CodeQL基础及语法
安装及环境
codeql解析引擎:https://github.com/github/codeql-cli-binaries/releases(可以添加环境变量)SDK:https://github.com/github/codeql
mkdir ~/codeql && cd ~/codeql
wget https://github.com/github/codeql-cli-binaries/releases/download/v2.8.4/codeql-osx64.zip && unzip codeql-osx64.zip
git clone https://github.com/github/codeql.git ql
vscode插件:需要配置解析引擎地址
基础使用
- 创建数据库常见命令
git clone https://github.com/l4yn3/micro_service_seclab.git
创建数据库
codeql database create ~/codeql/micro-service-seclab-database --language=java --command="mvn clean install --file pom.xml" --source-root=./micro_service_seclab
codeql database create workspqcedb\micro-service-seclab-database --language=java --command="mvn clean install --file pom.xml" --source -root=E:\code-project\java_project\micro_service_seclab
常见脚本命令:
cd /root/workspace/codeql
chmod 777 codeql
./codeql database create /root/workspace/ql/db --language="java" --command="mvn clean install --file pom.xml" --source-root=/root/workspace/sdl_server --overwrite
./codeql database analyze /root/workspace/ql/db /root/workspace/ql/java/ql/src/codeql-suites/java-security-and-quality.qls --format=sarifv2.1.0 --output=1.sarif
echo "本次CodeQL扫描到的漏洞"
cat 1.sarif | jq "[{vuln:.runs[].results[].rule.id}]"
- 导入vscode源码数据库
此处好像有个小bug,在当前时间点最新版本,如果系统设置了codeql的PATH环境变量则vscode则不用进行扩展设置,不然好像会出现找不到vscode的问题;

- 编写QL规则查询
在~/codeql/ql/java/ql/examples/test.ql中编写测试代码,因为examples目录下有qlpack.yml就不需要再新建了。Tip
codeQL规则有包结构/目录结构要求(qlpack.yml定义一个package),才能正常编译、执行。参考:https://codeql.github.com/docs/codeql-cli/using-custom-queries-with-the-codeql-cli/
编写后右键,然后点击Run Query即可出现运行结果。

寻找没有使用的参数
import java
from Parameter p
where not exists(p.getAnAccess())
select p
- 输出报告
codeql database analyze ~/codeql/micro-service-seclab-database ~/codeql/ql/java/ql/examples/test.ql --format=csv --output=result.csv --rerun
执行所有漏洞扫描:
codeql database analyze ~/codeql/micro-service-seclab-database ~/codeql/ql/java/ql/src/codeql-suites/java-security-extended.qls --format=csv --output=result.csv --rerun
基础语法规则
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/255721
https://codeql.github.com/docs/ql-language-reference/
标准库(名词查找):https://codeql.github.com/codeql-standard-libraries/
基础结构
/**
* @id java/examples/shiro
* @name shiro
* @description shiro
* @kind path-problem
* @problem.severity warning
*/
//定义元数据
import java // 导入使用的库
predicate myfunc(Expr expSrc, Expr expDest) {
//定义函数等
}
class myclass extends Class {
//定义类型
}
from /* ... 变量声明... */
where /* ... 逻辑公式 ... */
select /* ... 表达式 ... */
谓词
predicate封装我们的逻辑,让我们的查询部分逻辑更简明清晰,CodeQL中的函数原名叫predicate,翻译是谓词;
#获取名字为getStudent的方法的名称、参数和所属类
import java
predicate testFunc(Method method) {
exists( | method.hasName("getStudent") | method.getDeclaringType().toString()="IndexDb" )
}
from Method i
where testFunc(i)
select i.getName(),i.getAParameter(),i.getDeclaringType()
predicate表示当前方法没有返回值exists子查询,是CodeQL谓词语法里非常常见的语法结构,它根据内部的子查询返回trueorfalse,来决定筛选出哪些数据;|前后存在上下文关系,并列关系可以用and或者or。
类
CodeQL中,类用来代表符合某种逻辑的值;类必须是大写字母开头,其中和类名名称相同的方法为特征谓词,特征谓词中的this代表父类而不是和java一样代表本身,我们在特征谓词中加我们的逻辑,比如名字是main。
常用到的类库
| 名称 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| Method | 方法类,Method method表示获取当前项目中所有的方法 |
| MethodAccess | 方法调用类,MethodAccess call表示获取当前项目当中的所有方法调用 |
| Parameter | 参数类,Parameter表示获取当前项目当中所有的参数 |
import java
from Method method
where method.hasName("main")
select method.getName(), method.getDeclaringType()
- method.getName() 获取的是当前方法的名称
- method.getDeclaringType() 获取的是当前方法所属class的名称
- method.hasName() 判断是否有该方法
污点追踪(设置source和sink)
source
SDK自带的规则
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node source) { source instanceof RemoteFlowSource }
sink
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) { sink instanceof QueryInjectionSink }
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
exists(Method method, MethodAccess call |
method.hasName("query")
and
call.getMethod() = method and
sink.asExpr() = call.getArgument(0)
)
}
Flow数据流
设置好Source和Sink,一个受污染的变量,能够流转到危险函数,就可以确定漏洞存在。
这个连通工作是由CodeQL来完成的,我们调用内置的config.hasFlowPath(source, sink)方法来判断是否连通,其中source和sink需要自己定义
基本测试例
元数据是程序的一部分,不能删除;
/**
* @name SQL injection
* @description SQL注入
* @kind path-problem
* @problem.severity error
* @security-severity 9.8
* @precision high
* @id java/test/sql-injection
*/
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.TaintTracking
import semmle.code.java.security.QueryInjection
import DataFlow::PathGraph
class SQLInjectionConfiguration extends TaintTracking::Configuration {
SQLInjectionConfiguration() { this = "SQLInjection" }
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node source) { source instanceof RemoteFlowSource }
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) { sink instanceof QueryInjectionSink }
#消除SQL注入Long类型误报
override predicate isSanitizer(DataFlow::Node node) {
node.getType() instanceof PrimitiveType or
node.getType() instanceof BoxedType or
node.getType() instanceof NumberType or
exists(ParameterizedType pt| node.getType() = pt and pt.getTypeArgument(0) instanceof NumberType )
}
}
from DataFlow::PathNode source, DataFlow::PathNode sink, SQLInjectionConfiguration c
where c.hasFlowPath(source, sink)
select sink.getNode(), source, sink, "$@ flows to here and is sql injection vuln",source.getNode(), "vuln"
其他
instanceof
sink instanceof QueryInjectionSink表示判断sink是QueryInjectionSink类型
实现这种机制,只需要创建一个abstract抽象类,之后就可以通过像 src instanceof RemoteFlowSource进行instanceof,但是了解java的都知道我们继承一个abstract抽象类,但是没有实现方法,如何获取各种source呢?
CodeQL和Java不太一样,只要我们的子类继承了这个RemoteFlowSource类,那么所有子类就会被调用,它所代表的source也会被加载。
https://image.3001.net/images/20210808/1628394606_610f546eaa54d9e27ddaa.png!small
递归
在谓词方法的后面跟*或者+,来表示调用0次以上和1次以上(和正则类似)
public class StudentService {
class innerOne {
public innerOne(){}
class innerTwo {
public innerTwo(){}
public String Nihao() {
return "Nihao";
}
}
public String Hi(){
return "hello";
}
}
}
Codeql语法:
#非递归
import java
from Class classes
where classes.getName().toString() = "innerTwo"
select classes.getEnclosingType().getEnclosingType() // getEnclosingtype获取作用域
#递归
from Class classes
where classes.getName().toString() = "innerTwo"
select classes.getEnclosingType+() // 获取作用域
https://image.3001.net/images/20210808/1628394633_610f5489e0794ebb65f5e.png!small
类型过滤
通过.(type)进行类型过滤,可以理解成filter,它的意思是将前面的结果符合Type的数据保留
lombok
lombok:变量设置getter、setter引入@Data;最新版已经解决(Is there a way to process Lombok-ed source file in codeql · Issue #4984 · github/codeql · GitHub)
isAdditionalTaintStep
isAdditionalTaintStep方法也是TaintTracking::Configuration类中提供的方法;用于将中断的数据流重新连接起来;
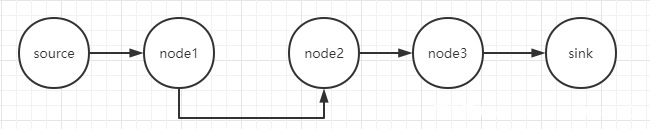
02.codeql检测shiro反序列化 · d4m1ts 知识库 (gm7.org)
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/255721
CodeQL不认为cookie和cookie.getvalue()是一个值,我们的source和sink设置的是两个方法的调用,CodeQL认为方法调用的值等于他的返回值,也就是a.getCookie()的值是cookie,cookie.getValue()的值是Value,所以这两个节点之间是断的,解决办法就是通过污点追踪的isAdditionalTaintStep()把这两个节点连起来,让cookie等于cookie.getValue()。getCookie到readValue中间都是断的
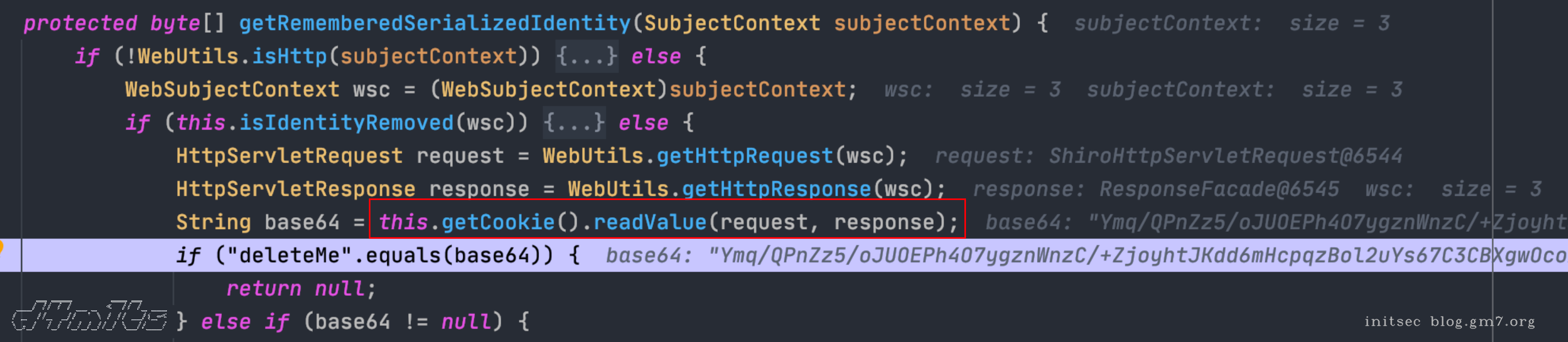
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataflow.FlowSources
import semmle.code.java.security.UnsafeDeserializationQuery
import DataFlow::PathGraph
/**
* 根据分析的连贯性,定位第一个节点和第二个节点
*/
predicate isCookie(Expr expSrc, Expr expDest) {
exists(MethodAccess ma |
expSrc.getType().toString() = "Cookie" // 第一个节点类型是Cookie
and expDest = ma
and ma.getMethod().getName() = "getValue" // 第二个节点的函数名
and ma.getMethod().getDeclaringType().toString() = "Cookie" // 第二个节点函数的返回类型
)
}
class TestShiro extends TaintTracking::Configuration {
TestShiro() { this = "TestShiro" }
override predicate isSource(DataFlow::Node source) {
exists(MethodAccess m|
m.getMethod().getName() = "getCookie" and source.asExpr() = m)
}
override predicate isSink(DataFlow::Node sink) {
exists(MethodAccess m |
m.getMethod().getName() = "readObject" and sink.asExpr() = m)
}
override predicate isAdditionalTaintStep(DataFlow::Node node1, DataFlow::Node node2) {
isCookie(node1.asExpr(), node2.asExpr())
}
}
from DataFlow::PathNode source, DataFlow::PathNode sink, TestShiro ts
where ts.hasFlowPath(source, sink)
select source, sink
CodeQL java
原理
原理:编写查询语句找出代码中的漏洞,codeql 内的编译器调用 extractor 将 java 代码编译成可查询的数据流,并以数据库的形式搭配 ql 库与编写的查询语句进行查询,得出结果并生成报告。

CodeQL的查询需要建立在一个数据库的基础之上,这个数据库是通过Extractor模块对源代码进行分析、提取后得到的。数据库建立之后,我们就可以使用CodeQL去探索源码,并发现代码中的一些已知问题。
- 对于编译型语言,CodeQL会在建立数据库时“模拟”编译的过程,在make等编译工具链调用gcc等编译器时,用相同的编译参数调用extractor模块取而代之,收集源代码的所有相关信息,如AST抽象语法树、函数变量类型、预处理器操作等等。
- 对于解释型语言,因为没有编译器的存在,CodeQL会以跟踪执行的方式获取类似的信息。
使用CodeQL CLI对代码仓库运行分析后,我们就得到了一个“快照数据库”(SnapshotDatabase),这个数据库中存储了代码仓库在特定时间点(数据库建立时)的层级表示方式,包括
- AST语法树
- CFG控制流程关系
- DFG数据流向关系
在这个数据库中,代码中的每一个要素,比如函数定义(Function)、函数调用(FunctionCall)、宏调用(MacroInvocation)都是可以被检索的实体。在这些基础上,我们再编写CodeQL语句对代码进行分析。
查询包括上图查询编译部分和执行部分,我们的查询会和库一起交给编译器编译,编译成功后会进行查询,去数据库中提取数据。
参考链接:
https://github.com/ASTTeam/CodeQL#02-codeql%E5%9F%BA%E7%A1%80 https://www.sec-in.com/article/2043 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1645870 https://www.wangan.com/p/7fy7fg448fb3b026
QL语法
0x01类型 Types
override:覆写成员谓词会导致(父类)函数会被复写?
CodeQL 是一种静态类型的语言,因此每个变量都必须有一个声明的类型。类型是一组值。例如,int 类型是一组整数。注意,一个值可以属于这些集合中的多个,这意味着它可以有多个类型。
- 整型(int)
- 浮点型(float)
- 日期型(date)
- 字符型(stirng)
- 布尔型(boolean)
1)日期型(date)
编写一个简单的实例用于计算从今年9月1日到今天(11月2日)一共过了多久:
from date start, date end where start = "01/09/2021".toDate() and end = "02/11/2021".toDate() select start.daysTo(end)
2)布尔型(boolean)
布尔型变量用来存放布尔值,即false(假)或者 true(真)。
编写一个简单的例子来实现两个布尔之间的和关系:
from boolean a, boolean b where a = true and b = false select a.booleanAnd(b)
0x02谓词Predicates
谓词有点类似于其他语言中的函数,但又与函数不同,谓词用于描述构成 QL 程序的逻辑关系。确切的说,谓词描述的是给定参数与元组集合的关系。
1)无结果谓词
没有结果的谓词以predicate作为开头,剩下的语法结构类似于定义函数。这种谓词只能在where语句中使用。
一个简单的例子如下:
predicate isCity(string city) {
city = "Beijing"
or
city = "ShangHai"
}
from string city
where city = "Beijing" and isCity(city)
select city

2)结果谓词
有结果的谓词的定义类似于c/c++语言的函数定义,以返回类型替代predicate作为开头。这种谓词可以在where与select语句中使用。
一个简单的例子如下:
int addOne(int i) {
result = i + 1 and
i in [1 .. 10]
}
from int v
where v = 9
select addOne(v)

3、绑定行为与绑定集
谓词所描述的集合通常不允许是无限的,换句话说,谓词只能包含有限数量的元组(It must be possible to evaluate a predicate in a finite amount of time, so the set it describes is not usually allowed to be infinite. In other words, a predicate can only contain a finite number of tuples.)
举个简单的正例和反例:
// 正例,i被限定在1到10内,或者你也可以给i赋一个确定的值如i=1
int addOne(int i) {
result = i + 1 and
i in [1 .. 10]
}
// 反例,i是无限数量值的,此时CodeQL编译器会报错: 'i' is not bound to a value
int addOne(int i) {
result = i + 1 and
i > 0
}
1)单个绑定集
为了使上述的反例谓词能够通过编译,我们可以使用绑定集(bindingset),但是当我们去调用这个谓词时,传递的参数还是只能在有限的参数集中。
上面的反例可以修改为如下:
bindingset[i]
int addOne(int i) {
result = i + 1 and
i > 0
}
// 此时我们可以去调用这个谓词,但是需要注意传递过来的参数还是只能在有限的参数集中
from int i
where i = 1
select addOne(i)

2)多个绑定集
我们同样可以添加多个绑定集,下面是一个例子:
bindingset[x] bindingset[y]
predicate plusOne(int x, int y) {
x + 1 = y
}
这个绑定集的意思是如果x或y绑定(bound)了,那么x和y都绑定,即至少有一个参数受到约束。
如果我们想要两者都受约束,可以将例子修改一下:
bindingset[x, y]
predicate plusOne(int x, int y) {
x + 1 = y
}
那么这个谓词就变为了一个类似于校验的函数,即x+1 == y。
0x03查询(Query)
查询是CodeQL的输出。查询有两种类型,分别是
- select子句
- 查询谓词,这意味着我们可以在当前模块中定义或者从其他模块中导入
1)select子句
select子句的格式如下:
[from] /* ... variable declarations ... */ [where] /* ... logical formula ... */ select /* ... expressions ... */
其中from和where语句是可选的。我们可以在from中定义变量,在where中给变量赋值和对查询结果的过滤,最后在select中显示结果。
在select语句中我们还可以使用一些关键字:
- as关键字,后面跟随一个名字。作用相当于sql中的as,为结果列提供了一个"标签",并允许在后续的select表达式中使用它们。
- order by关键字,后面跟随一个一个结果列名。作用相当于sql中的order by,用于排序结果,并且在结果列名后可选asc(升序)或desc(降序)关键字。
一个简单的例子如下:
from int x, int y where x = 3 and y in [0 .. 2] select x, y, x * y as product, "product: " + product
2)查询谓词
查询谓词是一个非成员谓词,并在最开头使用query作为注解。它返回谓词计算结果的所有元组,下面是一个简单的示例:
query int getProduct(int x, int y) { x = 3 and y in [0 .. 2] and result = x * y }
编写查询谓词而不是select子句的好处是我们可以在代码的其他部分中调用谓词。例如,我们可以在类中的特征谓词内部调用:
query int getProduct(int x, int y) {
x = 3 and
y in [0 .. 2] and
result = x * y
}
class MultipleOfThree extends int {
MultipleOfThree() { this = getProduct(_, _) }
}
from MultipleOfThree m
select m
模块 Modules
模块的名称可以是以大写或小写字母开头的任何标识符。
.ql 或者 .qll 文件可以隐式定义模块,还可以对模块进行注释,但只能对显式模块进行注释;
文件模块 File modules
与文件名同名,文件名中的任何空格都替换为下划线
库模块Library modules:
.qll文件进行定义,可以包含任何元素,但select子句除外;
OneTwoThreeLib.qll
class OneTwoThree extends int {
OneTwoThree() {
this = 1 or this = 2 or this = 3
}
}
查询模块Query modules
.ql文件定义,可以包含任何元素;
- 无法导入查询模块
- 查询模块的命名空间中必须至少有一个查询。这通常是一个 select 子句,但也可以是一个查询谓词
OneTwoQuery.ql
import OneTwoThreeLib
from OneTwoThree ott
where ott = 1 or ott = 2
select ott
显示模块 Explicit Modules
在其他模块中中定义一个模块。这是一个显式模块;
显式模块是关键字 module 后跟模块名称,然后用大括号括起来的模块主体。“模块主体”可以包含任何元素,但 select 子句除外。
...
module M {
class OneTwo extends OneTwoThree {
OneTwo() {
this = 1 or this = 2
}
}
}
将定义一个名为 M 的显式模块。该模块的主体定义了类 OneTwo
参数化模块 Parameterized moudles
与显示模块类似,参数化模块是QL的泛型编程方法;使用关键字 module 在其他模块中定义;在名称和模块主体之间声明一个或多个参数;
module M<transformer/1 first, transformer/1 second> {
bindingset[x]
int applyBoth(int x) {
result = second(first(x))
}
}
不能直接引用参数化模块。可以通过将括在尖括号 ( < 和 > ) 中的参数传递给模块来实例化模块。实例化的参数化模块可用作模块表达式,与显式模块引用相同。
bindingset[result] bindingset[x]
int increment(int x) { result = x + 1 }
module IncrementTwice = M<increment/1, increment/1>;
select IncrementTwice::applyBoth(40) // 42
模块主体 Module bodies
- Import statements 导入语句
- 导入模块时,会将其命名空间中的所有名称(私有名称除外)引入当前模块的命名空间
- Predicates 谓词
- Types (including user-defined classes)类型(包括用户定义的类)
- Aliases 别名
- Explicit modules 显式模块
- Select clauses (only available in a query module)选择子句(仅在查询模块中可用)
内置模块 built-in modules
EquivalenceRelation 模块是一个参数化的子模块,它接受一个类型 T 和一个在 T 上的二元基本关系 base 作为参数。base 的对称和传递闭包就产生了一个在 T 上的部分等价关系。如果 T 中的每个值都出现在 base 中,那么产生的关系就是 T 上的等价关系。
class Node extends int {
Node() { this in [1 .. 6] }
}
predicate base(Node x, Node y) {
x = 1 and y = 2
or
x = 3 and y = 4
}
module Equiv = QlBuiltins::EquivalenceRelation<Node, base/2>;
from int x, int y
where Equiv::getEquivalenceClass(x) = Equiv::getEquivalenceClass(y)
该 EquivalenceRelation 模块导出一个 getEquivalenceClass 谓词;
上面的 select 子句返回以下部分等价关系:
| x | y |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 4 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
签名 Signatures
参数化模块使用签名作为其参数的类型系统。签名分为三类:谓词签名、类型签名和模块签名。
- predicate signatures:声明模块参数为谓词,谓词的返回值和参数类型必须与 signature 匹配。例如:
signature int operator(int lhs, int rhs); - type signatures:声明模块参数为类型,类型可以指定超类型和必需的成员谓词。例如:
signature class CanBePrinted { string toString(); } - module signatures:声明模块参数为模块,模块必须包含指定名称和签名的类型和谓词。例如:
signature module Arithmetic { signature int operator(int lhs, int rhs); }
别名 aliases
模块别名
module ModAlias = ModuleName;
Type别名
class是type的一种
class TypeAlias = TypeName;
import java
import semmle.code.java.dataf1ow.DataFow
import semmle.code.java.dataf1ow.FlowSource
class DNode=DataFlow:Node;
from DNode source
select source
谓词别名
可以定义非成员谓词的别名
predicate PredAlias = PredicateName/Arity;
变量Variable
- 自由变量free
- 绑定变量bound
"hello".indexOf("l") = 1 #不包含任何变量
min(float f | f in [-3 .. 3]) = -3 #仅包含绑定变量
(i + 7) * 3 instanceof int #包含一个自由变量 i
exists(float y | x.sqrt() = y) #包含一个自由变量x和一个绑定变量y
表达式 Expressions
变量引用 Variable references
特殊的变量:this、result
常量 Literals
Boolean、Integer、Float、String
Date类型需要使用toDate谓词转换
2000-01-01 00:00:01".toDate()
括号表达式Parenthesized expressions
加括号可以用来增加可读性
范围 Ranges
大于等于N,小于等于M
[N..M]
常量表达式 Set literal expressions
给集合指定具体的数值
[N1, N2, N3, N4, N5]
超级表达式Super expressions
class A extends int {
A() { this = 1 }
int getANumber() { result = 2 }
}
class B extends int {
B() { this = 1 }
int getANumber() { result = 3 }
}
class C extends A, B {
// Need to define `int getANumber()`; otherwise it would be ambiguous
int getANumber() {
result = B.super.getANumber()
}
}
from C c
select c, c.getANumber()
调用含返回值的谓词 Calls to predicates (with result)
对带有结果的谓词的调用将计算为被调用谓词的 result 变量的值。
聚合表达式(Aggregations)
通用语法格式
<aggregate>(<variable declarations> | <formula> | <expression>)
在区域声明的变量被称为聚合变量(aggregation variables)
可以在区域使用order by关键字和asc/desc关键字来限定不同的顺序,默认使用asc关键字
- count 确定聚合变量的数量
count(File f | f.getTotalNumberOfLines() > 500 | f)
- min 最小值
- max 最大值
- avg 平均值
avg(int i | i = [0 .. 3] | i)
- sum 总和
sum(int i, int j | i = [0 .. 2] and j = [3 .. 5] | i * j)
- concat 连接字符串,
<expression>必须 是string类型;concat聚合还可以采用第二个表达式,用逗号与第一个表达式分隔。第二个表达式作为分隔符插入到每个连接值之间。
concat(int i | i = [0 .. 3] | i.toString() order by i desc)
concat(int i | i = [0 .. 3] | i.toString(), "|")
- rank 此聚合获取 的
<expression>可能值并对其进行排名。
rank[4](int i | i = [5 .. 15] | i)
- 排名索引从
1开始,因此rank[0](...)没有结果。 rank[1](...)与min(...)相同。- strictconcat, strictcount, and strictsum 工作方式和
concat,count, andsum类似,不过更为严格; - unique:返回存在的唯一值
聚合计算Evaluation of aggregates
select sum(int i, int j |
exists(string s | s = "hello".charAt(i)) and exists(string s | s = "world!".charAt(j)) | i)
可能的元组: (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (0, 3), (0, 4), (0, 5), (1, 0), (1, 1), ..., (4, 5)
所有 i 值: 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4
对上述值应用聚合函数 sum 以获得最终结果 60 。
select count(string s | s = "hello" | s.charAt(_))
s.charAt(_)生成四个不同的值h, e, l, o;应用于这些值, count 查询返回 4 .
省略部分内容Omitting parts of an aggregation
1、当你要写的聚合表达式形式这样时<aggregate>(<type> v | <expression> = v | v),你可以省略<variable declarations>部分和<formula> 部分
count(int i | i = "hello".indexOf("l") | i)
count("hello".indexOf("l"))
单聚合变量可以省略
avg(int i | i = [0 .. 3] | i)
avg(int i | i = [0 .. 3])
count(int i, int j | i in [1 .. 3] and j in [1 .. 3] | 1)
count(int i, int j | i in [1 .. 3] and j in [1 .. 3])
2、当只有一个聚合变量时,可以省略部分
avg(int i | i = [0 .. 3] | i)
avg(int i | i = [0 .. 3])
3、特例,即使有多个聚合变量时,你可以在count事件中省略部分
count(int i, int j | i in [1 .. 3] and j in [1 .. 3] | 1)
count(int i, int j | i in [1 .. 3] and j in [1 .. 3])
4、你可以省略部分,但是|符号需要保留
<aggregate>(<variable declarations> | | <expression>)
max(File f | | f.getTotalNumberOfLines())
5、你可以同时省略部分和部分
count(File f | any() | 1)
count(File f | | 1)
count(File f)
单调聚合Monotonic aggregates
示例:
string getPerson() { result = "Alice" or
result = "Bob" or
result = "Charles" or
result = "Diane"
}
string getFruit(string p) { p = "Alice" and result = "Orange" or
p = "Alice" and result = "Apple" or
p = "Bob" and result = "Apple" or
p = "Charles" and result = "Apple" or
p = "Charles" and result = "Banana"
}
int getPrice(string f) { f = "Apple" and result = 100 or
f = "Orange" and result = 100 or
f = "Orange" and result = 1
}
predicate nonmono(string p, int cost) {
p = getPerson() and cost = sum(string f | f = getFruit(p) | getPrice(f))
}
language[monotonicAggregates]
predicate mono(string p, int cost) {
p = getPerson() and cost = sum(string f | f = getFruit(p) | getPrice(f))
}
from string variant, string person, int cost
where variant = "default" and nonmono(person, cost) or
variant = "monotonic" and mono(person, cost)
select variant, person, cost
order by variant, person
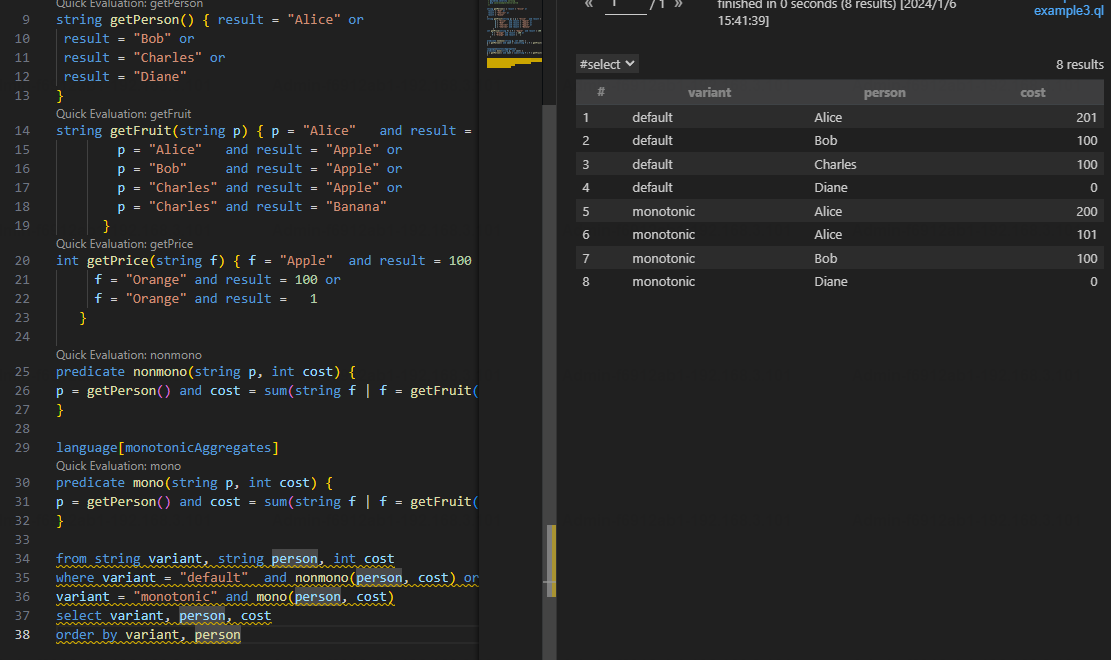
结果
| variant | person | cost |
|---|---|---|
| default 违约 | Alice 爱丽丝 | 201 |
| default 违约 | Bob | 100 |
| default 违约 | Charles 查尔斯 | 100 |
| default 违约 | Diane 黛 安 娜 | 0 |
| monotonic 单调 | Alice 爱丽丝 | 101 |
| monotonic 单调 | Alice 爱丽丝 | 200 |
| monotonic 单调 | Bob | 100 |
| monotonic 单调 | Diane 黛 安 娜 | 0 |
Any
any(<variable declarations> | <formula> | <expression>)
formula和expression可选;
| Expression 表达 | Values 值 |
|---|---|
| any(File f) | all File |
| s in the database 数据库中的所有 File | |
| S | |
| any(Element e | e.getName()) |
| s in the database 数据库中所有 Element | |
| S 的名称 | |
| any(int i | i = [0 .. 3]) |
| , 1 | |
| , 2 | |
| , and 3 | |
| 整数 、 0 | |
| 、 1 | |
| 、2 | |
| 和 3 | |
| any(int i | i = [0 .. 3] |
| , 1 | |
| , 4 | |
| , and 9 | |
| 整数 、 0 | |
| 、 1 | |
| 、4 | |
| 和 9 |
一元操作符(Unary operations)
一个一元操作由一个一元操作符+一个表达式构成
-6.28
+(10 - 4)
+avg(float f | f = 3.4 or f = -9.8)
-sum(int i | i in [0 .. 9] | i * i)
二元操作符(Binary operations)
一个二元操作由一个表达式+一个二元操作符+一个表达式构成
5 % 2
(9 + 1) / (-2)
"Q" + "L"
2 * min(float f | f in [-3 .. 3])
binary operators in QL:
| Name | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Addition/concatenation | + |
| Multiplication | * |
| Division | / |
| Subtraction | - |
| Modulo | % |
类型转换(casts)
后缀和前缀两种
where t.(Class).getASupertype().hasName("List")
where ((Class)t).getASupertype().hasName("List")
临时表达式(Don’t-care 表达式)
from string s
where s = "hello".charAt(_)
select s
等价于:
from string s,int i
where s = "hello".charAt(i)
select s
公式Formulas
官方文档
https://codeql.github.com/docs/ql-language-reference/formulas/
-
Comparisons 比较
-
Order 顺序运算符
-
, >=, <, <=
-
相等运算符
-
=, !=
-
对于表达式
A和B,如果存在一对相同的值(一个来自 ,一个来自AB),则公式A = B成立。换言之,A并且B至少有一个共同的值。 -
1 != [1..2] 成立,因为 1!=2
-
1 = [1..2] 成立,因为 1=1
-
not 1 = [1..2] 不成立
-
1 != none 不成立
-
1 = none 不成立
-
not 1=none 成立
-
Type checks 类型检查
-
instanceof
-
Range checks 范围检查
-
in
predicate getFoo(int i){
i in [1..9]
}
量化公式 Quantified formulas
- exists exists( | )
- forall forall( | <formula 1> | <formula 2>)
- forex forex( | <formula 1> | <formula 2>
逻辑连接词
默认优先级:not、if then else、and、or、implies
not
from File f
where not f.getFileType().isHtml()
select f
if ... then ... else
string visibility(Class c){
if c.isPublic()
then result = "public"
else result = "private"
}
and
from File f
where f.getExtension() = "js" and
f.getNumberOfLinesOfCode() < 200
select f
or
class OneTwoThree extends int {
OneTwoThree() {
this = 1 or this = 2 or this = 3
}
}
implies
A implies B
(not A) or B
注解 Annotations
某些注释作用于实体本身,而其他注释则作用于实体的特定名称:
- 实体:abstract
,cached,external,transient,override,pragma,language, andbindingset - 名称:deprecated
,library,private,final, andquery