A 01 Sequence
题意:
给定一个01字符串,一次删除操作可以选择一个1并删除两个相邻的点,或者将一个数01翻转。求最少的翻转操作使得一段区间被
删完,该区间的长度一定为3的倍数。每一段区间左右两点连接成环。
分析:
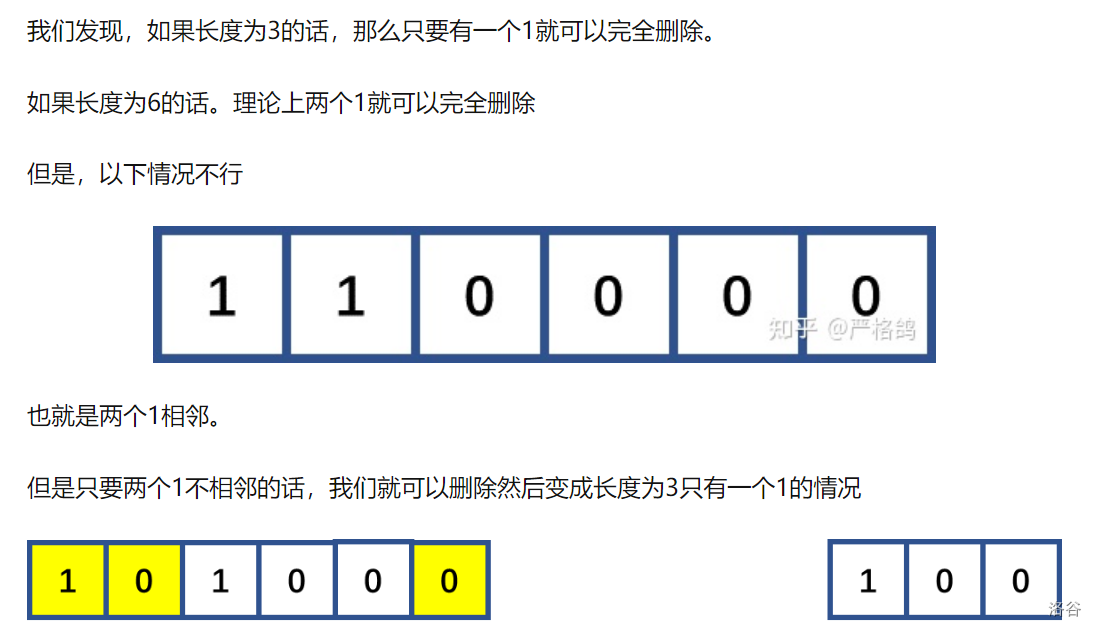
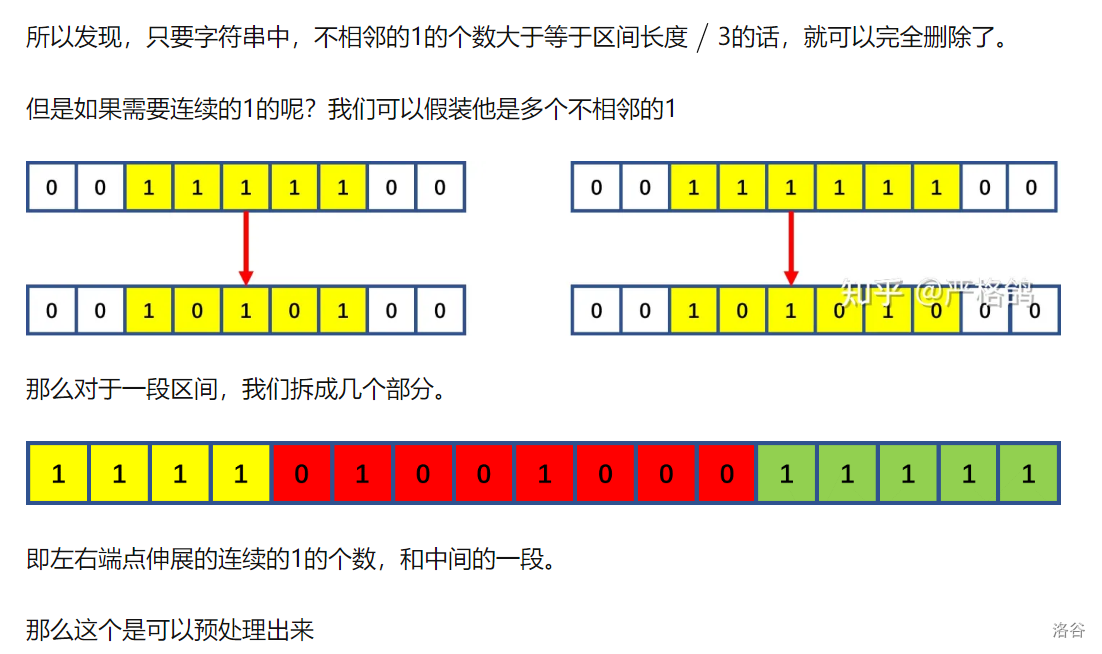
中间部分利用前缀和计算 两边部分合并起来 相当于一段连续的1
void slove() {
cin >> n >> m;
string s; cin >> s;
s = "?" + s;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (s[i] == '1') cnt++;
else cnt = 0;
f[i] = f[i - cnt - 1] + cnt / 2 + cnt % 2;
pre[i] = cnt;
}
cnt = 0;
for (int i = n; i; i--) {
if (s[i] == '1') cnt++;
else cnt = 0;
last[i] = cnt;
}
while (m--) {
int tmp = 0;
int l, r; cin >> l >> r;
tmp = pre[r] + last[l];
int st = f[r - pre[r]] - f[l + last[l]] + tmp / 2 + tmp % 2;
if ((r - l + 1) / 3 <= st) cout << 0 << endl;
else cout << (r - l + 1) / 3 - st << endl;
}
}
C Delete the Tree
题意:
给定一棵树,第一种操作:每次可以选择某一个节点的两个字节点,然后删除该节点,并在两个子节点之间连上一条边。第二种操作
是删除一个点。求删除完所有节点的第二种操作的最小操作次数。
分析:
显然只有叶子结点一定不会被操作1删除,更普遍的来说,所有度数为1的点其实都不可能被操作1删除。所有度数为2或者更多的点都
可以被操作1删除,因此答案就是树的度数为1的节点数量,其中要特判1的情况。
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
if(n == 1)
{
cout << 1 << endl;
return ;
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) d[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ )
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
d[a] ++, d[b] ++ ;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i ++ )
if(d[i] == 1) res ++ ;
cout << res << endl;
}
D. Find the Number
题意:
定义一个特殊数,其二进制表示中1的个数和末尾连续0的个数相同,求出任意一组在区间[l, r]范围内的解。
分析:
很明显的数位dp 发现区间内的特殊数最多只有5e5个 所以可以一边二分 一边数位dp找数 将找到的数存下来
因为随着r的增大 [1,r]内特殊数是单调不减的 所以二分性质能够满足
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 40;
int n, m, f[N][N][N][2];
int nums[N], len;
int last;
set<int> S;
int dfs(int pos, int cnt1, int cnt0, int limit, int lead)
{
int &v = f[pos][cnt1][cnt0][lead];
if(!limit && ~v) return v;
if(!pos) return (cnt1 && cnt1 == cnt0);
int up = limit ? nums[pos] : 1, res = 0;
res += dfs(pos - 1, cnt1, cnt0 + 1, limit & (up == 0), lead);
if(up == 1) res += dfs(pos - 1, cnt1 + 1, 0, limit & (up == 1), 0);
return limit ? res : v = res;
}
int dp(int x)
{
if(!x) return 0;
len = 0;
while(x) nums[++ len] = x & 1, x >>= 1;
return dfs(len, 0, 0, 1, 1);
}
bool check(int mid)
{
return dp(mid) >= last + 1;
}
void solve()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if(S.size())
{
int t = *S.lower_bound(a);
if(t >= a && t <= b)
{
cout << t << endl;
return ;
}
}
last = dp(a - 1);
int l = a, r = b;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
if(check(r))
{
cout << r << endl;
S.insert(r);
}
else puts("-1");
}
signed main()
{
memset(f, -1, sizeof f);
int T = 1;
cin >> T;
while(T -- ) solve();
return 0;
}
H Step Debugging
题意:
输入一个字符串,其中library表示进行一次运算,repeat ... for x times 表示将...操作循环x次,求出该程序的一共进行了几次运算。
分析:
第一种方法是栈,每一个for循环的repeat可以看作左括号,循环次数x表示右括号,该括号的计算次数是该括号 内所有括号的运算次
数 * 循环次数。我们不停的弹栈出栈即可。
比较好写的方法是dfs,每次循环进入dfs递归即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e5 + 10, mod = 20220911;
int res;
int dfs()
{
int res = 0;
string s;
while(cin >> s, s != "for")
{
if(s == "library") res ++ ;
else if(s == "repeat") res += dfs();
}
int num;
cin >> num;
cin >> s;
return num * res % mod;
}
signed main()
{
string s;
while(cin >> s, s != "fin")
{
if(s == "library") res ++ ;
else if(s == "repeat") res += dfs();
}
cout << res % mod << endl;
}
L LCS-like Problem
题意:
给定两个字符串,求出a的两个字符串的最长子序列使得该子序列的和b序列的最长公共子序列的长度不超过1。
分析
预处理数组d[i][j]表示对于匹配来说,如果你当前需要匹配j字符,则前面不能出现i字符。
预处理我们可以n*26在b字符串中递推出来。
接下来考虑动态规划数组f[i][j]表示在a字符串中匹配到i字符,并且最后一个匹配的字符是j。
那么我们很容易得出递推公式,枚举i和j,如果!d[j[i]那么可以递推,否则不可以。
特殊情况,s[i]在b字符串中从未出现过,那么一定会+1,因为一定可以取。
预处理所有的的f[i][s[i]] = 1。
对于不选的字符,我们直接继承上一位即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 2e6 + 10;
string s1, s2;
int f[N][26];
bool d[N][26];
bool st[26];
int n, m;
signed main()
{
cin >> s1 >> s2;
n = s1.size(), m = s2.size();
s1 = "?" + s1, s2 = "?" + s2;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++ )
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < 26 ; j ++ )
if(st[j]) d[j][s2[i] - 'a'] = true;
st[s2[i] - 'a'] = true;
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ) f[i][s1[i] - 'a'] = 1;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ )
{
if(!st[s1[i] - 'a'])
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < 26 ; j ++ )
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + 1;
}
else
{
for(int j = 0 ; j < 26 ; j ++ )
{
f[i][j] = max(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j]);
if(!d[j][s1[i] - 'a'])
f[i][s1[i] - 'a'] = max(f[i][s1[i] - 'a'], f[i - 1][j] + 1);
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i ++ )
res = max(res, f[n][i]);
cout << res << endl;
}