(本题解的所有图片使用 Geometry Widget 进行绘制)
(一)\(K=1\) 情况
\(K=1\) 是平凡的。
(二)\(K=2\) 情况
显然,对于平面内的两个不交正方形,存在至少一条平行于坐标轴的直线将它们划分到两侧。
以直线平行于 \(y\) 轴为例。
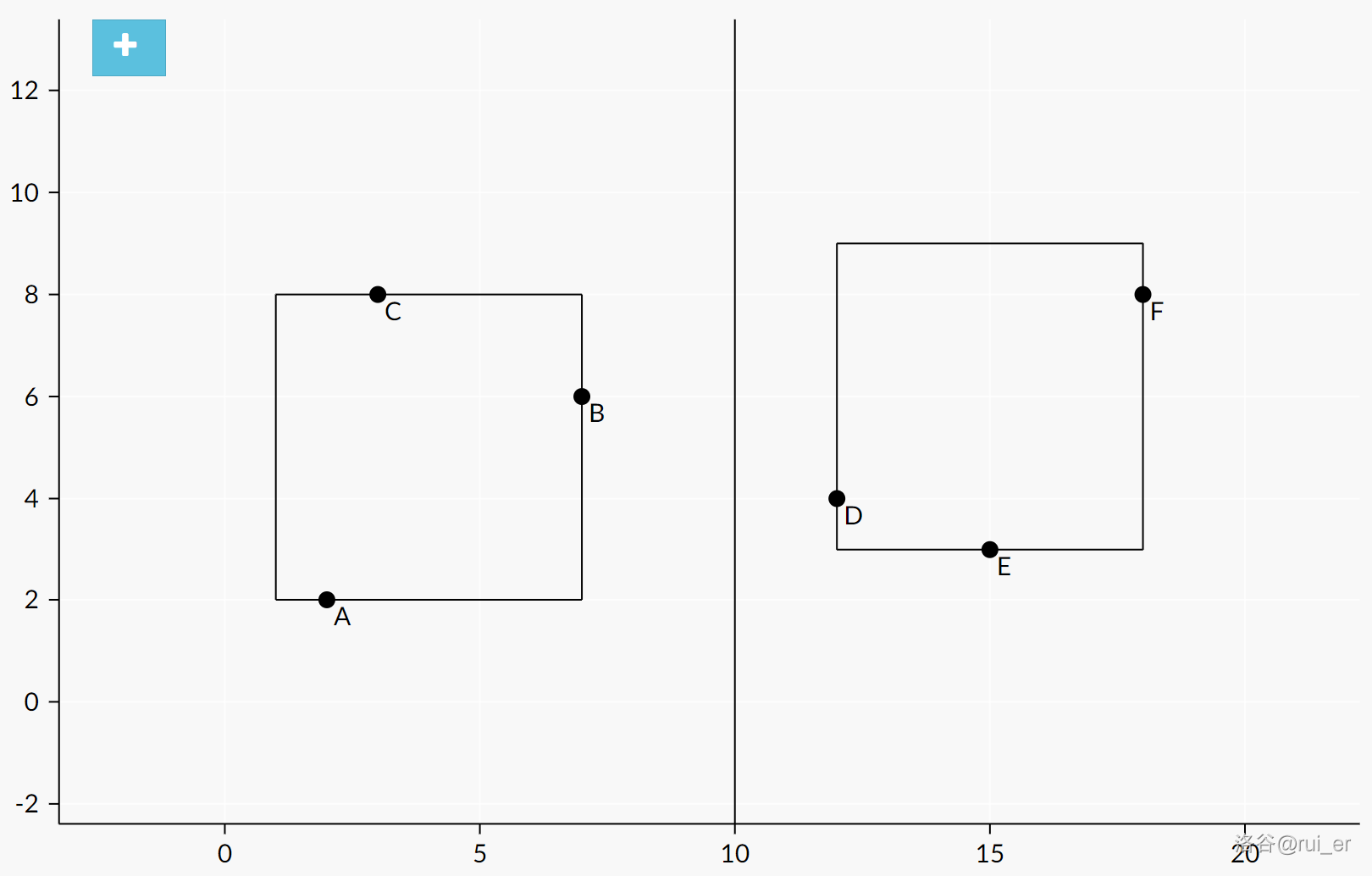
考虑按 \(x\) 轴正方向扫描线。先将点按照 \(x\) 坐标排序,维护前缀、后缀 \(y\) 坐标最小值、最大值。
对于所有 \(x_i\ne x_{i+1}\) 的位置,我们求出以直线 \(x=x_i+\epsilon\) 划分点集的最优解。此时为了保证正方形不交,左侧的点以 \(x\) 坐标最大值处为右边界向左作正方形,右侧的点以 \(x\) 坐标最小值处为左边界向右作正方形,解决两个 \(K=1\) 问题即可。
将所有答案进行比较,即可得到直线平行于 \(y\) 轴的最优解,平行于 \(x\) 轴是同理的。
(三)\(K=3\) 情况
首先二分答案,问题转化为检查规定 \(l_i\le L\) 时是否可行。
显然,对于平面内的三个不交正方形,存在至少一条平行于坐标轴的直线将它们划分到两侧,一侧有一个正方形,另一侧有两个正方形。
以直线平行于 \(y\) 轴,且左侧有一个正方形为例。
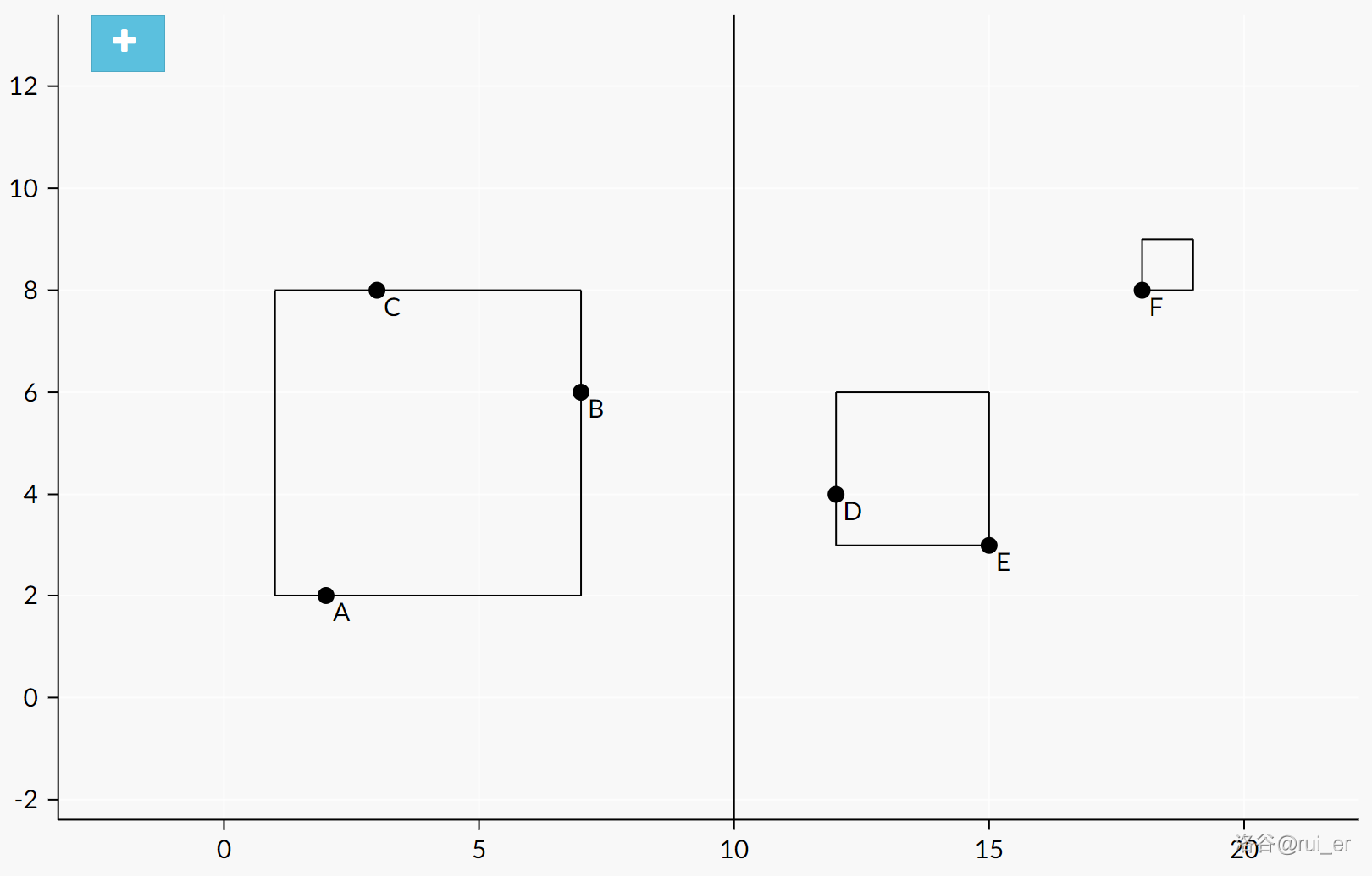
怎么知道直线的位置呢?
在二分答案后,显然我们会贪心地令左侧的正方形尽可能地包含更多点。因此,按 \(x\) 轴正方向扫描线,找到最后一个 \(x_0\),使得对于所有满足 \(x_i\le x_0\) 的 \(i\),有 \(\max\{x_{\max}-x_{\min},y_{\max}-y_{\min}\}\le L\)。
此时,我们只需要检查 \(x_i > x_0\) 的 \(i\) 是否能被两个边长不超过 \(L\) 的正方形覆盖即可。
右侧部分有两种形态:(我称之为 \(xx\) 形和 \(xy\) 形)
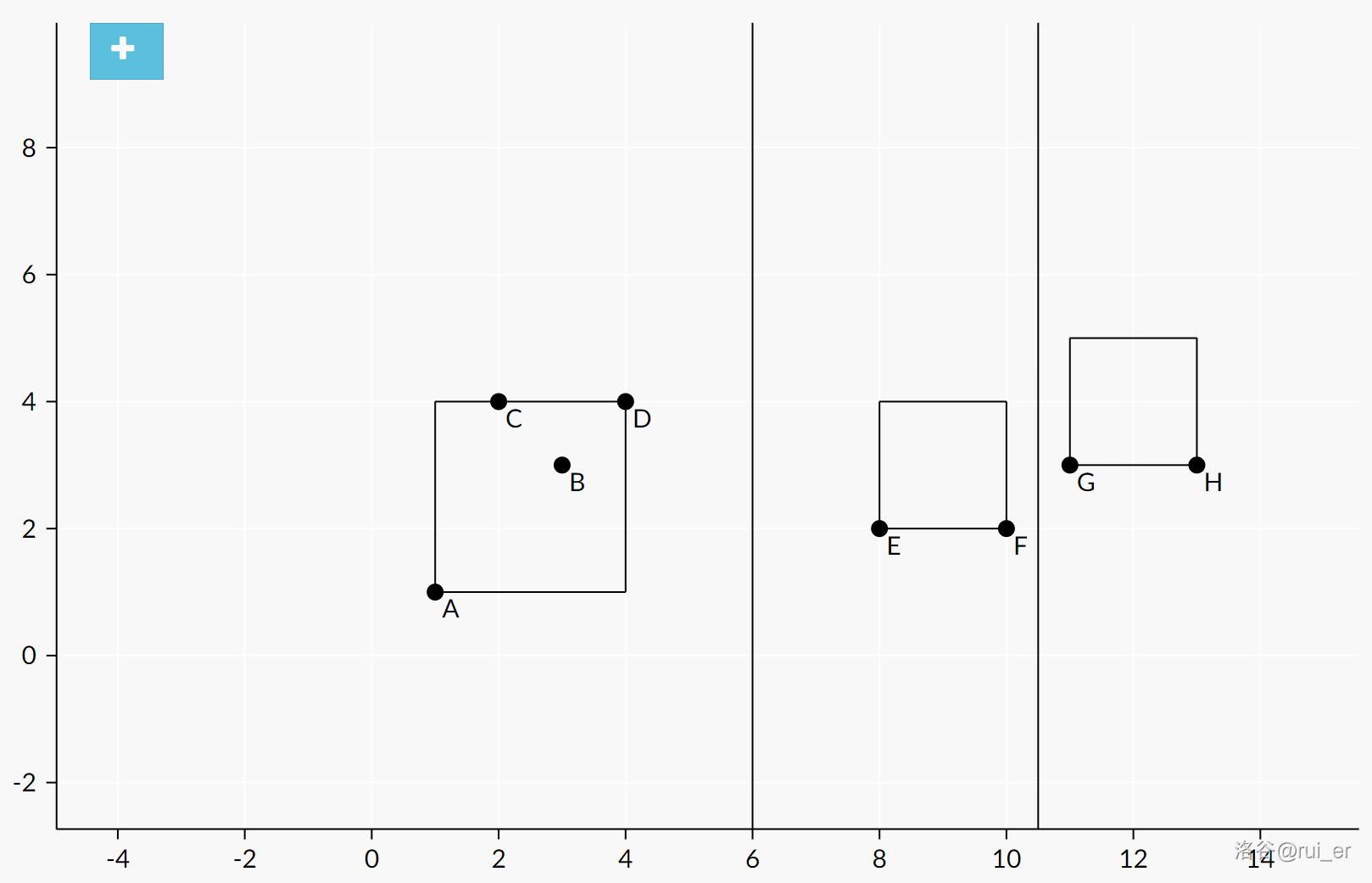
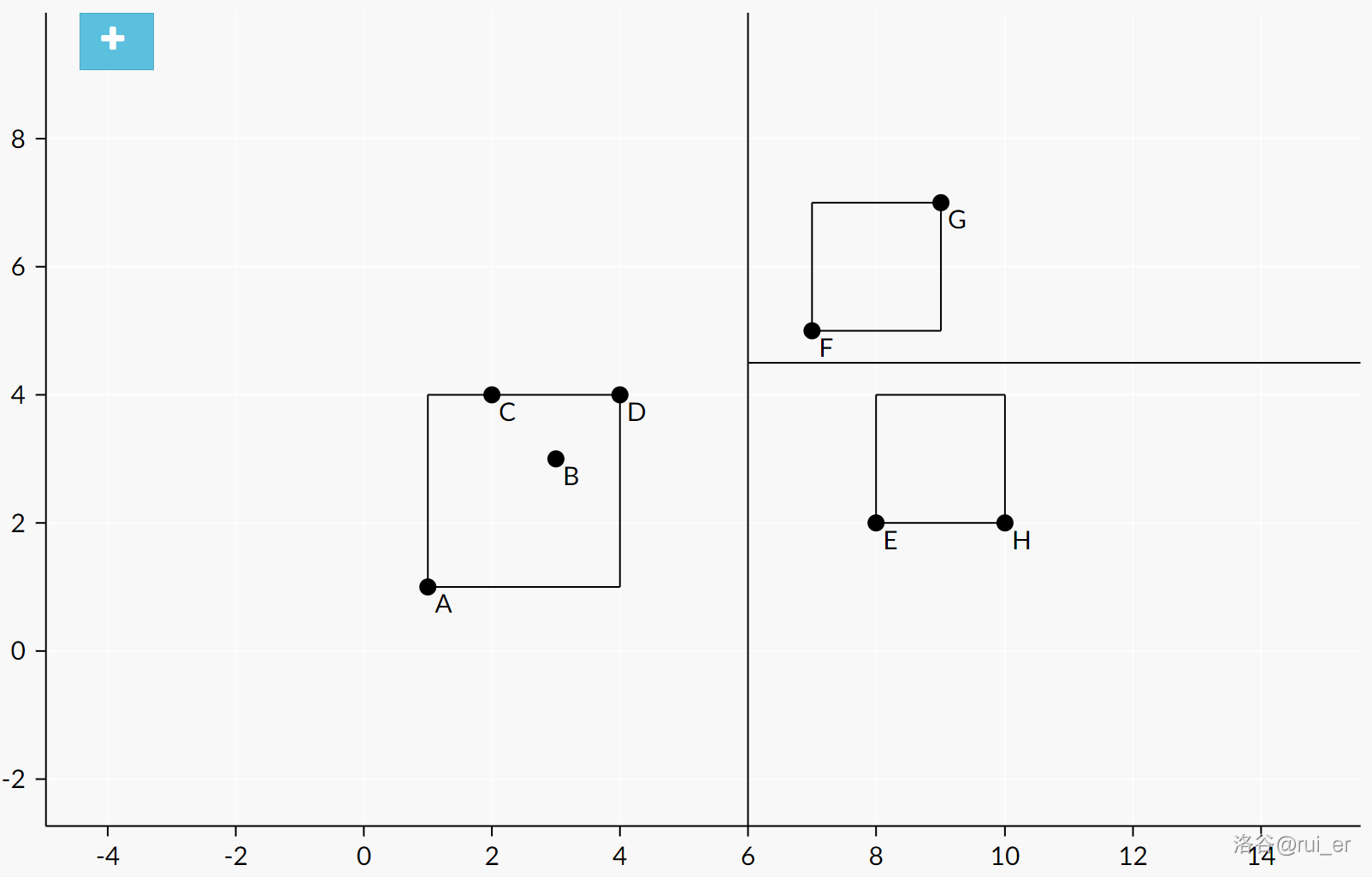
两种形态与 \(K=2\) 几乎相同,但是有额外的边长上限 \(L\)。而 \(xx\) 形还要更麻烦一点,还对中间正方形的左边界有要求,不能到达 \(x_0\) 及其左侧,这只需要调整一下中间正方形的位置即可。
于是扫描线求出 \(x_0\),并用类似于 \(K=2\) 的解法判断是否可行,即可实现直线平行于 \(y\) 轴,且左侧有一个正方形的判断。这种情况共有 \(4\) 种对称的情况,分别判一下即可。
(四)注意事项与实现细节
本题的 corner case 极多,且无论 \(K\) 取何值均存在。如果你遇到困难,可以尝试以下形状的测试点:
- \(N=1\)。
- \(\max\{x_{\max}-x_{\min},y_{\max}-y_{\min}\}\le 1\)。
- \(x_{\min}=y_{\min}=-10^9,x_{\max}=y_{\max}=10^9\)。
错误原因包括但不限于:
- \(l_i=0\)。
- 不覆盖任何点的垃圾正方形重合。
- 正方形左下角出界。
- \(xx\) 形未调整好中间正方形的位置。
在代码实现时,\(K=2\) 和 \(K=3\) 的一些对称的情况是通过旋转对称等变换转化为讲过的情况进行处理的。
(五)代码
一共写了 \(7.39\text{KB}\)。
// Problem: P8389 [COI2021] Izvanzemaljci
// Contest: Luogu
// URL: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P8389
// Memory Limit: 512 MB
// Time Limit: 2500 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
//By: OIer rui_er
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(x,y,z) for(ll x=(y);x<=(z);x++)
#define per(x,y,z) for(ll x=(y);x>=(z);x--)
#define debug(format...) fprintf(stderr, format)
#define fileIO(s) do{freopen(s".in","r",stdin);freopen(s".out","w",stdout);}while(false)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
mt19937 rnd(std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::nanoseconds>(std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch()).count());
ll randint(ll L, ll R) {
uniform_int_distribution<ll> dist(L, R);
return dist(rnd);
}
template<typename T> void chkmin(T& x, T y) {if(x > y) x = y;}
template<typename T> void chkmax(T& x, T y) {if(x < y) x = y;}
const ll inf = 3000000000LL;
struct Dot {
ll x, y;
Dot(ll x = 0, ll y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
friend bool operator<(const Dot& a, const Dot& b) {
if(a.x != b.x) return a.x < b.x;
return a.y < b.y;
}
};
struct Square {
ll x, y, L;
Square(ll x = 0, ll y = 0, ll L = 0) : x(x), y(y), L(L) {}
Square(Dot A, ll L) : x(A.x), y(A.y), L(L) {}
};
inline bool inside(const Dot& A, const Square& S) {
return S.x <= A.x && A.x <= S.x + S.L && S.y <= A.y && A.y <= S.y + S.L;
}
inline bool inside(const Dot& A, const vector<Square>& S) {
for(const Square& s : S) if(inside(A, s)) return true;
return false;
}
inline ll calc(const vector<Square>& S) {
ll L = 0;
for(const Square& s : S) chkmax(L, s.L);
return L;
}
vector<Square> solve1(const vector<Dot>& A) {
ll xmin = +inf, xmax = -inf, ymin = +inf, ymax = -inf;
for(const Dot& a : A) {
chkmin(xmin, a.x);
chkmax(xmax, a.x);
chkmin(ymin, a.y);
chkmax(ymax, a.y);
}
ll L = max({xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin, 1LL});
return {{xmin, ymin, L}};
}
vector<Square> solve2x(vector<Dot> A) {
ll n = (ll)A.size();
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
A.emplace_back(inf, 0);
vector<ll> sufymin(n+1), sufymax(n+1);
sufymin[n-1] = sufymax[n-1] = A[n-1].y;
per(i, n-2, 0) {
sufymin[i] = min(sufymin[i+1], A[i].y);
sufymax[i] = max(sufymax[i+1], A[i].y);
}
ll preymin = +inf, preymax = -inf, best = +inf;
vector<Square> ans;
rep(i, 0, n-1) { // where to split
chkmin(preymin, A[i].y);
chkmax(preymax, A[i].y);
if(A[i].x == A[i+1].x) continue;
ll L1 = max({A[i].x - A[0].x, preymax - preymin, 1LL});
ll L2 = max({A[n-1].x - A[i+1].x, sufymax[i+1] - sufymin[i+1], 1LL});
if(max(L1, L2) < best) {
best = max(L1, L2);
ans = {{A[i].x - L1, preymin, L1}, {A[i+1].x, sufymin[i+1], L2}};
}
}
return ans;
}
vector<Square> solve2(vector<Dot> A) {
// rotate 0
vector<Square> ans1 = solve2x(A);
// rotate pi/2
for(Dot& a : A) swap(a.x, a.y);
vector<Square> ans2 = solve2x(A);
for(Dot& a : A) swap(a.x, a.y);
for(Square& s : ans2) swap(s.x, s.y);
// compare
return calc(ans1) < calc(ans2) ? ans1 : ans2;
}
vector<Square> solve3x(vector<Dot> A, ll Llim, ll xlim) { // similar to solve2x
if(A.empty()) return {{-inf, -inf, 1}, {-inf+2, -inf+2, 1}};
ll n = (ll)A.size();
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
A.emplace_back(inf, 0);
vector<ll> sufymin(n+1), sufymax(n+1);
sufymin[n-1] = sufymax[n-1] = A[n-1].y;
per(i, n-2, 0) {
sufymin[i] = min(sufymin[i+1], A[i].y);
sufymax[i] = max(sufymax[i+1], A[i].y);
}
ll preymin = +inf, preymax = -inf, best = +inf;
vector<Square> ans;
rep(i, 0, n-1) {
chkmin(preymin, A[i].y);
chkmax(preymax, A[i].y);
if(A[i].x == A[i+1].x) continue;
ll L1 = max({A[i].x - A[0].x, preymax - preymin, 1LL});
ll L2 = max({A[n-1].x - A[i+1].x, sufymax[i+1] - sufymin[i+1], 1LL});
if(max(L1, L2) < best) {
ll x0 = min(A[0].x, A[i+1].x - L1 - 1);
if(x0 >= xlim) {
best = max(L1, L2);
ans = {{x0, preymin, L1}, {A[i+1].x, sufymin[i+1], L2}};
}
}
}
return best <= Llim ? ans : vector<Square>{};
}
vector<Square> solve3xx_xy(vector<Dot> A, ll Llim) {
ll n = (ll)A.size();
sort(A.begin(), A.end());
ll ymin = +inf, ymax = -inf, lstymin = ymin, lstymax = ymax, ptr = -1;
rep(l, 0, n) { // greedy
ll r = l;
lstymin = ymin;
lstymax = ymax;
while(r < n && A[l].x == A[r].x) {
chkmin(ymin, A[r].y);
chkmax(ymax, A[r].y);
++r;
}
if(l == n) {
if(lstymin == +inf) return vector<Square>{};
else {ptr = l; break;}
}
ll L = max({A[l].x - A[0].x, ymax - ymin});
if(L > Llim) {
if(lstymin == +inf) return vector<Square>{};
else {ptr = l; break;}
}
}
// check xx
{
vector<Dot> B;
rep(i, ptr, n-1) B.push_back(A[i]);
vector<Square> now = solve3x(B, Llim, A[ptr-1].x + 1);
if(!now.empty()) {
ll L = max({A[ptr-1].x - A[0].x, lstymax - lstymin, 1LL});
now.emplace_back(A[ptr-1].x - L, lstymin, L);
return now;
}
}
// check xy
{
vector<Dot> B;
rep(i, ptr, n-1) B.emplace_back(A[i].y, A[i].x);
vector<Square> now = solve3x(B, Llim, -inf);
if(!now.empty()) {
for(Square& s : now) swap(s.x, s.y);
ll L = max({A[ptr-1].x - A[0].x, lstymax - lstymin, 1LL});
now.emplace_back(A[ptr-1].x - L, lstymin, L);
return now;
}
}
return vector<Square>{};
}
vector<Square> check3(vector<Dot> A, ll Llim) {
vector<Square> now;
// rotate 0
now = solve3xx_xy(A, Llim);
if(!now.empty()) return now;
// rotate pi
for(Dot& a : A) a.x = -a.x;
now = solve3xx_xy(A, Llim);
if(!now.empty()) {
for(Square& s : now) s.x = -s.x - s.L;
return now;
}
for(Dot& a : A) a.x = -a.x;
// rotate pi/2
for(Dot& a : A) swap(a.x, a.y);
now = solve3xx_xy(A, Llim);
if(!now.empty()) {
for(Square& s : now) swap(s.x, s.y);
return now;
}
for(Dot& a : A) swap(a.x, a.y);
// rotate 3pi/2
for(Dot& a : A) {swap(a.x, a.y); a.x = -a.x;}
now = solve3xx_xy(A, Llim);
if(!now.empty()) {
for(Square& s : now) {s.x = -s.x - s.L; swap(s.x, s.y);}
return now;
}
for(Dot& a : A) {swap(a.x, a.y); a.x = -a.x;}
return vector<Square>{};
}
vector<Square> solve3(vector<Dot> A) {
ll l = 1, r = inf;
vector<Square> ans;
while(l < r) {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
vector<Square> now = check3(A, mid);
if(now.empty()) l = mid + 1;
else {r = mid; ans = now;}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ll n, k;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &k);
vector<Dot> A;
rep(i, 0, n-1) {
ll x, y;
scanf("%lld%lld", &x, &y);
A.emplace_back(x, y);
}
vector<Square> ans;
if(k == 1) ans = solve1(A);
else if(k == 2) ans = solve2(A);
else ans = solve3(A);
for(const Square& s : ans) printf("%lld %lld %lld\n", s.x, s.y, s.L);
return 0;
}