转载请注明出处❤️
作者:测试蔡坨坨
原文链接:caituotuo.top/c2d10f21.html
你好,我是测试蔡坨坨。
今天分享一个Python编写的小工具,实现XMind测试用例转Excel用例。
前言
XMind和Excel是在日常测试工作中最常用的两种用例编写形式,两者也有各自的优缺点。
使用XMind编写测试用例更有利于测试思路的梳理,以及更加便捷高效,用例评审效率更高,但是由于每个人使用XMind的方式不同,设计思路也不一样,可能就不便于其他人执行和维护。
使用Excel编写测试用例由于有固定的模板,所以可能更加形式化和规范化,更利于用例管理和维护,以及让其他人更容易执行用例,但是最大的缺点就是需要花费更多的时间成本。
由于项目需要,需要提供Excel形式的测试用例,同时编写两种形式的测试用例显然加大了工作量,于是写了个Python脚本,可快速将XMind用例转换成Excel用例。
设计思路
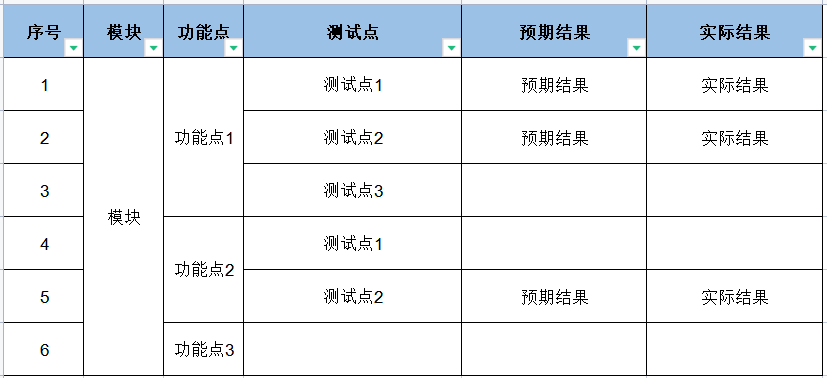
Excel测试用例模板样式如下图所示:

表头固定字段:序号、模块、功能点
为了让脚本更加灵活,后面的字段会根据XMind中每一个分支的长度自增,例如:测试点/用例标题、预期结果、实际结果、前置条件、操作步骤、优先级、编写人、执行人等
根据Excel模板编写对应的XMind测试用例:
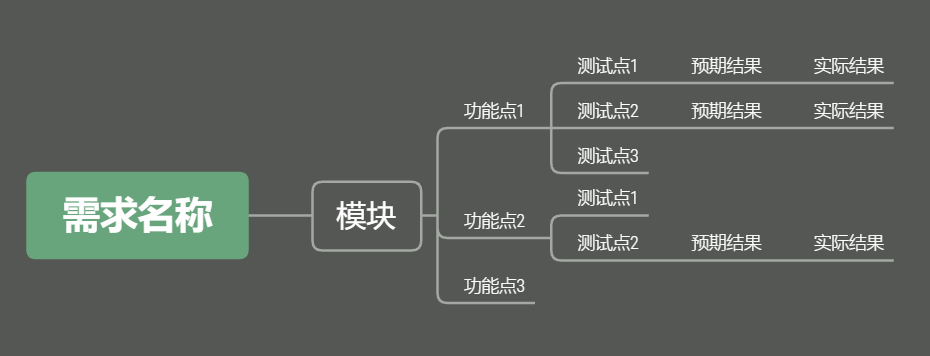
实现:
将XMind中的每一条分支作为一条序号的用例,再将每个字段写入Excel中的每一个单元格中
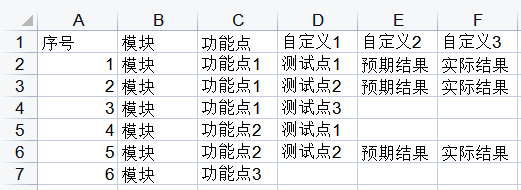
再手动调整美化一下表格:
完整代码
源码获取方式:关注公众号测试蔡坨坨,回复关键词源码
# author: 测试蔡坨坨
# datetime: 2022/8/16 22:44
# function: XMind转Excel
from typing import List, Any
import xlwt
from xmindparser import xmind_to_dict
def resolve_path(dict_, lists, title):
"""
通过递归取出每个主分支下的所有小分支并将其作为一个列表
:param dict_:
:param lists:
:param title:
:return:
"""
# 去除title首尾空格
title = title.strip()
# 若title为空,则直接取value
if len(title) == 0:
concat_title = dict_["title"].strip()
else:
concat_title = title + "\t" + dict_["title"].strip()
if not dict_.__contains__("topics"):
lists.append(concat_title)
else:
for d in dict_["topics"]:
resolve_path(d, lists, concat_title)
def xmind_to_excel(list_, excel_path):
f = xlwt.Workbook()
# 生成单sheet的Excel文件,sheet名自取
sheet = f.add_sheet("XX模块", cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 第一行固定的表头标题
row_header = ["序号", "模块", "功能点"]
for i in range(0, len(row_header)):
sheet.write(0, i, row_header[i])
# 增量索引
index = 0
for h in range(0, len(list_)):
lists: List[Any] = []
resolve_path(list_[h], lists, "")
# print(lists)
# print('\n'.join(lists)) # 主分支下的小分支
for j in range(0, len(lists)):
# 将主分支下的小分支构成列表
lists[j] = lists[j].split('\t')
# print(lists[j])
for n in range(0, len(lists[j])):
# 生成第一列的序号
sheet.write(j + index + 1, 0, j + index + 1)
sheet.write(j + index + 1, n + 1, lists[j][n])
# 自定义内容,比如:测试点/用例标题、预期结果、实际结果、操作步骤、优先级……
# 这里为了更加灵活,除序号、模块、功能点的标题固定,其余以【自定义+序号】命名,如:自定义1,需生成Excel表格后手动修改
if n >= 2:
sheet.write(0, n + 1, "自定义" + str(n - 1))
# 遍历完lists并给增量索引赋值,跳出for j循环,开始for h循环
if j == len(lists) - 1:
index += len(lists)
f.save(excel_path)
def run(xmind_path):
# 将XMind转化成字典
xmind_dict = xmind_to_dict(xmind_path)
# print("将XMind中所有内容提取出来并转换成列表:", xmind_dict)
# Excel文件与XMind文件保存在同一目录下
excel_name = xmind_path.split('\\')[-1].split(".")[0] + '.xlsx'
excel_path = "\\".join(xmind_path.split('\\')[:-1]) + "\\" + excel_name
print(excel_path)
# print("通过切片得到所有分支的内容:", xmind_dict[0]['topic']['topics'])
xmind_to_excel(xmind_dict[0]['topic']['topics'], excel_path)
if __name__ == '__main__':
xmind_path_ = r"F:\Desktop\coder\python_operate_files\用例模板.xmind"
run(xmind_path_)
代码解析
1. 调用xmind_to_dict()方法将XMind中所有内容取出并转成字典
xmind_dict = xmind_to_dict(xmind_path)
[{'title': '画布 1', 'topic': {'title': '需求名称', 'topics': [{'title': '模块', 'topics': [{'title': '功能点1', 'topics': [{'title': '测试点1', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}, {'title': '测试点2', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}, {'title': '测试点3'}]}, {'title': '功能点2', 'topics': [{'title': '测试点1'}, {'title': '测试点2', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}]}, {'title': '功能点3'}]}]}, 'structure': 'org.xmind.ui.logic.right'}]
2. 通过切片得到所有分支的内容
xmind_dict[0]['topic']['topics']
[{'title': '模块', 'topics': [{'title': '功能点1', 'topics': [{'title': '测试点1', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}, {'title': '测试点2', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}, {'title': '测试点3'}]}, {'title': '功能点2', 'topics': [{'title': '测试点1'}, {'title': '测试点2', 'topics': [{'title': '预期结果', 'topics': [{'title': '实际结果'}]}]}]}, {'title': '功能点3'}]}]
3. 通过递归取出每个主分支下的所有小分支并将其作为一个列表
def resolve_path(dict_, lists, title):
"""
通过递归取出每个主分支下的所有小分支并将其作为一个列表
:param dict_:
:param lists:
:param title:
:return:
"""
# 去除title首尾空格
title = title.strip()
# 若title为空,则直接取value
if len(title) == 0:
concat_title = dict_["title"].strip()
else:
concat_title = title + "\t" + dict_["title"].strip()
if not dict_.__contains__("topics"):
lists.append(concat_title)
else:
for d in dict_["topics"]:
resolve_path(d, lists, concat_title)
for h in range(0, len(list_)):
lists: List[Any] = []
resolve_path(list_[h], lists, "")
print(lists)
print('\n'.join(lists)) # 主分支下的小分支
for j in range(0, len(lists)):
# 将主分支下的小分支构成列表
lists[j] = lists[j].split('\t')
print(lists[j])
lists:
['模块\t功能点1\t测试点1\t预期结果\t实际结果', '模块\t功能点1\t测试点2\t预期结果\t实际结果', '模块\t功能点1\t测试点3', '模块\t功能点2\t测试点1', '模块\t功能点2\t测试点2\t预期结果\t实际结果', '模块\t功能点3']
主分支下的小分支:
模块 功能点1 测试点1 预期结果 实际结果
模块 功能点1 测试点2 预期结果 实际结果
模块 功能点1 测试点3
模块 功能点2 测试点1
模块 功能点2 测试点2 预期结果 实际结果
模块 功能点3
将主分支下的小分支构成列表:
['模块', '功能点1', '测试点1', '预期结果', '实际结果']
['模块', '功能点1', '测试点2', '预期结果', '实际结果']
['模块', '功能点1', '测试点3']
['模块', '功能点2', '测试点1']
['模块', '功能点2', '测试点2', '预期结果', '实际结果']
['模块', '功能点3']
4. 写入Excel(生成单sheet的Excel文件、生成固定的表头标题、列序号取值、固定标题外的自定义标题)
f = xlwt.Workbook()
# 生成单sheet的Excel文件,sheet名自取
sheet = f.add_sheet("签署模块", cell_overwrite_ok=True)
# 第一行固定的表头标题
row_header = ["序号", "模块", "功能点"]
for i in range(0, len(row_header)):
sheet.write(0, i, row_header[i])
for n in range(0, len(lists[j])):
# 生成第一列的序号
sheet.write(j + index + 1, 0, j + index + 1)
sheet.write(j + index + 1, n + 1, lists[j][n])
# 自定义内容,比如:测试点/用例标题、预期结果、实际结果、操作步骤、优先级……
# 这里为了更加灵活,除序号、模块、功能点的标题固定,其余以【自定义+序号】命名,如:自定义1,需生成Excel表格后手动修改
if n >= 2:
sheet.write(0, n + 1, "自定义" + str(n - 1))