A. 道路
考虑修改后的树任意两点间距离与修改前的关系。
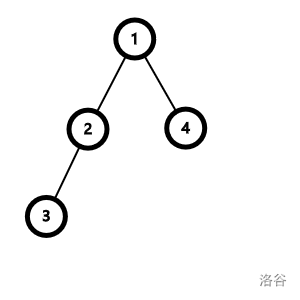
例如,\(1\) 和 \(3\) 原本距离为 \(2\),现在距离为 \(1\);\(3\) 和 \(4\) 原本距离为 \(3\),现在距离为 \(2\)。
我们发现,对于原树中两点间的距离 \(\operatorname{dis}\),现在的距离为 \(\lfloor \frac{dis + 1}{2} \rfloor\)。
考虑把这个式子转化一下,变成
\[\left\lfloor \frac{dis + 1}{2} \right\rfloor=\dfrac{\operatorname{dis}+\left[ \operatorname{dis}\equiv1(\!\!\!\!\mod 2 ) \right]}{2} \]那么我们代入题目给出的式子,得到
\[\sum^{n}_{i=1}\sum^{n}_{j=i+1}(\dfrac{\operatorname{dis}(i,j)+\left[ \operatorname{dis}(i,j)\equiv1(\!\!\!\!\mod 2 ) \right]}{2}) \]很显然,我们发现,最终答案与边权的奇偶性和原树边权和有关。
考虑如何求路径长度?两点间距离为
\[\operatorname{dis}(i,j)=\operatorname{dep}_i+\operatorname{dep}_j-2\times \operatorname{dep_{\operatorname{lca}(i,j)}} \]其中后面 \(-2\times \operatorname{dep_{\operatorname{lca}(i,j)}}\) 的部分与路径长度的奇偶性无关,那么直接统计 \(\operatorname{dep}_i\) 和 \(\operatorname{dep}_j\) 奇偶性不同的点对数量就可以求出路径长度为奇数的路径数量。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200500;
int n;
struct Edge{
int next,to;
}e[N << 1];
int h[N],cnt;
void Add(int u,int v) {
cnt ++;
e[cnt].next = h[u];
h[u] = cnt;
e[cnt].to = v;
}
namespace SOL{
long long ans = 0;
int size[N],cnt[N];
void dfs(int x,int fa,int dep) {
cnt[dep ^ 1] ++;
size[x] = 1;
for(int i = h[x];i;i = e[i].next) {
int to = e[i].to;
if(to == fa)
continue;
dfs(to,x,dep ^ 1);
size[x] += size[to];
}
ans += 1ll * (n - size[x]) * size[x];
}
void Work() {
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
memset(size,0,sizeof(size));
dfs(1,1,0);
ans = ans + 1ll * cnt[0] * cnt[1];
ans /= 2;
cout << ans << "\n";
return ;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1,u,v;i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
Add(u,v);
Add(v,u);
}
SOL::Work();
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
B. 集合
正解好像是 0-1 Trie,不过我们可以乱搞搞过去。
考虑第二个限制,我们可以转化为 \(k \mid x \land k \mid v\),那么 \(x\) 和 \(v\) 都是 \(k\) 的倍数,我们可以预处理加入集合的数 \(u\),把它加入所有它因数的集合里。
这样我们在后面查找 \(v\) 就直接在 \(k\) 的集合中查找就能够保证满足第二个条件。
对于查询操作,我们直接找到小于等于 \(s-x\) 的数,然后在集合中从大到小遍历。
我们知道,两个数异或值最大就是两个数的值相加,如果我们当前记录的最大异或值 Max 已经大于遍历到的 x + v,后面的部分肯定不会再对答案产生贡献了,可以直接退出循环。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100500;
int n;
int opt,u,x,k,s;
set<int> S[N];
// S[i] 中的任意数 x 满足 i | x
// 即存的是 i 的倍数
// 用于第二个条件
long long ans,Max;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++) {
cin >> opt;
if(opt == 1) {
cin >> u;
for(int i = 1;i <= floor(sqrt(u)); i++) {
if(u % i == 0) {
S[i].insert(u);
S[u / i].insert(u);
}// 记录的是其倍数
}
}
else {
cin >> x >> k >> s;
ans = -1;
Max = -1;
if(x % k != 0) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
set<int>::iterator it = S[k].upper_bound(s - x);
// 找到大于 x 的最小的数
if(it == S[k].begin() || S[k].empty()) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
it --;
// 现在的 it 指向的是满足第一个条件和第二个条件的最大的数
while(it != S[k].begin()) {
int v = *it;
if(Max > x + v)
break;
// 异或最大值就是 x + v
// Max 已经超过 x + v 肯定不能更新答案
if(Max < (v ^ x)) {
Max = v ^ x;
ans = v;
}
it --;
}
if((*it ^ x) > Max)
ans = *it;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
C. 科目五
模拟赛 T3,考场思路是直接二分,对每辆车进行二分,答案取每辆车答案的最大值,时间复杂度 \(\operatorname{O}(nm \log n)\)。
这样显然会 TLE,我们考虑优化。
- 考虑判一下记录的答案能否支持当前这辆车走完全程,如果可以,那就不用二分这辆车了,因为它的答案一定比原先的答案小,计算出来也不会更新答案。
- 对于第一条情况,我们把每辆车的顺序打乱重排能获得更优的期望复杂度。
跑的飞快,直接薄纱正解。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 550;
inline int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while( ch < '0' || ch > '9' ) {if( ch == '-' ) f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) {x=x*10+(ch-48);ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
int n,m;
long long pos[N];
struct Trip{
int s,t;
long long c,r;
}a[250500];
int Max[N][N];
int i;
bool Check(long long &V) {
long long dis,need,times = 0,remain = V;
if(Max[a[i].s][a[i].t] * a[i].c > V)
return 0;
for(int j = a[i].s;j < a[i].t; j++) {
dis = pos[j + 1] - pos[j];
need = dis * a[i].c;
if(need <= remain)
remain -= need;
else {
times ++;
remain = V - need;
}
}
if(times > a[i].r)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int main() {
#ifdef ONLINE_JUDGE == 1
freopen("drive.in","r",stdin);
freopen("drive.out","w",stdout);
#endif
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++)
pos[i] = read();
for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++) {
a[i].s = read();
a[i].t = read();
a[i].c = read();
a[i].r = read();
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++){
long long maxn = 0;
for(int j = i + 1;j <= n; j++) {
maxn = max(maxn,pos[j] - pos[j - 1]);
Max[i][j] = maxn;
}
}
random_shuffle(a + 1,a + m + 1);
long long ans = 0;
for(i = 1;i <= m; i++) {
if(Check(ans))
continue;
long long l = max(Max[a[i].s][a[i].t] * a[i].c,ans + 1);
long long r = (pos[a[i].t] - pos[a[i].s]) * a[i].c;
long long mid,res = r;
while(l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(Check(mid)) {
r = mid - 1;
res = mid;
}
else
l = mid + 1;
}
ans = max(ans,res);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
D. 监狱
咕了。
标签:27,int,Max,operatorname,dep,ch,CSP,模拟,dis From: https://www.cnblogs.com/baijian0212/p/csp-27.html