ] == 0 )
q[ c[ i ] ].push_back( i );
}
int gt = 0 , ret = 0;
while( gt < n ){
while( q[ st ].size() ){
int who = q[ st ].back();
q[ st ].pop_back();
gt ++;
ret ++;
for( auto tmp : v[ who ] ){
tind[ tmp ] --;
if( tind[ tmp ] == 0 ){
q[ c[ tmp ] ].push_back( tmp );
}
}
}
if( gt == n ) break;
ret ++;
st = ( st + nxt + 3 ) % 3;
}
return ret;
}
void solve(){
int ans = N * N;
for( int st = 0 ; st < 3 ; st ++ )
ans = min( ans , go( st , 1 ) );
printf( "%d\n" , ans );
}
int main(){
build();
//__ = getint();
while( __ -- ){
init();
solve();
}
}
{% endnote %}
408B. Garland
题意:有一些颜色的纸若干张,每张面积为 \(1\),你需要拼成一定的彩带,要求每个位置的颜色对应。你可以将纸剪开,但不能拼起来。问最多能有多大面积或回答无法拼成。
显然对于每种颜色单独考虑。一种颜色如果纸比目标多,那一定是目标的面积。如果比目标少,则可以全部用上。所以答案为二者取 \(\min\)。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[26],b[26];
signed main() {
string s,t;
cin>>s>>t;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
a[s[i]-'a']++;
for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++)
b[t[i]-'a']++;
int ans=0,flag=1;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
ans+=min(a[i],b[i]);
if(a[i]==0&&b[i]>0) flag=0;
}
if(flag) cout<<ans<<endl;
else cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
408C. Triangle
题意:一个直角三角形的两条边为 \(a,b\),问是否可以选三个整点满足条件。输出方案。
显然可以钦定直角顶点在 \((0,0)\)。
首先可以预处理出所有勾股数组 \((a,b,c)\) 使得 \(a,b,c\) 为整数,存到 \(c\) 的 vector 里。
假设 \(a,b\) 为直角边,则若 \(A\) 的坐标为 \((x,y)\),则 \(B\) 的坐标为 \((ky,-kx)\)。从 vector 里枚举判断斜率是否相同即可。
假设有直角边 \(c\),设 \(a\) 为短边,则 \(c=\sqrt{b^2-a^2}\),此时两条直角边为 \(a,c\),从 vector 里枚举 \(A\) 的坐标,判断旋转 \(90\) 度后按 \(a,c\) 比例放缩是否为整点即可。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double eps=1e-7;
signed main() {
map<int,vector<pair<int,int> > > s;
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++) {
double t=sqrt(i*i+j*j);
if(abs(t-floor(t+eps))<=eps)
s[floor(t+eps)].push_back({i,j});
}
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
if(a>b) swap(a,b);
auto va=s[a],vb=s[b];
for(auto x:s[a]) for(auto y:s[b]) {
if(x.first*y.second==y.first*x.second) {
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
cout<<0<<" "<<0<<endl;
cout<<x.first<<" "<<x.second<<endl;
cout<<y.second<<" "<<-y.first<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
if(a==b) {
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
double c=sqrt(a*a+b*b);
for(auto x:s[a]) {
pair<double,double> y=x;
y.first*=1.0*c/a,y.second*=1.0*c/a;
if(abs(y.first-floor(y.first+eps))<=eps)
if(abs(y.second-floor(y.second+eps))<=eps) {
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
cout<<0<<" "<<0<<endl;
cout<<x.first<<" "<<x.second<<endl;
cout<<floor(y.second+eps)<<" "<<-floor(y.first+eps)<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
399B. Red and Blue Balls
题意:有一个栈,栈的大小为 \(n\),初始时有 \(n\) 个球,每个球是红蓝两种颜色之一。每次操作将栈顶的所有红球弹出栈,将剩下的栈顶的蓝球变为红球,然后用蓝球进栈补齐空位。问全部变成红球的步数。
思考可以发现,将红球看作 \(1\),蓝球看作 \(0\),则操作为二进制的 \(+1\)。所以答案为二进制 \(111\cdots1\) 减去初始值。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main() {
int n;
string s;
cin>>n>>s;
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
ans+=(s[i]=='R')*(1ll<<i);
cout<<(1ll<<n)-ans-1<<endl;
return 0;
}
399C. Cards
题意:你需要构造一个 \(01\) 串,其中 \(0,1\) 的个数分别为 \(a,b\)。串的权值定义为,考虑每一个极长的连续子段,如果这一段全为 \(1\),则权值加上长度的平方;如果为 \(0\),则权值减去长度的平方。最大化权值。
很显然是 \(0,1\) 互相分隔开。显然要让 \(0\) 尽可能分散,而 \(1\) 尽可能集中,所以两端一定是 \(0\)。考虑枚举用了 \(i\) 段 \(1\) 来分隔,则 \(0\) 的段数为 \(i+1\)。在段数确定的情况下,为了最大化权值,\(1\) 一定是 \(i-1\) 个长度为 \(1\) 的孤点和一个长度为 \(a-i+1\) 的集中段,而 \(0\) 一定是尽可能均匀分布。对所有段数情况取 \(\max\) 即可。注意特判 \(a,b\) 为 \(0\) 的情况。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main() {
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
if(a==0) {
cout<<-(b*b)<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=b;i++) cout<<'x';
cout<<endl;
}
else if(b==0) {
cout<<a*a<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=a;i++) cout<<'o';
cout<<endl;
}
else {
int ans=-1e18,maxi;
for(int i=1;i<=min(a,b);i++) {
int tmp=i-1+(a-i+1)*(a-i+1);
tmp-=(b/(i+1))*(b/(i+1))*(i+1)+(2*(b/(i+1))+1)*(b%(i+1));
if(tmp>ans) ans=tmp,maxi=i;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=maxi;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=b/(maxi+1)+(i<=b%(maxi+1));j++)
cout<<'x';
if(i==1) {
for(int j=1;j<=a-maxi+1;j++)
cout<<'o';
}
else cout<<'o';
}
for(int j=1;j<=b/(maxi+1);j++)
cout<<'x';
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
397B. On Corruption and Numbers
题意:多次询问,每次给你 \(n,l,r\),判断 \(n\) 是否能由若干个 \(l,r\) 之间的数相加组成。
考虑如果全用 \(l\),取到小于等于 \(n\) 的最大个数,假设为 \(k\) 个 \(l\),则只需要判断用 \(k\) 个 \(r\) 是否能大于等于 \(n\) 即可。如果用 \(k\) 个 \(r\) 大于等于 \(n\),根据介值定理,一定可以取到 \(n\)(逐步增加即可);如果用了 \(k\) 个 \(r\) 还不够,那么由于 \(k\) 是用 \(l\) 小于等于 \(n\) 的最大值,则 \(k+1\) 个 \(l\) 一定超过 \(n\),也不可行。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--) {
int n,l,r;
cin>>n>>l>>r;
if(n<=n/l*r) cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
397C. On Number of Decompositions into Multipliers
题意:给你一个数 \(m\),用 \(n\) 个数乘积的形式给出。问构造一个长度为 \(n\) 的序列,乘积为 \(m\) 的方案数 \(\pmod{10^9+7}\)。
显然构造的这 \(n\) 个数需要不重不漏不多余地覆盖 \(m\) 的每个质因数,所以考虑逆向思考:对于质因数分解的每项 \(p^r\),都相当于把这 \(r\) 个 \(p\) 分布到序列的 \(n\) 个位上,而每项独立,可以直接乘起来。将 \(r\) 个没有区分的数分布到 \(n\) 个位上,可以有空(空即为乘 \(p^0\)),方案数可由插板法求出,为 \(\binom{r+n-1}{n-1}\)。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int MAXV=20000;
int inv[MAXV+10],jc[MAXV+10],invjc[MAXV+10];
int ksm(int a,int b,int res=1) {
for(;b;a=a*a%mod,b>>=1)
if(b&1) res=res*a%mod;
return res;
}
void init() {
jc[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=MAXV;i++)
jc[i]=jc[i-1]*i%mod;
invjc[MAXV]=ksm(jc[MAXV],mod-2);
for(int i=MAXV;i>0;i--)
invjc[i-1]=invjc[i]*i%mod;
for(int i=1;i<=MAXV;i++)
inv[i]=jc[i-1]*invjc[i]%mod;
}
int C(int x,int y) {
return jc[x]*invjc[y]%mod*invjc[x-y]%mod;
}
signed main() {
init();
int n;
cin>>n;
map<int,int> mp;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
int x;
cin>>x;
for(int j=2;j*j<=x;j++)
while(x%j==0) x/=j,mp[j]++;
if(x>1) mp[x]++;
}
int ans=1;
for(auto tmp:mp)
(ans*=C(tmp.second+n-1,n-1))%=mod;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
443B. Kolya and Tandem Repeat
题意:给你一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串,可以在结尾任意插入 \(k\) 个字符,要选出尽可能长的偶数长度子串,使得前后两半相同。
由于后面可以任意插入,所以 \([n+1,n+k]\) 这段区间可以认为完全合法。可以枚举长度 \(len\),然后将 \(s_i=s_{i+len}\) 的位置打上合法标记,当出现连续 \(len\) 个合法标记时就合法。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool ok[410];
signed main() {
string s;
int k,ans=0;
cin>>s>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=(s.size()+k)/2;i++) {
memset(ok,0,sizeof(ok));
for(int j=0;j+i<s.size()+k;j++)
if(j+i>=s.size()||s[j]==s[j+i]) ok[j]=1;
int lst=0,now=0;
for(int j=0;j<s.size()+k;j++)
if(ok[j]==0) now=max(now,j-lst),lst=j+1;
if(now>=i) ans=max(ans,i*2);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
443C. Borya and Hanabi
题意:你有若干张卡片背面向上,每张由花色和点数描述(花色和点数各五种)。你知道拥有的卡片集合,但不知道对应哪张。你可以获取若干次提示,每次提示你可以指定一个颜色,告诉你该花色的卡片有哪些;或指定一个点数,告诉你该点数的卡片有哪些。问最小提示次数。
显然相同的卡片没有影响,先去重。枚举需要获取的提示的所有可能 \(2^{10}\) 种,只需判断是否可以确定卡片。
显然颜色和点数都确定的卡片是确定的。之后,对于一张卡片,如果它的点数确定了,在这个点数中只剩一种颜色没确定,那么它的颜色也就被确定了,反之亦然。最后,只剩下一张卡片,就算点数和颜色都没确定也是可以确定的。模拟缩小范围即可。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,a[6][6],k1[6],k2[6],ans=25,done[6][6];
char tt[]={' ','R','G','B','Y','W'};
int get(char c) {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
if(tt[i]==c) return i;
}
int main() {
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
string s;
cin>>s;
a[get(s[0])][s[1]-'0']=1;
}
for(int i=0;i<(1<<5);i++) {
for(int j=0;j<(1<<5);j++) {
memset(k1,0,sizeof(k1));
memset(k2,0,sizeof(k2));
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
if(i&(1<<(k-1))) k1[k]=1;
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
if(j&(1<<(k-1))) k2[k]=1;
memset(done,0,sizeof(done));
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
for(int l=1;l<=5;l++)
if(a[k][l]&&k1[k]&&k2[l]) done[k][l]=1;
while(1) {
bool flag=0;
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++){
if(!k1[k]) continue;
int tot=0,p=0;
for(int l=1;l<=5;l++)
if(a[k][l]&&!done[k][l]) tot++,p=l;
if(tot==1) done[k][p]=1,flag=1;
}
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++){
if(!k2[k]) continue;
int tot=0,p=0;
for(int l=1;l<=5;l++)
if(a[l][k]&&!done[l][k]) tot++,p=l;
if(tot==1) done[p][k]=1,flag=1;
}
if(!flag) break;
}
int cnt=0;
for(int k=1;k<=5;k++)
for(int l=1;l<=5;l++)
if(a[k][l]&&!done[k][l]) cnt++;
if(cnt<=1) ans=min(ans,__builtin_popcount(i)+__builtin_popcount(j));
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
465B. Inbox (100500)
题意:有一个邮件列表,有未读邮件和已读邮件。初始时你在列表界面。每次操作可以从列表界面跳到任意一封邮件界面、从邮件界面跳回列表界面、移到上一封/下一封邮件。问全部读完的最小操作数。
稍微思考可得,连续的一定直接走,不连续的一定跳。答案为邮件数+连续段数-1。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool a[1010];
signed main() {
int n,cnt=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
a[++n]=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
if(a[i]==1) {
cnt++;
if(a[i+1]==0) cnt++;
}
cout<<max(0,cnt-1)<<endl;
return 0;
}
465C. No to Palindromes!
给你一个字符串,只能用前 \(m\) 个字母。找出字典序排序的,下一个“不包含回文子串”的字符串。
思考可以发现,包含回文子串和包含长度为 \(2\) 或 \(3\) 的回文子串是等价的,于是大大简化。
考虑第一个出现的回文子串位置 \(i-2,i-1,i\) 或 \(i-1,i\),它后面无论怎么增加都不可行,必须要更改这个回文子串本身。
考虑将第 \(i\) 位改成什么字符能和前面两位都不同(且必须比原先字典序大,否则不符合要求)。改完之后,对于后面每一位也一次这样改(但没有比原先大的要求,因为第一位已经比原先大了),每一位让字典序尽可能小。如果出现一位无解,则第 \(i\) 位改这个字符不可行,考虑下一个字符。如果第 \(i\) 位改成什么都不行,则只能尝试改第 \(i-1\) 位。以此类推。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
void nxt(string &s) {
s[s.size()-1]++;
for(int i=s.size()-1;i>1;i--)
if(s[i]-'a'>m-1)
s[i]='a',s[i-1]++;
else break;
if(s[1]-'a'>m-1) {
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
exit(0);
}
}
signed main() {
string s;
cin>>n>>m>>s;
if(m==1) {
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
if(m==2&&n>=3) {
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
s=" "+s;
nxt(s);
int flag=-1;
for(int i=2;i<s.size();i++)
if(s[i]==s[i-1]||s[i]==s[i-2]) {
flag=i;
break;
}
if(flag==-1) {
cout<<s.substr(1,s.size()-1)<<endl;
return 0;
}
for(int i=flag;i>=1;i--) {
string t=s;
bool okok=1;
for(int j=i;j<s.size();j++) {
bool ok=0;
for(char ch=(j==i?s[j]+1:'a');ch<='a'+m-1;ch++) {
if(ch!=s[j-1]&&(j==1||ch!=s[j-2])) {
s[j]=ch;
ok=1;
break;
}
}
if(!ok) okok=0;
}
if(okok==0) {s=t;continue;}
else {
cout<<s.substr(1,s.size()-1)<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
408D. Long Path
题意:有 \(n+1\) 个房间,第 \(i\) 个房间有一个传送门传送至 \(p_i\)(\(p_i\le i\))。你初始在房间 \(1\),要走到房间 \(n+1\)。每次操作你会先打一次标记,然后看标记的奇偶性:如果为偶则到 \(i+1\),否则传送到 \(p_i\)。求到 \(n\) 的步数。
首先会发现,当走到一个房间 \(i\) 时,前 \(i-1\) 个房间一定全为偶数,因为如果要走出房间 \(i\),\(i\) 必须为偶数,用数学归纳法可证明 \(i\) 之前的任意房间都为偶数。
于是现在便没有了后效性,可以考虑 DP。如果设 \(f[i]\) 表示 \(1\) 走到 \(i\) 的步数,会发现无法转移,因为要先送到 \(p_i\),再走到 \(i\)(为了出现偶数次),才能到 \(i+1\),而从 \(p_i\) 走到 \(i\) 难以计算。
于是考虑区间 DP。设 \(f[l][r]\) 表示从 \(l\) 走到 \(r\) 的步数,则有 \(f[l][r]=f[l][r-1]+1+f[p_{r-1}][r-1]+1\)。因为一定是从 \(l\) 经过若干步走到 \(r-1\),再跳回去一次,再走到第二次 \(r-1\),方可走到 \(r\)。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int p[1010],f[1010][1010];
signed main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>p[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
f[i][i]=0;
for(int r=1;r<=n;r++)
for(int l=1;l<r;l++)
f[l][r]=(f[l][r-1]+1+f[p[r-1]][r-1]+1)%mod;
cout<<(f[1][n]+1+f[p[n]][n]+1)%mod<<endl;
return 0;
}
然而事实上,第一个 DP 是可行的。从 \(p_i\) 走到 \(i\) 的时间可以计算:考虑假设从 \(i\) 穿越回了 \(1\),则需要重走一遍 \(f[i]\),而穿越只回到了 \(p_i\),所以从 \(1\) 到 \(p_i\) 的那一段可以省掉。又因为是否省掉对后续没有影响(只要到 \(p_i\) 前面都会变成偶数),所以可以直接减去 \(f[p_i]\)。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int mod=1e9+7;
int p[1010],f[1010];
signed main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>p[i];
f[1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
f[i+1]=((f[i]+1+f[i]-f[p[i]]+1)%mod+mod)%mod;
cout<<f[n+1]<<endl;
return 0;
}
399D. Painting The Wall
题意:有一个矩阵,初始时有些格子被涂上了漆。你需要将这个矩阵涂漆,直到每行每列都至少有一个格子有漆。每次涂漆会随机选一个格子(无论是否涂漆)并涂上漆,每次消耗一分钟(无论是否涂漆)。问期望时间。
转化一下可以发现,每次涂漆选择的行和列如果都已经有漆了,则不会有任何贡献,如果没有漆会造成贡献。而没有漆的行/列是没有区分的,有漆的行/列也没有区分。于是这启示我们可以 DP。
设 \(f[i][j]\) 表示有 \(i\) 行涂过漆,有 \(j\) 列涂过漆,要涂完的期望时间,则转移方程为:
\[\begin{aligned} f[i][j]&=\frac{ij}{n^2}f[i][j]+\frac{(n-i)j}{n^2}f[i+1][j]\\ &+\frac{i(n-j)}{n^2}f[i][j+1]+\frac{(n-i)(n-j)}{n^2}f[i+1][j+1] \end{aligned} \]通过移项处理掉自环即可。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
bool vis[2010][2010],done[2010][2010];
double f[2010][2010];
double dfs(int x,int y) {
if(done[x][y]) return f[x][y];
done[x][y]=1;
if(x==n&&y==n) return f[x][y]=0;
double t=n*n;
if(x<n) f[x][y]+=(n-x)*y/t*dfs(x+1,y);
if(y<n) f[x][y]+=x*(n-y)/t*dfs(x,y+1);
if(x<n&&y<n) f[x][y]+=(n-x)*(n-y)/t*dfs(x+1,y+1);
f[x][y]=(f[x][y]+1)/(1-x*y/t);
return f[x][y];
}
signed main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
int a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
vis[a][b]=1;
}
int ansx=0,ansy=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
bool flag=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
flag|=vis[i][j];
ansx+=flag;
}
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) {
bool flag=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
flag|=vis[i][j];
ansy+=flag;
}
printf("%.5lf\n",dfs(ansx,ansy));
return 0;
}
还有一种 DP 是 \(f[i][j]\) 表示还剩 \(i\) 行 \(j\) 列要填完的时间,本质上完全相同但实现上较为简洁,这里就贴个代码。
By ihave33cm
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
double dp[2005][2005]={0};
set<int> X,Y;
int main(){
int n,m,x,y,i,j,a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
X.insert(a);
Y.insert(b);
}
a=n-X.size();
b=n-Y.size();
for(i=0;i<=a;i++)
for(j=0;j<=b;j++){
double tmp=n*n;
if(i+j==0) continue;
if(i) tmp+=dp[i-1][j]*i*(n-j);
if(j) tmp+=dp[i][j-1]*j*(n-i);
if(i && j) tmp+=dp[i-1][j-1]*i*j;
dp[i][j]=tmp/n/n;
dp[i][j]/=(1.0-(n-i)*(n-j)*1.0/n/n);
}
printf("%.12lf\n",dp[a][b]);
}
465D. Restore Cube
题意:给你三维空间中八个整点,但 \(xyz\) 是打乱的,求一种方案组成正方体或判断无解。
显然可以枚举每个点 \(xyz\) 的排列(可以搜索),方案为 \((3!)^8\approx 10^6\),于是剩下需要在可接受的时间内进行检查。
检查时可以先找出这八个点的中点,判断是否关于中点一一对应(是否都有对角的顶点);然后判断到中点的距离是否都相同。如果满足了以上两点条件,剩下的就是判断是否是直角了。
这里可以任意选定一个点,枚举其他点,根据对角线长可以推断出边长,从而判断这个点是否与选定点相邻。处理出三个相邻点后,判断三条线段是否两两垂直,可以使用向量点积是否为 \(0\) 来判断。以上的做法在精度和效率上都非常优秀,check 的复杂度为 \(3\times 8+3*3*3\),可以通过。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
double eps=1e-7;
array<int,3> a[9];
void check() {
array<int,3> x{0,0,0};
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
x[j]+=a[i][j];
if(x[0]%4||x[1]%4||x[2]%4) return;
x[0]/=4,x[1]/=4,x[2]/=4;
set<array<int,3> > s;
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
s.insert(a[i]);
if(s.size()!=8) return;
int len=0;
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
len+=(x[j]-a[1][j]*2)*(x[j]-a[1][j]*2);
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++) {
array<int,3> tmp{0,0,0};
int tmplen=0;
for(int j=0;j<3;j++) {
tmp[j]=x[j]-a[i][j];
tmplen+=(x[j]-a[i][j]*2)*(x[j]-a[i][j]*2);
}
if(tmplen!=len) return;
if(s.find(tmp)==s.end()) return;
}
vector<int> v;
for(int i=2;i<=8;i++) {
double tmp=0;
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
tmp+=pow(a[1][j]-a[i][j],2);
if(fabs(tmp*3-len)<=eps) v.push_back(i);
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<3;j++) {
int tmp=0;
for(int k=0;k<3;k++)
tmp+=(a[v[i]][k]-a[1][k])*(a[v[j]][k]-a[1][k]);
if(tmp!=0) return;
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cout<<a[i][j]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
exit(0);
}
void dfs(int now) {
if(now==9) return check();
array<int,3> k={1,2,3},b=a[now];
map<array<int,3>,bool> mp;
do {
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
a[now][i]=b[k[i]-1];
if(mp[a[now]]) continue;
else mp[a[now]]=1;
dfs(now+1);
} while(next_permutation(k.begin(),k.end()));
a[now]=b;
}
signed main() {
for(int i=1;i<=8;i++)
for(int j=0;j<3;j++)
cin>>a[i][j];
dfs(1);
puts("NO");
return 0;
}
还有一种更为简洁的做法:只需要枚举七个点的排列,即 \((3!)^7\approx 3\times 10^5\),剩下一个点可以计算得出,这大大减轻了 check 的效率负担。
By Xellos
int main() {
cin.sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
long long C[8][3];
for(int i =0; i < 8*3; i++) cin >> C[i/3][i%3];
long long P[6][3] ={
{0,1,2},
{0,2,1},
{1,0,2},
{1,2,0},
{2,0,1},
{2,1,0}};
long long Cs[8][3];
for(int k =0; k < 279936; k++) {
for(int i =0; i < 3; i++) Cs[0][i] =C[0][i];
int x =k;
for(int j =1; j < 8; j++) {
for(int i =0; i < 3; i++) Cs[j][i] =C[j][P[x%6][i]];
x /=6;}
vector<long long> D(7,0);
for(int j =1; j < 8; j++) for(int i =0; i < 3; i++)
D[j-1] +=(Cs[0][i]-Cs[j][i])*(Cs[0][i]-Cs[j][i]);
long long a =1000000000000000LL;
for(int i =0; i < 7; i++) a =min(a,D[i]);
int t =0,s =0,q =0;
for(int i =0; i < 7; i++) {
if(D[i] == a) t++;
if(D[i] == 2*a) s++;
if(D[i] == 3*a) q++;}
if(a == 0 || t != 3 || s != 3 || q != 1) continue;
bool ok =true;
for(int i =1; i < 8; i++) if(ok) {
s =t =q =0;
for(int j =0; j < 8; j++) if(i != j) {
long long d =0;
for(int l =0; l < 3; l++) d +=(Cs[i][l]-Cs[j][l])*(Cs[i][l]-Cs[j][l]);
if(d == a) s++;
if(d == 2*a) t++;
if(d == 3*a) q++;}
if(s != 3 || t != 3 || q != 1) ok =false;}
if(!ok) continue;
cout << "YES\n";
for(int i =0; i < 8; i++) for(int j =0; j < 3; j++)
cout << Cs[i][j] << ((j == 2)?"\n":" ");
return 0;}
cout << "NO\n";
return 0;
}
397D. On Sum of Fractions
题意:定义 \(v(n),u(n)\) 分别表示小于等于 \(n\) 的最大质数和大于 \(n\) 的最小质数,求 \(\sum\limits_{i=2}^{n}\frac{1}{v(i)u(i)}\)。
可以发现在两个相邻质数区间 \([a,b)\) 内的值均为 \(\frac{1}{ab}\),一共有 \(b-a\) 个,所以合并为 \(\frac{b-a}{ab}=\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1}{b}\),于是可以消项,得到质数 \(p\) 之前的值为 \(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{p}\)。对于 \(n\),暴力枚举判断得出 \(v,u\),\(v\) 之前的计算得出,再加上 \(\frac{n-v+1}{uv}\) 即可。由于 \(10^9\) 内相邻质数间距很小,所以复杂度不会有问题。
By lisang
inline bool IsPrime(ll n) {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; ++i) if (n % i == 0) return false;
return true;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y) {
while(x && y) {
if (x < y) y %= x;
else x %= y;
}
return x + y;
}
int main() {
ll t, n;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
cin >> n;
ll l = n, r = n + 1;
while(!IsPrime(l)) --l;
while(!IsPrime(r)) ++r;
ll u = l * r - 2 * r + 2 * n - 2 * l + 2;
ll d = 2 * l * r;
ll g = gcd(u, d);
u /= g, d /= g;
cout << u << "/" << d << endl;
}
return 0;
}
443D. Andrey and Problem
题意:有 \(n\) 个特殊的硬币,第 \(i\) 个正面向上的概率为 \(p_i\),你需要选择其中若干个硬币抛,使恰好一个正面的概率尽可能大。求最大概率。
推一下式子(假设选了 \(k\) 个,分别为 \(p_1,p_2\cdots p_k\)):
\[\begin{aligned} ans&=\sum\limits_{i=1}^k \left(p_i\cdot\prod\limits_{j\ne i} (1-p_j)\right)\\ &=\left(\sum\limits_{i=1}^k \frac{p_i}{1-p_i}\right)\cdot\prod\limits_{i=1}^k (1-p_i) \end{aligned} \]设前面的求和当前为 \(nowa\),后面的乘积为 \(nowb\),则当前的 \(ans=nowa\cdot nowb\),考虑再加入一个概率为 \(p\) 的硬币会发生什么变化:
\[\begin{aligned} ans'&=\left(nowa+\frac{p}{1-p}\right)\cdot nowb\cdot (1-p)\\ &=nowa\cdot nowb\cdot (1-p)+p\cdot nowb\\ &=nowa\cdot nowb+p\cdot nowb\cdot(1-nowa) \end{aligned} \]容易发现,新旧 \(ans\) 的大小关系只取决于 \(nowa\) 和 \(1\) 的关系:如果 \(nowa\ge 1\),则一定不会加入元素,否则一定会加入元素。而如果只考虑加入单个元素的话,显然 \(p\) 越大越优,于是可以猜测要贪心地选 \(p\) 最大的若干个元素放。
考虑使用反证法:假设最优答案不是贪心选最大的。首先这个最优答案一定有 \(nowa\ge 1\)(终止条件),我们可以将最小的元素删掉,此时 \(nowa\) 一定 \(<1\)(否则这个元素不会被加入)。此时一定可以换一个 \(p\) 更大的元素加入(因为原来不是最大的),答案变优,与假设矛盾,所以最优答案一定为贪心选最大的。
By cxm1024
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double eps=1e-7;
double a[110];
signed main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i];
if(1.0-a[i]<=eps) {
cout<<1<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,greater<double>());
double nowa=0,nowb=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(nowa<1) nowa+=a[i]/(1-a[i]),nowb*=(1-a[i]);
printf("%.10lf\n",nowa*nowb);
return 0;
}
837D. Round Subset
题意:给你 \(n\) 个数,从中选 \(k\) 个,使乘积末尾的 \(0\) 尽可能多。
末尾的 \(0\) 即为 \(2\) 的次数和 \(5\) 的次数取 \(\min\),可以预处理每个数内 \(2\) 和 \(5\) 的次数 \(a,b\),然后 DP。
设 \(f[i][j][k]\) 表示前 \(i\) 个数选 \(j\) 个,在有 \(k\) 个 \(5\) 的情况下最多能有几个 \(2\)。显然有 \(f[i][j][k]=\max(f[i-1][j][k],f[i-1][j-b_i]+a_i)\)。刷表法同理。其中第一维可以省略,优化空间。
By LHiC
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define mp make_pair
#define pb push_back
typedef long long ll;
typedef long long llong;
typedef long double ld;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
using namespace std;
template <typename T> void dprint(T begin, T end) {
for (auto i = begin; i != end; i++) {
cerr << (*i) << " ";
}
cerr << "\n";
}
const int MX = 26 * 205;
const int INF = 100000;
int n, k;
int dp[205][MX];
vector<pair<int, int> > vv;
int main() {
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ll x;
cin >> x;
int c1 = 0, c2 = 0;
while (x % 2 == 0)
++c1, x /= 2;
while (x % 5 == 0)
++c2, x /= 5;
vv.push_back(make_pair(c1, c2));
}
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j < MX; ++j)
dp[i][j] = -INF;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int x = vv[i].second;
int y = vv[i].first;
for (int j = min(k - 1, i); j >= 0; --j)
for (int l = 0; l + x < MX; ++l)
dp[j + 1][l + x] = max(dp[j + 1][l + x], dp[j][l] + y);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < MX; ++i)
ans = max(ans, min(dp[k][i], i));
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
225C. Barcode
题意:一个黑白矩阵,你需要将其修改成条形码,即:每列全部相同,且每根竖线(无论黑白)的宽度在 \([x,y]\) 之间。求最小操作次数。
可以对于每一列预处理出黑白格子的个数,然后设 \(f[i][0/1]\) 表示只考虑前 \(i\) 列,结尾为黑/白的最小次数,则转移考虑枚举最后一列的宽度,更改颜色即可。刷表法和填表法都可以。
By Archon.JK
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 1000000007;
char a[1005][1005];
int dp[2005][2],cnt[1005],sum[1005];
int main(){
int n,m,x,y;
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&n,&m,&x,&y);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%s",a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
if(a[i][j]=='#') cnt[j]++;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) sum[i+1]=sum[i]+cnt[i];
memset(dp,63,sizeof(dp));
dp[0][0]=dp[0][1]=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=x;j<=y;j++){
if(i+j>m) break;
dp[i+j][0]=min(dp[i+j][0],dp[i][1]+sum[i+j]-sum[i]);
dp[i+j][1]=min(dp[i+j][1],dp[i][0]+n*j-(sum[i+j]-sum[i]));
}
}
printf("%d\n",min(dp[m][0],dp[m][1]));
}
946D. Timetable
题意:有 \(n\) 周,每周 \(m\) 天,\(n\times m\) 天中有些天有课。对于每一周,在校时间为最后一节课的天数减去第一节课的天数加一,如果一周没课则在校 \(0\) 天。你有 \(k\) 次翘课机会,问最小在校时间。
预处理出第 \(i\) 周翘 \(j\) 次课后的最小在校时间 \(cost[i][j]\)(可以通过枚举上课的左右端点做到 \(n^2\)),然后 DP。设 \(f[i][j]\) 表示前 \(i\) 周,翘 \(j\) 次课的最小时间,枚举第 \(i\) 周翘几次课,根据 \(cost\) 数组 \(O(1)\) 转移即可。
By KrK
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Inf = 1000000000;
const int Maxn = 505;
int n, m, k;
char B[Maxn][Maxn];
int tot[Maxn];
int cost[Maxn][Maxn];
int dp[Maxn][Maxn];
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%s", B[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
tot[i] += B[i][j] == '1';
fill(cost[i], cost[i] + Maxn, Inf);
cost[i][0] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int cur = 0;
for (int j2 = j; j2 < m; j2++) {
cur += B[i][j2] == '1';
cost[i][cur] = min(cost[i][cur], j2 - j + 1);
}
}
}
fill((int*)dp, (int*)dp + Maxn * Maxn, Inf);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= k; j++) if (dp[i][j] < Inf)
for (int l = 0; l <= tot[i] && j + l <= k; l++)
dp[i + 1][j + l] = min(dp[i + 1][j + l], dp[i][j] + cost[i][tot[i] - l]);
int res = Inf;
for (int j = 0; j <= k; j++)
res = min(res, dp[n][j]);
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
1633D. Make Them Equal
题意:有 \(n\) 个数初始为 \(1\),你每次操作可以选一个 \(a_i\) 和一个 \(x\),将 \(a_i\text{+=}\lfloor\frac{a_i}{x}\rfloor\)。结束时对于每个 \(a_i=b_i\),会产生 \(c_i\) 的贡献,问 \(k\) 次操作以内的最大贡献。
显然对于不会造成贡献的位置一次操作也不会有,所以每个位置要么花一定操作造成贡献,要么不花操作不造成贡献。这显然是一个 \(01\) 背包问题,DP 解决即可。
问题只剩下求花费的过程。由于初始为均 \(1\),可以从 \(1\) 开始 BFS,每次更新出边;也可以用 DP,设 \(f[i]\) 表示走到 \(i\) 的最小花费,刷表法更新即可。朴素是 \(n^2\) 的,可以通过本题,用数论分块也可以做到 \(n\sqrt{n}\)。
最后,对于 \(01\) 背包的状态,由于 \(k\) 达到了 \(10^6\),\(O(nk)\) 是不行的。思考可以发现,任意一个数的花费上界均不会超过 \(20\) 步(一般方法如倍增+二分),而实际上只需要 \(12\) 步就能到达任意数。所以总步数不会超过 \(12n\),复杂度 \(12n^2\)。
By jiangly
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using i64 = long long;
constexpr int N = 1000;
int dp[N + 1];
void solve() {
int n, k;
std::cin >> n >> k;
std::vector<int> b(n), c(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::cin >> b[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::cin >> c[i];
}
k = std::min(k, 12 * n);
std::vector<int> f(k + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = k; j >= dp[b[i]]; j--) {
f[j] = std::max(f[j], f[j - dp[b[i]]] + c[i]);
}
}
std::cout << f[k] << "\n";
}
int main() {
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(nullptr);
std::fill(dp, dp + N + 1, 1E9);
dp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
if (i + i / j <= N) {
dp[i + i / j] = std::min(dp[i + i / j], dp[i] + 1);
}
}
}
int t;
std::cin >> t;
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
1110D. Jongmah
题意:有 \(n\) 张卡片,卡片上有权值。你每次可以打出三张权值相同的卡片,或三张权值连续的卡片。问最多能打多少次。
首先将卡片转化到值域上,转化为每次在一位减三,或在相邻三位减一,即竖着消或横着消。显然对于横着的任意位置,横着消不会超过两次,因为一旦消三次就可以转化为竖着消三次。于是状态非常少,考虑 DP。
设 \(f[i][j][k]\) 表示考虑到第 \(i\) 张卡片,以 \(i-1\) 为左端点的横消进行了 \(j\) 次,以 \(i\) 为左端点的横消进行了 \(k\) 次,能消的最多次数。这个状态是无后效性的,因为第 \(i+1\) 张卡片能如何消只取决于 \(i\) 和 \(i-1\) 为左端点的横消次数,而与前面的竖消次数无关。同样,以第 \(i+1\) 张卡片为左端点的横消也完全不会影响到 \(i\) 之前的结果。
于是显然有 \(f[i][j][k]=\max\{f[i-1][l][i]+k+(a[i]-(i+j+k))/3\}\),转移条件是 \(i+j+k\le a[i]\),即 \(i\) 位置被横消的次数必须小于等于自己的总次数。然后加上剩余位置容许的竖消次数即可。
这样的状态还有一个好处是非常容易统计答案。由于以 \(n-1\) 和 \(n\) 为左端点的横消是不可行的(\(n+1\) 位置没有元素),所以答案即为 \(f[n][0][0]\)。
By tourist
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int cc, n;
cin >> cc >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < cc; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
x--;
a[x]++;
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(3, vector<int>(3, 0));
for (int c : a) {
vector<vector<int>> new_dp(3, vector<int>(3, 0));
for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < 3; y++) {
for (int z = 0; z < 3; z++) {
if (x + y + z <= c) {
new_dp[y][z] = max(new_dp[y][z], dp[x][y] + z + (c - x - y - z) / 3);
}
}
}
}
swap(dp, new_dp);
}
cout << dp[0][0] << '\n';
return 0;
}
这个题还有一种做法为,\(f[i][j][k]\) 表示前 \(i\) 个,最后两个还剩 \(j,k\) 张。此时后两维的状态需要到 \(6\)(因为有 \({2,4,6,4,2}\) 的情况)。这两种做法都需要非常注意边界问题,即最后统计答案需要注意不能选超过值域的。以下举个例子:
错误代码:
By Um_nik
const int N = (int)1e6 + 7;
int a[N];
int dp[N][3][3];
int n, m;
int main()
{
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(n--) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
a[x + 1]++;
}
m += 3;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 2; i++)
for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < 3; y++) {
int p = a[i] - x - y;
int q = a[i + 1] - y;
int r = a[i + 2];
for (int z = 0; z < 3; z++) {
if (p < z || q < z || r < z) continue;
dp[i + 1][y][z] = max(dp[i + 1][y][z], dp[i][x][y] + z + (p - z) / 3);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < 3; y++)
ans = max(ans, dp[i][x][y]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
正确代码:
By Um_nik
const int N = (int)1e6 + 77;
int a[N];
int dp[N][3][3];
int n, m;
int main()
{
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
while(n--) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
a[x + 1]++;
}
m += 10;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 2; i++)
for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < 3; y++) {
int p = a[i] - x - y;
int q = a[i + 1] - y;
int r = a[i + 2];
for (int z = 0; z < 3; z++) {
if (p < z || q < z || r < z) continue;
dp[i + 1][y][z] = max(dp[i + 1][y][z], dp[i][x][y] + z + (p - z) / 3);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
for (int x = 0; x < 3; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < 3; y++)
ans = max(ans, dp[i][x][y]);
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
这两份代码唯一的区别就在于,一个将 \(m\) 加了 \(3\),一个加了 \(10\)。这里将 \(m\) 增加一些是处理结尾的边界情况的一个不错的方法,因为在 \(>m\) 的位置的 \(a\) 一定是 \(0\),可以在 DP 时就考虑掉。
标签:std,int,题解,CF,long,++,ans,include,杂题 From: https://www.cnblogs.com/cxm1024/p/17168418.html