title: JDBC学习
excerpt:
tags: [Java, MySQL]
categories:
- [学习, Java]
- [学习, MySQL]
index_img: https://picture-store-repository.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/PicGo/jdbc.png
banner_img: https://picture-store-repository.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/PicGo/process.png
date: 2021-02-07 19:49:11
comment: true
MySQL学习笔记(狂神说Java)
狂神说B站视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1NJ411J79W?p=1
MySQL官网:https://www.mysql.com/
MySQL教程:https://www.runoob.com/mysql/mysql-tutorial.html
一、数据库驱动
驱动:声卡、显卡、数据库
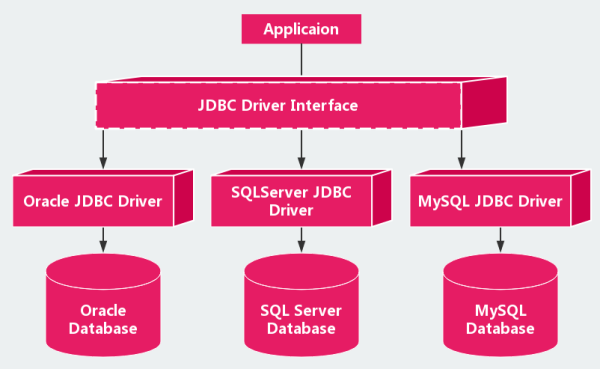
我们的程序会通过数据库驱动和数据库打交道!
二、JDBC
三、第一个JDBC程序
1.创建测试数据库
-- JDBC
CREATE DATABASE jdbcStudy CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
USE jdbcStudy;
CREATE TABLE `users`(
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(40),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(40),
email VARCHAR(60),
birthday DATE
);
INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday)
VALUES(1,'zhansan','123456','[email protected]','1980-12-04'),
(2,'lisi','123456','[email protected]','1981-12-04'),
(3,'wangwu','123456','[email protected]','1979-12-04')
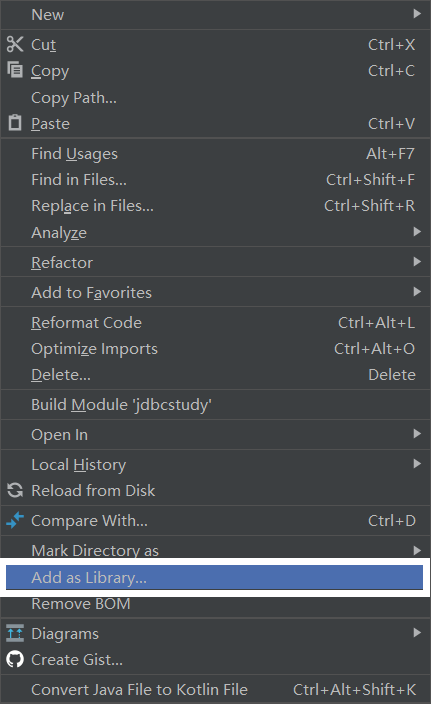
2.导入数据库驱动
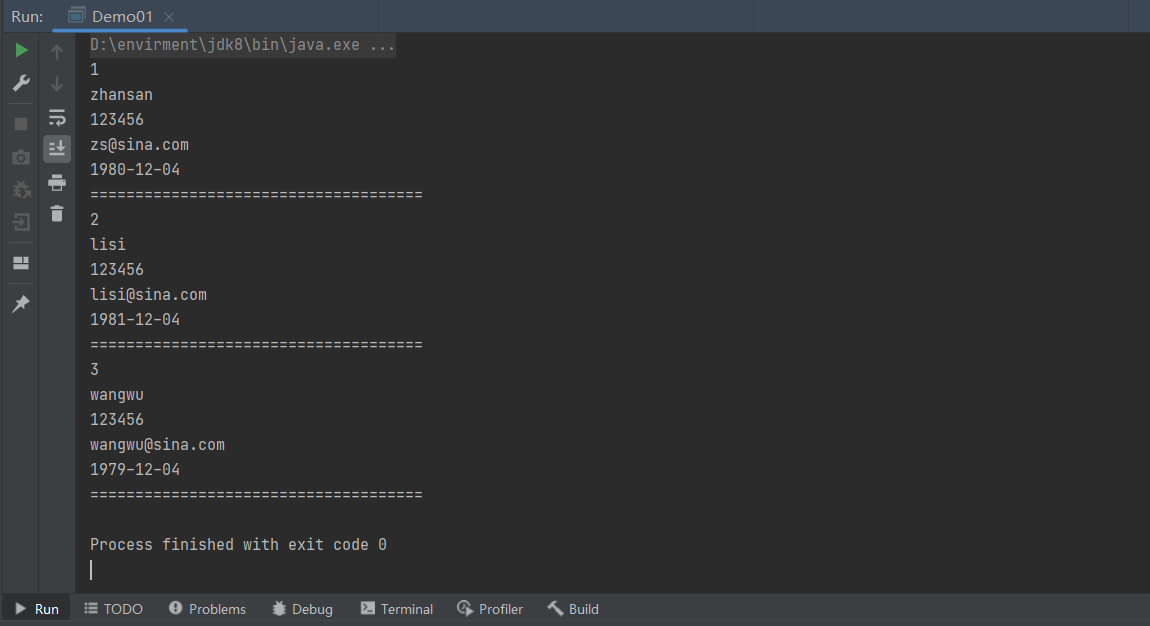
3.编写测试代码
package JDBC;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
// 1 加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //固定写法
// 2 url 和 用户信息
// useUnicode=true :使用Unicode编码 支持中文
// characterEncoding=utf8 :设定中文字符集为 UTF-8
// useSSL=true :使用安全的连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost|:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
// 3 建立连接 connection代表数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
// 4 新建 SQL操作对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 5 执行 SQL操作对象
String sql = "select * from users";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);//链表类型,返回的结果集,结果集中封装了全部的查询对象
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================================");
}
// 6 释放连接 后创建的先释放
statement.close();
connection.close();
connection.close();
}
}
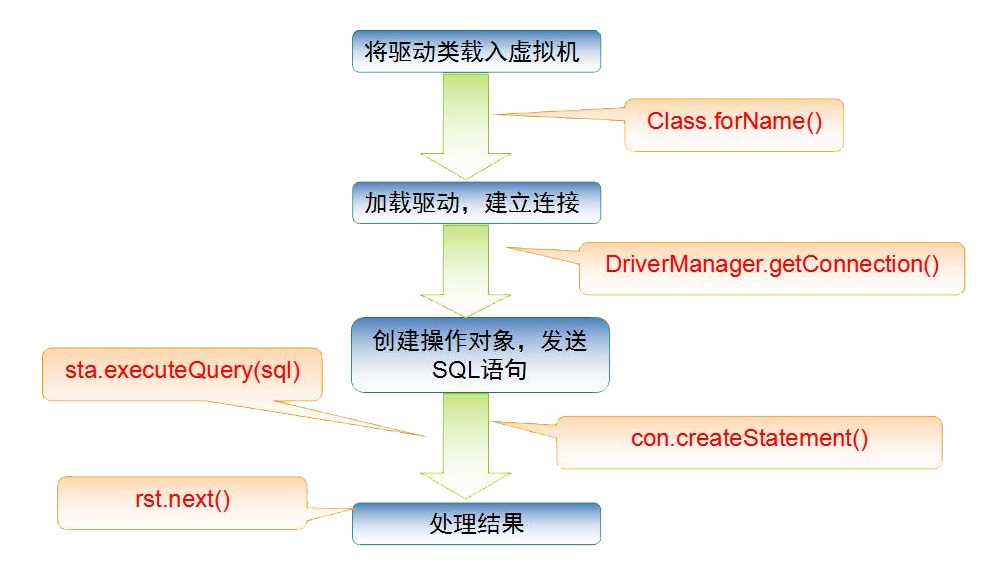
步骤总结: 加载驱动 - 连接数据库(DriverManager) - 获取执行对象(Statement) - 获得返回结果集 - 释放连接
4.常用对象分析
DriverManager
//DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //固定写法
//connection代表数据库对象
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
connection.commit(); //事务提交
connection.rollback();//数据库回滚
connection.setAutoCommit();//数据库设置自动提交
URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true";
// useUnicode=true :使用Unicode编码 支持中文
// characterEncoding=utf8 :设定中文字符集为 UTF-8
// useSSL=true :使用安全的连接
jdbc:mysql//主机地址:3306/数据库名?参数1&参数2&参数3
//musql - 3306
//oralce - 1521
//jdbc:oralce:thin:@localhost:1521:sid
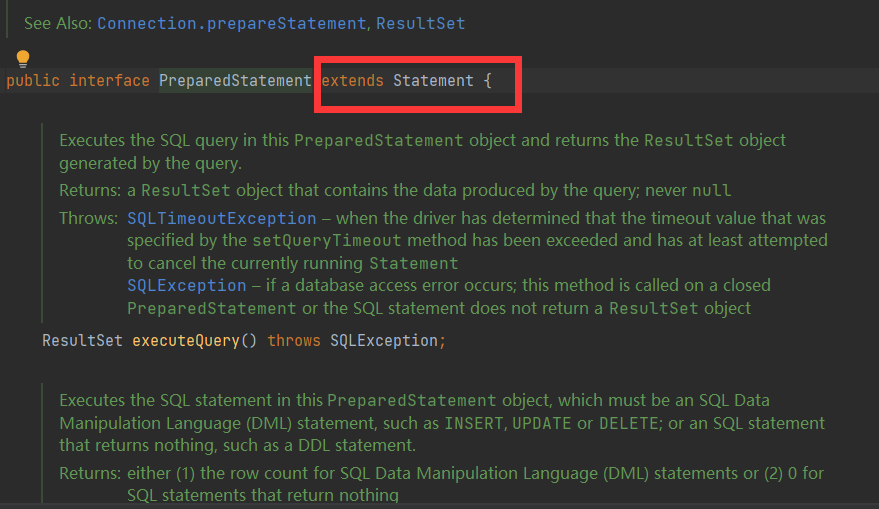
Statement
PreparedStatement //同为执行SQL的对象
//新建 SQL对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from users";//编写SQL
statement.executeQuery(); //查询操作,返回ResultSet数据集
statement.executeUpdate(); //更新、插入、删除,返回受影响的行数
statement.execute(); //执行任何SQL
statement.clearBatch(); //执行SQL的批处理
ResultSet
//查询的结果集 封装了所有查询结果
获得指定数据类型
//在不知道类类型的情况下使用,如果知道就用指定类型
resultSet.getObject();
resultSet.getDouble();
resultSet.getString();
resultSet.getFloat();
resultSet.getInt();
.....
遍历(指针)
resultSet.beforeFirst(); //移动到最前面
resultSet.afterLast(); //移动到最后面
resultSet.next(); //移动到下一个数据
resultSet.previous(); //移动到前一行
resultSet.absolute(row); //移动到指定行
释放资源
statement.close();
connection.close();
connection.close();
四、statement对象
JDBC中的statement对象用于向数据库发送SQL语句,想完成对数据库的增删改查,只需要通过这个对象向数据库发送增删改查语句即可。
Statement对象的executeUpdate方法,用于向数据库发送增、删、改的sql语句,executeUpdate执行完后,将会返回一个整数(即增删改语句导致了数据库几行数据发生了变化)。
Statement.executeQuery方法用于向数据库发送查询语句,executeQuery方法返回代表查询结果的ResultSet对象。
1.db.properties
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
username=root
password=123456
2.jdbcUtils
package com.baixf.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try {
//返回一个输入流
InputStream resourceAsStream = jdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 1 驱动只需要加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 2 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
// 3 释放连接
public static void release(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException {
if(resultSet!=null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.CRUD操作
Create
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据添加操作,示例操作:
statement st = conn.createstatement(;
string sq1 = "insert into user(... . ) values .... . ) ";
int num = st.executeupdate(sq1);
if(num>0){
system.out.println("插入成功!!! ");
}
Read
使用executeQuery(String sql)方法完成数据查询操作,示例操作:
statement st = conn.createstatement(;
string sql = "select t from user where id=1";Resu7tset rs = st.executeupdate(sq1);
while(rs.next({
//根据获取列的数据类型,分别调用rs的相应方法映射到java对象中
}
Update
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据修改操作,示例操作:
statement st = conn. createstatementO;
string sql = "update user set name='" where name='" ";int num = st.executeupdate(sq1);
if(num>0){
system.out.print1n(“修改成功!!! ");
}
Delete
使用executeUpdate(String sql)方法完成数据删除操作,示例操作:
statement st = conn.createstatementO;
string sql = "delete from user where id=1";
int num = st.executeupdate(sq1);
if(num>0){
system.out. println(“删除成功!!! ");
}
4.编写增删改查操作
添加数据
//插入数据
package com.baixf.lesson02;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException ,NullPointerException{
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();//获取数据库连接
statement = connection.createStatement();//获得SQL的执行对象
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday)" +
"VALUES(6,'wangwu','password','[email protected]','2020-12-25')" ;
int i = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
assert statement != null;
jdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
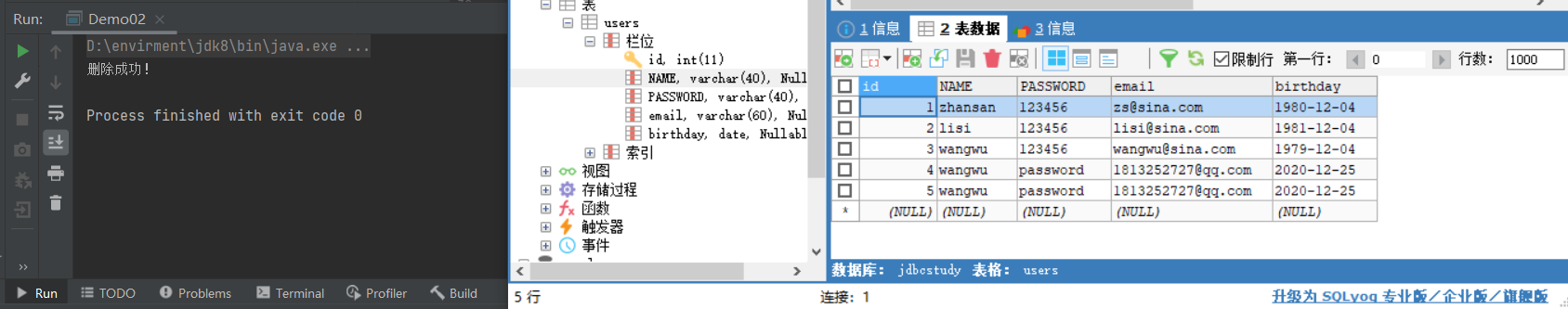
删除数据
package com.baixf.lesson02;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
//创建数据库连接
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//获得 SQL对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//编写 SQL语句
String str = "DELETE FROM users WHERE `ID`=6;";
int i = statement.executeUpdate(str);
if (i>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
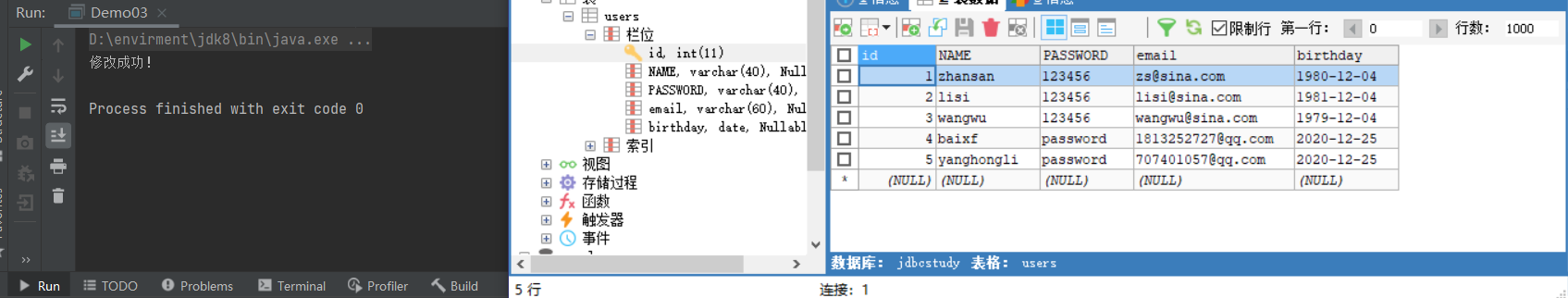
更新数据
package com.baixf.lesson02;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
//创建数据库连接
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//获得 SQL对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//编写 SQL语句
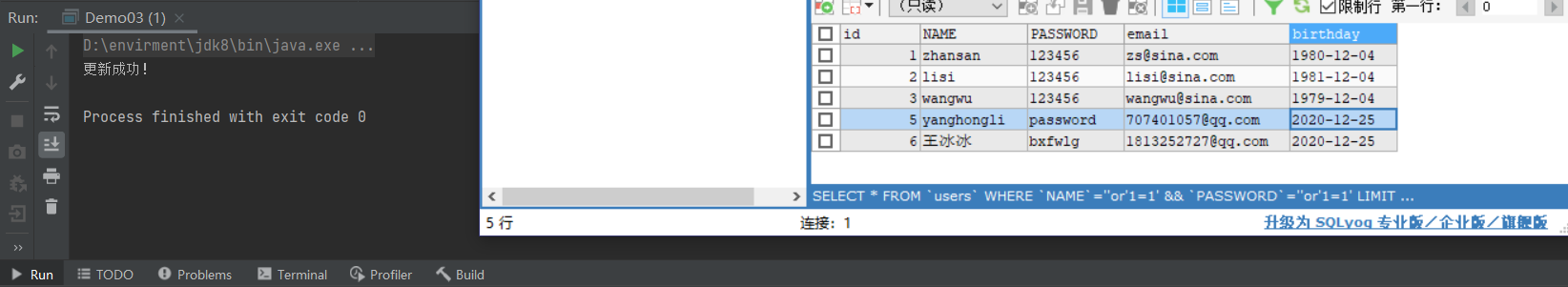
String str = "UPDATE users SET `NAME`='yanghongli',`email`='[email protected]' WHERE `id`=5";
int i = statement.executeUpdate(str);
if (i>0){
System.out.println("修改成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
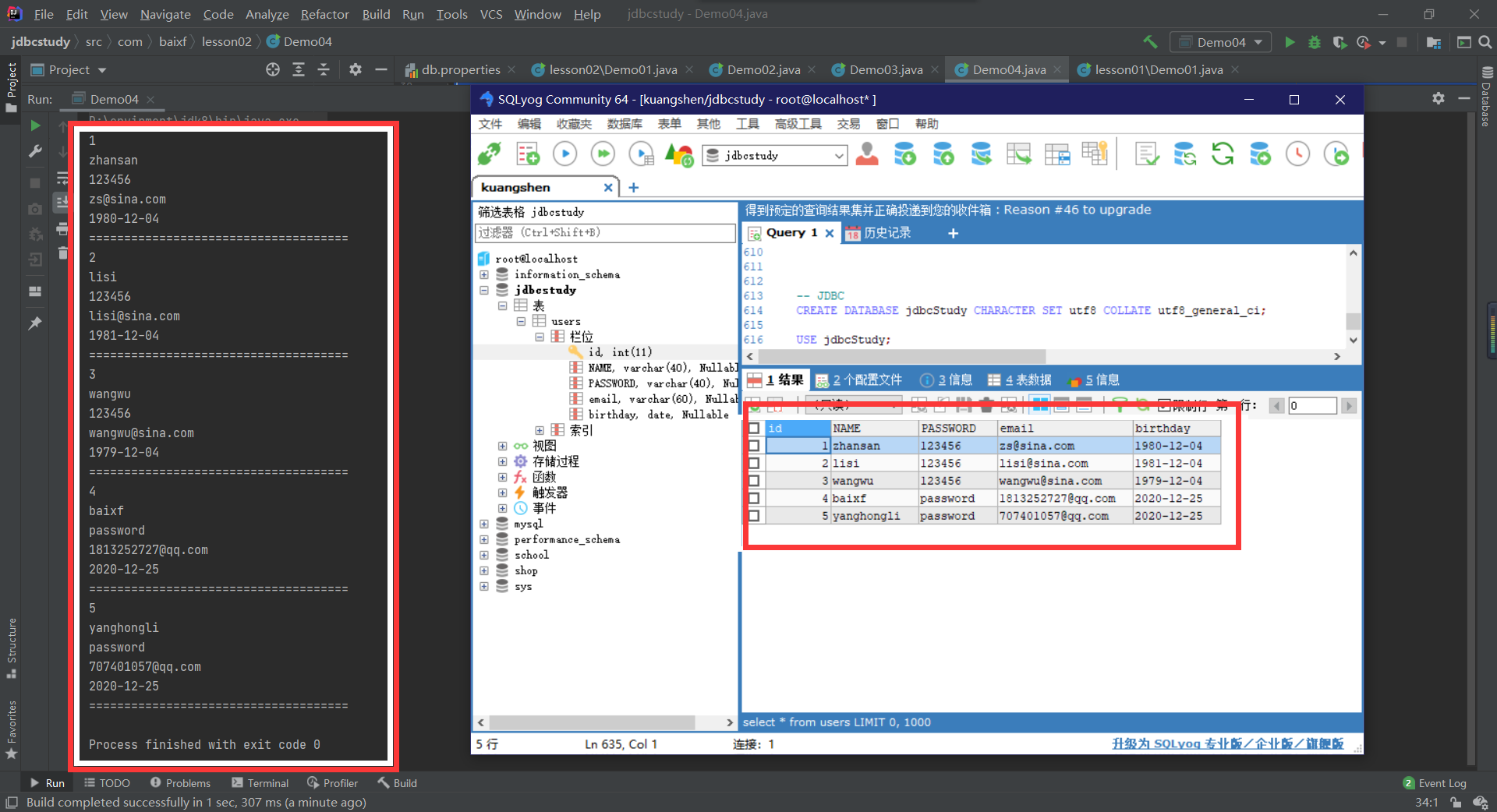
查询数据
package com.baixf.lesson02;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
// 建立连接
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 创建SQL对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 执行sql语句
String str = "SELECT * FROM users";
// resultset接收数据集
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(str);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
}
}
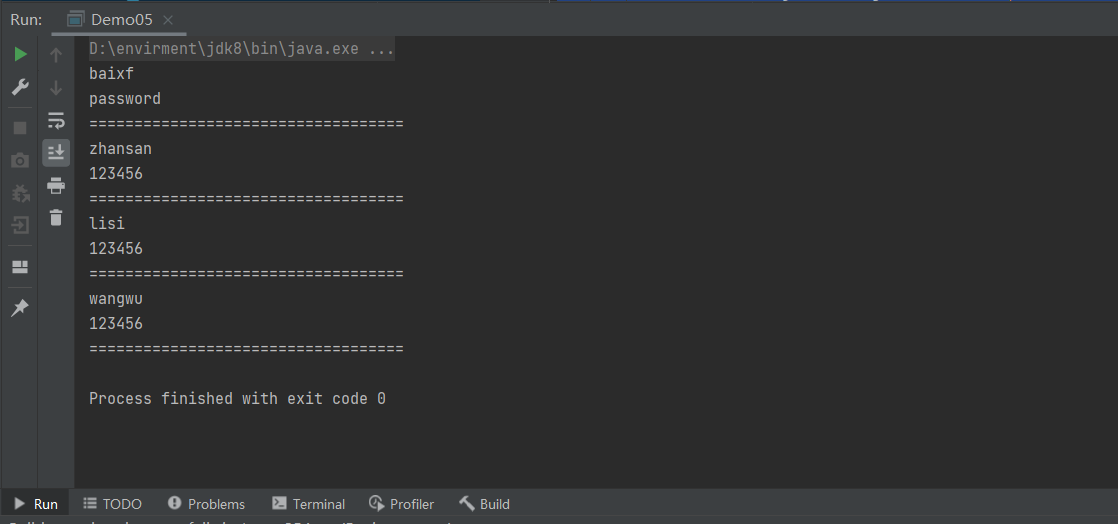
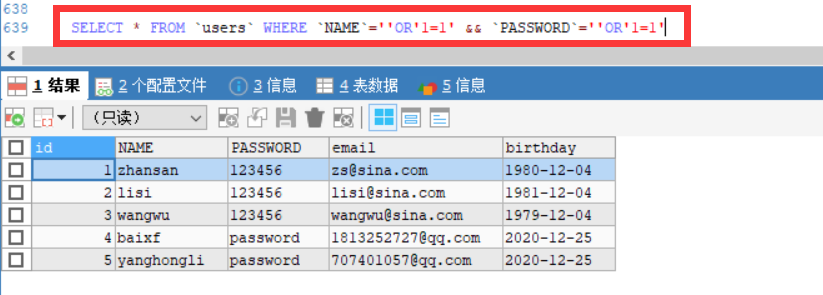
SQL注入问题
SQL存在漏洞,会被攻击导致数据泄露,SQL会被拼接。
SQL注入是比较常见的网络攻击方式之一,它不是利用操作系统的BUG来实现攻击,而是针对程序员编写时的疏忽,通过SQL语句,实现无账号登录,甚至篡改数据库。
package com.baixf.lesson02;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo05 {
// SQL 注入
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
login("baixf","password");
//login("baixf","");
login("","password");
login("'or '1=1","123456");
}
public static void login(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 建立连接
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 创建SQL对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
// 执行sql语句
String str = "SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `NAME`='" + username + "' && `PASSWORD`='" + password + "'";
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(str);
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("===================================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
}
}
五、PreparedStatement 对象
PreparedStatement 对象可以防止SQL注入,而且效率更快。
1.db.properties
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true
username=root
password=123456
2.jdbcUtils
package com.baixf.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try {
//返回一个输入流
InputStream resourceAsStream = jdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 1 驱动只需要加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
}catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 2 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
// 3 释放连接
public static void release(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException {
if(resultSet!=null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.CRUD操作
增加数据
package com.baixf.lesson03;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
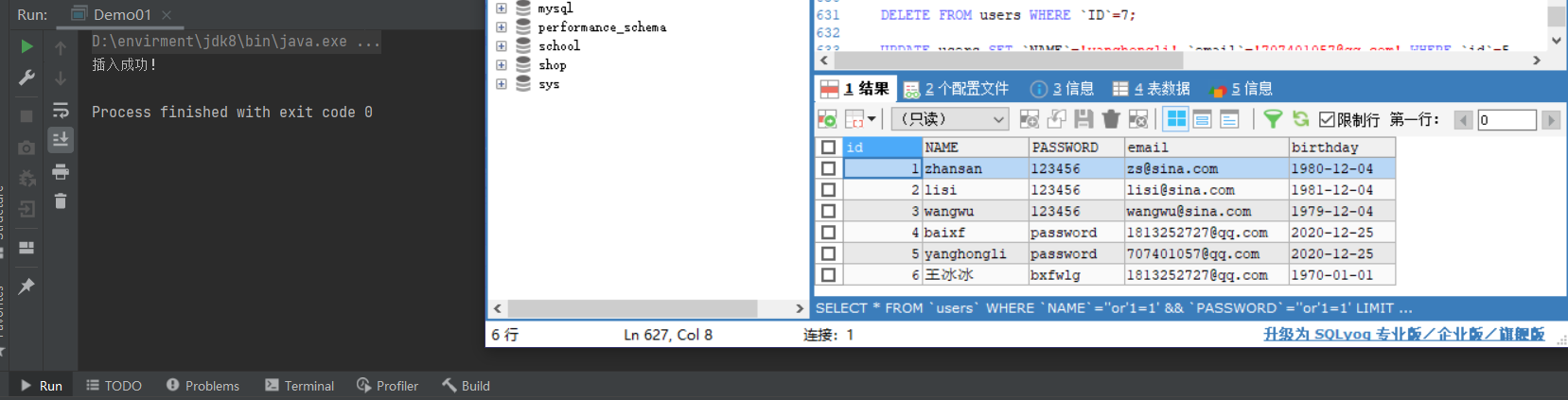
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别 : 使用 ? 占位符
String str = "INSERT INTO `users`(id,NAME,PASSWORD,email,birthday) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?)";
//预编译 SQL ,先写 SQL 然后赋值
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(str);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,6);
preparedStatement.setString(2,"王冰冰");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"bxfwlg");
preparedStatement.setString(4,"[email protected]");
preparedStatement.setDate(5, new Date(2000));
//执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
删除数据
package com.baixf.lesson03;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.Date;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
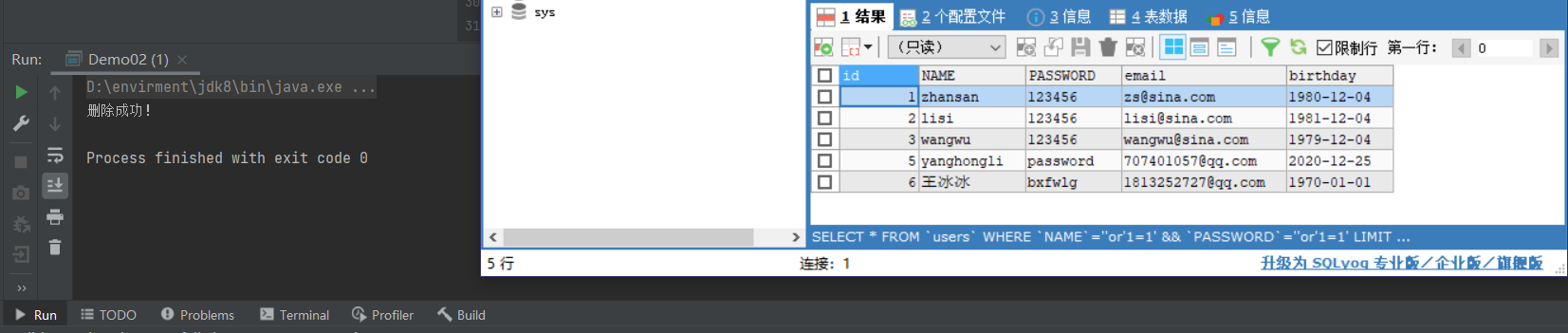
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别 : 使用 ? 占位符
String str = "delete from users where name = ?";
//预编译 SQL ,先写 SQL 然后赋值
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(str);
//赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"baixf");
//执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
更新数据
package com.baixf.lesson03;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别 : 使用 ? 占位符
String str = "update users set birthday = ? where name = ?";
//预编译 SQL ,先写 SQL 然后赋值
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(str);
//赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,"2020-12-25");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"王冰冰");
//执行
int i = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
if (i>0){
System.out.println("更新成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
查询数据
package com.baixf.lesson03;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//区别 : 使用 ? 占位符
String str = "select * from users where name = ?";
//预编译 SQL ,先写 SQL 然后赋值
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(str);
//赋值
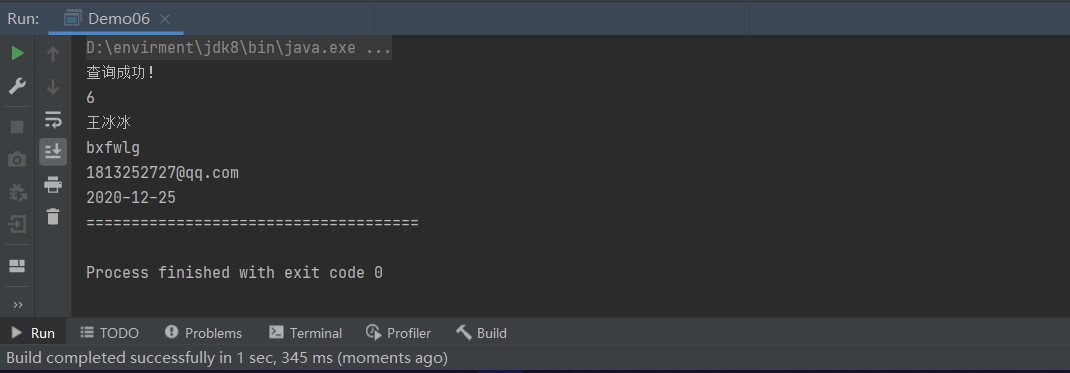
preparedStatement.setString(1,"王冰冰");
//执行并使用数据集接收数据
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println("查询成功!");
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println("=====================================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,null);
}
}
}
防止注入问题
PreparedStatement 对象防止SQL注入的本质:把传递的参数当作字符
假设存在转义字符,将直接被忽略 ,例如 ' (引号)
package com.baixf.lesson03;
import com.baixf.lesson02.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo07 {
// 防止 SQL 注入
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//login("baixf","password");
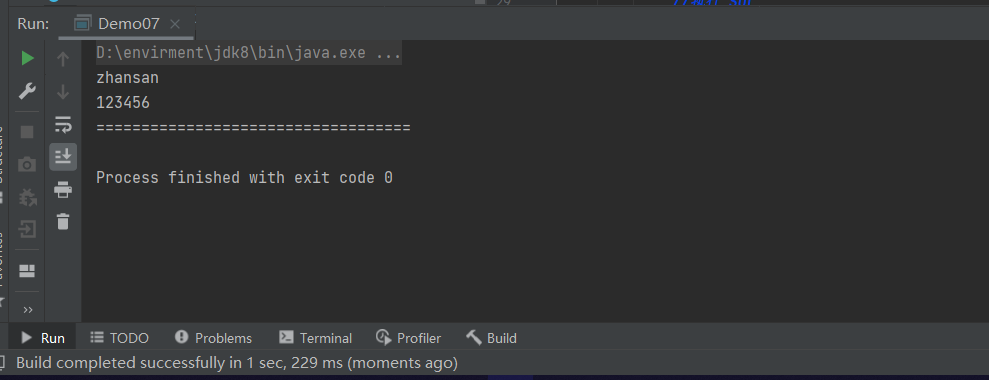
login("zhansan","123456");
//login("","password");
login("'or '1=1","'or '1=1");
}
public static void login(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
// 建立连接
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
// 预编译 sql语句
String str = "SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE `NAME`=? && `PASSWORD`=?"; //Mybatis
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(str);
//赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,username);
preparedStatement.setString(2,password);
//执行 SQL
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("NAME"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getObject("PASSWORD"));
System.out.println("===================================");
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
}
}
}
六、使用IDEA连接数据库
1.建立连接
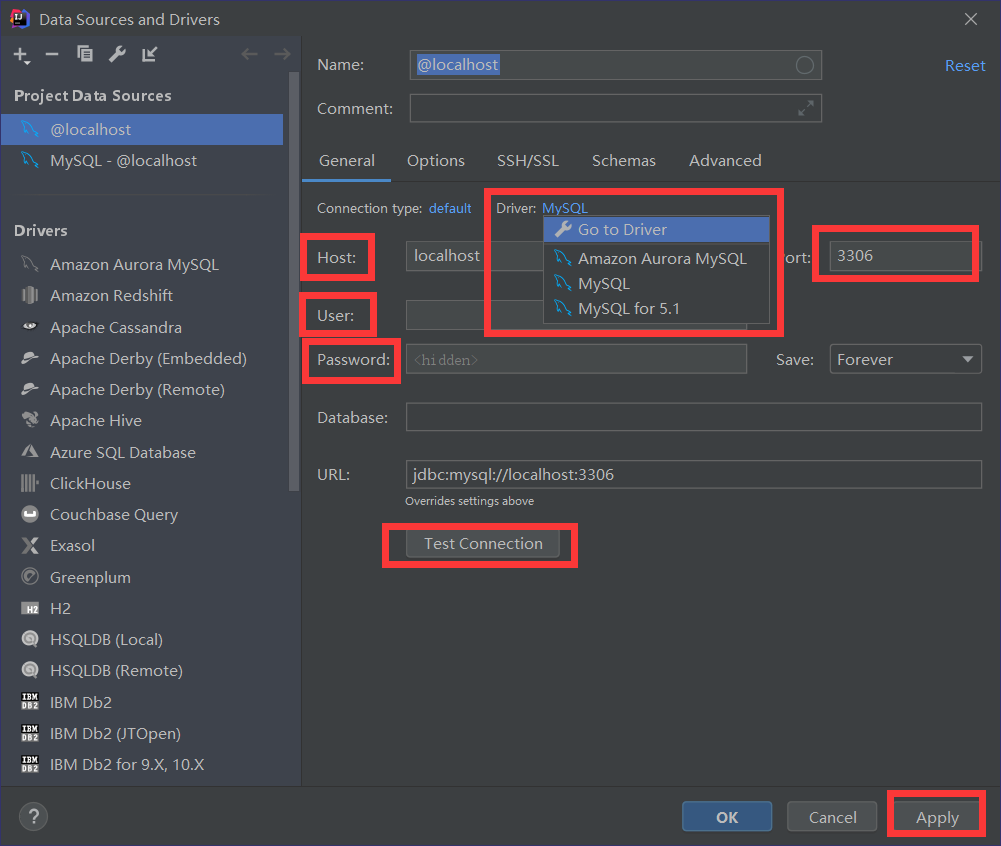
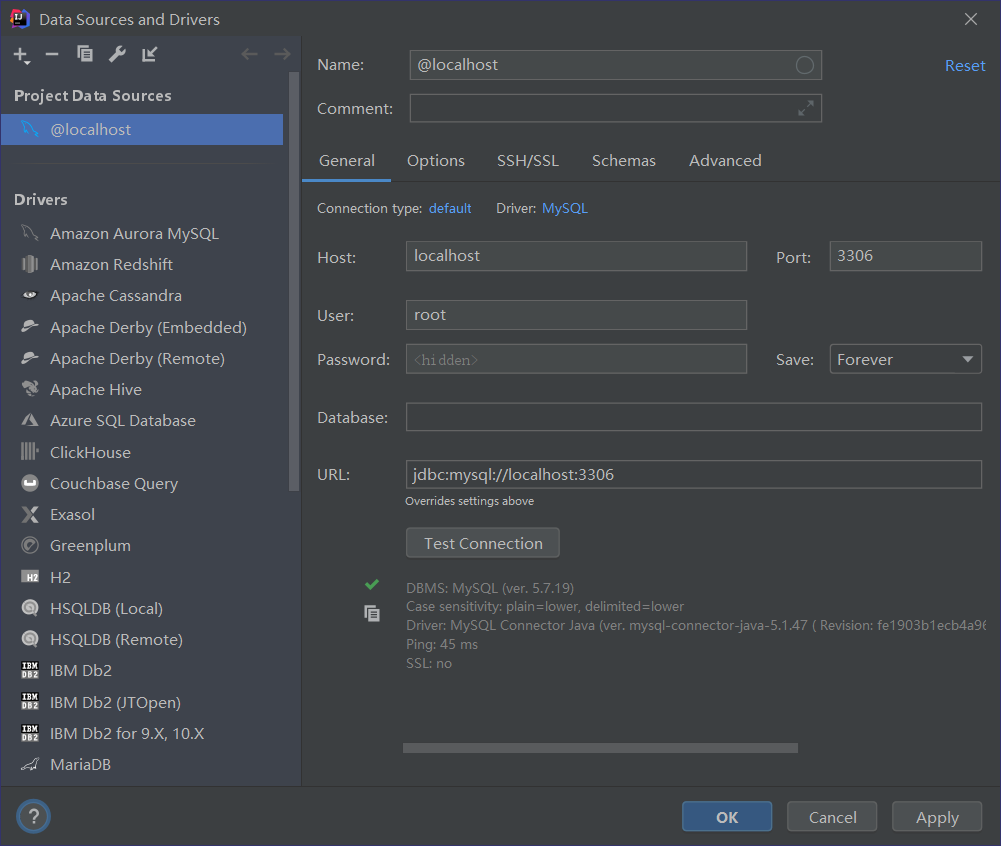
2.连接成功后选择数据库
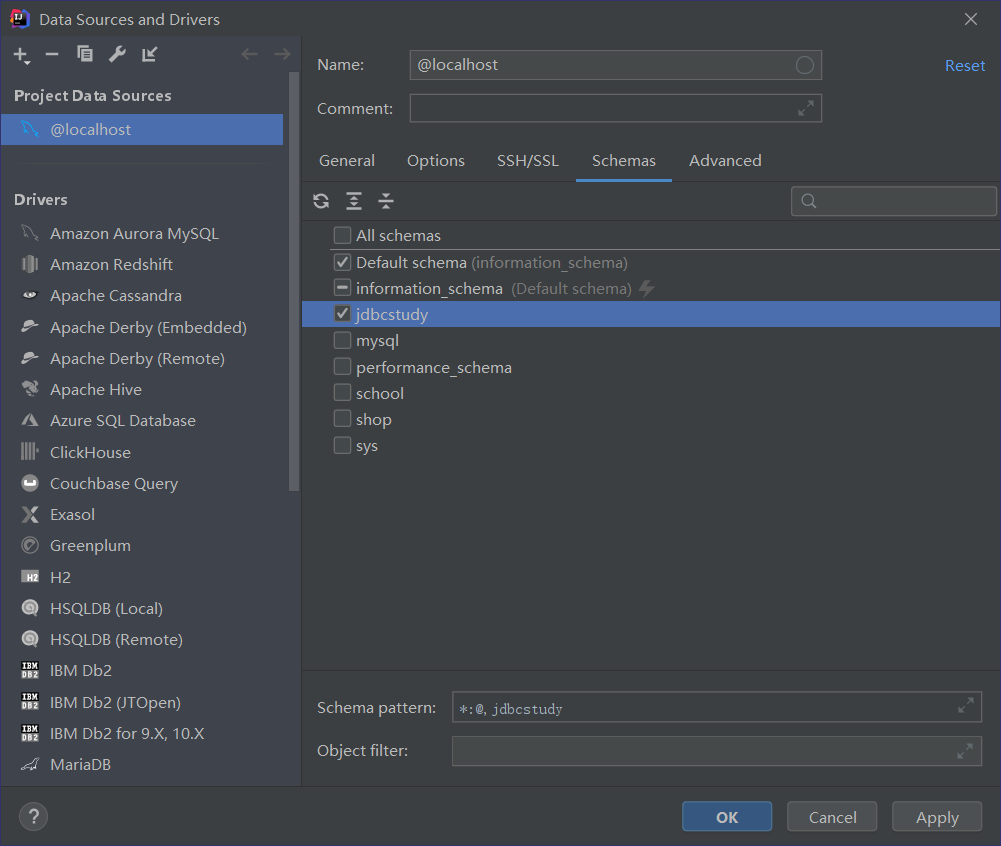
3.查看数据库中的内容
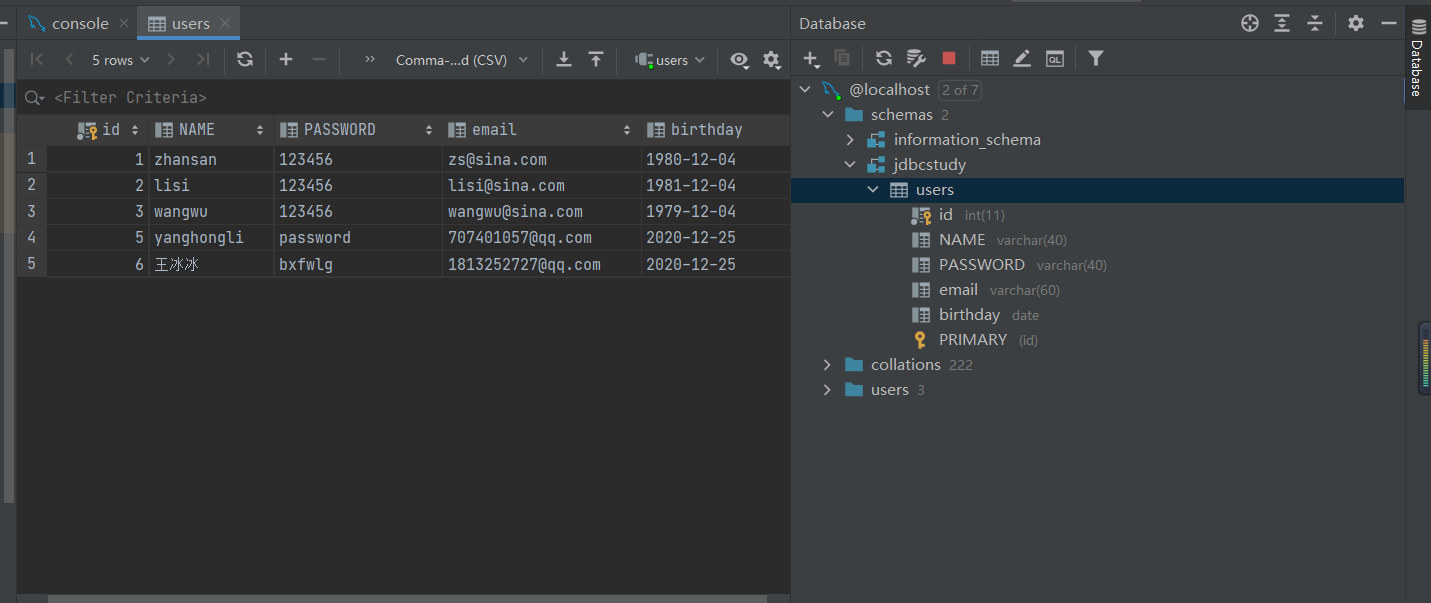
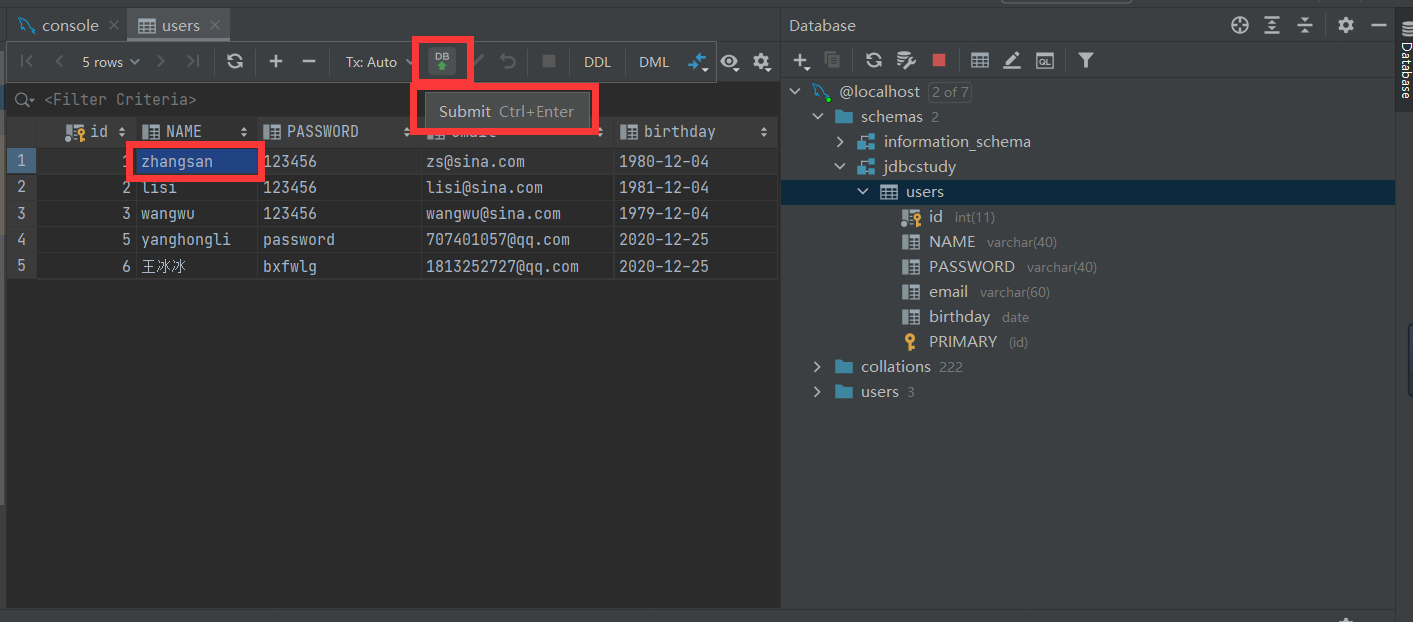
4.CRU操作
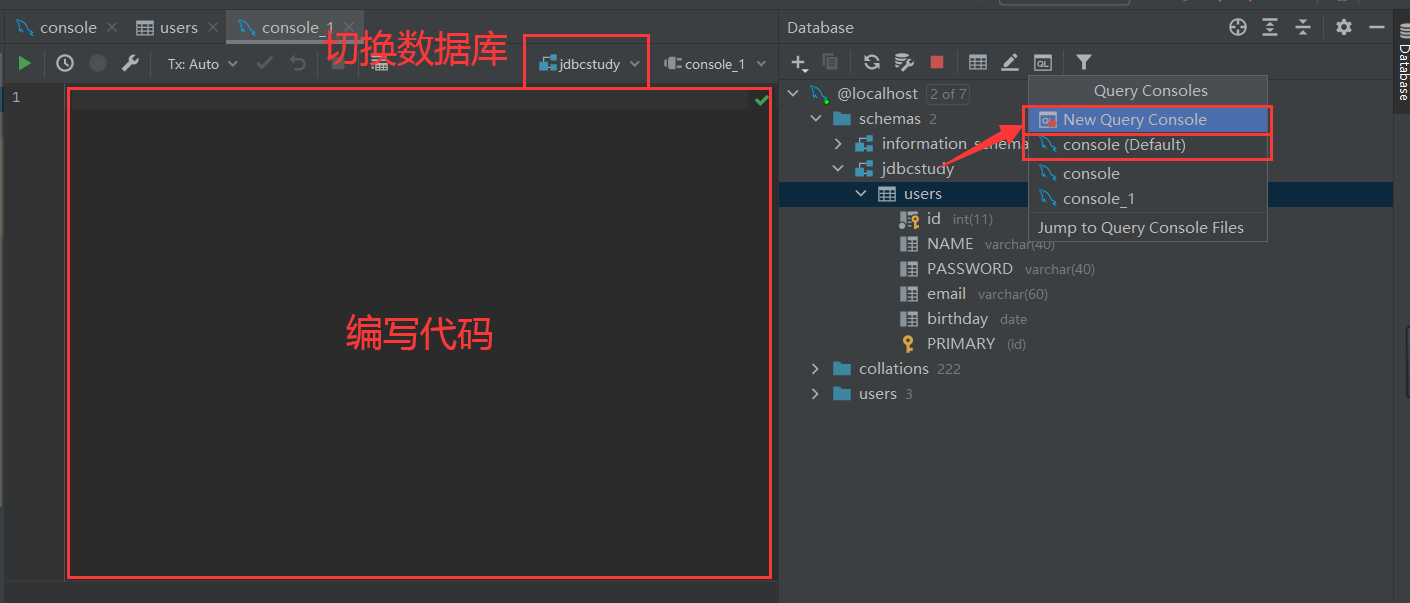
5.其他操作
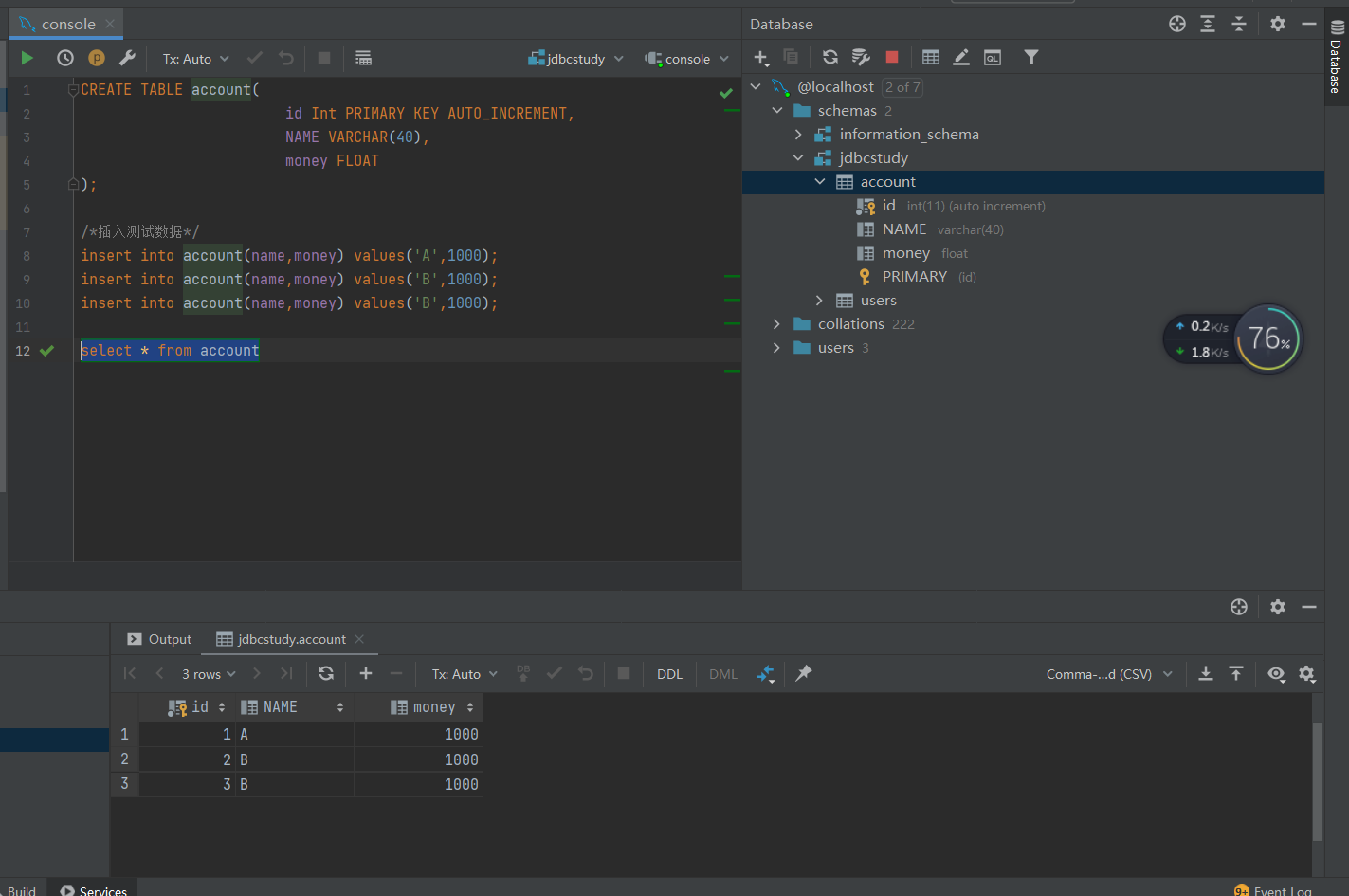
七、事务
要么都成功,要么都失败!
1.ACID原则
- 原子性:要么全部完成,要么不完成
- 一致性:总数不变
- 隔离性:多个进程互不干扰
- 持久性:一旦提交不可逆
2.代码实现
1.开启事务。
2.一组业务执行完毕,提交事务。
3.可以在catch语句中显示的定义 回滚语句,但默认失败就会回滚。
package com.baixf.lesson04;
import com.baixf.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Transaction {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
//关闭数据库自动提交
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//关闭数据库自动提交,自动开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
String sql1 = "UPDATE ACCOUNT SET `money` = `money` - 100 WHERE NAME='A'";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
String sql2 = "UPDATE ACCOUNT SET `money` = `money` + 100 WHERE NAME='B'";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
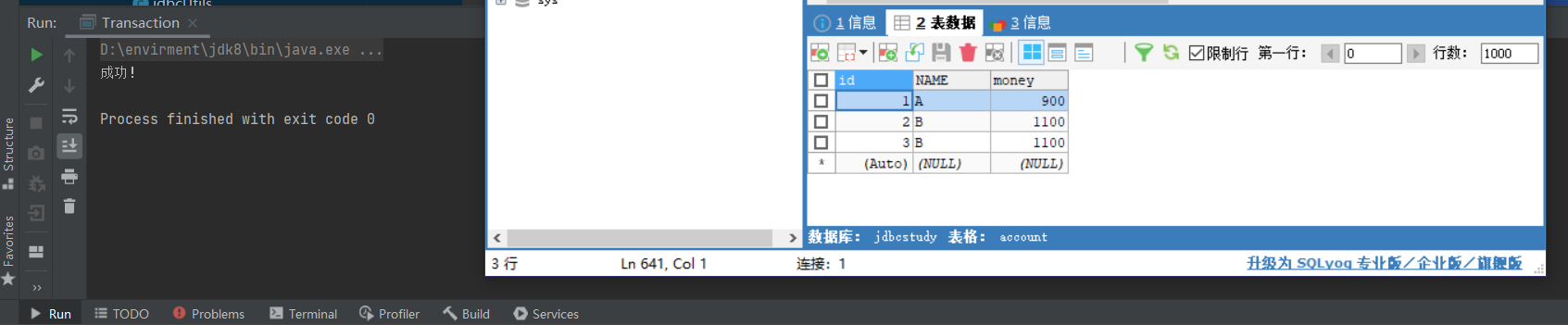
//业务完毕,提交事务
connection.commit();
System.out.println("成功!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
connection.rollback();//如果失败则回滚
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
}
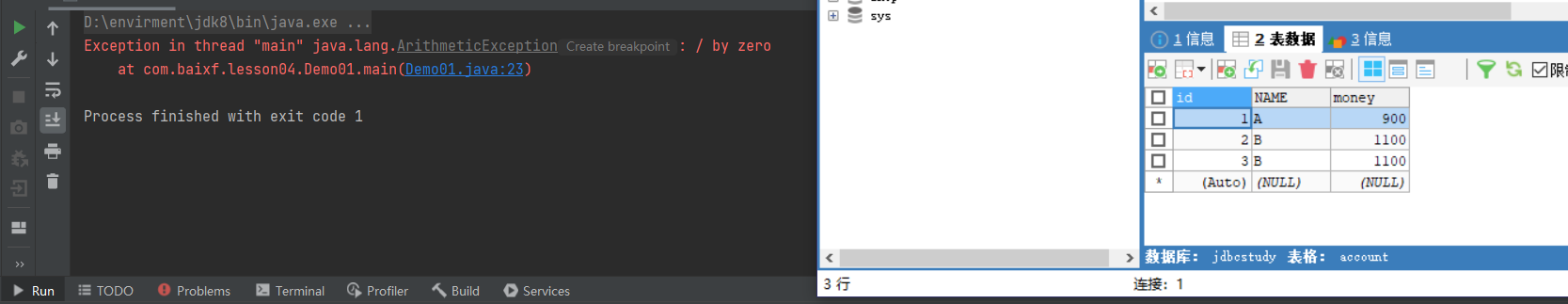
失败案例
回滚!
package com.baixf.lesson04;
import com.baixf.utils.jdbcUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet=null;
try {
//关闭数据库自动提交
connection = jdbcUtils.getConnection();
//关闭数据库自动提交,自动开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
String sql1 = "UPDATE ACCOUNT SET `money` = `money` - 100 WHERE NAME='A'";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql1);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
int x=1/0;
String sql2 = "UPDATE ACCOUNT SET `money` = `money` + 100 WHERE NAME='B'";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql2);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//业务完毕,提交事务
connection.commit();
System.out.println("成功!");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
connection.rollback();//如果失败则回滚
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
jdbcUtils.release(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
}
八、数据库连接池
数据库连接--执行完毕--释放
连接 ---》释放十分浪费资源
池化技术:准备一些预先的资源,过来就连接预先准备好的
常用连接数:10
最小连接数:10
最大连接数:100
编写连接池,实现一个接口:Datasource
1.开源数据源实现
使用了这些数据库连接池,项目中就不需要编写连接数据库的代码!
-
DBCP (需要用到commons-dbcp-1.4.jar、commons-pool-1.6.jar包)
-
C3P0 (需要用到c3p0-0.9.5.5.jar、mchange-commons-java-0.2.19.jar包)
-
Druid:Alibaba
2.jdbcUtils_DBCP.properties
#连接设置 DBCP数据源定义!
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bank
username=root
password=123456
#初始化连接
initialSize=10
#最大连接数量
maxActive=50
#最大空闲连接
maxIdle=20
#最小空闲连接
minIdle=5
#超时等待时间
maxWait=60000
#JDBC驱动建立连接时附带的连接属性属性的格式必须为这样:[属性名=property;]
#注意:“user” 与 “password” 两个属性会被明确地传递,因此这里不需要包含他们。
connectionProperties=useUnicode=true;characterEncoding=UTF8
#指定由连接池所创建的连接的自动提交(auto-commit)状态。
defaultAutoCommit=true
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的事务级别(TransactionIsolation)。
#可用值为下列之一:(详情可见javadoc。)NONE,READ_UNCOMMITTED, READ_COMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE
defaultTransactionIsolation=READ_UNCOMMITTED
package com.baixf.utils;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class jdbcUtils_DBCP {
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
static {
try {
InputStream in = jdbcUtils_DBCP.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
//创建数据源 工厂模式 -- 》 创建
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 2 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return dataSource.getConnection();//从数据源中获取连接
}
// 3 释放连接
public static void release(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException {
if(resultSet!=null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.c3p0-config.xml
<c3p0-config>
<!-- 使用默认的配置读取连接池对象 -->
<default-config>
<!-- 连接参数 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">root</property>
<!-- 连接池参数 -->
<!--初始化申请的连接数量-->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<!--最大的连接数量-->
<property name="maxPoolSize">10</property>
<!--超时时间-->
<property name="checkoutTimeout">3000</property>
</default-config>
<named-config name="otherc3p0">
<!-- 连接参数 -->
<property name="driverClass">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="jdbcUrl">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<property name="user">root</property>
<property name="password">root</property>
<!-- 连接池参数 -->
<property name="initialPoolSize">5</property>
<property name="maxPoolSize">8</property>
<property name="checkoutTimeout">1000</property>
</named-config>
</c3p0-config>
package com.itheima.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
//自定义的JDBC工具类, 结合配置文件使用.
public class JDBCUtils2 {
//1. 构造方法私有化.
private JDBCUtils2(){}
//2. 定义一些私有的静态的成员变量, 用来记录配置文件中的信息.
private static String driverClass;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
//3. 定义方法loadProperties(), 用来读取配置文件, 并将读取到的数据赋值给变量.
public static void loadProperties() {
//3.1 定义Properties集合
Properties pp = new Properties();
//3.2 加载配置文件中的文件到集合中.
try {
pp.load(JDBCUtils2.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3.3 给成员变量赋值.
driverClass = pp.getProperty("driverClass");
url = pp.getProperty("url");
username = pp.getProperty("username");
password = pp.getProperty("password");
}
//4. 通过静态代码块, 用来注册驱动.
static {
try {
//核心细节: 方法只有被调用, 才会执行.
//调用loadProperties()方法, 读取配置文件.
loadProperties();
//注册驱动.
Class.forName(driverClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//5. 对外提供一个公共的访问方式, 用来获取: 连接对象.
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
//6. 释放资源.
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement stat, ResultSet rs) {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
rs = null; //GC会优先回收null对象.
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (stat != null) {
stat.close();
stat = null;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
conn = null;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void release(Connection conn, Statement stat) {
try {
if (stat != null) {
stat.close();
stat = null;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
conn = null;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}