STL和基本数据结构
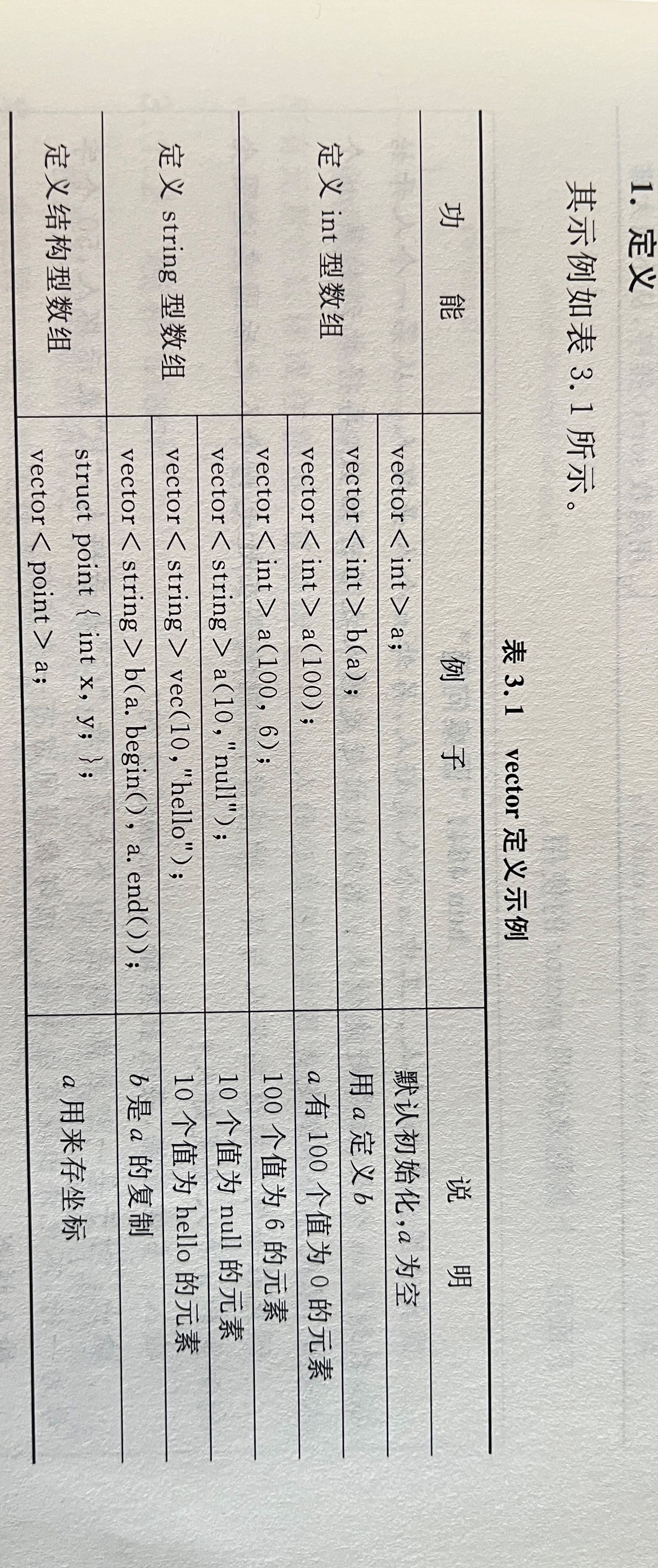
一、vector
用法:vector是STL的动态数组。
圆桌问题
****Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ***
Memory Limit: 65535/32768 K (Java/Others)
*
Problem Description
圆桌上围坐着2n个人。其中n个人是好人,另外n个人是坏人。如果从第一个人开始数数,数到第m个人,则立即处死该人;然后从被处死的人之后开始数数,再将数到的第m个人处死……依此方法不断处死围坐在圆桌上的人。试问预先应如何安排这些好人与坏人的座位,能使得在处死n个人之后,圆桌上围坐的剩余的n个人全是好人。
Input
多组数据,每组数据输入:好人和坏人的人数n(<=32767)、步长m(<=32767);
Output
对于每一组数据,输出2n个大写字母,‘G’表示好人,‘B’表示坏人,50个字母为一行,不允许出现空白字符。相邻数据间留有一空行。
Sample Input
2 3
2 4
Sample Output
GBBG
BGGB
Source
代码展示:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int >table; // 创建一个整型向量table
int n, m;
while (cin >> n >> m) { // 当输入n和m时循环
table.clear(); // 清空table向量
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) {
table.push_back(i); // 向table中添加元素,编号从0到2n-1
}
int pos = 0; // 初始化位置变量pos
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 循环n次
pos = (pos + m - 1) % table.size(); // 计算要删除的位置
table.erase(table.begin() + pos); // 删除指定位置的元素
}
int j = 0; // 初始化计数变量j
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) { // 循环2n次
if (!(i % 50) && i) cout << endl; // 每50个字符换行
if (j < table.size() && i == table[j]) { // 如果i在table中
j++;
cout << "G"; // 输出G
}
else
cout << "B"; // 否则输出B
}
cout << endl << endl; // 输出两个换行
}
return 0;
}
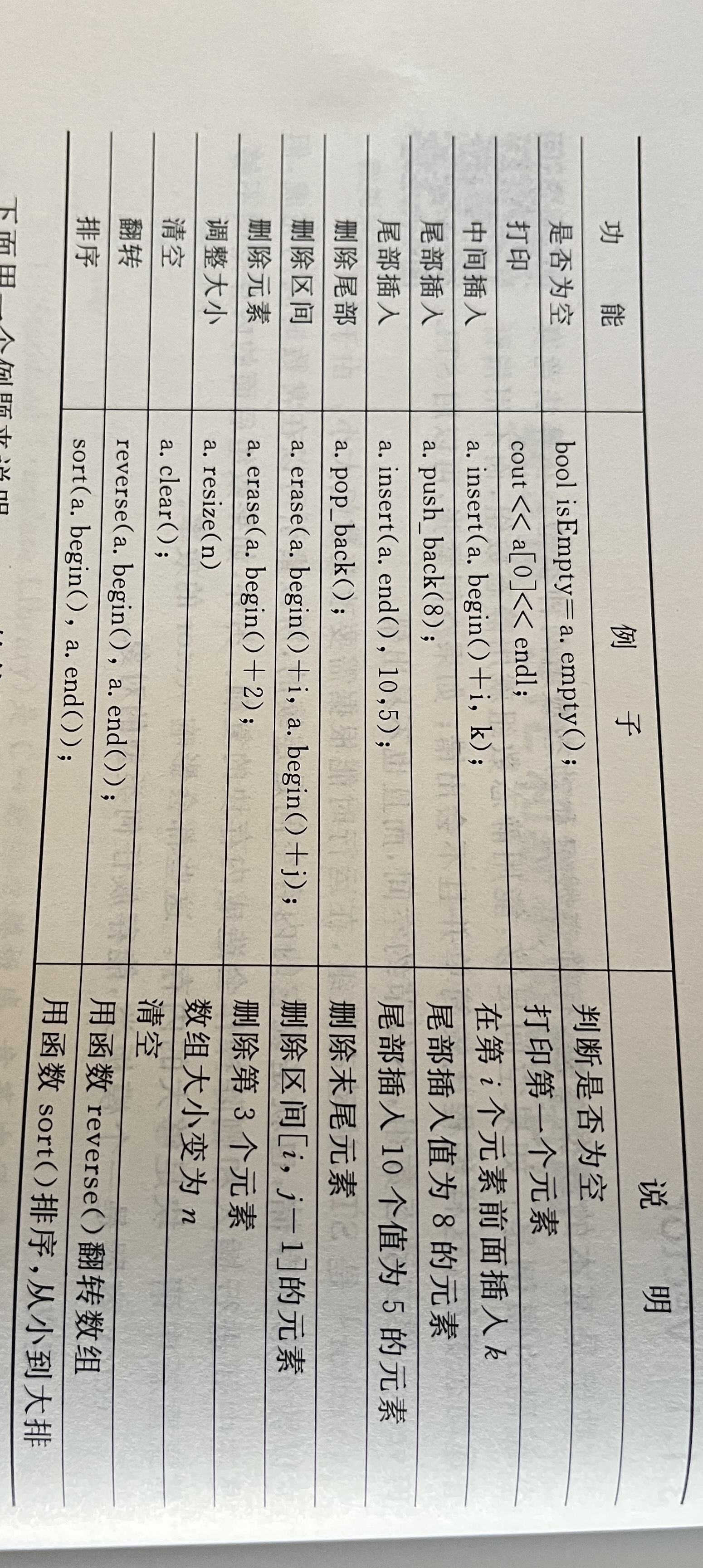
hdu 4841的vector程序用erase()来删除中间元素,需要把这个元素后面的所有元素往后移或往前移,复杂度是O(n),如果频繁移动,效率很低。
二、栈和stack

文本反转
****时间限制:2000/1000 MS(Java/其他) ***
内存限制:65536/32768 K(Java/其他)
*
问题描述
伊格内修斯喜欢用相反的方式写字。给定 Ignatius 编写的一行文本,您应该反转所有单词,然后输出它们。
输入
输入包含多个测试用例。输入的第一行是一个整数 T,它是测试用例的数量。接下来是 T 个测试用例。
每个测试用例都包含一行包含多个单词的行。一行最多有 1000 个字符。
输出
对于每个测试用例,您应该输出已处理的文本。
示例输入
3
olleh !dlrow
m'I morf .udh
I ekil .mca
示例输出
hello world!
I'm from hdu.
I like acm.
提示
记住使用 getchar() 在中间 T 之后读取 '\n',然后你可以使用 gets() 读取一行并处理它。
作者
伊格内修斯.L
来源
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
char ch;
cin >> n;
getchar();
while (n--) {
stack<char>s;
while (1) {
//cin >> ch;
ch = getchar();
if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\n' || ch == EOF) {
while (!s.empty()) {
cout << s.top();
s.pop();
}
if (ch == '\n' || ch == EOF) break;
cout << " ";
}
else
s.push(ch);
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
三、队列和queue:
“先进先出”
1.常用函数
- push() 在队尾插入一个元素
- pop() 删除队列第一个元素
- size() 返回队列中元素个数
- empty() 如果队列空则返回true
- front() 返回队列中的第一个元素
- back() 返回队列中最后一个元素
queue
ACboy needs your help again!
****时间限制:1000/1000 MS(Java/其他) ***
***内存限制:32768/32768 K(Java/其他)
****
问题描述
ACboy被绑架了!!
他非常想念他的母亲,现在非常害怕。你无法想象他被关进的房间有多黑,:(很差。
作为一个聪明的 ACMer,你想让 ACboy 走出怪物的迷宫。但当你到达迷宫的大门时,怪物说:“我听说你很聪明,但如果不能解决我的问题,你就会和ACboy一起死。
怪物的问题显示在墙上:
每个问题的第一行是一个整数N(命令的数量),以及一个单词“FIFO”或“FILO”。(你很高兴,因为你知道“FIFO”代表“先进先出”,而“FILO”代表“先进先出”)。
而接下来的N行,每行都是“IN M”或“OUT”,(M代表一个整数)。
而问题的答案就是一扇门的通行证,所以如果你想拯救ACboy,请仔细回答问题!
输入
输入包含多个测试用例。
第一行有一个整数,表示测试用例的数量。
每个子问题的输入如上所述。
输出
对于每个命令“OUT”,您应该根据单词“FIFO”或“FILO”输出一个整数,或者如果您没有任何整数,则输出一个单词“None”。
示例输入
4
4 FIFO
IN 1
IN 2
OUT
OUT
4 FILO
IN 1
IN 2
OUT
OUT
5 FIFO
IN 1
IN 2
OUT
OUT
OUT
5 FILO
IN 1
IN 2
OUT
IN 3
OUT
示例输出
1
2
2
1
1
2
None
2
3
源
[2007省赛集训队练习赛(1)
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t, n, temp;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
string str, str1;
queue<int>Q;
stack<int>S;
cin >> n >> str;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (str == "FIFO") {
cin >> str1;
if (str1 == "IN") {
cin >> temp;
Q.push(temp);
}
if (str1 == "OUT") {
if (Q.empty())
cout << "None" << endl;
else
{
cout << Q.front() << endl;
Q.pop();
}
}
}
else {
cin >> str1;
if (str1 == "IN") {
cin >> temp;
S.push(temp);
}
if (str1 == "OUT") {
if (S.empty())
cout << "None" << endl;
else {
cout << S.top() << endl;
S.pop();
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
四、set
set就是集合。STL的set用二叉搜索树实现,集合中的每个元素值出现一次,并且是排好序的。访问元素的时间复杂度是O(log2 n),很高效!
set<Type> s //定义一个set容器
set<Type> s(s1) //定义一个set容器,并用容器s1来初始化
set<Type> s(b, e) //b和e分别为迭代器的开始和结束的标记
set<Type> s(s1.begin(), s1.begin()+3) //用容器s1的第0个到第2个值初始化s
set<Type> s(a, a + 5) //将a数组的元素初始化vec向量,不包括a[4]
set<Type> s(&a[1], &a[4]) //将a[1]~a[4]范围内的元素作为s的初始值
s.begin() //返回指向第一个元素的迭代器
s.end() //返回指向最后一个元素的迭代器
s.clear() //清除所有元素
s.count() //返回某个值元素的个数
s.empty() //如果集合为空,返回true,否则返回false
s.equal_range() //返回集合中与给定值相等的上下限的两个迭代器
s.erase() //删除集合中的元素
s.find(k) //返回一个指向被查找到元素的迭代器
s.insert() //在集合中插入元素
s.lower_bound(k) //返回一个迭代器,指向键值大于等于k的第一个元素
s.upper_bound(k) //返回一个迭代器,指向键值大于k的第一个元素
s.max_size() //返回集合能容纳的元素的最大限值
s.rbegin() //返回指向集合中最后一个元素的反向迭代器
s.rend() //返回指向集合中第一个元素的反向迭代器
s.size() //集合中元素的数目
例题:
产生冠军
****Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ***
Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
*
Problem Description
有一群人,打乒乓球比赛,两两捉对撕杀,每两个人之间最多打一场比赛。
球赛的规则如下:
如果A打败了B,B又打败了C,而A与C之间没有进行过比赛,那么就认定,A一定能打败C。
如果A打败了B,B又打败了C,而且,C又打败了A,那么A、B、C三者都不可能成为冠军。
根据这个规则,无需循环较量,或许就能确定冠军。你的任务就是面对一群比赛选手,在经过了若干场撕杀之后,确定是否已经实际上产生了冠军。
Input
输入含有一些选手群,每群选手都以一个整数n(n<1000)开头,后跟n对选手的比赛结果,比赛结果以一对选手名字(中间隔一空格)表示,前者战胜后者。如果n为0,则表示输入结束。
Output
对于每个选手群,若你判断出产生了冠军,则在一行中输出“Yes”,否则在一行中输出“No”。
Sample Input
3
Alice Bob
Smith John
Alice Smith
5
a c
c d
d e
b e
a d
0
Sample Output
Yes
No
原题链接:Problem - 2094 (hdu.edu.cn)
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<string>A, B;
string s1, s2;
int n;
while (cin >> n && n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s1 >> s2;
A.insert(s1);
A.insert(s2);
B.insert(s2);
}
if (A.size() - B.size() == 1)
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else
cout << "No" << endl;
A.clear(), B.clear();
}
return 0;
}
五、map
一对一映射,给予关键字快速查找,不允许重复值。
购物
*时间限制:10000/5000 MS(Java/其他)
*** 内存限制:32768/32768 K(Java/其他)
****
问题描述
每个女孩都喜欢购物,蒲公英也是如此。现在她发现店里每天都在涨价,因为春节快到了。她喜欢一家名为“记忆”的商店。现在她想知道这家店的价格在每天变化后排名如何。
输入
一行连数n(n<=10000),代表商店数量。
然后是n行,每行包含一个字符串(长度小于31,只包含小写字母和大写字母。代表商店的名称。
然后一条直线连续一个数字 m (1<=m<=50),代表天。
然后 m 个零件,每个零件连数 n 行,每行连数一个数字 s 和一个字符串 p,代表这一天,商店 p 的价格上涨了 s。
输出
包含m行,在第i行中打印第i天后商店“内存”的排名。我们将排名定义为:如果有t家商店的价格高于“内存”,则其排名为t+1。
示例输入
3
memory
kfc
wind
2
49 memory
49 kfc
48 wind
80 kfc
85 wind
83 memory
示例输出
1
2
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, m, p;
map<string, int>shop;
while (cin >> n) {
string s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> s;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> p >> s;
shop[s] += p;
}
int rank = 1;
map<string, int>::iterator it;//迭代器
for (it = shop.begin(); it != shop.end(); it++) {
if (it->second > shop["memory"])
rank++;
}
cout << rank << endl;
}
shop.clear();
}
return 0;
}
六、next_permutation()
STL提供求下一个排列组合的函数next_permutation()。例如求abc的全排列。
返回值:如果没有下一个排列组合,返回false,否则返回true。每执行一次next_permutation(),就会把新的排列放到原来的空间里。
复杂度:O(n)。范围[first,last)
例题:
字典序最小指的是在一组字符串中,按照从前往后的顺序,第一个不同的字符在字母表中较小的字符串排在前面。
购物
****时间限制:10000/5000 MS(Java/其他) ***
内存限制:32768/32768 K (Java/其他)*
问题描述
每个女孩都喜欢购物,蒲公英也是如此。现在她发现店里每天都在涨价,因为春节快到了。她喜欢一家名为“记忆”的商店。现在她想知道这家店的价格在每天变化后排名如何。
输入
一行连数n(n<=10000),代表商店数量。
然后是n行,每行包含一个字符串(长度小于31,只包含小写字母和大写字母。代表商店的名称。
然后一条直线连续一个数字 m (1<=m<=50),代表天。
然后 m 个零件,每个零件连数 n 行,每行连数一个数字 s 和一个字符串 p,代表这一天,商店 p 的价格上涨了 s。
输出
包含m行,在第i行中打印第i天后商店“内存”的排名。我们将排名定义为:如果有t家商店的价格高于“内存”,则其排名为t+1。
示例输入
3
memory
kfc
wind
2
49 memory
49 kfc
48 wind
80 kfc
85 wind
83 memory
示例输出
1
2
代码示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
int a[1001];
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, m;
while (cin >> n >> m) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
a[i] = i;
int b = 1;
do {
if (b == m)
break;
b++;
} while (next_permutation(a + 1, a + 1 + n));
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << a[n] << endl;
}
return 0;
}