作者:杨尚晓
前言
虚拟摇杆在移动端游戏中是最常见看的,用来实现游戏中的精灵移动。本案例中使用jspai中的div和image组件来实现的虚拟摇杆组件,然后监听touch事件获取滑动的方向和位置x,y。
开发环境说明
- 工具版本:OpenHarmony DevEco Studio 3.0 Release
- SDK版本:3.0.0.993(API Version 8 Beta3)
- 组要组件:组件名称yg-rocker
展示效果
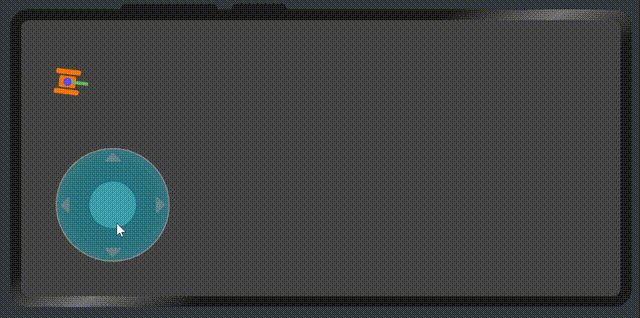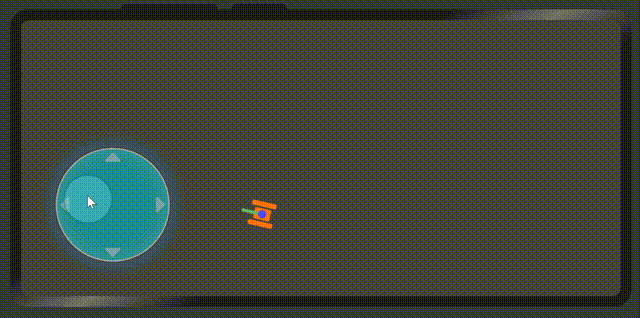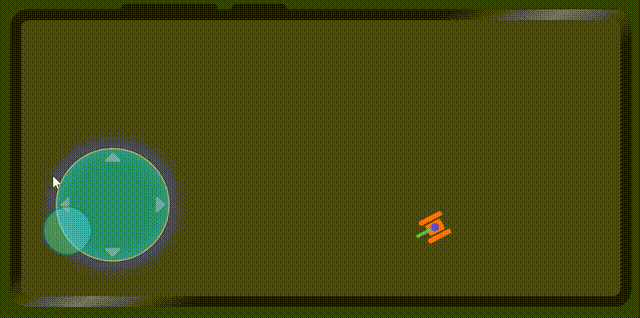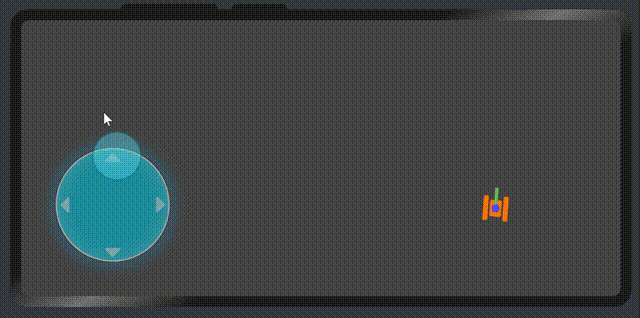
属性
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| rocker-data | Object | - | 配置摇杆的参数,参考下面rockerData |
rockerData
| 属性名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ou_width | Number | 140 | 摇杆外圆宽度 |
| ou_height | Number | 140 | 摇杆外圆高度 |
| in_width | Number | 60 | 摇杆内圆宽度 |
| in_height | Number | 60 | 摇杆内圆高度 |
| ou_img | Image | - | 摇杆外圆图片 |
| in_img | Image | - | 摇杆内圆图片 |
组件事件
| 属性名 | 类型 | 返回值 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| play | Function | {x:Number, y:Number, angle:Number} | x: 摇杆滑动的x, y: 摇杆滑动的y, angle: 对应x方向的角度 |
调用实现
hml部分
<element name="yg-rocker" src="../../common/component/ygRocker.hml"></element>
<div class="container" ref="box">
<yg-rocker
rocker-data="{{rockerData}}"
@play="play"
></yg-rocker>
</div>
js部分
import Log from '../../common/utils/log.js'
const log = new Log('index.js页面')
export default {
data: {
rockerData: {
ou_width: 140,
ou_height: 140,
in_width: 60,
in_height: 60,
ou_img: '/common/images/rocker_bg.png',
in_img: '/common/images/rocker.png',
},
d_x: 0,
d_y: 0,
window: {
w: 720,
h: 332
},
angle: 0
},
onInit() {
},
onShow(){
let d = this.$refs.box.getBoundingClientRect();
this.window.w = d.width || 720;
this.window.h = d.height || 332;
},
play(e){
let opt = e.detail
let {x, y, angle} = opt;
this.angle = angle;
this.d_x = x;
this.d_y = y;
}
}
实现过程
1. 首先渲染虚拟摇杆的外圆和内圆
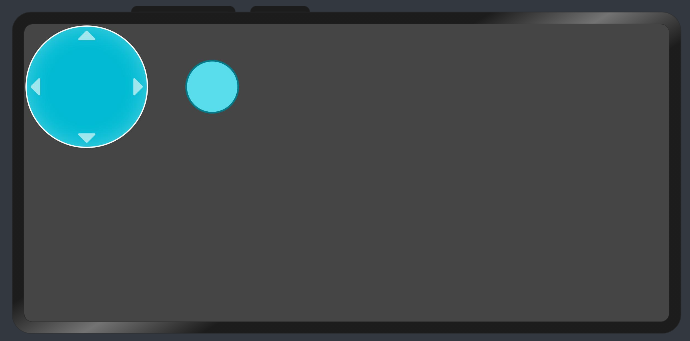 通过css调整
通过css调整
.yg-rocker{
position: fixed;
bottom: 40px;
left: 40px;
}
.yg-rocker div image{
opacity: .4;
}
.yg-rocker-bg .active-bg{
box-shadow: 0fp 0 10px 5px rgba(0,170,255,.2);
opacity: .6;
}
.yg-rocker .yg-rocker-item{
position: absolute;
}
最后得到

2. 给虚拟摇杆添加touch事件
<div
class="yg-rocker-bg"
ref="ygRockerBg"
@touchstart="touchStart"
@touchmove="touchMove"
@touchend="touchEnd"
>
touchStart触摸开始事件
- 在开始触摸时,记录当前手势按压的位置x,y。
- 获取摇杆内圆的位置,
d = this.$refs.ygRockerItem.getBoundingClientRect()。 - 记录当前内圆的圆心在屏幕的位置 this.x, this.y
- isTouch记录当前在触摸,后面需要做定时器逻辑判断。
- setSide(t)方法传入一个x,y坐标,计算当前内圆的位置,下面详细讲解。
- ani(time)传入一个毫秒级的时间,作为定时器刷新时间,下面详细讲解。
touchStart(e){
let t = e.touches[0];
let d = this.$refs.ygRockerItem.getBoundingClientRect();
this.x = d.left + d.width / 2;
this.y = d.top + d.height / 2;
this.isTouch = true;
this.setSide(t);
this.ani(10);
},
触摸滑动事件和触摸结束事件
// 触摸滑动事件也交给setSide方法处理
touchMove(e){
let t = e.touches[0];
this.setSide(t);
},
// 触摸结束,摇杆内圆回归到最开始位置
touchEnd(){
this.isTouch = false;
// 回到中心位置
this.top = 0;
this.left = 0;
},
3. 对滑动的位置处理
-
setSide(t)方法传入一个对象{x,y},表示当前手势触摸在屏幕的位置。
-
计算当前触摸手指的位置到摇杆内圆初始圆心的半径为temp,如下图。
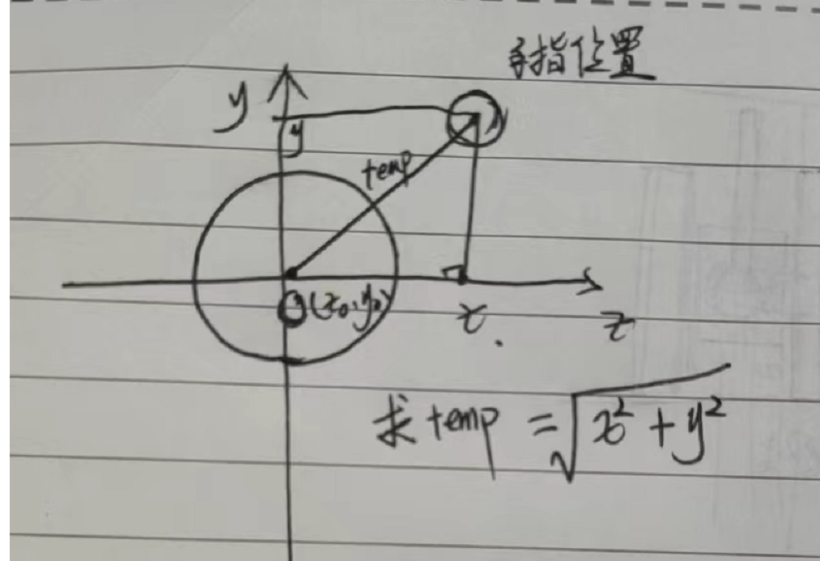 通过勾股定理,我们得到temp=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x,2) + Math.pow(y,2));
通过勾股定理,我们得到temp=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x,2) + Math.pow(y,2)); -
让手指所在的位置和当前摇杆外圆的半径对比,如果超出外圆,就让内圆在外圆的边上滑动,不让内圆跟着手指超出外圆范围。
-
最后通过三角函数求得内圆在屏幕上的位置left,top。
-
speed记录滑动处理后的坐标速度。
-
getAngle获取当前手指和内圆圆心所在x轴方向的角度。后续用来判断物体的方向。
-
setFlag记录坐标所在的以内圆圆心位坐标原点的象限。
setSide(t){
let x = this.x - t.globalX;
let y = this.y - t.globalY;
// 获取到当前位置到圆心半径
let temp = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x,2) + Math.pow(y,2));
let r = this.rockerData.ou_width / 2;
let r2 = temp <= r ? r : temp;
let top = Math.sin(y/r2) * (this.rockerData.ou_width / 2);
let left = Math.sin(x/r2) * (this.rockerData.ou_width / 2);
this.top = this.setFlag(top);
this.left = this.setFlag(left);
this.xx = -1 * x * this.speed;
this.yy = -1 * y * this.speed;
this.angle = this.getAngle({x: (-1 * x), y});
},
setFlag(num){
return num > 0 ? 0 - num : Math.abs(num);
},
4. 获取角度
获取当前手指和内圆圆心所在x轴方向的角度。用来判断物体的方向。 因为通过css的rotate来判断实现物体方向,所以以x轴方向为起点,顺时针为递增从0到360° 圆的周长为2Πr,也就是说2Π为圆的360°,一个Π就是180°,使用三角函数的反正切可求得当前位置对应圆心的角度。 但是因为是正切,所以取值只有0到90°或者是-0到-90°。 所以需要根据在象限的位置来计算内圆圆心为坐标原点,x轴为起边的顺时针角度。
getAngle(obj){
let {x, y} = obj;
//返回角度,不是弧度
let res = 180 * Math.atan(y / x) / Math.PI;
if(x > 0 && y > 0){
res = 90 - Math.abs(res)
}
if(x > 0 && y < 0){
res = 90 + Math.abs(res)
}
if(x < 0 && y < 0){
res = 180 + (90-Math.abs(res))
}
if(x < 0 && y > 0){
res = 270 + Math.abs(res)
}
return res === res ? res.toFixed(2) : 0;
}
5. 动画帧处理
ani传入一个定时器的时间,表示这个时间段刷新一次动画。 因为我们触摸的时候,如果在一个方向触摸停止了,但是操作的物体不应该是停止的。而是根据这个方向继续根据当前速度前进。所以需要使用定时器操作刷新这个动画帧。
ani(t){
clearInterval(this.timer);
this.timer = setInterval(()=>{
if(!this.isTouch){
clearInterval(this.timer)
} else {
this.d_x = this.d_x + this.xx;
this.d_y = this.d_y + this.yy;
this.$emit('play', {x: this.d_x, y: this.d_y, angle: this.angle})
// 下面的操作都是为了防止物体(坦克)离开屏幕画面。
if(this.d_x <= 0){
this.d_x = 0;
}
if(this.d_x >= 680){
this.d_x = 680;
}
if(this.d_y <= 0){
this.d_y = 0;
}
if(this.d_y >= 292){
this.d_y = 292;
}
}
},t)
},
最后的效果就出来了

6. 最后,画一个坦克来验证虚拟摇杆的数据。
<div class="tank" style="transform: rotate({{angle}}deg); top: {{d_y}}px; left: {{d_x}}px;">
<div class="l1"></div>
<div class="l2"></div>
<div class="c"></div>
<div class="g"></div>
<div class="r"></div>
</div>
最后我们再次看一下效果
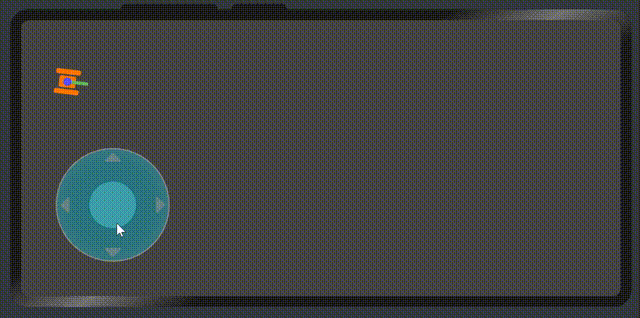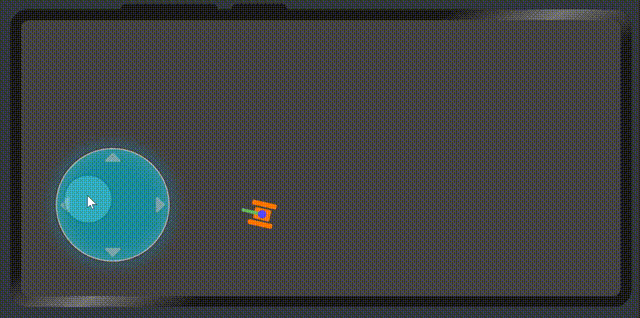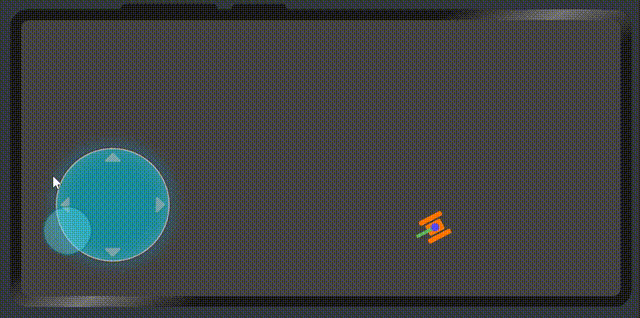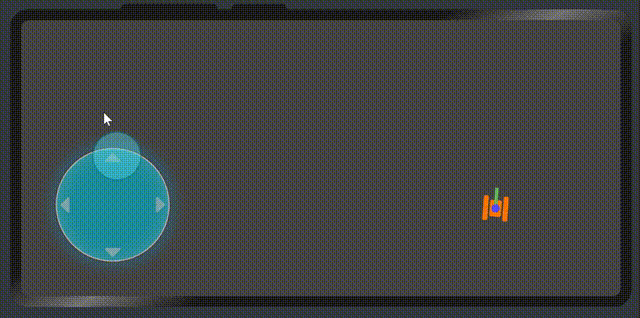
代码地址
https://gitee.com/yango520/yg-rocker
总结
整体的实现就是这样,逻辑也比较简单,当然也有些bug,比如滑动的速度没有限制超出摇杆外圆的时候而限制。坦克用div画的,如果需要做更复杂的操作,需要使用canvas来作为画布场景。
更多原创内容请关注:中软国际 HarmonyOS 技术团队
入门到精通、技巧到案例,系统化分享HarmonyOS开发技术,欢迎投稿和订阅,让我们一起携手前行共建鸿蒙生态。
https://ost.51cto.com/#bkwz
标签:rocker,触摸,res,JS,摇杆,let,打卡,Math From: https://blog.51cto.com/harmonyos/5765463