树形DP
1、没有上司的舞会(选或不选)
题目描述
某大学有 \(n\) 个职员,编号为 \(1\ldots n\)。
他们之间有从属关系,也就是说他们的关系就像一棵以校长为根的树,父结点就是子结点的直接上司。
现在有个周年庆宴会,宴会每邀请来一个职员都会增加一定的快乐指数 \(r_i\),但是呢,如果某个职员的直接上司来参加舞会了,那么这个职员就无论如何也不肯来参加舞会了。
所以,请你编程计算,邀请哪些职员可以使快乐指数最大,求最大的快乐指数。
输入格式
输入的第一行是一个整数 \(n\)。
第 \(2\) 到第 \((n + 1)\) 行,每行一个整数,第 \((i+1)\) 行的整数表示 \(i\) 号职员的快乐指数 \(r_i\)。
第 \((n + 2)\) 到第 \(2n\) 行,每行输入一对整数 \(l, k\),代表 \(k\) 是 \(l\) 的直接上司。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数代表最大的快乐指数。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
7
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 3
2 3
6 4
7 4
4 5
3 5
样例输出 #1
5
提示
数据规模与约定
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,保证 \(1\leq n \leq 6 \times 10^3\),\(-128 \leq r_i\leq 127\),\(1 \leq l, k \leq n\),且给出的关系一定是一棵树。
思路
- 令
dp[u][0]表示以u为根节点,不选u的最大快乐指数 - 令
dp[u][1]表示以u为根节点,选u的最大快乐指数 - 通过
dfs自根节点向下递,再从叶子节点网上归,传递转移最大值
代码
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
input = lambda: sys.stdin.readline().strip()
r1 = lambda: int(input())
r2 = lambda: map(int, input().split())
r3 = lambda: [*map(int, input().split())]
def solve():
n = r1()
a = [0] * (n + 1)
for i in range(1,n + 1):
a[i] = r1()
g = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
st = [0] * (n + 1)
for _ in range(n - 1):
u,v = r2()
g[v].append(u)
st[u] = 1
root = 0
for i in range(1,n + 1):
if not st[i]:
root = i
break
dp = [[0,0] for _ in range(n + 1)]
def dfs(u):
dp[u][0] = 0
dp[u][1] = a[u]
for v in g[u]:
dfs(v)
dp[u][0] += max(dp[v][0],dp[v][1])
dp[u][1] += dp[v][0]
dfs(root)
print(max(dp[root][0],dp[root][1]))
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = 1
for _ in range(t):
solve()
2.Tree Painting(换根)
题面翻译
给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树 初始全是白点
要求你做 \(n\) 步操作,每一次选定一个与一个黑点相隔一条边的白点,将它染成黑点,然后获得该白点被染色前所在的白色联通块大小的权值。
第一次操作可以任意选点。
求可获得的最大权值。
题目描述
You are given a tree (an undirected connected acyclic graph) consisting of $ n $ vertices. You are playing a game on this tree.
Initially all vertices are white. On the first turn of the game you choose one vertex and paint it black. Then on each turn you choose a white vertex adjacent (connected by an edge) to any black vertex and paint it black.
Each time when you choose a vertex (even during the first turn), you gain the number of points equal to the size of the connected component consisting only of white vertices that contains the chosen vertex. The game ends when all vertices are painted black.
Let's see the following example:
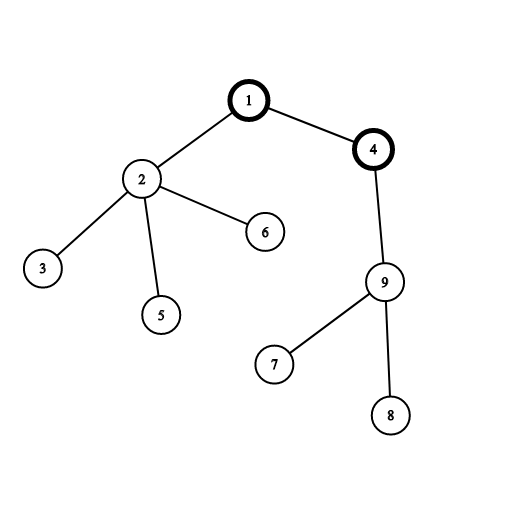
Vertices $ 1 $ and $ 4 $ are painted black already. If you choose the vertex $ 2 $ , you will gain $ 4 $ points for the connected component consisting of vertices $ 2, 3, 5 $ and $ 6 $ . If you choose the vertex $ 9 $ , you will gain $ 3 $ points for the connected component consisting of vertices $ 7, 8 $ and $ 9 $ .
Your task is to maximize the number of points you gain.
输入格式
The first line contains an integer $ n $ — the number of vertices in the tree ( $ 2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5 $ ).
Each of the next $ n - 1 $ lines describes an edge of the tree. Edge $ i $ is denoted by two integers $ u_i $ and $ v_i $ , the indices of vertices it connects ( $ 1 \le u_i, v_i \le n $ , $ u_i \ne v_i $ ).
It is guaranteed that the given edges form a tree.
输出格式
Print one integer — the maximum number of points you gain if you will play optimally.
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
9
1 2
2 3
2 5
2 6
1 4
4 9
9 7
9 8
样例输出 #1
36
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
5
1 2
1 3
2 4
2 5
样例输出 #2
14
提示
The first example tree is shown in the problem statement.
思路
- 理解题意,每次将一个白点涂成黑点加上的权值就是以这个点为根的子树大小,先用
dfs求以1为根的各节点尺寸大小 - 考虑
换根dp,将u、v互换,size[u],size[v] = n - size[v],n,其余的都没改变,那么对答案的影响也就是u、v的尺寸大小变换。 - python
dfs会爆栈与内存,改成bfs即可!
代码(dfs)
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
input = lambda: sys.stdin.readline().strip()
r1 = lambda: int(input())
r2 = lambda: map(int, input().split())
r3 = lambda: [*map(int, input().split())]
def solve():
n = r1()
g = [[] for _ in range(n + 1)]
for _ in range(n - 1):
u, v = r2()
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
size = [0] * (n + 1)
def dfs(u, fa):
size[u] = 1
for v in g[u]:
if v == fa:
continue
dfs(v, u)
size[u] += size[v]
dfs(1,0)
total = 0
for i in range(1,n + 1):
total+= size[i]
ans = 0
def reroot(u,fa,total):
nonlocal ans
for v in g[u]:
if v == fa:
continue
cnt1,cnt2 = size[u],size[v]
size[u],size[v] = n - size[v],n
ans = max(ans,total - (cnt2 - size[u]))
reroot(v,u,total - (cnt2 - size[u]))
size[u],size[v] = cnt1,cnt2
reroot(1,0,total)
print(ans)
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = 1
for _ in range(t):
solve()
3.城市环路
题目描述
一座城市,往往会被人们划分为几个区域,例如住宅区、商业区、工业区等等。
B 市就被分为了以下的两个区域——城市中心和城市郊区。在这两个区域的中间是一条围绕 B 市的环路,环路之内便是 B 市中心。
整个城市可以看做一个 \(n\) 个点,\(n\) 条边的单圈图(保证图连通),唯一的环便是绕城的环路。保证环上任意两点有且只有 \(2\) 条简单路径互通。图中的其它部分皆隶属城市郊区。
现在,有一位名叫 Jim 的同学想在 B 市开店,但是任意一条边的 \(2\) 个点不能同时开店,每个点都有一定的人流量,第 \(i\) 个点的人流量是 \(p_i\),在该点开店的利润就等于 \(p_i×k\),其中 \(k\) 是一个常数。
Jim 想尽量多的赚取利润,请问他应该在哪些地方开店?
输入格式
第一行一个整数 \(n\),代表城市中点的个数。城市中的 \(n\) 个点由 \(0 \sim n-1\) 编号。
第二行有 \(n\) 个整数,第 \((i + 1)\) 个整数表示第 \(i\) 个点的人流量 \(p_i\)。
接下来 \(n\) 行,每行有两个整数 \(u, v\),代表存在一条连接 \(u\) 和 \(v\) 的道路。
最后一行有一个实数,代表常数 \(k\)。
输出格式
输出一行一个实数代表答案,结果保留一位小数。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4
1 2 1 5
0 1
0 2
1 2
1 3
2
样例输出 #1
12.0
提示
数据规模与约定
- 对于 \(20\%\) 的数据,保证 \(n \leq 100\)。
- 另有 \(20\%\) 的数据,保证环上的点不超过 \(2000\) 个。
- 对于 \(100\%\) 的数据,保证 \(1 \leq n \leq 10^5\),\(1 \leq p_i \leq 10^4\),\(0 \leq u, v < n\),\(0 \leq k \leq 10^4\),\(k\) 的小数点后最多有 \(6\) 位数字。
思路
-
找到树上的基环,可用并查集,拓扑排序,dfs
-
在基环上的取相邻两点,将环断开成普通树,再利用选或不选的常规树形DP思路即可
代码
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
input = lambda: sys.stdin.readline().strip()
r1 = lambda: int(input())
r2 = lambda: map(int, input().split())
r3 = lambda: [*map(int, input().split())]
def solve():
n = r1()
a = r3()
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
fa = [i for i in range(n)]
def find(x):
if x != fa[x]:
fa[x] = find(fa[x])
return fa[x]
p1, p2 = 0, 0
for _ in range(n):
u, v = r2()
fu, fv = find(u), find(v)
if fu == fv:
p1, p2 = u, v
continue
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
fa[fv] = fu
p = float(input())
dp = [[0, 0] for _ in range(n)]
def dfs(u, fa):
dp[u][0], dp[u][1] = 0,a[u]
for v in g[u]:
if v == fa:
continue
dfs(v,u)
dp[u][0] += max(dp[v][0],dp[v][1])
dp[u][1] += dp[v][0]
dfs(p1,-1)
ans = dp[p1][0]
dfs(p2,-1)
ans = max(ans,dp[p2][0])
print("%.1f" % (ans * p))
if __name__ == "__main__":
t = 1
for _ in range(t):
solve()