什么是AQS
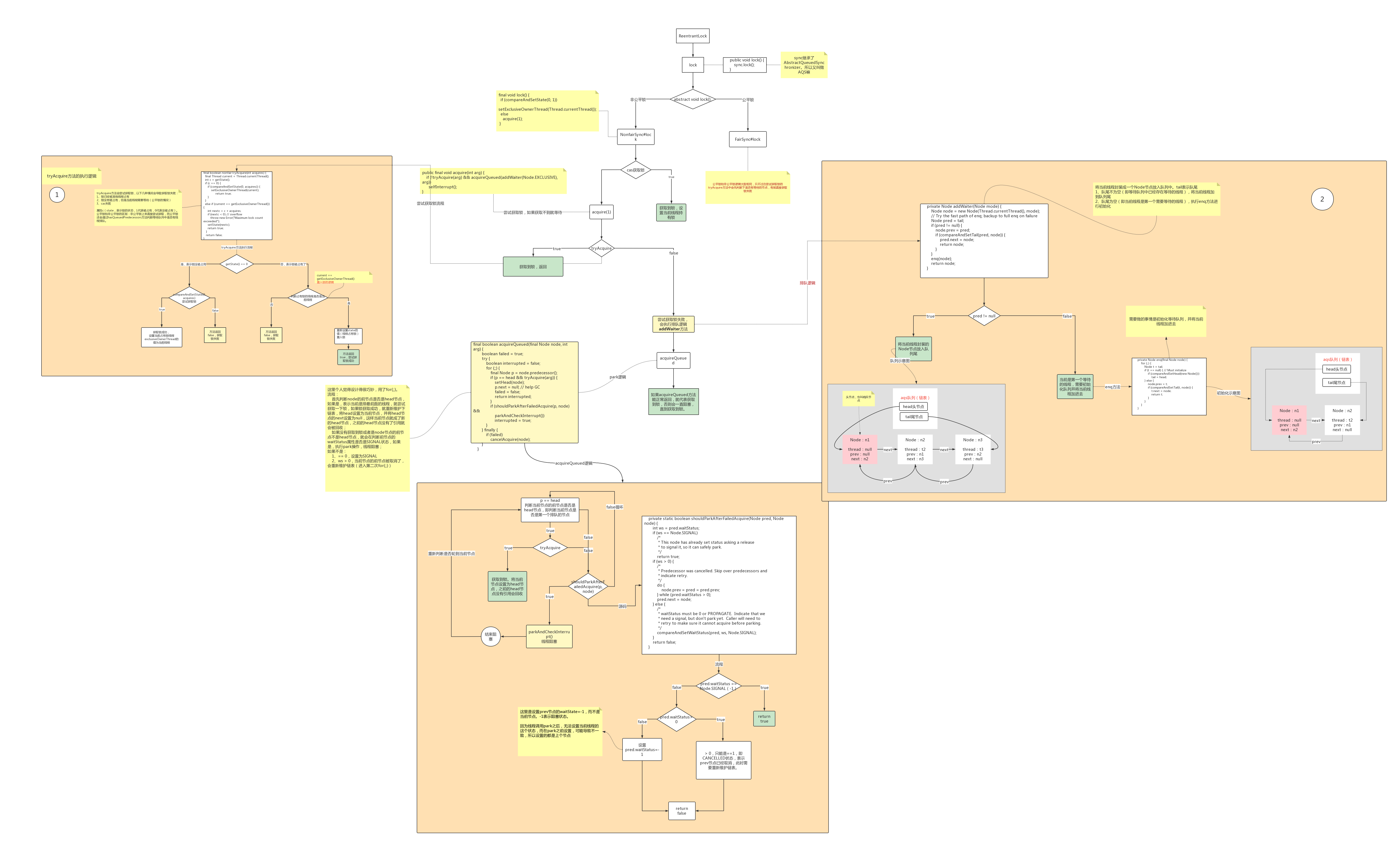
AQS全名:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,是并发容器J.U.C(java.util.concurrent)下locks包内的一个类。它实现了一个FIFO(FirstIn、FirstOut先进先出)的队列。底层实现的数据结构是一个双向链表。这个双向链表是由线程封装成的Node节点组成的,其中有几个比较重要的概念:
- prev。表示前节点
- next。表示后节点
- head。表示头节点
- tail。表示尾节点
- waitState。表示节点状态
- state。表示锁的状态,0表示可用,1表示不可用
类如其名,抽象的队列式的同步器,AQS定义了一套多线程访问共享资源的同步器框架,许多同步类实现都依赖于它,如常用的ReentrantLock/Semaphore/CountDownLatch等,是多线程中一个基础框架。
源代码跟踪
public class AqsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
lock.lock(); // ReentrantLock -> NoFairSync
lock.unlock();;
}
}
以ReentrantLock的非公平锁为例。
public void lock() {
sync.lock(); // 会调用sync的lock方法,而sync继承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(aqs)
}
private final Sync sync;
/**
* Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed
* into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to
* represent the number of holds on the lock.
*/
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {}
final void lock() {
// 修改state的值,成功就将当前线程设置为工作线程
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 失败就执行acquire方法获取锁
acquire(1);
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && // 尝试获取锁
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) // 将节点添加到队列中
selfInterrupt();
}
以非公平锁为例,公平锁和非公平锁在尝试获取锁的这块逻辑相似,只不过公平锁会先判断队列中是否有排队的线程,如果有,就会返回false,不会插队,而非公平锁直接获取锁。这也是公平锁和非公平锁的来由。
/**
* Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in
* subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method.
*/
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取锁状态
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 如果锁状态==0(没被占用),重新设置锁状态,如果成功设置当前线程为工作线程,返回true,获取锁成功
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 否则判断当前线程是否是工作线程(当前占有锁的线程,防止高并发场景下数据不一致),如果是,重新设置锁状态,返回true获取锁成功
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
// 否则获取锁失败,返回false
return false;
}
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程封装成一个Node节点,队列中放的都是Node节点。
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
// 如果队列不为空,将当前节点的prev节点设置为tail节点,即将当前节点跟到tail节点后作为新的tail节点
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { // 重新设置tail尾节点
pred.next = node; // 将之前尾节点的next节点设置为当前节点
return node;
}
}
// 如果队列为空,执行enq方法初始化队列
enq(node);
return node;
}
/**
* Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.
* @param node the node to insert
* @return node's predecessor
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
// 自旋
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
// 如果尾节点为空,会进行初始化
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 否则将node节点的prev节点设置为尾节点,也就是将node节点插入到尾节点后面作为新的尾节点
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
enq方法做的事情就是初始化队列,但是在这里用了一个自旋。因为第一次进来的时候队列尾空,走if分支,会创建一个head节点;循环的第二次就会把node节点插入到head节点后面,太牛逼了。
接着就会调用acquireQueued方法获取队列。
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 判断node的前节点是否是head节点
// 如果是head节点同时获取锁成功
// 就会重新维护队列,将前head节点出栈
// 当前node作为新的head节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 如果当前节点需要阻塞,就会阻塞在这里,等待unpark方法
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
原理总结