Django 请求到来与路由匹配
说明:本部分主要讲述请求到来与路由匹配的部分;
1. 请求到来
上次分析到了 wsgi 的函数内部处理信息,我们已经知道请求到了之后会执行__call__方法,下面将继续分析__call__方法。
class WSGIHandler(base.BaseHandler):
# 继承 BaseHandler
request_class = WSGIRequest # 聚合 WSGIRequest, 该类继承与 HttpRequest
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs) # 首先执行父类的初始化方法;
self.load_middleware() # 加载中间件, 注意生命周期现在还没有进入路由匹配
def __call__(self, environ, start_response): # 实现 wsgi 服务, 接收 environ 、 start_response
set_script_prefix(get_script_name(environ)) # 设置线程
signals.request_started.send(sender=self.__class__, environ=environ)
# 请求, 封装 request
request = self.request_class(environ) # 执行 WSGIRequest 的 init 函数, 对请求信息进行疯转
# 响应
response = self.get_response(request) # 为请求对象初始化返回指定响应对象 HttpResponse
response._handler_class = self.__class__
status = '%d %s' % (response.status_code, response.reason_phrase) # 设置 status
response_headers = [
*response.items(), # 响应字典解析成为 (key,value) 的形式
*(('Set-Cookie', c.output(header='')) for c in response.cookies.values()),
] # 请求响应头
start_response(status, response_headers) # wsgi 的方法
# 反射查看 file_to_stream 是否为空 和 wsgi.file_wrapper
if getattr(response, 'file_to_stream', None) is not None and environ.get('wsgi.file_wrapper'):
# If `wsgi.file_wrapper` is used the WSGI server does not call
# .close on the response, but on the file wrapper. Patch it to use
# response.close instead which takes care of closing all files.
response.file_to_stream.close = response.close # 关闭文件流
# 设置响应头中的流和长度
response = environ['wsgi.file_wrapper'](response.file_to_stream, response.block_size)
return response # 返回 响应对象
源码被引用的类
class WSGIRequest(HttpRequest):
""" 请求类, 对 request 进行封装;
"""
def __init__(self, environ):
script_name = get_script_name(environ)
# If PATH_INFO is empty (e.g. accessing the SCRIPT_NAME URL without a
# trailing slash), operate as if '/' was requested.
path_info = get_path_info(environ) or '/'
self.environ = environ
self.path_info = path_info
# be careful to only replace the first slash in the path because of
# http://test/something and http://test//something being different as
# stated in https://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2396.txt
self.path = '%s/%s' % (script_name.rstrip('/'),
path_info.replace('/', '', 1))
self.META = environ # 将请求环境设置为字典
self.META['PATH_INFO'] = path_info
self.META['SCRIPT_NAME'] = script_name
self.method = environ['REQUEST_METHOD'].upper() # 请求的方法大写
# Set content_type, content_params, and encoding.
self._set_content_type_params(environ)
try:
content_length = int(environ.get('CONTENT_LENGTH'))
except (ValueError, TypeError):
content_length = 0
self._stream = LimitedStream(self.environ['wsgi.input'], content_length)
self._read_started = False
self.resolver_match = None
def _get_scheme(self):
return self.environ.get('wsgi.url_scheme')
@cached_property
def GET(self):
# The WSGI spec says 'QUERY_STRING' may be absent.
raw_query_string = get_bytes_from_wsgi(self.environ, 'QUERY_STRING', '')
return QueryDict(raw_query_string, encoding=self._encoding)
def _get_post(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_post'):
self._load_post_and_files()
return self._post
def _set_post(self, post):
self._post = post
@cached_property
def COOKIES(self):
raw_cookie = get_str_from_wsgi(self.environ, 'HTTP_COOKIE', '')
return parse_cookie(raw_cookie)
@property
def FILES(self):
if not hasattr(self, '_files'):
self._load_post_and_files()
return self._files
POST = property(_get_post, _set_post)
封装到 request 中的 META 打印结果如下;
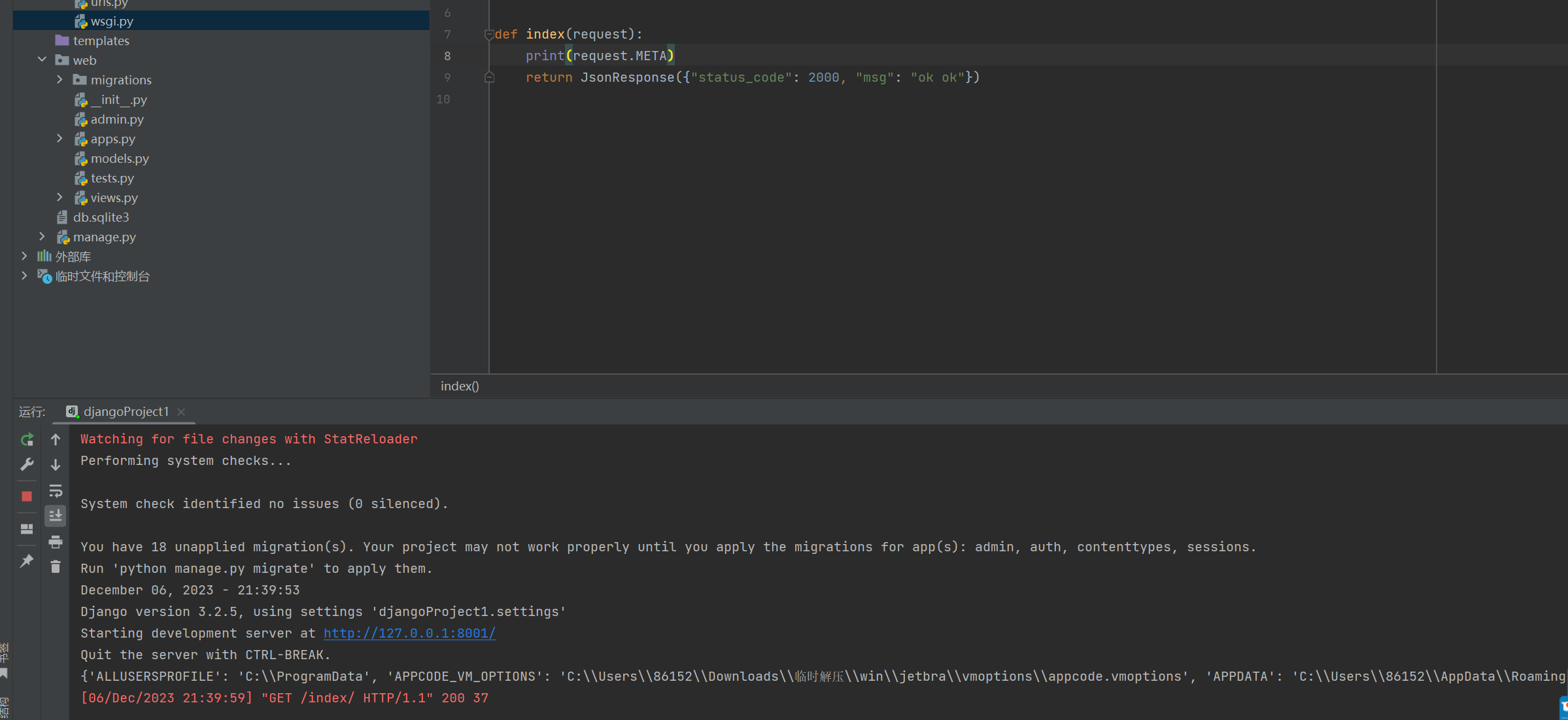
请求对象封装完成之后,边开始构造返回体,下面看引用函数的解析;
# 根据请求对象返回响应对象;
from asgiref.local import Local
_urlconfs = Local() #
def set_urlconf(urlconf_name):
"""
Set the URLconf for the current thread (overriding the default one in
settings). If urlconf_name is None, revert back to the default.
"""
if urlconf_name:
_urlconfs.value = urlconf_name # 设置线程中的一个值
else:
if hasattr(_urlconfs, "value"):
del _urlconfs.value
def get_response(self, request):
"""Return an HttpResponse object for the given HttpRequest."""
# Setup default url resolver for this thread
set_urlconf(settings.ROOT_URLCONF) # 配置文件中的信息是 ROOT_URLCONF = 'djangoProject1.urls'
response = self._middleware_chain(request) # 执行的是父类的 _middleware_chain 方法;
response._resource_closers.append(request.close)
if response.status_code >= 400:
log_response(
'%s: %s', response.reason_phrase, request.path,
response=response,
request=request,
)
return response
父类的 BaseHandler 的代码信息;
class BaseHandler:
_view_middleware = None
_template_response_middleware = None
_exception_middleware = None
_middleware_chain = None
def load_middleware(self, is_async=False):
# 该方法被执行了两次, 一次是在 __call__中执行, 还有一次是在 WSGIHandler的初始化方法中执行,
# 而且是同一个对象的操作,第二次再次执行的时候,列表已经不为空了;
""" 加载中间件; 项目启动的时候会进行加载,请求到来的时候也会执行中间件的操作.
Populate middleware lists from settings.MIDDLEWARE.
Must be called after the environment is fixed (see __call__ in subclasses).
"""
# 设置对象的私有列表: 视图中间件列表, 响应模板中间件,异常中间件 的三个列表
self._view_middleware = []
self._template_response_middleware = []
self._exception_middleware = []
# 使用三元表达式设置 get_response, 返回一个
get_response = self._get_response_async if is_async else self._get_response
handler = convert_exception_to_response(get_response) # 异常转换;
handler_is_async = is_async
# 使用反射获取路径的信息, 再使用 import_module 导入相关的中间件;
for middleware_path in reversed(settings.MIDDLEWARE):
middleware = import_string(middleware_path) # 使用 import_module 进行动态的导入;
middleware_can_sync = getattr(middleware, 'sync_capable', True)
middleware_can_async = getattr(middleware, 'async_capable', False)
if not middleware_can_sync and not middleware_can_async:
raise RuntimeError(
'Middleware %s must have at least one of '
'sync_capable/async_capable set to True.' % middleware_path
)
elif not handler_is_async and middleware_can_sync:
middleware_is_async = False
else:
middleware_is_async = middleware_can_async
try:
# Adapt handler, if needed.
adapted_handler = self.adapt_method_mode(
middleware_is_async, handler, handler_is_async,
debug=settings.DEBUG, name='middleware %s' % middleware_path,
)
mw_instance = middleware(adapted_handler)
except MiddlewareNotUsed as exc:
if settings.DEBUG:
if str(exc):
logger.debug('MiddlewareNotUsed(%r): %s', middleware_path, exc)
else:
logger.debug('MiddlewareNotUsed: %r', middleware_path)
continue
else:
handler = adapted_handler
if mw_instance is None:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'Middleware factory %s returned None.' % middleware_path
)
if hasattr(mw_instance, 'process_view'):
self._view_middleware.insert(
0,
self.adapt_method_mode(is_async, mw_instance.process_view),
)
if hasattr(mw_instance, 'process_template_response'):
self._template_response_middleware.append(
self.adapt_method_mode(is_async, mw_instance.process_template_response),
)
if hasattr(mw_instance, 'process_exception'):
# The exception-handling stack is still always synchronous for
# now, so adapt that way.
self._exception_middleware.append(
self.adapt_method_mode(False, mw_instance.process_exception),
)
handler = convert_exception_to_response(mw_instance)
handler_is_async = middleware_is_async
# Adapt the top of the stack, if needed.
handler = self.adapt_method_mode(is_async, handler, handler_is_async)
# We only assign to this when initialization is complete as it is used
# as a flag for initialization being complete.
self._middleware_chain = handler
def adapt_method_mode(
self, is_async, method, method_is_async=None, debug=False, name=None,
):
"""
Adapt a method to be in the correct "mode":
- If is_async is False:
- Synchronous methods are left alone
- Asynchronous methods are wrapped with async_to_sync
- If is_async is True:
- Synchronous methods are wrapped with sync_to_async()
- Asynchronous methods are left alone
"""
if method_is_async is None:
method_is_async = asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(method)
if debug and not name:
name = name or 'method %s()' % method.__qualname__
if is_async:
if not method_is_async:
if debug:
logger.debug('Synchronous %s adapted.', name)
return sync_to_async(method, thread_sensitive=True)
elif method_is_async:
if debug:
logger.debug('Asynchronous %s adapted.', name)
return async_to_sync(method)
return method
def get_response(self, request):
"""Return an HttpResponse object for the given HttpRequest."""
# Setup default url resolver for this thread
set_urlconf(settings.ROOT_URLCONF)
response = self._middleware_chain(request) # 该方法的调用私有变量;
# 该方法实例化的时候是 None, 通过 load_middleware 进行赋值;
response._resource_closers.append(request.close)
if response.status_code >= 400:
log_response(
'%s: %s', response.reason_phrase, request.path,
response=response,
request=request,
)
return response # 返回响应结果给 wsgi 的了类;
async def get_response_async(self, request):
"""
Asynchronous version of get_response.
Funneling everything, including WSGI, into a single async
get_response() is too slow. Avoid the context switch by using
a separate async response path.
"""
# Setup default url resolver for this thread.
set_urlconf(settings.ROOT_URLCONF)
response = await self._middleware_chain(request)
response._resource_closers.append(request.close)
if response.status_code >= 400:
await sync_to_async(log_response, thread_sensitive=False)(
'%s: %s', response.reason_phrase, request.path,
response=response,
request=request,
)
return response
def _get_response(self, request):
# 解析并调用视图函数;
"""
Resolve and call the view, then apply view, exception, and
template_response middleware. This method is everything that happens
inside the request/response middleware.
"""
response = None # 初始响应对象
# 调用 resolve_request 方法;
# resolve_request 返回值的类已经重写了 __getitem__方法, 直接进行元组的解包,返回视图函数等信息
callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs = self.resolve_request(request)
# Apply view middleware 应用视图函数中间件.
for middleware_method in self._view_middleware:
response = middleware_method(request, callback, callback_args, callback_kwargs)
if response:
break # 如果中间件进行了返回直接进行终止;
# 中间件的响应对象是空的时候执行以下的逻辑;
if response is None:
# 传入的参数是视图函数,对视图视图函数进行原子化的操作,保证视图函数中的数据库的操作,返回的还是视图函数
wrapped_callback = self.make_view_atomic(callback)
# If it is an asynchronous view, run it in a subthread.
if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(wrapped_callback):
wrapped_callback = async_to_sync(wrapped_callback) # 异步执行的函数
try:
# 视图函数 + (request, 以及其他参数的执行)
response = wrapped_callback(request, *callback_args, **callback_kwargs)
except Exception as e:
response = self.process_exception_by_middleware(e, request)
if response is None:
raise
# Complain if the view returned None (a common error).
self.check_response(response, callback)
# If the response supports deferred rendering, apply template
# response middleware and then render the response
if hasattr(response, 'render') and callable(response.render):
for middleware_method in self._template_response_middleware:
response = middleware_method(request, response)
# Complain if the template response middleware returned None (a common error).
self.check_response(
response,
middleware_method,
name='%s.process_template_response' % (
middleware_method.__self__.__class__.__name__,
)
)
try:
response = response.render()
except Exception as e:
response = self.process_exception_by_middleware(e, request)
if response is None:
raise
# 对结果进行一些处理返回;
return response
def resolve_request(self, request):
"""
Retrieve/set the urlconf for the request. Return the view resolved,
with its args and kwargs.
"""
# Work out the resolver.
if hasattr(request, 'urlconf'):
# 是否设置urlconf设置后执行该函数
urlconf = request.urlconf
set_urlconf(urlconf)
resolver = get_resolver(urlconf)
else:
resolver = get_resolver()
# Resolve the view, and assign the match object back to the request.
resolver_match = resolver.resolve(request.path_info) # 执行方法
request.resolver_match = resolver_match
return resolver_match
def check_response(self, response, callback, name=None):
"""
Raise an error if the view returned None or an uncalled coroutine.
"""
if not(response is None or asyncio.iscoroutine(response)):
return
if not name:
if isinstance(callback, types.FunctionType): # FBV
name = 'The view %s.%s' % (callback.__module__, callback.__name__)
else: # CBV
name = 'The view %s.%s.__call__' % (
callback.__module__,
callback.__class__.__name__,
)
if response is None:
raise ValueError(
"%s didn't return an HttpResponse object. It returned None "
"instead." % name
)
elif asyncio.iscoroutine(response):
raise ValueError(
"%s didn't return an HttpResponse object. It returned an "
"unawaited coroutine instead. You may need to add an 'await' "
"into your view." % name
)
# Other utility methods.
def make_view_atomic(self, view):
non_atomic_requests = getattr(view, '_non_atomic_requests', set())
for db in connections.all():
if db.settings_dict['ATOMIC_REQUESTS'] and db.alias not in non_atomic_requests:
if asyncio.iscoroutinefunction(view):
raise RuntimeError(
'You cannot use ATOMIC_REQUESTS with async views.'
)
view = transaction.atomic(using=db.alias)(view)
return view
def process_exception_by_middleware(self, exception, request):
"""
Pass the exception to the exception middleware. If no middleware
return a response for this exception, return None.
"""
for middleware_method in self._exception_middleware:
response = middleware_method(request, exception)
if response:
return response
return None
2. 路由匹配
本部分的开始之前进行下知识的补充;
2.1 描述符与正则的补充
2.1.1 描述符
参考文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/336926012
class Base:
def __get__(self, instance, cls=None):
return 10
class Foo:
obj = Base()
print(Foo.obj)
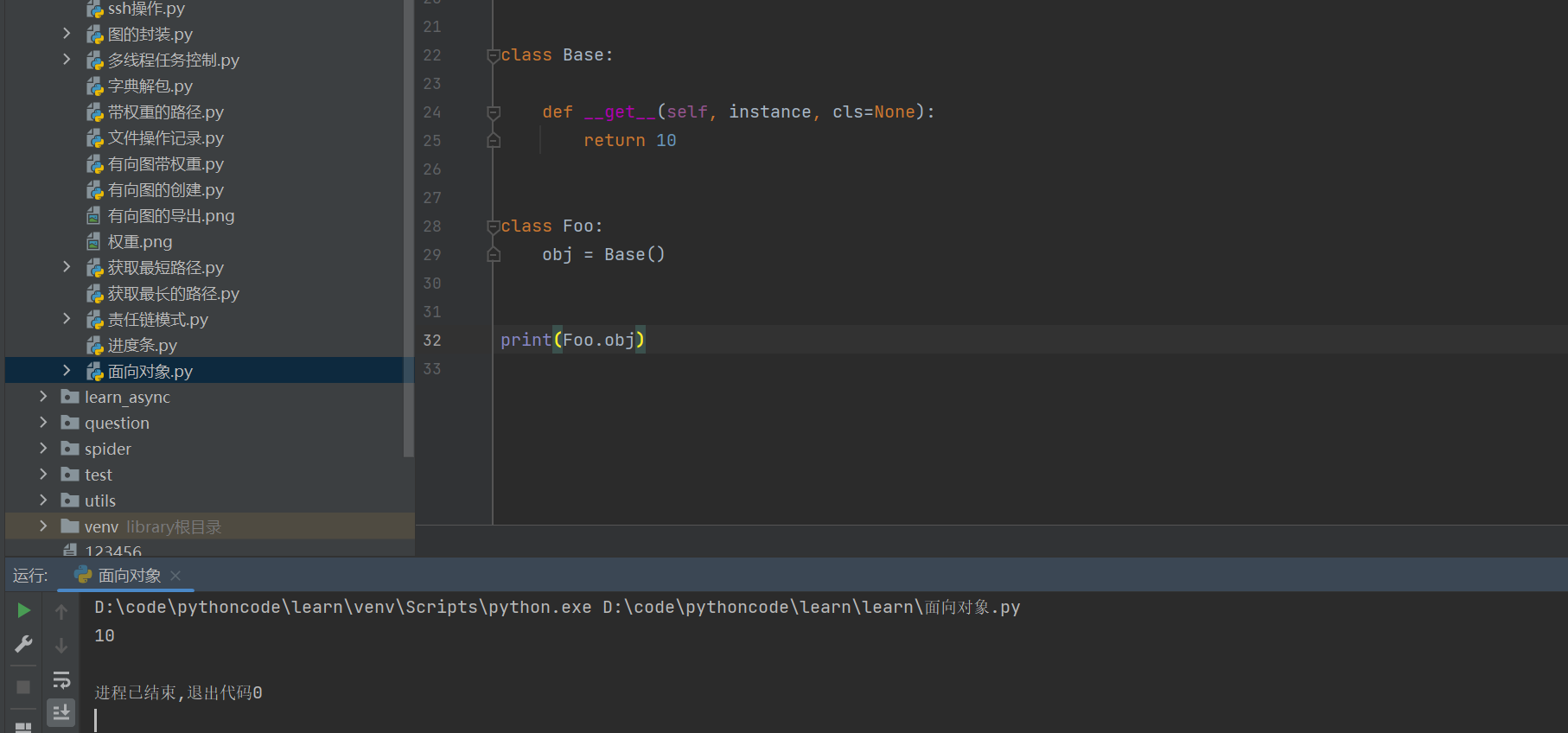
在把类当做属性的时候,使用__get__方法进行加载的时候可以执行该方法;
2.1.2 正则匹配
django 中路由的匹配是基于正则表达式进行的匹配;
-
search 方法
search 方法扫描整个字符串并且返回第一个结果,
import re # search 方法的补充; s = "ssss/index/ddd" v = re.search("/index/", s) print(v)存在则返回匹配的对象,不存在返回 None
-
match 方法
match 方法默认从第一位开始匹配
import re v = re.match("hello", "dddhello world") # 匹配失败 v = re.match("hello", "hello world") # 匹配成功 v = re.match(r"[hH]ello", "hello world").group() # 提取到返回的结果 v = re.match(r"[hH]ello", "hello world").end() # 返回匹配的字符串中的最后一个字符串; print(v) -
group 方法
group 方法是用来根据正则表达式中的分组来提取结果的匹配函数;
import re v = re.match(r"[hH]ello", "hello world").group() print(v) -
groupdict 方法
import re v = re.match(r"(?P<first_name>\w+) (?P<last_name>\w+)", "Mike Job").groupdict() print(v)groupdict 方法返回的是一个匹配结果的字典,key 是正则中匹配的名字。
2.2 路由加载
上半部分请求到来之后执行到响应初始化的对象,进行路由的匹配。
""" 特别注意, 此时视图函数还为执行;
"""
def resolve_request(self, request):
"""
Retrieve/set the urlconf for the request. Return the view resolved,
with its args and kwargs.
"""
# Work out the resolver.
if hasattr(request, 'urlconf'):
# 是否设置urlconf设置后执行该函数
urlconf = request.urlconf
set_urlconf(urlconf)
resolver = get_resolver(urlconf)
else:
resolver = get_resolver() # 执行 get_resolver, 返回 URLResolver() 对象
# Resolve the view, and assign the match object back to the request.
resolver_match = resolver.resolve(request.path_info) # 调用 resolve, 返回的是 ResolverMatch 对象;
request.resolver_match = resolver_match # 将解析的信息封装到 requests 中
return resolver_match # 返回该信息;
内置的函数
# 设置配置文件的信息为 urlconf
def get_resolver(urlconf=None):
if urlconf is None:
urlconf = settings.ROOT_URLCONF
return _get_cached_resolver(urlconf)
@functools.lru_cache(maxsize=None) # 缓存装饰器;
def _get_cached_resolver(urlconf=None):
return URLResolver(RegexPattern(r'^/'), urlconf)
实例化类 RegexPattern 进行正则的匹配:
class CheckURLMixin:
def describe(self):
"""
Format the URL pattern for display in warning messages.
"""
description = "'{}'".format(self)
if self.name:
description += " [name='{}']".format(self.name)
return description
def _check_pattern_startswith_slash(self):
"""
Check that the pattern does not begin with a forward slash.
"""
regex_pattern = self.regex.pattern
if not settings.APPEND_SLASH:
# Skip check as it can be useful to start a URL pattern with a slash
# when APPEND_SLASH=False.
return []
if regex_pattern.startswith(('/', '^/', '^\\/')) and not regex_pattern.endswith('/'):
warning = Warning(
"Your URL pattern {} has a route beginning with a '/'. Remove this "
"slash as it is unnecessary. If this pattern is targeted in an "
"include(), ensure the include() pattern has a trailing '/'.".format(
self.describe()
),
id="urls.W002",
)
return [warning]
else:
return []
class LocaleRegexDescriptor:
def __init__(self, attr):
self.attr = attr # "_regx"
def __get__(self, instance, cls=None):
"""
返回基于活动语言的已编译正则表达式。
Return a compiled regular expression based on the active language.
"""
if instance is None:
return self
# As a performance optimization, if the given regex string is a regular
# string (not a lazily-translated string proxy), compile it once and
# avoid per-language compilation.
pattern = getattr(instance, self.attr) # 执行的是 getattr(instace)
if isinstance(pattern, str):
instance.__dict__['regex'] = instance._compile(pattern)
return instance.__dict__['regex']
language_code = get_language()
if language_code not in instance._regex_dict:
instance._regex_dict[language_code] = instance._compile(str(pattern))
return instance._regex_dict[language_code]
# 调用的是该类中的 match 函数;
class RegexPattern(CheckURLMixin):
# 继承的类与聚合的类已经贴到了上面;
regex = LocaleRegexDescriptor('_regex') # 此时会直接执行 __get__ 方法;
def __init__(self, regex, name=None, is_endpoint=False):
self._regex = regex # 设置成为私有的变量,匹配规则 '^/'
self._regex_dict = {} # 设置私有初始变量
self._is_endpoint = is_endpoint
self.name = name
self.converters = {}
def match(self, path): # 传入的是路由待匹配的路径; /index/ 执行聚合类的 search 方法;
match = self.regex.search(path) # 是聚合的类进行匹配传入的字符串的信息;
if match:
# If there are any named groups, use those as kwargs, ignoring
# non-named groups. Otherwise, pass all non-named arguments as
# positional arguments.
kwargs = match.groupdict() # 提取正则中的参数信息;.
args = () if kwargs else match.groups() # 提取正则中的空字符串;
kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if v is not None} # 过滤掉空值的参数;
# 返回信息 路由匹配后的参数信息, 匿名参数, 命名的正则参数;
return path[match.end():], args, kwargs
return None
def check(self):
warnings = []
warnings.extend(self._check_pattern_startswith_slash())
if not self._is_endpoint:
warnings.extend(self._check_include_trailing_dollar())
return warnings
def _check_include_trailing_dollar(self):
regex_pattern = self.regex.pattern
if regex_pattern.endswith('$') and not regex_pattern.endswith(r'\$'):
return [Warning(
"Your URL pattern {} uses include with a route ending with a '$'. "
"Remove the dollar from the route to avoid problems including "
"URLs.".format(self.describe()),
id='urls.W001',
)]
else:
return []
def _compile(self, regex):
"""Compile and return the given regular expression."""
try:
return re.compile(regex)
except re.error as e:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'"%s" is not a valid regular expression: %s' % (regex, e)
) from e
def __str__(self):
return str(self._regex)
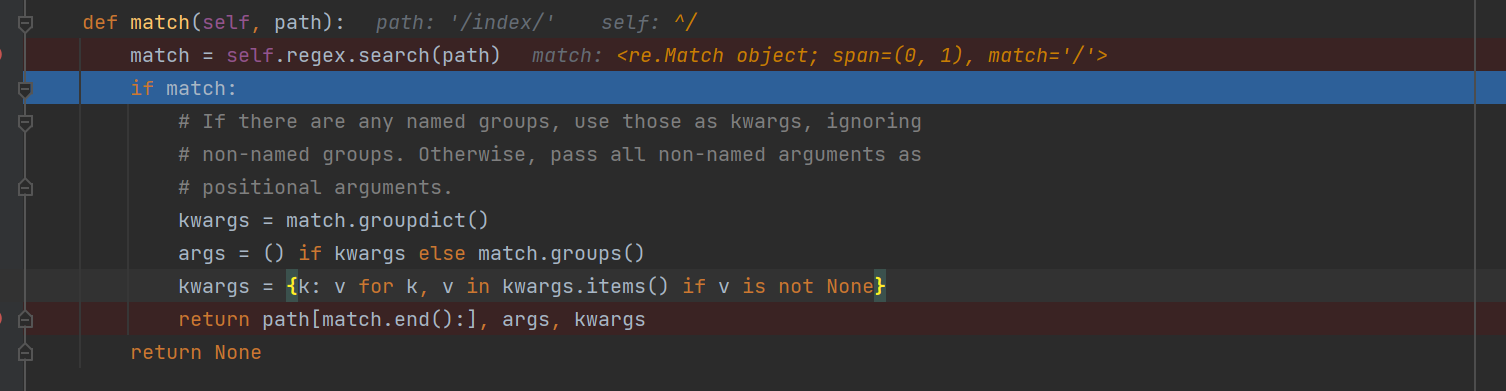
此时使用 Debug 显示是当前的对象是 re.match 的方法;
实例化类 URLResolver 进行匹配:
class URLResolver:
def __init__(self, pattern, urlconf_name, default_kwargs=None, app_name=None, namespace=None):
self.pattern = pattern
# urlconf_name is the dotted Python path to the module defining
# urlpatterns. It may also be an object with an urlpatterns attribute
# or urlpatterns itself.
self.urlconf_name = urlconf_name
self.callback = None
self.default_kwargs = default_kwargs or {}
self.namespace = namespace
self.app_name = app_name
self._reverse_dict = {}
self._namespace_dict = {}
self._app_dict = {}
# set of dotted paths to all functions and classes that are used in
# urlpatterns
self._callback_strs = set()
self._populated = False
self._local = Local()
@staticmethod
def _extend_tried(tried, pattern, sub_tried=None):
if sub_tried is None:
tried.append([pattern])
else:
tried.extend([pattern, *t] for t in sub_tried)
def resolve(self, path):
# get_response 会执行到此方法; resolve, path 是当前的路径请求信息;
path = str(path) # path may be a reverse_lazy object
tried = []
match = self.pattern.match(path) # partten 是实例化对象传入的第一个参数:类 RegexPattern 的对象
if match:
new_path, args, kwargs = match # 得到的是路由, 参数字典, 参数的信息
for pattern in self.url_patterns:
# 调用下方被缓存装饰器修饰的属性, 因此此时是列表中的 path 对象;
# 获得的是列表转换成为的迭代器对象, 因此 pattern 是路由列表中的 path 对象;
try:
# 子路由的匹配, path() 函数根据偏函数的分析返回的是 URLPattern()实例化对象
sub_match = pattern.resolve(new_path) # 执行当前对象的resolve 方法,完成对参数的封装;
except Resolver404 as e:
self._extend_tried(tried, pattern, e.args[0].get('tried'))
else:
if sub_match:
# Merge captured arguments in match with submatch
sub_match_dict = {**kwargs, **self.default_kwargs} # 合并两个字典
# Update the sub_match_dict with the kwargs from the sub_match.
sub_match_dict.update(sub_match.kwargs) # 使用字典的 update 方法进行更新;
# If there are *any* named groups, ignore all non-named groups.
# Otherwise, pass all non-named arguments as positional arguments.
sub_match_args = sub_match.args # 获取元组的参数信息.
if not sub_match_dict:
sub_match_args = args + sub_match.args
# 使用三元表达式对路由类型进行判断
current_route = '' if isinstance(pattern, URLPattern) else str(pattern.pattern)
self._extend_tried(tried, pattern, sub_match.tried) # 将信息添加到tried 列表中
# 返回解析匹配对象;
return ResolverMatch(
sub_match.func, # 视图函数
sub_match_args, # 路由参数
sub_match_dict, # 正则字典的参数
sub_match.url_name, # 别名 name
[self.app_name] + sub_match.app_names,
[self.namespace] + sub_match.namespaces,
self._join_route(current_route, sub_match.route), #子路由的拼接
tried,
)
tried.append([pattern])
raise Resolver404({'tried': tried, 'path': new_path}) # 匹配失败抛出 404 的界面信息;
raise Resolver404({'path': path})
@cached_property
def urlconf_module(self):
if isinstance(self.urlconf_name, str): # 检查类型是否是 字符串的类型
return import_module(self.urlconf_name) # 进行数据的导入;动态导入包的信息;
else:
return self.urlconf_name
@cached_property
def url_patterns(self):
# 该方法调用上述的方法
# urlconf_module might be a valid set of patterns, so we default to it
# 使用动态导包的方式,获取脚本中的列表, urlpatterns
patterns = getattr(self.urlconf_module, "urlpatterns", self.urlconf_module)
try:
iter(patterns) # 接受列表并且转换成为迭代器的对象;
except TypeError as e:
msg = (
"The included URLconf '{name}' does not appear to have any "
"patterns in it. If you see valid patterns in the file then "
"the issue is probably caused by a circular import."
)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg.format(name=self.urlconf_name)) from e
return patterns # 返回一个迭代器的列表
def resolve_error_handler(self, view_type):
callback = getattr(self.urlconf_module, 'handler%s' % view_type, None)
if not callback:
# No handler specified in file; use lazy import, since
# django.conf.urls imports this file.
from django.conf import urls
callback = getattr(urls, 'handler%s' % view_type)
return get_callable(callback)
中间调用的对象的函数的信息:
""" URLPattern 类, 以及被的类
"""
class ResolverMatch:
def __init__(self, func, args, kwargs, url_name=None, app_names=None, namespaces=None, route=None, tried=None):
self.func = func # 视图函数
self.args = args # 元组参数
self.kwargs = kwargs # 字典参数
self.url_name = url_name # 路由名称
self.route = route
self.tried = tried
# If a URLRegexResolver doesn't have a namespace or app_name, it passes
# in an empty value.
self.app_names = [x for x in app_names if x] if app_names else []
self.app_name = ':'.join(self.app_names)
self.namespaces = [x for x in namespaces if x] if namespaces else []
self.namespace = ':'.join(self.namespaces)
if not hasattr(func, '__name__'):
# A class-based view
self._func_path = func.__class__.__module__ + '.' + func.__class__.__name__
else:
# A function-based view
self._func_path = func.__module__ + '.' + func.__name__
view_path = url_name or self._func_path # 视图函数的路径
self.view_name = ':'.join(self.namespaces + [view_path])
def __getitem__(self, index):
# 返回元组并且进行自动解包;
return (self.func, self.args, self.kwargs)[index]
def __repr__(self):
return "ResolverMatch(func=%s, args=%s, kwargs=%s, url_name=%s, app_names=%s, namespaces=%s, route=%s)" % (
self._func_path, self.args, self.kwargs, self.url_name,
self.app_names, self.namespaces, self.route,
)
class URLPattern:
def __init__(self, pattern, callback, default_args=None, name=None):
self.pattern = pattern
self.callback = callback # the view
self.default_args = default_args or {}
self.name = name
def __repr__(self):
return '<%s %s>' % (self.__class__.__name__, self.pattern.describe())
def check(self):
warnings = self._check_pattern_name()
warnings.extend(self.pattern.check())
return warnings
def _check_pattern_name(self):
"""
Check that the pattern name does not contain a colon.
"""
if self.pattern.name is not None and ":" in self.pattern.name:
warning = Warning(
"Your URL pattern {} has a name including a ':'. Remove the colon, to "
"avoid ambiguous namespace references.".format(self.pattern.describe()),
id="urls.W003",
)
return [warning]
else:
return []
def resolve(self, path):
match = self.pattern.match(path) # 代指当前对象的 pattern, 进行正则的匹配;
if match:
new_path, args, kwargs = match # 匹配信息
# Pass any extra_kwargs as **kwargs.
kwargs.update(self.default_args) # 设置默认的参数到
# 传入的函数信息是当前对象的 callback 函数*(视图函数), 相关的参数;
# 完成了对信息的封装
return ResolverMatch(self.callback, args, kwargs, self.pattern.name, route=str(self.pattern))
个人编写的时候会将路径编写到 path 里面;
from django.urls import path
from web.views import index
urlpatterns = [
path('index/', index),
]
内置的源码如下的形式
""" 原生的 path 函数被设置成为了偏函数, 实际上使用的是 _path 方法,
"""
def _path(route, view, kwargs=None, name=None, Pattern=None):
if isinstance(view, (list, tuple)): # 除了路由之外将其他的参数封装成为元组或列表;
# For include(...) processing.
pattern = Pattern(route, is_endpoint=False) # 设置成为 Pattern 对象;
urlconf_module, app_name, namespace = view # 进行元组的解包
return URLResolver(
pattern, # Pattern 对象
urlconf_module,
kwargs,
app_name=app_name,
namespace=namespace,
) # 返回相关的对象信息;
elif callable(view): # 第二个参数是视图函数
# 参数只有视图函数的时候执行类的实例化, 返回 URLPatter 类的实例化;
pattern = Pattern(route, name=name, is_endpoint=True)
return URLPattern(pattern, view, kwargs, name)
else:
raise TypeError('view must be a callable or a list/tuple in the case of include().')
path = partial(_path, Pattern=RoutePattern)
re_path = partial(_path, Pattern=RegexPattern)
上述的偏函数_path返回的对象有两个分别是 URLResolver 和 URLPattern 两种情况,根据不同的情况进行判断,传入的参数元组和列表的信息,因为我们写路由信息的时候分成两种情况,一是直接写视图函数,还有一种是分发到 app 中的子路由,使用 include 函数。直接传入视图函数的是第二种情况,因此可以判断 include 就是第一种情况,并且_path内部也处理了 include 的相关参数。
""" include 函数源码,
"""
def include(arg, namespace=None):
app_name = None
if isinstance(arg, tuple):
# Callable returning a namespace hint.
try:
urlconf_module, app_name = arg
except ValueError:
if namespace:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'Cannot override the namespace for a dynamic module that '
'provides a namespace.'
)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'Passing a %d-tuple to include() is not supported. Pass a '
'2-tuple containing the list of patterns and app_name, and '
'provide the namespace argument to include() instead.' % len(arg)
)
else:
# No namespace hint - use manually provided namespace.
urlconf_module = arg
if isinstance(urlconf_module, str):
urlconf_module = import_module(urlconf_module)
patterns = getattr(urlconf_module, 'urlpatterns', urlconf_module)
app_name = getattr(urlconf_module, 'app_name', app_name)
if namespace and not app_name:
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'Specifying a namespace in include() without providing an app_name '
'is not supported. Set the app_name attribute in the included '
'module, or pass a 2-tuple containing the list of patterns and '
'app_name instead.',
)
namespace = namespace or app_name # 不存在命名空间的话默认是 app_name 的信息;
# Make sure the patterns can be iterated through (without this, some
# testcases will break).
if isinstance(patterns, (list, tuple)):
for url_pattern in patterns:
pattern = getattr(url_pattern, 'pattern', None)
if isinstance(pattern, LocalePrefixPattern):
raise ImproperlyConfigured(
'Using i18n_patterns in an included URLconf is not allowed.'
)
return (urlconf_module, app_name, namespace) # 返回的是一个元组, 满足了偏函数的处理逻辑
3.流程的图形化复现

继续努力,终成大器!
标签:匹配,name,pattern,self,middleware,Django,path,response,路由 From: https://www.cnblogs.com/Blogwj123/p/17964373