目录

1. ArrayList的缺陷
上节课已经熟悉了 ArrayList 的使用,并且进行了简单模拟实现。通过源码知道, ArrayList 底层使用数组来存储元素:public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
// ...
// 默认容量是10
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//...
// 数组:用来存储元素
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// 有效元素个数
private int size;
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
// ...}2. 链表
2.1 链表的概念及结构
链表是一种 物理存储结构上非连续 存储结构,数据元素的 逻辑顺序 是通过链表中的 引用链接 次序实现的 。
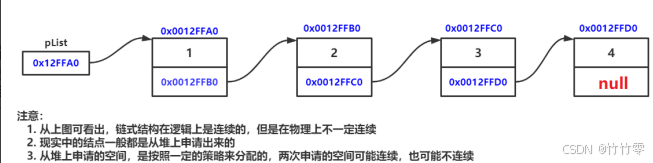
链表是由一个个结点组成,而这些结点又是由数据域和next域构成(双向链表还会多一个prev域)
其中,data域存放数据,next域存放下一个结点的地址(prev域则存放前一个结点的地址)。
什么是“头”?
“头”,就是头节点的意思,它的组成如图:

头节点的data域是不存放元素的。
2.2 链表结构
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有 8 种链表结构: 1. 单向或者双向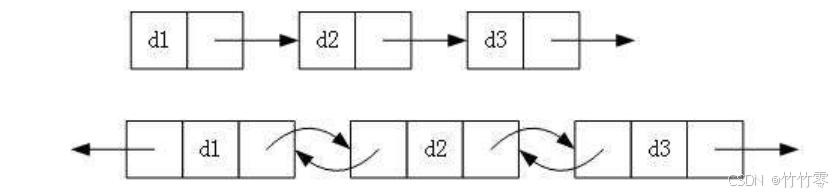 2.
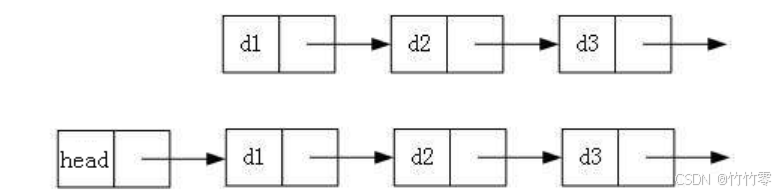
带头或者不带头
2.
带头或者不带头
 3.
循环或者非循环
3.
循环或者非循环
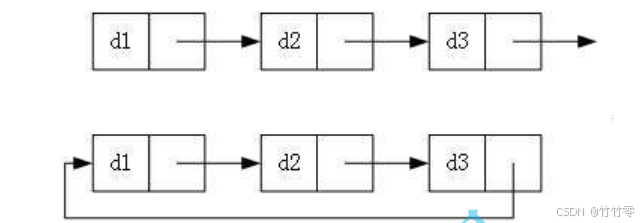
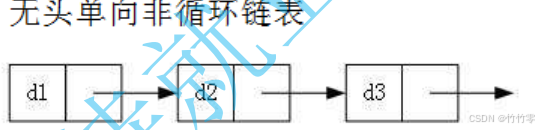
怎么从第一个节点走向第二个节点? head=head.next; 链表什么时候遍历完? 尾指针为空虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们重点掌握两种 : 无头单向非循环链表 : 结构简单 ,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为 其他数据结构的子 结构 ,如 哈希桶、图的邻接表 等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试 中出现很多。
 无头双向链表
:在
Java
的集合框架库中
LinkedList
底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
2.2
链表的实现
无头双向链表
:在
Java
的集合框架库中
LinkedList
底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
2.2
链表的实现
// 1、无头单向非循环链表实现
public class SingleLinkedList {
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
return -1;
}
public void clear() {
}
public void display() {}
}
2.2.1头插法

 插入带向右箭头的节点,每次将指针所指接点插在最前端
插入带向右箭头的节点,每次将指针所指接点插在最前端
@Override
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}
尾插法

 插入带向右箭头的节点,每次将指针所指接点插在最末端
插入带向右箭头的节点,每次将指针所指接点插在最末端
@Override
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {//cur.next代表走到最后一个元素
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
在指定位置插入元素
思路:实例化一个结点,让index(指定位置)位置前一个结点next指向该结点,该结点的next指向index位置的结点。
在插入中需要特别考虑以下三种情况
pos 可能不合法
try {
chackIdex(pos);
}catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
在头位置 插入
if (pos==0) {
insertFirst(val);
return;
}
在 尾位置 插入
if (pos==length()) {
insertLast(val);
return;
}

假设指定位置index为2
问题:
1.得找到index位置的前一个**不能像之前一样直接让cur走到index位置,因为单向链表无法获取前一个结点的信息。
cur走index-1步
2.如何连接
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node
private ListNode SearchPrev(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index-1) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
2.2.2删除元素
思路:如果链表为空,则返回“链表为空”;如果链表没有对应的元素则返回“没找到对应的元素”;如果找到了:前一个结点的next指向删除结点del的next。
当pos 位置不合法时
try {
chackIdex(pos);
}catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
如果链表为空 时
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
头部位置删除时
if (pos==0) {
removeFirst();
return;
}

public void removeValAll(int val) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
ListNode pre=head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
cur=cur.next;
} else {
pre.next=cur;
pre=pre.next;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
pre.next=null;
if (head.val==val) {
removeFirst();
}
}
2.2.3清空方法(clear方法)
思路,把每个结点都制空
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode cur =head;
while (head != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
//cur.val = null 引用数据类型加上这句
cur.next = null;
cur = curNext;
}
head = null;
}
2.2.4修改元素
主要过程是先 从头节点开始遍历 ,当找到该数据就返回 下标位置
然后找到该小标位置就返回该节点,对这个 节点 的数据进行 修改
@Override
public void modify(int pos, int val) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode des=indexFind(pos);
if (des==null) {
return;
}
des.val=val;
}
如果链表为 空 ,我们就 不需要修改 了
if (des==null) {
return;
}
主函数逻辑的实现
package singlinklist;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ISingleLinkList msl =new MySingleLinkedList();
// 插入
System.out.println("=====插入========");
// 尾插
msl.insertFirst(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(6);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(2);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(3);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.insertLast(1);
msl.display();
// System.out.println("======删除=======");
//
// msl.remove(3);
// msl.removeFirst();
// msl.removeLast();
// msl.display();
//
//
// System.out.println("======修改=====");
// msl.modify(1,2);
// msl.display();
//
//
// System.out.println("=====查找=====");
// System.out.println(msl.contains(2));
// System.out.println(msl.contains(3));
// System.out.println(msl.length());
//
// msl.clear();
System.out.println("=======");
// msl.removeVal(0);
// msl.removeVal(1);
// msl.removeVal(2);
// msl.removeVal(3);
// msl.display();
msl.removeValAll(1);
msl.display();
msl.insertLast(2);
msl.insertLast(3);
msl.insert(3,9);
msl.insertFirst(0);
msl.display();
System.out.println("======删除=======");
msl.remove(3);
msl.removeFirst();
msl.removeLast();
msl.display();
System.out.println("======修改=====");
msl.modify(1,2);
msl.display();
System.out.println("=====查找=====");
System.out.println(msl.contains(2));
System.out.println(msl.contains(3));
System.out.println(msl.length());
msl.clear();
}
}
2.3.单链表的优化
单链表如果 限定死了 ,只能存放 整型或者 浮点型 那就太单一了
所以如果我们要对 单链表优化 的话,那么我们不得不请出我们的 泛型 啦
1.功能接口
package generarraysinglinklist;
public interface IGSingleLinkList<T> {
// 打印数据
public void display();
// 尾删数据
public void removeLast();
// 头删
public void removeFirst();
// 指定位置删除数据
public void remove(int pos);
// 删除指定数据
public void removeVal(T val);
// 删除指定的所有数据
public void removeValAll(T val);
// 头插
public void insertFirst(T val);
// 尾插数据
public void insertLast(T val);
// 指定位置插入数据
public void insert(int pos,T val);
// 确定数据是否存在
public boolean contains(T val);
// 修改数据
public void modify(int pos ,T val);
// 清空单链表
public void clear();
// 链表长度
public int length();
}
2. 功能实现
package generarraysinglinklist;
import singlinklist.ISingleLinkList;
import singlinklist.IndexNotLegalException;
public class GMySingleLinkedList<T> implements IGSingleLinkList<T> {
public ListNode head;
public static class ListNode<T> {
// 存放数据
public T val;
// 指向下一个节点的next
public ListNode<T> next;
public ListNode(T val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public GMySingleLinkedList(T val) {
this.head = new ListNode<T>(val);
}
// 打印单链表
@Override
public void display() {
checknull();
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
cur=cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
@Override
public void insertFirst(T val) {
checknull();
ListNode node=new ListNode(val);
node.next=head;
head=node;
}
@Override
public void insertLast(T val) {
checknull();
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next !=null) {
cur=cur.next;
}
ListNode node =new ListNode(val);
// 本身 cur.next=null 这行可加可不加
// node.next=cur.next;
cur.next=node;
}
// 指定位置插入
@Override
public void insert(int pos, T val) {
checknull();
if (pos==0) {
insertFirst(val);
return;
}
if (pos==length()) {
insertLast(val);
return;
}
ListNode des= indexFind(pos);
if (des==null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next != des) {
cur=cur.next;
}
ListNode node=new ListNode(val);
node.next=des;
cur.next=node;
}
@Override
public void removeLast() {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
if (cur.next==null) {
head=null;
return;
}
while (cur.next.next != null) {
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=null;
}
@Override
public void removeFirst() {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
head=head.next;
cur=null;
}
@Override
public void remove(int pos) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (pos==0) {
removeFirst();
return;
}
ListNode dec=indexFind(pos);
if (dec==null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur.next !=dec) {
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}
// 删除特定数据
@Override
public void removeVal(T val) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head;
if (cur.val.equals(val)) {
removeFirst();
return;
}
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val.equals(val)) {
cur.next=cur.next.next;
return;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
}
// 删除特定的所有数据
@Override
public void removeValAll(T val) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode cur=head.next;
ListNode pre=head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val .equals(val) ) {
cur=cur.next;
} else {
pre.next=cur;
pre=pre.next;
cur=cur.next;
}
}
pre.next=null;
if (head.val.equals(val)) {
removeFirst();
}
}
// //删除单链表中所有的keyword
方法一:
// public void removeValAll(int val){
// ListNode cur=head;
//
// while(cur.next!=null){
// if(cur.next.val.equals(val)){
// ListNode ret=cur.next;
// cur.next=ret.next;//这里ret.next和直接写cur.next.next是一样的;
// } else {
// cur=cur.next;
//
// }
// if(cur==null){
// break;
// }
// }
//
// if(head.val.equals(val)){
// head=head.next;
// }
// }
// 搜索是否含有该数据
@Override
public boolean contains(T val) {
checknull();
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val.equals(val)) {
return true;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void modify(int pos, T val) {
checknull();
if (isEmpty()) {
return;
}
ListNode des=indexFind(pos);
if (des==null) {
return;
}
des.val=val;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
ListNode<T> cur=head;
while (cur != null) {
cur.val=null;
cur=cur.next;
}
head=null;
}
private void checknull() {
if (head==null) {
System.out.println("单链表为null");
}
}
private ListNode indexFind(int pos) {
try {
chackIdex(pos);
}catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
ListNode cur=head;
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
cur=cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
@Override
public int length() {
int count=0;
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur=cur.next;
}
return count;
}
// 检查链表是否长度为 0
private boolean isEmpty() {
return length()==0;
}
// 检查下标是否合法
private void chackIdex(int pos) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (pos <0 || pos >= length()) {
throw new IndexNotLegalException();
}
}
}
3. 其他处理
package generarraysinglinklist;
import generarraylist.GMyArrayList;
import generarraylist.IGList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IGSingleLinkList<String> c=new GMySingleLinkedList<>("1");
System.out.println("--------增加数据----------");
c.insertLast("1");
c.insertLast("3");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insert(1,"2");
c.insertFirst("0");
c.display();
System.out.println("--------删除数据-----------");
c.removeValAll("2");
c.removeLast();
c.display();
System.out.println("--------查找数据-------------");
String str= "0";
boolean b= c.contains(str);
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println("---------修改数据-----------");
c.modify(1,"2");
c.display();
}
}
- 自定义一个异常来检查下标合法性
到这里,竹竹零就要和大家说再见了
标签:head,Linkedlist,val,next,链表,msl,public,cur From: https://blog.csdn.net/2301_80062351/article/details/142601281