Describe:
你要维护一张无向简单图(即没有自环,没有重边的无向图)。你被要求加入删除一条边及查询两个点是否连通。
- 0:加入一条边。保证它不存在。
- 1:删除一条边。保证它存在。
- 2:查询两个点是否联通。
允许离线
Solution:
对于离线做法,可以用线段树分治加可撤销并查集,时间仅 \(O(n\log^2 n)\),虽然不及 LCT 的 \(O(n\log n)\),但是它好打好调啊!
线段树分治是基于时间的分治。对于一条在 \(l\) 时出现、\(r\) 时消失的一条边,就在线段树对应的 \(\left[l,r\right]\) 上加入该边的影响。当线段树进入该子树时就加入这条边的影响,离开时还原这条边的影响。对于每一条边,因为树深最多为 \(\log n\),所以每条边的操作复杂度也只有 \(O(\log n)\),所有边就是 \(O(n\log n)\)。最后对线段树进行递归,处理询问即可。
struct trnode
{
int l,r,lc,rc;
PII q;
std::vector<std::pair<int,int>>id;
}tr[M<<1];int trlen;
#define lc tr[now].lc
#define rc tr[now].rc
void build(int l,int r)
{
int now=++trlen;
tr[now]={l,r};
if(l==r)
return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
lc=trlen+1;build(l,mid);
rc=trlen+1;build(mid+1,r);
}
void modify(int now,int l,int r,PII op)
{
if(tr[now].l==l&&tr[now].r==r)
return tr[now].id.push_back(op),void();
int mid=(tr[now].l+tr[now].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid)
modify(lc,l,r,op);
else if(l>=mid+1)
modify(rc,l,r,op);
else
modify(lc,l,mid,op),modify(rc,mid+1,r,op);
}
void add_query(int now,int x,PII op)
{
if(tr[now].l==tr[now].r)
return tr[now].q=op,void();
int mid=(tr[now].l+tr[now].r)>>1;
if(x<=mid)
add_query(lc,x,op);
else
add_query(rc,x,op);
}
void query(int now)
{
int tp=top;
for(auto x:tr[now].id)
merge(x.first,x.second);
if(tr[now].q.first)
puts(findfa(tr[now].q.first)==findfa(tr[now].q.second)?"Y":"N");
if(tr[now].l!=tr[now].r)
query(lc),query(rc);
recover(tp);
}
处理联通性当然是非并查集不可。但这里的并查集要求能还原,于是路径压缩优化就不可使用了。路径压缩会失去原有的父子关系,导致无法还原。就比如说是这样的一个图:
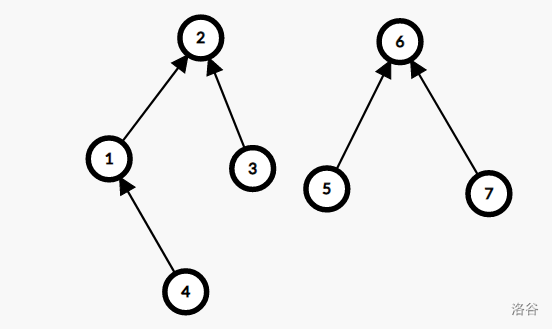
路径压缩后是这样:
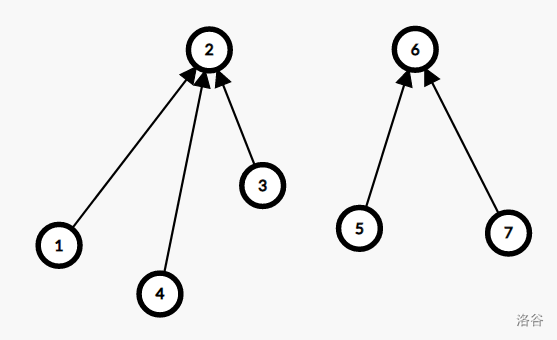
现在加入一条 \(2 \to 6\) 的边:
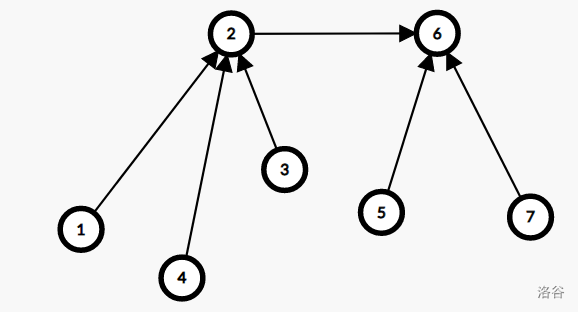
路径压缩后是这样:
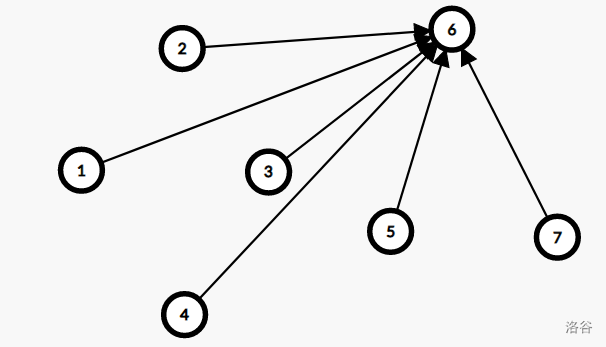
可以看到,\(1,2,3,4\) 的父亲都发生了改变,还原时就需要把它们都还原。这无论是代码复杂度还是时间复杂度都是接受不了的。所以就只能使用按秩合并了。可证明时间复杂度 \(O(\log n)\)。在还原时,可以在全局开一个栈,开一个变量记录当时的栈高,再存下加入的操作,当需要还原时,还原到原先的栈高即可。
int fa[N],siz[N],top;
PII sta[N];
void clear()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i,siz[i]=1;
}
int findfa(int x)
{
return fa[x]==x?x:findfa(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
int tx=findfa(x),ty=findfa(y);
if(tx==ty)
return ;
if(siz[tx]>siz[ty])
{
sta[++top]={tx,ty};
fa[ty]=tx;
siz[tx]+=siz[ty];
}
else
{
sta[++top]={ty,tx};
fa[tx]=ty;
siz[ty]+=siz[tx];
}
}
void recover(int tp)
{
while(top>tp)
{
int tx=sta[top].first,ty=sta[top].second;
fa[ty]=ty;
siz[tx]-=siz[ty];
top--;
}
}
总时间复杂度 \(O(n \log^2 n)\)。
Code:
完整代码如下:
bool _Start;
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
namespace IO
{
#define TP template<typename T>
#define TP_ template<typename T,typename ... T_>
#ifdef DEBUG
#define gc() (getchar())
#else
char buf[1<<20],*p1,*p2;
#define gc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,1<<20,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
#endif
#ifdef DEBUG
void pc(const char &c)
{
putchar(c);
}
#else
char pbuf[1<<20],*pp=pbuf;
void pc(const char &c)
{
if(pp-pbuf==1<<20)
fwrite(pbuf,1,1<<20,stdout),pp=pbuf;
*pp++=c;
}
struct IO{~IO(){fwrite(pbuf,1,pp-pbuf,stdout);}}_;
#endif
TP void read(T &x)
{
x=0;static int f;f=0;static char ch;ch=gc();
for(;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=gc())ch=='-'&&(f=1);
for(;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=gc())x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch^48);
f&&(x=-x);
}
TP void write(T x)
{
if(x<0)
pc('-'),x=-x;
static T sta[35],top;top=0;
do
sta[++top]=x%10,x/=10;
while(x);
while(top)
pc(sta[top--]^48);
}
TP_ void read(T &x,T_&...y){read(x);read(y...);}
TP void writeln(const T x){write(x);pc('\n');}
TP void writesp(const T x){write(x);pc(' ');}
TP_ void writeln(const T x,const T_ ...y){writesp(x);writeln(y...);}
TP void debugsp(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d ",x);}
TP void debug(const T x){fprintf(stderr,"%d\n",x);}
TP_ void debug(const T x,const T_...y){debugsp(x);debug(y...);}
TP inline T max(const T &a,const T &b){return a>b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T max(const T &a,const T_&...b){return max(a,max(b...));}
TP inline T min(const T &a,const T &b){return a<b?a:b;}
TP_ inline T min(const T &a,const T_&...b){return min(a,min(b...));}
TP inline void swap(T &a,T &b){static T t;t=a;a=b;b=t;}
TP inline T abs(const T &a){return a>0?a:-a;}
#undef TP
#undef TP_
}
using namespace IO;
using std::cerr;
using PII=std::pair<int,int>;
using LL=long long;
constexpr int N=5e3+10;
constexpr int M=5e5+10;
int n,m;
int fa[N],siz[N],top;
PII sta[N];
void clear()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i,siz[i]=1;
}
int findfa(int x)
{
return fa[x]==x?x:findfa(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
int tx=findfa(x),ty=findfa(y);
if(tx==ty)
return ;
if(siz[tx]>siz[ty])
{
sta[++top]={tx,ty};
fa[ty]=tx;
siz[tx]+=siz[ty];
}
else
{
sta[++top]={ty,tx};
fa[tx]=ty;
siz[ty]+=siz[tx];
}
}
void recover(int tp)
{
while(top>tp)
{
int tx=sta[top].first,ty=sta[top].second;
fa[ty]=ty;
siz[tx]-=siz[ty];
top--;
}
}
struct trnode
{
int l,r,lc,rc;
PII q;
std::vector<std::pair<int,int>>id;
}tr[M<<1];int trlen;
#define lc tr[now].lc
#define rc tr[now].rc
void build(int l,int r)
{
int now=++trlen;
tr[now]={l,r};
if(l==r)
return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
lc=trlen+1;build(l,mid);
rc=trlen+1;build(mid+1,r);
}
void modify(int now,int l,int r,PII op)
{
if(tr[now].l==l&&tr[now].r==r)
return tr[now].id.push_back(op),void();
int mid=(tr[now].l+tr[now].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid)
modify(lc,l,r,op);
else if(l>=mid+1)
modify(rc,l,r,op);
else
modify(lc,l,mid,op),modify(rc,mid+1,r,op);
}
void add_query(int now,int x,PII op)
{
if(tr[now].l==tr[now].r)
return tr[now].q=op,void();
int mid=(tr[now].l+tr[now].r)>>1;
if(x<=mid)
add_query(lc,x,op);
else
add_query(rc,x,op);
}
void query(int now)
{
int tp=top;
for(auto x:tr[now].id)
merge(x.first,x.second);
if(tr[now].q.first)
puts(findfa(tr[now].q.first)==findfa(tr[now].q.second)?"Y":"N");
if(tr[now].l!=tr[now].r)
query(lc),query(rc);
recover(tp);
}
int v[N][N];
bool _End;
int main()
{
// fprintf(stderr,"%.2 MBlf\n",(&_End-&_Start)/1048576.0);
read(n,m);
clear();
build(1,m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int op,x,y;read(op,x,y);
switch(op)
{
case 0:
v[x][y]=v[y][x]=i;
break;
case 1:
{
modify(1,v[x][y],i,{x,y});
v[x][y]=v[y][x]=0;
break;
}
case 2:
add_query(1,i,{x,y});
break;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
if(v[i][j])
modify(1,v[i][j],m,{i,j});
query(1);
return 0;
}
强制在线
Solution:
施工中...(等 AC 了再来写)
标签:连通性,tx,ty,int,tr,动态图,now,op From: https://www.cnblogs.com/lofty2007/p/18036700