2023-10-18:用go语言,给定一个数组arr,长度为n,表示有0~n-1号设备,
arr[i]表示i号设备的型号,型号的种类从0~k-1,一共k种型号,
给定一个k*k的矩阵map,来表示型号之间的兼容情况,
map[a][b] == 1,表示a型号兼容b型号,
map[a][b] == 0,表示a型号不兼容b型号,
兼容关系是有向图,也就是a型号兼容b型号,不代表b型号同时兼容a型号,
如果i设备的型号兼容j设备的型号,那么可以从i设备修建一条去往j设备的线路,
修建线路的代价是i设备到j设备的距离:|i-j|,
你的目标是从0号设备到达n-1号设备,并不一定每个设备都联通,只需要到达即可。
返回最小的修建代价,如果就是无法到达返回-1。
1 <= n <= 1000,
1 <= k <= 50。
来自招商银行。
来自左程云。
答案2023-10-18:
大体步骤:
1.创建一个二维切片 own,长度为 k,用于记录每个型号的设备编号。
2.创建一个二维切片 nexts,长度为 k,用于记录每个型号兼容的下一个型号。
3.遍历数组 arr,将每个设备的编号添加到对应型号的 own 中。
4.遍历兼容矩阵 m,将每个型号兼容的下一个型号添加到对应型号的 nexts 中。
5.创建一个二叉堆 heap,并定义排序函数,按照修建代价升序排列。
6.将起始设备 (0, 0) 添加到堆中,表示从 0 号设备开始,修建代价为 0。
7.创建一个长度为 n 的布尔型切片 visited,用于标记设备是否被访问过。
8.当堆不为空时,进行以下操作:
-
弹出堆顶元素
t,表示当前位置和当前的修建代价。 -
获取当前位置
cur的设备编号和修建代价。 -
如果当前位置为目标位置
n-1,则返回当前的修建代价。 -
将当前位置标记为已访问。
9.获取当前设备的型号 model。
10.遍历下一个兼容的型号 nextModel,以及拥有下一个型号 nextModel 的设备位置 nextPosition:
- 如果设备位置未被访问过,则将 `(nextPosition, cost + abs(nextPosition, position))` 添加到堆中。
11.如果无法到达目标位置,返回 -1。
12.在 main 函数中调用 minCost 函数,并输出结果。
总的时间复杂度为 $O(nk^2logn)$,其中 n 是设备数量,k 是型号数量。遍历拥有型号的设备位置的过程复杂度为 O(n),堆操作的复杂度为 O(logn),遍历所有可能的型号和设备位置的复杂度为 $O(k^2$),所以总的时间复杂度为 $O(nk^2logn)$。
总的额外空间复杂度为 O(n),其中 n 是设备数量。需要额外的空间来存储 own、nexts、visited 和堆 heap,它们的空间复杂度都为 O(n)。
go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/trees/binaryheap"
)
func minCost(arr []int, m [][]int, n int, k int) int {
// 0 : {4,7,13,26}
// 1 : {5,45,3,17}
own := make([][]int, k)
nexts := make([][]int, k)
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
own[i] = []int{}
nexts[i] = []int{}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
own[arr[i]] = append(own[arr[i]], i)
}
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
for j := 0; j < k; j++ {
if m[i][j] == 1 {
nexts[i] = append(nexts[i], j)
}
}
}
heap := binaryheap.NewWith(func(a, b interface{}) int {
return a.([]int)[1] - b.([]int)[1]
})
heap.Push([]int{0, 0})
visited := make([]bool, n)
for heap.Size() > 0 {
t, _ := heap.Pop()
cur := t.([]int)
position := cur[0]
cost := cur[1]
if !visited[position] {
visited[position] = true
if position == n-1 {
return cost
}
model := arr[position]
for _, nextModel := range nexts[model] {
for _, nextPosition := range own[nextModel] {
if !visited[nextPosition] {
heap.Push([]int{nextPosition, cost + abs(nextPosition, position)})
}
}
}
}
}
return -1
}
func abs(a, b int) int {
if a-b < 0 {
return b - a
}
return a - b
}
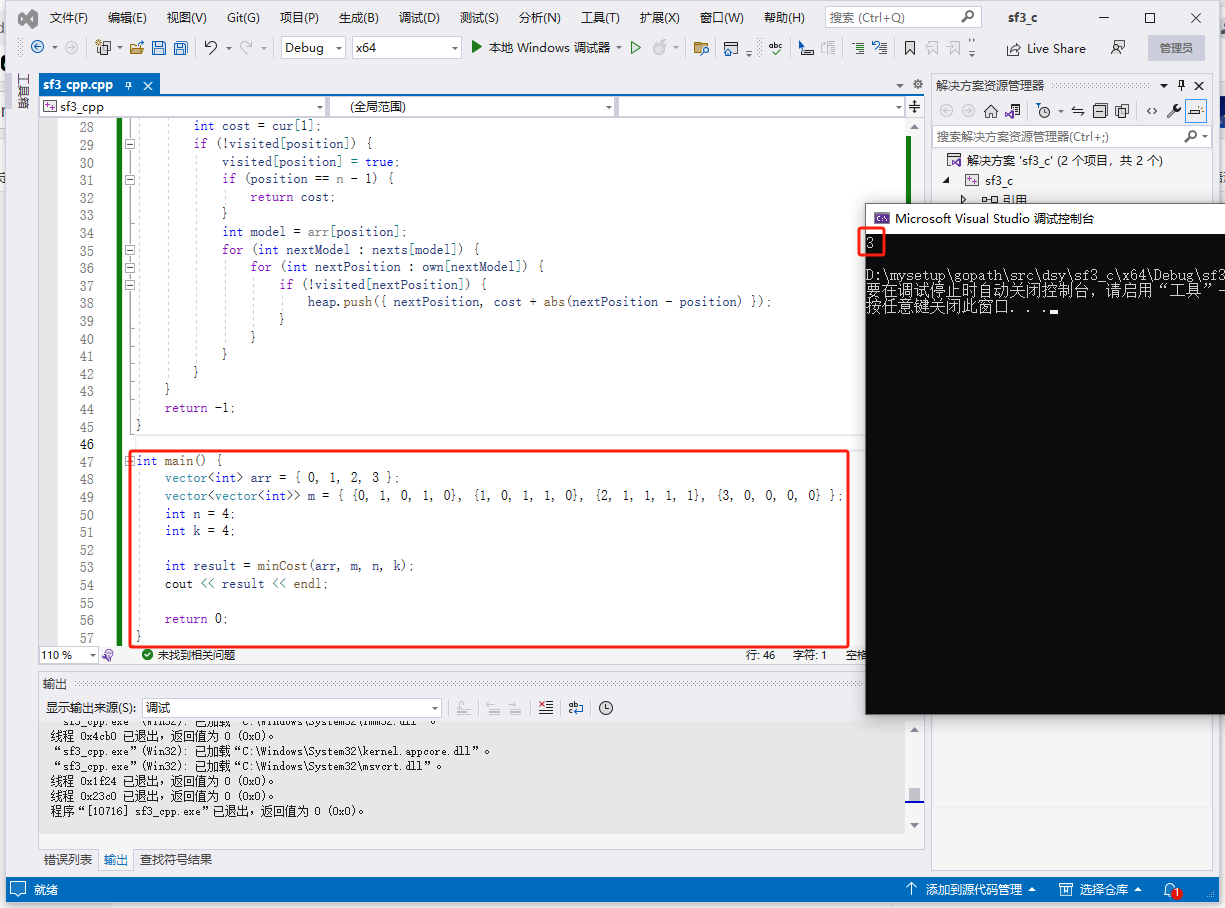
func main() {
arr := []int{0, 1, 2, 3}
m := [][]int{{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 0}, {2, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {3, 0, 0, 0, 0}}
n := 4
k := 4
result := minCost(arr, m, n, k)
fmt.Println(result)
}
rust完整代码如下:
use std::cmp::Reverse;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
fn min_cost(arr: &[i32], map: &[Vec<i32>], n: usize, k: usize) -> i32 {
let mut own: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![Vec::new(); k];
let mut nexts: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![Vec::new(); k];
for (i, &value) in arr.iter().enumerate() {
own[value as usize].push(i as i32);
}
for (i, row) in map.iter().enumerate() {
for (j, &value) in row.iter().enumerate() {
if value == 1 {
nexts[i as usize].push(j as i32);
}
}
}
let mut heap: BinaryHeap<(i32, i32)> = BinaryHeap::new();
heap.push((0, 0));
let mut visited: Vec<bool> = vec![false; n];
while let Some((position, cost)) = heap.pop() {
let position = position as usize;
let cost = cost;
if !visited[position] {
visited[position] = true;
if position == n - 1 {
return cost;
}
let model = arr[position] as usize;
for &next_model in &nexts[model] {
for &next_position in &own[next_model as usize] {
if !visited[next_position as usize] {
heap.push((
next_position,
cost + (next_position - position as i32).abs(),
));
}
}
}
}
}
-1
}
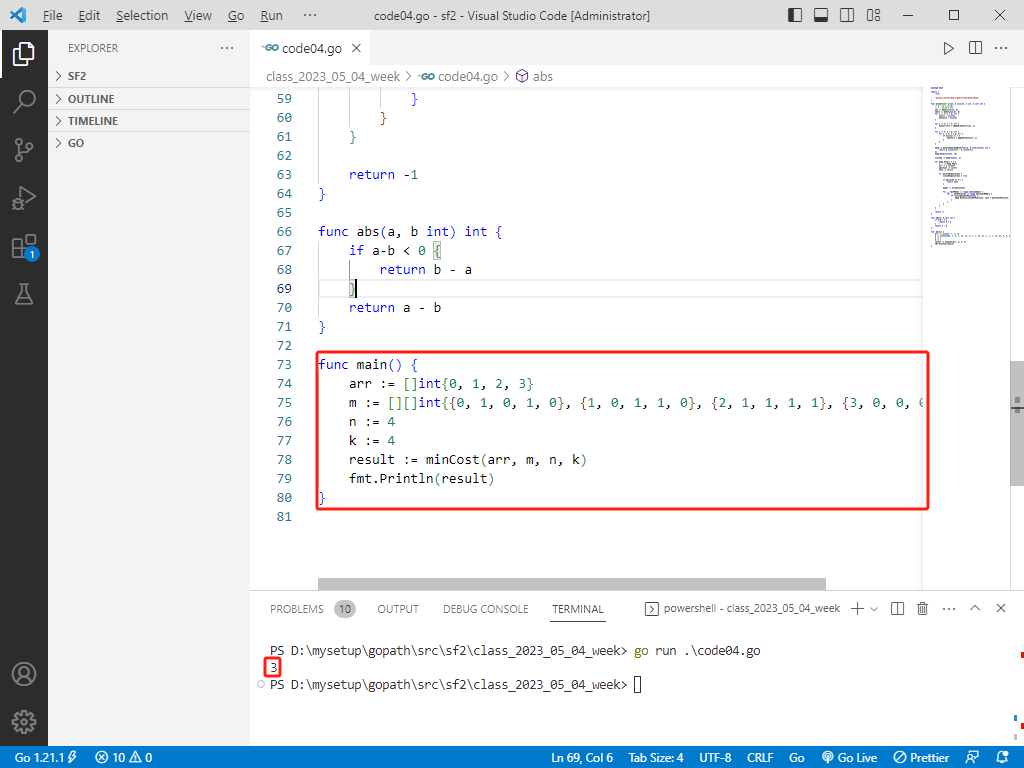
fn main() {
let arr = [0, 1, 2, 3];
let m = [
vec![0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
vec![1, 0, 1, 1, 0],
vec![2, 1, 1, 1, 1],
vec![3, 0, 0, 0, 0],
];
let n = 4;
let k = 4;
let result = min_cost(&arr, &m, n, k);
println!("Minimum Cost: {}", result);
}
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int minCost(vector<int>& arr, vector<vector<int>>& map, int n, int k) {
vector<vector<int>> own(k);
vector<vector<int>> nexts(k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
own[arr[i]].push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
if (map[i][j] == 1) {
nexts[i].push_back(j);
}
}
}
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, greater<vector<int>>> heap;
heap.push({ 0, 0 });
vector<bool> visited(n, false);
while (!heap.empty()) {
vector<int> cur = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int position = cur[0];
int cost = cur[1];
if (!visited[position]) {
visited[position] = true;
if (position == n - 1) {
return cost;
}
int model = arr[position];
for (int nextModel : nexts[model]) {
for (int nextPosition : own[nextModel]) {
if (!visited[nextPosition]) {
heap.push({ nextPosition, cost + abs(nextPosition - position) });
}
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
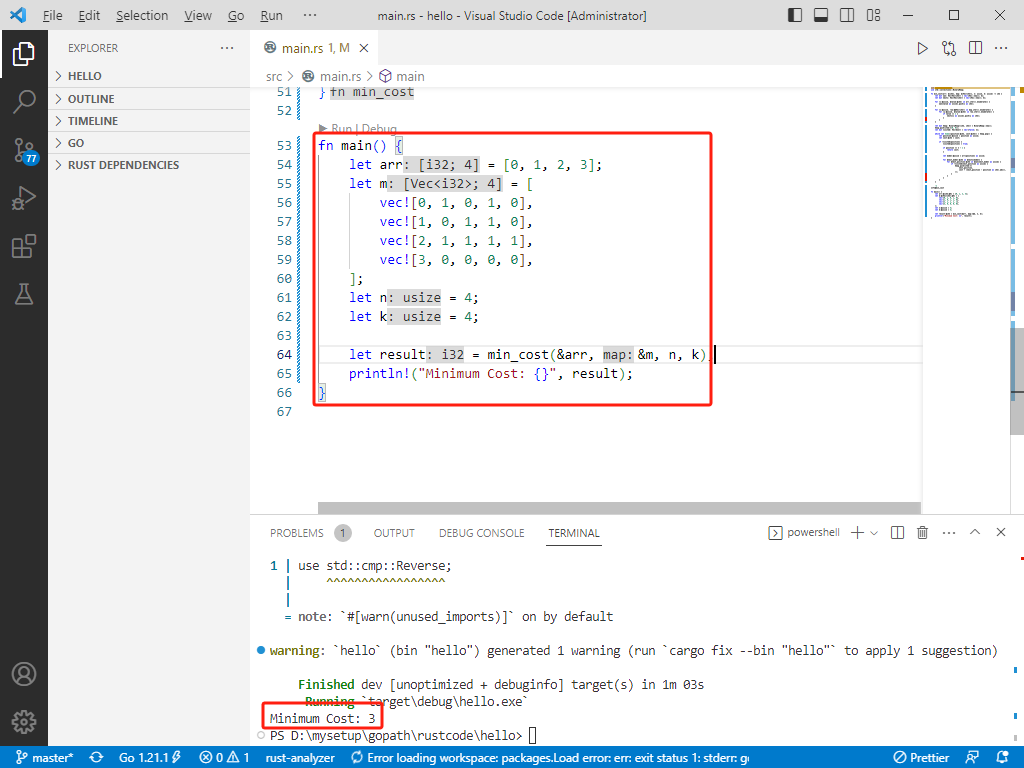
int main() {
vector<int> arr = { 0, 1, 2, 3 };
vector<vector<int>> m = { {0, 1, 0, 1, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 1, 0}, {2, 1, 1, 1, 1}, {3, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
int n = 4;
int k = 4;
int result = minCost(arr, m, n, k);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}