864. Shortest Path to Get All Keys
You are given an m x n grid grid where:
'.'is an empty cell.'#'is a wall.'@'is the starting point.- Lowercase letters represent keys.
- Uppercase letters represent locks.
You start at the starting point and one move consists of walking one space in one of the four cardinal directions. You cannot walk outside the grid, or walk into a wall.
If you walk over a key, you can pick it up and you cannot walk over a lock unless you have its corresponding key.
For some 1 <= k <= 6, there is exactly one lowercase and one uppercase letter of the first k letters of the English alphabet in the grid. This means that there is exactly one key for each lock, and one lock for each key; and also that the letters used to represent the keys and locks were chosen in the same order as the English alphabet.
Return the lowest number of moves to acquire all keys. If it is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
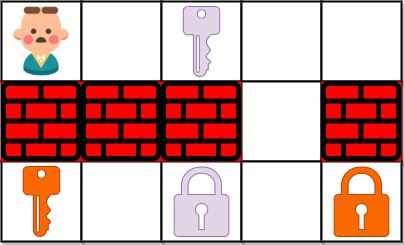
Input: grid = ["@.a..","###.#","b.A.B"] Output: 8 Explanation: Note that the goal is to obtain all the keys not to open all the locks.
Example 2:
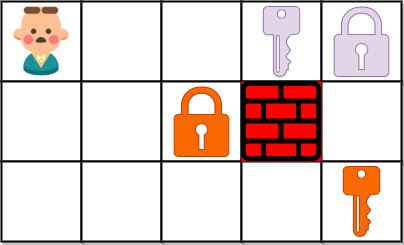
Input: grid = ["@..aA","..B#.","....b"] Output: 6
Example 3:

Input: grid = ["@Aa"] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 30grid[i][j]is either an English letter,'.','#', or'@'.- The number of keys in the grid is in the range
[1, 6]. - Each key in the grid is unique.
- Each key in the grid has a matching lock.
class Solution {
/*
关键点:
1.图中的点可以重复访问,因为拿到的钥匙状态不同,说不定可以解锁之前不能去的节点
2.但是同一个点在同样的钥匙状态下不能重复访问
3.使用bitmask 来记录钥匙的状态
4.巧妙使用了java新特性record,可以简化程序实现
*/
record State(int keys, int i, int j) {}
public int shortestPathAllKeys(String[] grid) {
int x = -1, y = -1, m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length(), max = -1;
//1.拿到起点
//2.拿到钥匙的数量
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
char c = grid[i].charAt(j);
if (c == '@') {
x = i;
y = j;
}
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f') {
max = Math.max(c - 'a' + 1, max);
}
}
}
//下面开始bfs
State start = new State(0, x, y);
Queue<State> q = new LinkedList<>();
//记录已经访问过的点
Set<State> visited = new HashSet<>();
//从起点开始进行bfs
visited.add(start);
q.offer(start);
int[][] dirs = new int[][]{{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int step = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while (size-- > 0) {
State cur = q.poll();
//11111 各位都为1,说明所有的锁都解了
if (cur.keys == (1 << max) - 1) {
return step;
}
//遍历4个方向
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int i = cur.i + dir[0];
int j = cur.j + dir[1];
//当前拿到钥匙的状态
int keys = cur.keys;
//如果在界内的话
if (i >= 0 && i < m && j >= 0 && j < n) {
char c = grid[i].charAt(j);
//如果是wall,直接跳过
if (c == '#') {
continue;
}
//如果是钥匙,那么将这把钥匙所在bit位置为1
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'f') {
keys |= 1 << (c - 'a');
}
//如果是锁,但是对应的钥匙还未找到的话,只能跳过
if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'F' && ((keys >> (c - 'A')) & 1) == 0) {
continue;
}
//判定这个位置在相同钥匙状态下是否已经访问过,如果是,那么可以跳过,
State s = new State(keys, i, j);
if (!visited.contains(s)) {
visited.add(s);
q.offer(s);
}
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
}
847. Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes
Hard
You have an undirected, connected graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an array graph where graph[i] is a list of all the nodes connected with node i by an edge.
Return the length of the shortest path that visits every node. You may start and stop at any node, you may revisit nodes multiple times, and you may reuse edges.
Example 1:
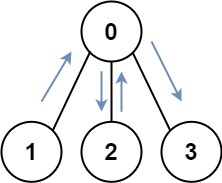
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0],[0],[0]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [1,0,2,0,3]
Example 2:
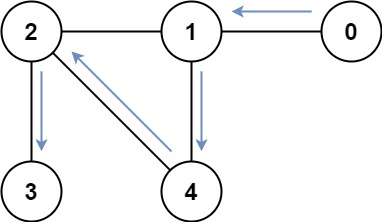
Input: graph = [[1],[0,2,4],[1,3,4],[2],[1,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [0,1,4,2,3]
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 120 <= graph[i].length < ngraph[i]does not containi.- If
graph[a]containsb, thengraph[b]containsa. - The input graph is always connected.
class Solution {
//mask:经过的节点集,bit位=1表示已经访问过 pos:节点编号
record Node(int mask, int pos){}
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
Set<Node> visited = new HashSet();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList();
//将所有节点都作为初始节点放入queue
for(int i = 0; i < graph.length; i++){
Node node = new Node(1 << i, i);
queue.offer(node);
visited.add(node);
}
int step = 0;
//当所有bit位都为1时,代表已经访问完毕所有点
int FINISH = (1 << graph.length) - 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
Node curr = queue.poll();
if(curr.mask == FINISH) return step;
for(int other : graph[curr.pos]){
Node next = new Node(1 << other | curr.mask, other);
if(visited.contains(next)) continue;
queue.offer(next);
visited.add(next);
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
}
标签:int,graph,length,bfs,keys,bitmask,grid,new From: https://www.cnblogs.com/cynrjy/p/16818349.html