日期-时间
LocalDateTime
/**
* LocalDateTime
* 获取本地日期时间对象:年-月-日T时:分:秒.纳秒
* LocalDateTime.now();获取当前日期
* LocalDateTime.of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth, int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond);获取指定日期
* 注意:LocalDateTime()修改日期,不会将原有日期修改,会返回一个新的日期对象
* 注意前缀
* with:直接修改某个信息
* plus:将某个信息添加多少
* minus:将某个信息减多少
* to:转换为某个日期或这时间对象
*
* isAfter():判断某个时间是否在某一时间之后
* isBefore():判断某个时间是否在某一时间之前
* equals():判断两个时间是否相等
*/
@Test
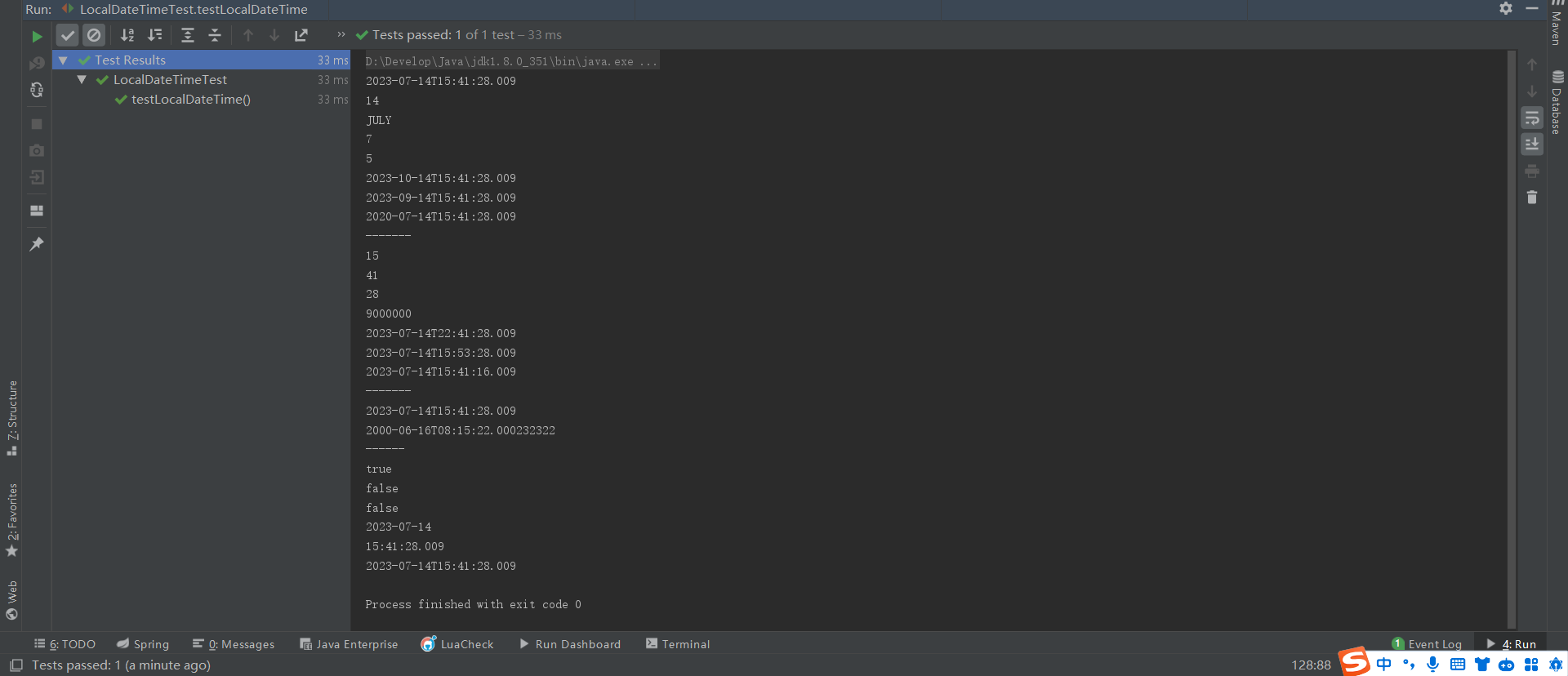
void testLocalDateTime(){
//获取本地日期和时间对象:年-月-日T时:分:秒.纳秒 2023-07-14T15:21:00.524
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime of = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 06, 16, 8, 15, 22, 232322);
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(now.getDayOfMonth());//某月的第几天
System.out.println(now.getMonth());//某月英文
System.out.println(now.getMonthValue());//某月的数值
System.out.println(now.getDayOfWeek().getValue());//星期几
System.out.println(now.withMonth(10));//修改月份为10,并且返回这个对象
System.out.println(now.plusMonths(2));//月份添加2
System.out.println(now.minusYears(3));//年份减少3
System.out.println("-------");
System.out.println(now.getHour());//获取当前小时
System.out.println(now.getMinute());//获取当前分钟
System.out.println(now.getSecond());//获取当前秒数
System.out.println(now.getNano());//获取当前纳秒
System.out.println(now.withHour(22));//修改小时为22
System.out.println(now.plusMinutes(12));//分钟加12
System.out.println(now.minusSeconds(12));//秒数减12
System.out.println("-------");
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(of);
System.out.println("------");
System.out.println(now.isAfter(of));
System.out.println(now.isBefore(of));
System.out.println(now.equals(of));
LocalDate localDate = now.toLocalDate();//转换为日期对象
System.out.println(localDate);
LocalTime localTime = now.toLocalTime();//转换为时间对象
System.out.println(localTime);
}
结果如下:
2023-07-14T15:41:28.009
14
JULY
7
5
2023-10-14T15:41:28.009
2023-09-14T15:41:28.009
2020-07-14T15:41:28.009
-------
15
41
28
9000000
2023-07-14T22:41:28.009
2023-07-14T15:53:28.009
2023-07-14T15:41:16.009
-------
2023-07-14T15:41:28.009
2000-06-16T08:15:22.000232322
------
true
false
false
2023-07-14
15:41:28.009
2023-07-14T15:41:28.009
Process finished with exit code 0
LocalDate
/**
* LocalDate
* 获取本地日期对象:年-月-日
* LocalDate.now();获取当前日期
* LocalDate.of(year,month,dayOfMonth);获取指定日期
* 注意:LocalDate()修改日期,不会将原有日期修改,会返回一个新的日期对象
* 注意前缀
* with:修改某个信息
* plus:将某个信息添加多少
* minus:将某个信息减多少
* isAfter():判断某个日期是否在某一日期之后
* isBefore():判断某个日期是否在某一日期之前
* equals():判断两个日期是否相等
*/
@Test
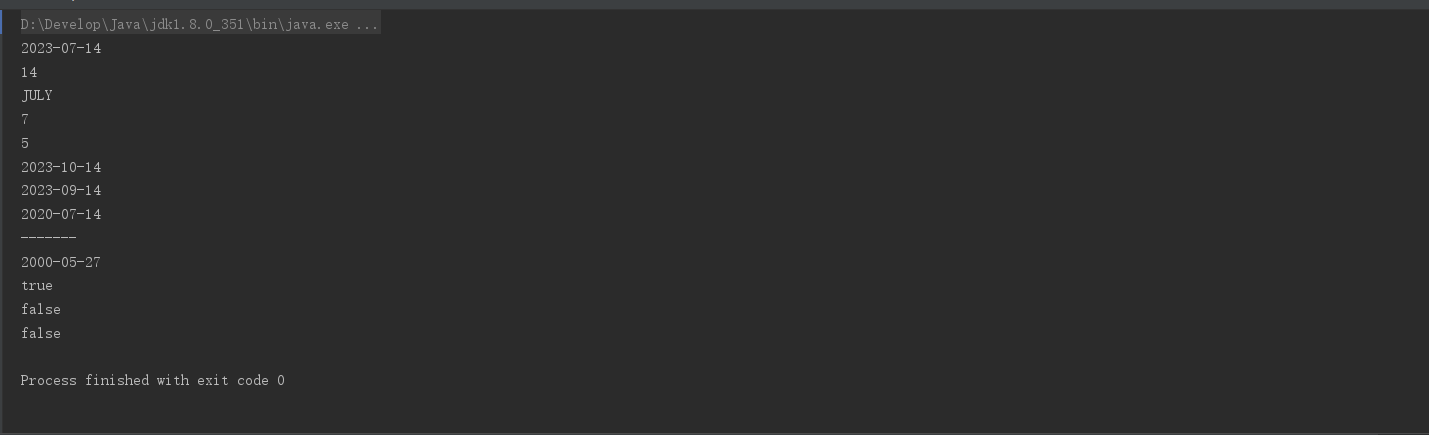
void testLocalDate(){
//获取本地日期对象:年-月-日
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println(now);//2023-07-14
System.out.println(now.getDayOfMonth());//某月的第几天
System.out.println(now.getMonth());//某月英文
System.out.println(now.getMonthValue());//某月的数值
System.out.println(now.getDayOfWeek().getValue());//星期几
System.out.println(now.withMonth(10));//修改月份为10,并且返回这个对象
System.out.println(now.plusMonths(2));//月份添加2
System.out.println(now.minusYears(3));//年份减少3
System.out.println("-------");
LocalDate of = LocalDate.of(2000, 5, 27);//获取指定的日期对象
System.out.println(of);
System.out.println(now.isAfter(of));
System.out.println(now.isBefore(of));
System.out.println(now.equals(of));
}
结果如下:
LocalTime
/**
*
* LocalTime
* 获取本地时间对象:时:分:秒.纳秒
* LocalTime.now();获取当前时间
* LocalTime.of(int hour, int minute, int second, int nanoOfSecond);获取指定时间
* 注意:LocalTime()修改时间,不会将原有时间修改,会返回一个新的时间对象
* 注意前缀
* with:直接修改某个信息
* plus:将某个信息添加多少
* minus:将某个信息减多少
* isAfter():判断某个时间是否在某一时间之后
* isBefore():判断某个时间是否在某一时间之前
* equals():判断两个时间是否相等
*/
@Test
void testLocalTime(){
//获取本地时间对象:时:分:秒.纳秒
LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();
LocalTime of = LocalTime.of(22, 30, 33, 6666);
System.out.println(now);//获取当前时间
System.out.println(now.getHour());//获取当前小时
System.out.println(now.getMinute());//获取当前分钟
System.out.println(now.getSecond());//获取当前秒数
System.out.println(now.getNano());//获取当前纳秒
System.out.println(now.withHour(22));//修改小时为22
System.out.println(now.plusMinutes(12));//分钟加12
System.out.println(now.minusSeconds(12));//秒数减12
System.out.println("------");
System.out.println(of);
System.out.println(now.isAfter(of));//now在of之前?
System.out.println(now.isBefore(of));//now在of之后?
System.out.println(now.equals(of));//now和of是否相等
}
结果如下:

ZoneId ZonedDateTime
/**
* ZoneId ZonedDateTime
* 时区
* ZonedDateTime与LocalDateTime中获取日期时间的方法基本一致
*/
@Test
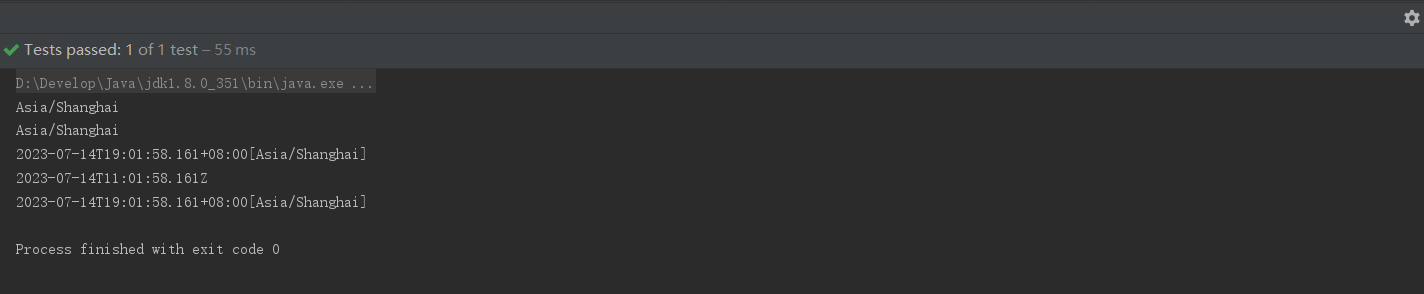
void testZoneId(){
ZoneId zoneId = ZoneId.systemDefault();
System.out.println(zoneId.getId());//获取当前系统默认时区
System.out.println(zoneId);//相当与调用该toString()方法,在这个方法中又调用了getId();
// System.out.println(ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds());//获取Java支持的全部时区Id
ZoneId zoneId1 = ZoneId.of("America/New_York");//将某个时区id封装成ZoneId对象
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(zoneId);//获取某个时区的ZonedDateTime对象
System.out.println(now);
ZonedDateTime now1 = ZonedDateTime.now(Clock.systemUTC());//世界标准时间
System.out.println(now1);
System.out.println(ZonedDateTime.now());//系统默认时区的时间
}
Instant
/**
* Instant
* 通过获取Instant的对象可以拿到此刻的时间,该时间由两部分组成:从1970-01-01 00:00:00开始走到此刻的总秒数+不够1秒的纳秒数
*
* 通常用来做代码的性能分析,或者记录用户的操作时间点
* 作用:可以用来记录代码的执行时间,或用于记录用户操作的某个事件的时间点
*/
@Test
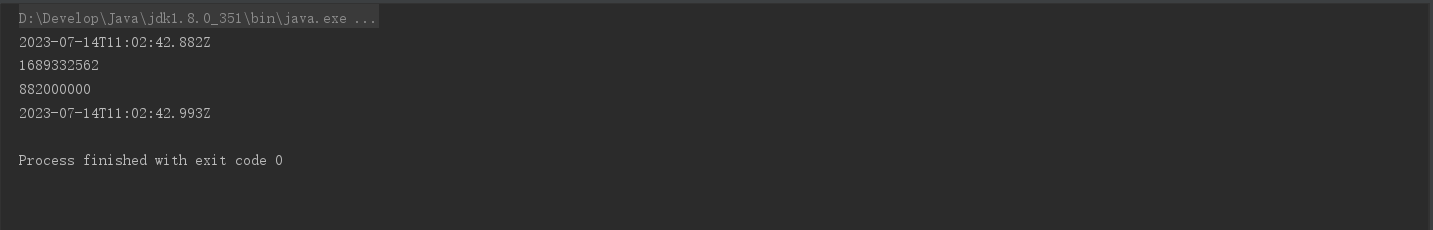
void testInstant(){
Instant now = Instant.now();//不可变对象
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(now.getEpochSecond());//获取总秒数
System.out.println(now.getNano());//不够一秒的纳秒数
System.out.println(now.plusMillis(111));//纳秒加111
}
DateTimeFormatter
/**
* DateTimeFormatter
* 时间格式化器
*/
@Test
void testDateTimeFormatter(){
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");//创建时间格式化器对象
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter);
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();//对时间进行格式化
System.out.println(now);
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(now));//dateTimeFormatter对象对时间对象now进行格式化
System.out.println(now.format(dateTimeFormatter));//now对象使用dateTimeFormatter时间格式化器进行格式化
// 解析时间2000年03月23日 17:14:07
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse("2000年03月23日 17:14:07", dateTimeFormatter);
System.out.println(parse);
}
Period
/**
* Period(一段时期)LocalDate
* 用于计算两个LocalDate对象 香肠的年数、月数、天数
*/
@Test
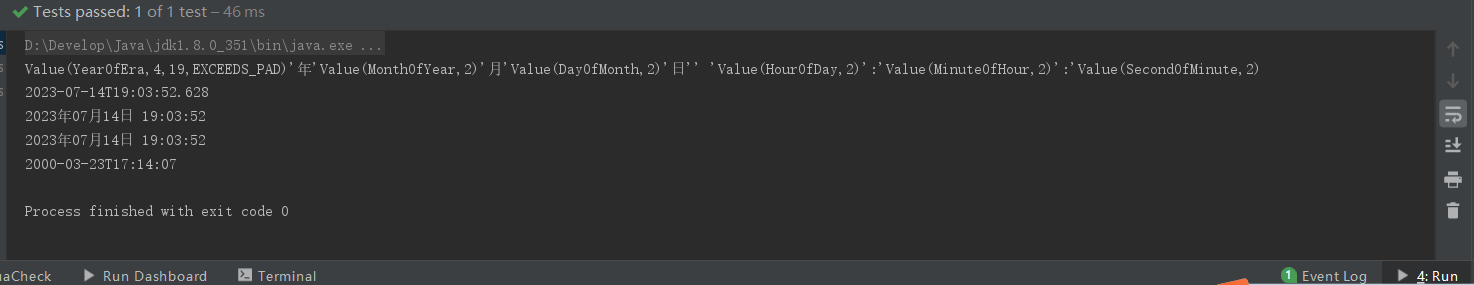
void testPeriod(){
LocalDate start = LocalDate.of(2000, 1, 1);
LocalDate end = LocalDate.of(2020, 8, 12);
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now();
Period between = Period.between(start, end);
System.out.println(between);
System.out.println(between.getYears());//间隔年份
System.out.println(between.getMonths());//间隔月份
System.out.println(between.getDays());//间隔天数
System.out.println();
}
Duration
/**
* Duration(持续时间)LocalTime、LocalDateTime、Instant
* 用于计算两个时间对象相差的天数、小时数、分数、秒数、纳秒数;支持LocalTime、LocalDateTime、Instant等时间
*
*/
@Test
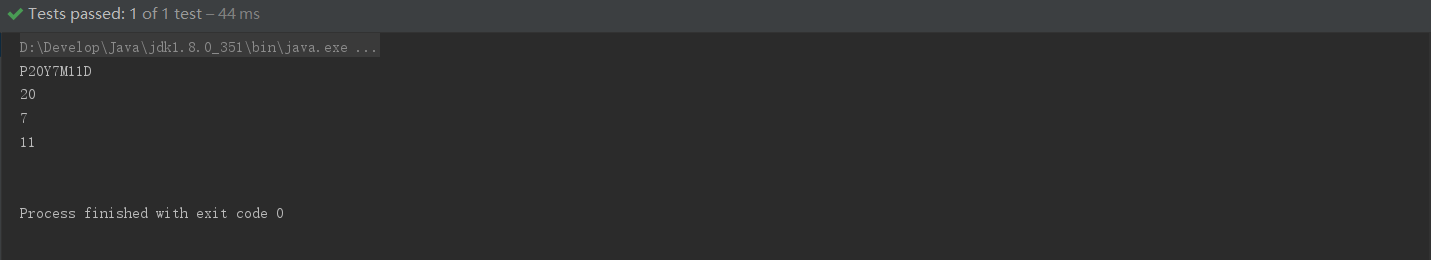
void testDuration(){
LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2000, 06, 16, 8, 15, 22, 232322);
LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.of(2011, 9, 22, 22, 17, 22, 64454);
Duration between = Duration.between(start, end);
System.out.println(between);
System.out.println(between.toDays());//天数
System.out.println(between.toHours());//小时
System.out.println(between.toMinutes());//分钟
System.out.println(between.getSeconds());
System.out.println(between.toMillis());//毫秒
System.out.println(between.toNanos());//纳秒
System.out.println(between.getNano());
}
Arrays(数组)
int[] arr={2,31,5,88,44,22,66,3};
arr.toString()//返回数组的内容
int[] ints = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr, 0, arr.length);//拷贝arr数组中内容到ints中
int[] ints1 = Arrays.copyOf(arr, 10);//将数组arr中内容拷贝到ints1中并指定长度
Arrays.setAll(ints1, new IntUnaryOperator() {//将ints1中的数值扩大两倍
@Override
public int applyAsInt(int operand) {.
return ints1[operand]*2;
}
});
Arrays.sort(arr);//排序,升序
Arrays.setAll(ints1, operand->ints1[operand]*3);//lambd
Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式
注意:Lambda表达式并不是说能简化所有的匿名内部类的方法,只能简化函数式接口的匿名内部类。有且仅有一个抽相关方法的接口成为为函数式接口,
注意:大部分函数式接口,上面会有一个@FunctionalInterface的注解,有该注解的接口就必定是函数式接口
参数类型可以不写,
如果只有一个参数,参数类型可以省略,同时()也可以省略
如果Lambda表达式中的方法体代码只有一行代码,可以省略大括号不写,同时要省略分号!此时,如果这行代码是return语句,也必须去掉return不写
interface Animal{
public void run();
}
@Test
void test1(){
Animal animal = new Animal() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("我是Animal");
}
};
animal.run();
Animal a =( () -> System.out.println("我是Animal"));//Lambda表达式对上述简写的
a.run();
}
interface TestLa{
public int test(int a,int b);
}
@Test
void test2(){
int a=39,b=33;
TestLa testLa = new TestLa() {//匿名内部类
@Override
public int test(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
};
System.out.println(testLa.test(a,b));
TestLa testLa1= (d,f)->d+f;//lambda表达式
System.out.println(testLa.test(33, 22));
}
方法引用
静态方法引用
类名::静态方法
使用场景
如果某个Lambda表达式里只调用一个静态方法,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用静态方法引用!
class CompareByData{
public static int compareByAge(People o1,People o2){
return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();
}
}
@Test
void test3(){
People[] p=new People[4];
p[0] = new People("a", "a", "a", 131);
p[1] = new People("b", "a", "a", 14);
p[2] = new People("c", "a", "a", 1153);
p[3] = new People("d", "a", "a", 1213);
//根据年龄进行升序排序
Arrays.sort(p,(o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
// Arrays.sort(p, Comparator.comparingInt(People::getAge));//简写
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));
Arrays.sort(p,CompareByData::compareByAge);//静态方法引用
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));
}
实例方法引用
对象名::实例方法
使用场景
如果某个Lambda表达式里只有调用一个实例方法,并且前后参数的形式一致,就可以使用实例方法引用。
class CompareByData{
public static int compareByAge(People o1,People o2){
return o2.getAge()-o1.getAge();
}
public int compareByAgeDesc(People o1,People o2){
return o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
}
}
@Test
void test3(){
People[] p=new People[4];
p[0] = new People("a", "a", "a", 131);
p[1] = new People("b", "a", "a", 14);
p[2] = new People("c", "a", "a", 1153);
p[3] = new People("d", "a", "a", 1213);
//根据年龄进行升序排序
Arrays.sort(p,(o1,o2)->o1.getAge()-o2.getAge());
// Arrays.sort(p, Comparator.comparingInt(People::getAge));//简写
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));
Arrays.sort(p,CompareByData::compareByAge);//静态方法引用
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));
CompareByData compareByData = new CompareByData();
//升序
Arrays.sort(p,compareByData::compareByAgeDesc);//实例方法引用
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(p));
}
特定类型方法引用
类型::方法
使用场景
如果某个Lambda表达式里只是调用一个实例方法,并且前面参数列表中的第一个参数是作为方法的主调,后面所有参数都是作为该实例方法的入参的,则此时就可以使用特定类型的方法引用。
@Test
void test4(){
String[] names = {"Alice", "bob", "carlie", "bovid", "Eve", "arank", "Grace", "Henry"};
// 排序(默认按照首字符编号进行升序排序)
Arrays.sort(names);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));//[Alice, Eve, Grace, Henry, arank, bob, bovid, carlie]
System.out.println();
// 忽略大小写
/* Arrays.sort(names, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2);//忽略大小写
}
});
Arrays.sort(names,(o1,o2)->o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2));//简写*/
Arrays.sort(names,String::compareToIgnoreCase);//特定类型方法引用
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(names));
}
构造器引用
类名::new
使用场景
如果某个Lambda表达式里只是在创建对象,并且前后参数情况一致,就可以使用构造器引用。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class TestCase {
@Test
void test1(){
Create create = new Create() {//一般引用方式
@Override
public People testPeople(String name, int age) {
return new People(name, age);
}
};
System.out.println(create.testPeople("a",22).toString());
Create create2 =People::new;//构造器引用
System.out.println(create.testPeople("b",33).toString());
}
}
interface Create{
People testPeople(String name,int age);
}
class People{
private String name;
private int age;
public People() {
}
public People(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
stream流
链式编程
stream()://创建流 map集合先转换为单列集合再创建流
Stream.of(arr):Stream<T> of(T t)//数组创建流的方法
Arrays.stream(arr)://数组创建流的方法
distinct()://避免重复
filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)://过滤器
map(Function<T, R> mapper)`: 该方法将流中的每个元素通过给定的函数进行映射,生成一个新的流。
forEach(Consumer<? super T> action)://循环遍历-终结操作
详细
filter(Predicate<T> predicate): 该方法用于过滤流中的元素,只保留满足给定条件的元素。map(Function<T, R> mapper): 该方法将流中的每个元素通过给定的函数进行映射,生成一个新的流。flatMap(Function<T, Stream<R>> mapper): 该方法将流中的每个元素通过给定的函数进行映射,并将结果流扁平化为一个新的流。distinct(): 该方法用于去除流中的重复元素,保留唯一的元素。sorted()和sorted(Comparator<T> comparator):sorted()方法用于对流中的元素进行自然排序,要求元素实现Comparable接口;sorted(Comparator<T> comparator)则用于根据给定的比较器对流中的元素进行排序。limit(long maxSize): 该方法用于截断流,保留前面指定数量的元素。skip(long n): 该方法用于跳过流中的前 n 个元素,返回一个新的流。forEach(Consumer<T> action): 该方法对流中的每个元素执行给定的操作。collect(Collector<T, A, R> collector): 该方法将流中的元素收集到一个结果容器中,使用给定的收集器。reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)和reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator):reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)用于将流中的元素逐个进行累积操作;reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)则允许指定一个初始值。anyMatch(Predicate<T> predicate)、allMatch(Predicate<T> predicate)和noneMatch(Predicate<T> predicate): 这三个方法分别用于判断流中是否存在任意满足、全部满足或没有满足给定条件的元素。findFirst()和findAny():findFirst()用于返回流中的第一个元素;findAny()则返回流中的任意一个元素。count(): 该方法用于返回流中元素的数量。
authors.stream()//匿名内部类形式
.distinct()
.filter(new Predicate<Author>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Author author) {
return author.getAge()<18;
}
})
.forEach(new Consumer<Author>() {
@Override
public void accept(Author author) {
System.out.println(author.getName());
}
});
authors.stream()//lambda简写形式
.distinct()
.filter(author -> author.getAge()<18)
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
Map集合
/**
* map集合先转换为单列集合再创建流
*/
private static void test03() {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a",15);
map.put("b",22);
map.put("c",26);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map.entrySet();//转换为单列
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> stream = entries.stream();//创建流
stream.filter(new Predicate<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
@Override
public boolean test(Map.Entry<String, Integer> stringIntegerEntry) {
return stringIntegerEntry.getValue()<23;
}
}).forEach((ss)-> System.out.println(ss));
}
中间操作
filter
/***
* filter
* 获取年龄小于20的作家年龄和名字
*/
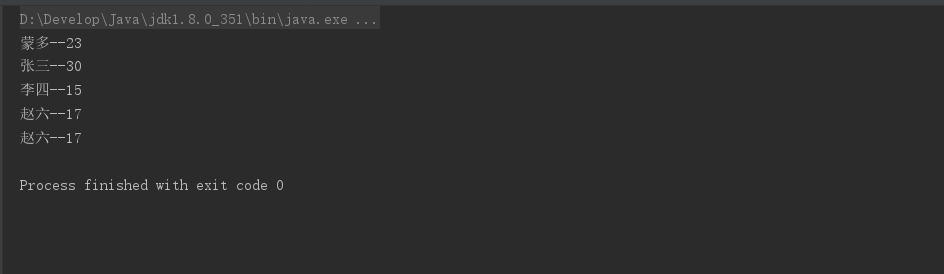
private static void test06() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.filter(author -> author.getAge()<20)//查询年龄小于20的
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()+"--"+author.getName()));
}
map
map(Function<T, R> mapper): 该方法将流中的每个元素通过给定的函数进行映射,生成一个新的流。
/**
* map
* 打印所有作家的姓名
*/
private static void test07() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getName()+"--"+author.getAge())//转换为字符串返回
.forEach(a-> System.out.println(a));
}
distinct
distinct(): 该方法用于去除流中的重复元素,保留唯一的元素。
/**
* distinct 去除重复元素
*
*/
private static void test08() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()//去除重复元素
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
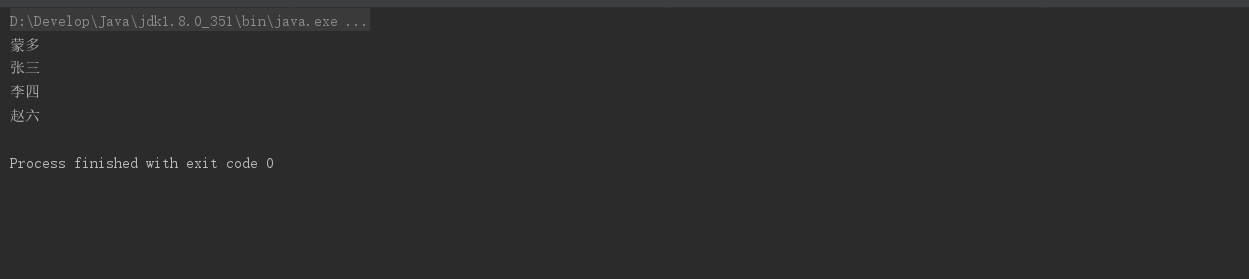
sorted
排序
sorted() 和 sorted(Comparator<T> comparator): sorted() 方法用于对流中的元素进行自然排序,要求元素实现 Comparable 接口;sorted(Comparator<T> comparator) 则用于根据给定的比较器对流中的元素进行排序。
/**
* sorted 排序
* 对流中的元素按照年龄进行排序,要求不要有重复的元素
*/
private static void test09() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.distinct()
.sorted((a,b)->a.getAge()-b.getAge())//排序,传入对象a,b,然后通过对象获取年龄,通过对象获取年龄相减的顺序进行排序,前后一致升序,不一致降序
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()));
}
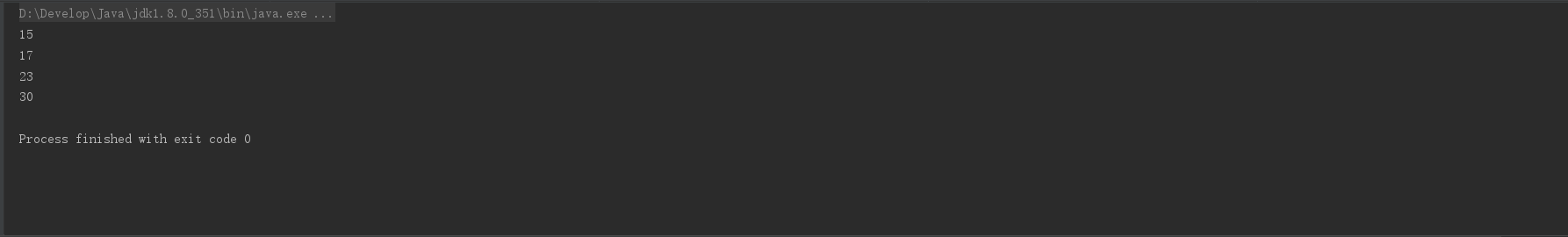
limit
limit(long maxSize): 该方法用于截断流,保留前面指定数量的元素。
/**
* limit
* 保留指定数量元素
*/
private static void test10() {
//获取前三个姓名
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.limit(3)//获取前三个姓名
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
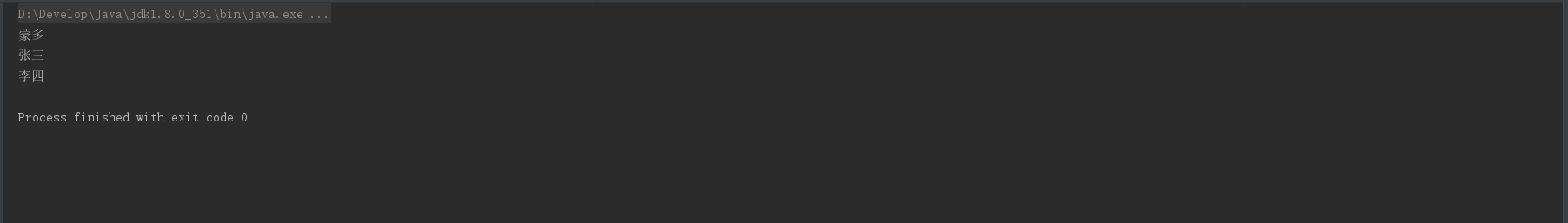
skip
skip(long n): 该方法用于跳过流中的前 n 个元素,返回一个新的流。
/**
* skip 跳过几个元素
*/
private static void test11() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
// 跳过年龄最小的
authors.stream()
.sorted((a,b)->a.getAge()-b.getAge())//找出从小到大排列
.skip(1)//跳过第一个
.forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()+"--"+author.getAge()));
}
flatMap
flatMap(Function<T, Stream<R>> mapper): 该方法将流中的每个元素通过给定的函数进行映射,并将结果流扁平化为一个新的流。
/**
* flatMap
* 可以返回多个对象
*/
private static void test12() {
//打印所有书籍的名字并去重
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.forEach(a-> System.out.println(a.getName()));
}
/**
* flatMap
* 可以返回多个对象
*/
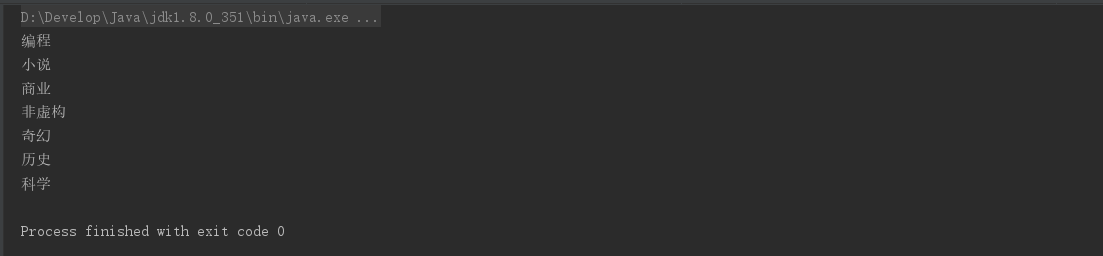
private static void test13() {
//打印现有数据的所有分类,要求去重,
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
authors.stream()
.flatMap(author -> author.getBooks().stream())
.distinct()
.flatMap(author -> Arrays.stream(author.getCategory().split(",")))
.distinct()
.forEach(a-> System.out.println(a));
}
终结操作
forEach
forEach(Consumer<T> action): 该方法对流中的每个元素执行给定的操作。
/**
* forEach
* 对流中的每个元素执行给定的操作。
*/
private static void test14() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
// 获取所有作家的姓名
authors.stream().forEach(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}

count
count(): 该方法用于返回流中元素的数量。
/**
* count
* 返回元素中的个数
*/
private static void test15() {
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
// 获取所有作家的姓名
long count = authors.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
}

collect
collect(Collector<T, A, R> collector): 该方法将流中的元素收集到一个结果容器中,使用给定的收集器。
/**
* collect
*/
private static void test17() {
//获取所有存放所有作者名字的集合
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
List<String> collect = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}

/**
* collect
*/
private static void test18() {
//获取所有存放所有作者名字的集合
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Set<String> collect = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getName())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());//转换为set集合
System.out.println(collect);
}
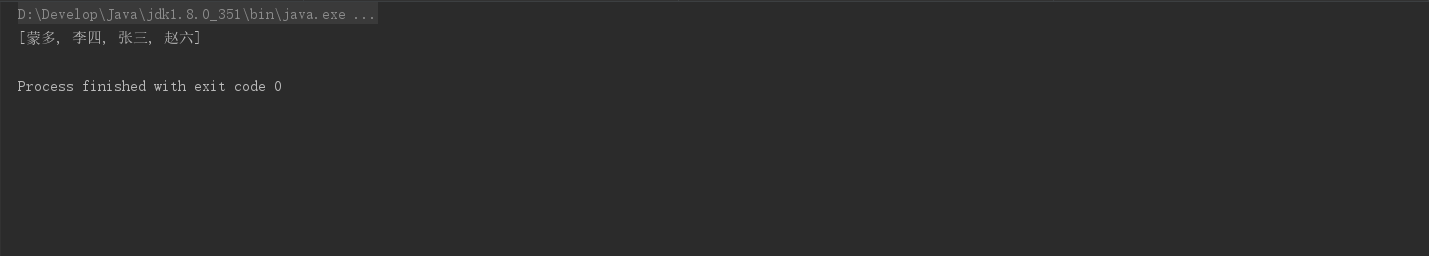
/**
* collect
*/
private static void test19() {
//获取一个map集合,map的key为作者名,value为List<Book>
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Map<String, List<Book>> collect = authors.stream()
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(author -> author.getName(), author -> author.getBooks()));//转换为map集合
System.out.println(collect);
}

anyMatch、allMatch、noneMatch
anyMatch(Predicate<T> predicate)、allMatch(Predicate<T> predicate) 和 noneMatch(Predicate<T> predicate): 这三个方法分别用于判断流中是否存在任意满足、全部满足或没有满足给定条件的元素。
/**
*anyMatch
*/
private static void test20() {
//判断是否有年龄小于20的作家
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream().anyMatch(author -> author.getAge() < 20);
System.out.println(b);
}
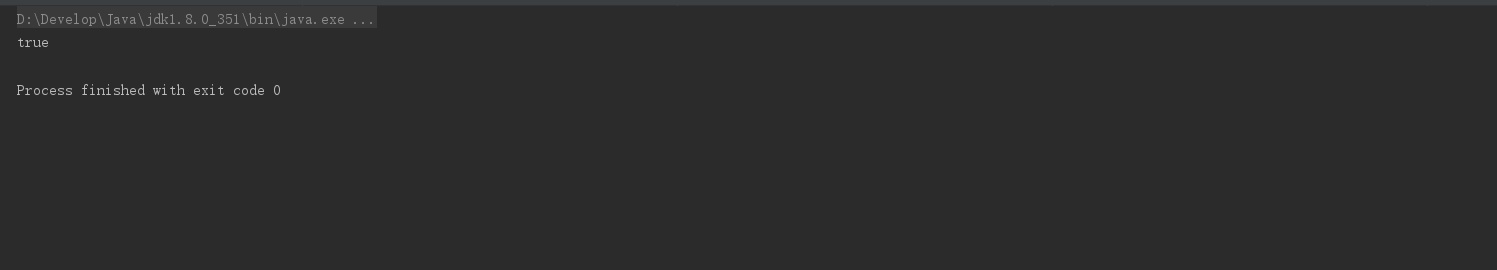
/**
*allMatch
*/
private static void test21() {
//判断是否有年龄小于20的作家
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream().allMatch(author -> author.getAge() < 20);
System.out.println(b);
}

/**
*noneMatch
*/
private static void test22() {
//判断是否有年龄小于20的作家
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
boolean b = authors.stream().noneMatch(author -> author.getAge() < 20);
System.out.println(b);
}

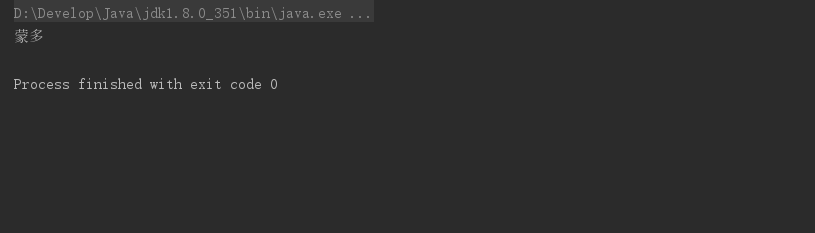
findAny()
findAny() 则返回流中的任意一个元素。
/**
* findAny
*/
private static void test23() {
//获取任意一个年龄大于20的作家,如果存在就输出他的名字
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> any = authors.stream()
.filter(author -> author.getAge()>90)
.findAny();
any.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
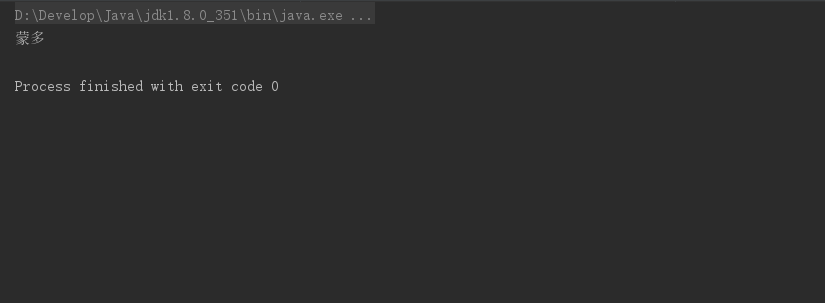
findFirst()
findFirst() 用于返回流中的第一个元素;
/**
* findFirst
*/
private static void test24() {
//获取任意一个年龄大于20的作家,如果存在就输出他的名字
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Author> any = authors.stream()
.filter(author -> author.getAge()>20)
.findFirst();
any.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getName()));
}
reduce*
归并
reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) 和 reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator):
reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) :用于将流中的元素逐个进行累积操作;
reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator) :则允许指定一个初始值。
/**
*reduce
*/
private static void test27() {
//使用reduce求所有作者中年龄的最小值
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer reduce = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MAX_VALUE, (age1, age2) -> age1 < age2?age1:age2);
System.out.println("最小值:"+reduce);
}
/**
*reduce
*/
private static void test26() {
//使用reduce求所有作者中年龄的最大值
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer reduce = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(Integer.MIN_VALUE, (age1, age2) -> age1 > age2?age1:age2);
System.out.println("最大值:"+reduce);
}
/**
*reduce
*/
private static void test25() {
// 使用reduce计算所有作者年龄的和
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Integer reduce = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce(0, (sum, age) -> sum + age);
System.out.println("和:"+reduce);
}

/**
*reduce
传入单个参数
*/
private static void test28() {
//使用reduce求所有作者中年龄的最小值,传入一个参数计算
List<Author> authors = getAuthors();
Optional<Integer> reduce = authors.stream()
.map(author -> author.getAge())
.reduce((age1, age2) -> age1 < age2 ? age1 : age2);
reduce.ifPresent(age-> System.out.println(age));
}
注意事项:
惰性求值1(如果没有终结操作,没有中间操作是不会得到执行的)
流是一次性的(一旦一个流对象经过一个终结操作后。这个流就不能再被使用)
不会影响原数据(我们在流中可以多数据做很多处理。但是正常情况下是不会影响原来集合中的元素的。这往往也是我们期望的)
Optional
方法
在 JDK 8 中,java.util.Optional 是一个用于表示可能包含或不包含非空值的容器类。它主要用于避免空指针异常,可以更优雅地处理可能为空的值。以下是 Optional 类的一些常用方法:
-
Optional.of(T value):创建一个包含指定非空值的 Optional 对象。如果传入的值为 null,将抛出 NullPointerException。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.of("Hello"); -
Optional.ofNullable(T value):创建一个 Optional 对象,如果传入的值为 null,则返回一个空的 Optional 对象。String nullableValue = null; Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.ofNullable(nullableValue); -
Optional.empty():创建一个空的 Optional 对象。Optional<String> emptyOptional = Optional.empty(); -
boolean isPresent():判断 Optional 对象是否包含非空值。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.of("Hello"); boolean isPresent = optionalString.isPresent(); // true -
T get():获取 Optional 对象中的值。注意,如果 Optional 对象为空,调用此方法会抛出 NoSuchElementException。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.of("Hello"); String value = optionalString.get(); // "Hello" -
T orElse(T other):获取 Optional 对象中的值,如果 Optional 为空,则返回指定的默认值。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.ofNullable(null); String value = optionalString.orElse("Default Value"); // "Default Value" -
T orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> other):与orElse类似,但是通过 Supplier 提供一个生成默认值的函数。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.ofNullable(null); String value = optionalString.orElseGet(() -> "Default Value"); // "Default Value" -
T orElseThrow(Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier):获取 Optional 对象中的值,如果 Optional 为空,则通过 Supplier 提供的函数抛出一个异常。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.ofNullable(null); String value = optionalString.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("Value is not present")); -
void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer):如果 Optional 对象中包含值,则执行传入的消费者函数。Optional<String> optionalString = Optional.of("Hello"); optionalString.ifPresent(val -> System.out.println("Value: " + val)); // Output: Value: Hellofilter方法,用于在 Optional 对象包含非空值时,根据指定条件进行过滤。如果满足条件,返回原始 Optional 对象,否则返回一个空的 Optional 对象。filter方法接受一个Predicate函数式接口作为参数,该接口用于定义过滤的条件。map方法,用于对Optional对象中的值进行转换。该方法接受一个Function函数式接口作为参数,用于定义值转换的逻辑。如果Optional对象包含值,则map方法将对该值应用函数,然后返回一个包含转换后值的新Optional对象。
public class OptionalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Author author = getAuthor();
Optional<Author> optionalAuthor = Optional.ofNullable(author);
optionalAuthor.ifPresent(author1 -> System.out.println(author1.getAge()));//解决传参出现空值出现空指针异常的情况
}
private static Author getAuthor() {
Author author1 = new Author(2L, "张三", 30, "喜欢探索科学的人", null);
return null;//模拟返回空值
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {/*
Author author = getAuthor();
Optional<Author> optionalAuthor = Optional.ofNullable(author);
optionalAuthor.ifPresent(author1 -> System.out.println(author1.getAge()));//解决传参出现空值出现空指针异常的情况*/
Optional<Author> optionalAuthor = getOptionalAuthor();
optionalAuthor.ifPresent(author -> System.out.println(author.getAge()));
}
private static Optional<Author> getOptionalAuthor() {
Author author1 = new Author(2L, "张三", 30, "喜欢探索科学的人", null);
return Optional.ofNullable(author1);//直接进行封装,封装为Optional类型的
}