B. Before an Exam
链接
这个题使用贪心的方法先将总时间按每个时间点最小的分配如果不够就打印no如果够了就从第一个时间点分配到最大值,直到sum为0,这样就是yes的情况,如果全部都分配给最大值的话最后的sum还有剩余的话,打印no
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
struct data {
int x, y;//x代表最小值,y代表最大值
int res;//res储存最后的结果
};
struct data a[50];
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int d, sum;
cin >> d >> sum;
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y;
}//读入
int flag = 1;
//1代表yes,0代表no
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
a[i].res += a[i].x;
sum = sum - a[i].x;//先给每个时间点分配最小值
}
if (sum < 0) {//如果此时sum<0,就失败了
flag = 0;
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
//检查每一次sum好不好变成0
if (sum - (a[i].y - a[i].x) >= 0) {
a[i].res = a[i].res + (a[i].y - a[i].x);
sum = sum - (a[i].y - a[i].x);
} else {
a[i].res = a[i].res + sum;
sum = 0;
break;//变成0直接退出
}
}
}
if (sum > 0) { //如果最后大于0也是不符合条件的
flag = 0;
}
//打印结果
if (flag == 1) {
yes;
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) {
cout << a[i].res << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
} else {
no;
}
return 0;
}
B. Divisors of Two Integers
链接
因为数组是两个数的全部约数那么最大的那个值一定是其中一个我们只小于将其中一个数的约数全部去除,那么剩下的那个数列里面的最大值就是另外一个约数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 150;
struct data {
int x;
bool falg;
};
bool cmp(struct data a, struct data b) {
return a.x < b.x; //先排序
}
struct data a[N];
int st[20000];//用来标志这个数有没有被使用
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].x;
}
sort(a, a + n, cmp);//先排序
int res1 = a[n - 1].x;//最大的那个一定是其中一个数
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//我们保证如果两个数重复只去掉其中一个数就是a[i].flag==true
if (a[n - 1].x % a[i].x == 0 && st[a[i].x] == false) {
st[a[i].x] = true;
a[i].falg = true;
}
}
int res2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//遍历没被去除的数然后找出最大的
if (a[i].falg == false && a[i].x > res2) {
res2 = a[i].x;
}
}
cout << res1 << ' ' << res2;//打印
return 0;
}
C1. k-LCM (easy version)
链接
我们对于奇数和偶数可以发现一个很明显的规律,具体看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n, k;
cin >> n;
cin >> k;
int a[4] = {0};
if (n % 2 == 0) {
//如果n为偶数的话
if ((n / 2) % 2 == 1) {//如果n/2为奇数的话让(n-2/2)都分配给a[0]a[1]的话最后剩下2
//这样的话(n-2/)2一定时偶数数
a[0] = (n - 2) / 2;
a[1] = (n - 2) / 2;
a[2] = 2;
//所以gcd一定小于n/2
} else {
//如果n/2为偶数的话那么直接分成三份,这三份的gcd就是a[0]即n/2;
a[0] = n / 2;
a[1] = n / 4;
a[2] = n / 4;
}
} else {
//当n为奇数时让n-1,n会变成偶数我们让a[0]和a[1]都为偶数,让a[2]为1可以证明只要时奇数这样总是正确的
n = n - 1;
a[0] = n / 2;
a[1] = n / 2;
a[2] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << a[i] << ' ';//打印结果
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
B. GCD Length
链接
这个题直接拿10来构造就几位数就可以.即1,10,100最后让其中一个数加上gcd就可以了,这样总能满足条件
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
int gcd = 1;
c--;
while (c--) {
gcd = gcd * 10;
}
//构造gcd以10为基准
int x = 1;
a--;
while (a--) {
x = x * 10;
}
//建立x为位数的整十整百的数
int y = 1;
b--;
while (b--) {
y = y * 10;
}
//建立y为位数的整十整百的数
x = x + gcd;
//让其中一个数加上gcd
cout << x << ' ' << y << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
B. Phoenix and Puzzle
链接
这个题还是比较有意思的,一共有两种方法构造这种图,如下图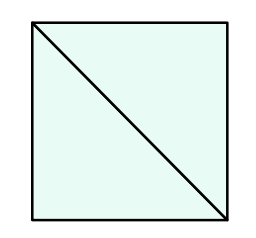 形
形
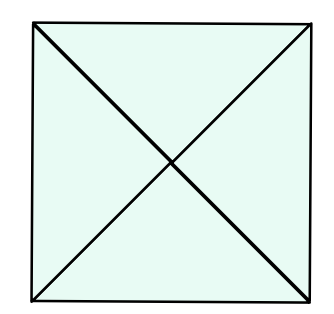
可以发现这两种正方形的边长是不一样的所以是不能拼到一块的而且组成正方形的时候只能当前正方形数量的平方(其实这里我还是不太能理解)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <cmath>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#define int long long
#define yes cout<<"YES"<<'\n'
#define no cout<<"NO"<<'\n'
using namespace std;
bool chick(int x) {
int a = sqrt(x);
if (a * a == x) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
signed main () {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
if (n % 2 == 1) {
no;
continue;
}
int flag = 0;
//首先要保证n是2或者4的倍数
if (n % 2 == 0) {
//然后检查一下n/2或者n/4是不是某个数的平方根
//如果是的话,就肯定能组成正方形
if (chick(n / 2) == true) {
flag = 1;
}
}
if (n % 4 == 0) {
if (chick(n / 4) == true) {
flag = 1;
}
}
//两种条件满足其中之一就可以
if (flag == 1) {
yes;
} else {
no;
}
}
return 0;
}
B. Maximum Product
未完待续
标签:02,cout,22,int,sum,long,define,include,刷题 From: https://www.cnblogs.com/harper886/p/17146312.html