目录
1 限流方案
1.1 引言
限流对于一个微服务架构系统来说具有非常重要的意义,否则其中的某个微服务将成为整个系统隐藏的雪崩因素,为什么这么说?
举例来讲,某个平台有100多个微服务应用,但是作为底层的某个或某几个应用来说,将会被所有上层应用频繁调用,业务高峰期时,如果底层应用不做限流处理,该应用必将面临着巨大的压力,尤其是那些个别被高频调用的接口来说,最直接的表现就是导致后续新进来的请求阻塞、排队、响应超时...最后直到该服务所在JVM资源被耗尽。
1.2 常用限流策略
不管是哪种限流组件,其底层的限流实现算法大同小异,这里列举几种常用的限流算法以供了解。
点击了解Nginx中漏桶算法,令牌桶算法和滑动时间窗口算法
在微服务应用中,比较通用的做法是,利用 AOP技术+自定义注解实现对特定的方法或接口进行限流,下面基于这个思路来分别介绍下几种常用的限流方案的实现。
1.3 基于guava限流实现
guava为谷歌开源的一个比较实用的组件,利用这个组件可以帮助开发人员完成常规的限流操作,接下来看具体的实现步骤。
1.3.1 引入guava依赖
版本可以选择更高的或其他版本
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>23.0</version>
</dependency>
1.3.2 自定义限流注解
自定义一个限流用的注解,后面在需要限流的方法或接口上面只需添加该注解即可;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RateConfigAnno {
String limitType();
double limitCount() default 5d;
}
1.3.3 限流AOP类
通过 AOP 前置通知的方式拦截添加了上述自定义限流注解的方法,解析注解中的属性值,并以该属性值作为guava提供的限流参数,该类为整个实现的核心所在。
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONObject;
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class GuavaLimitAop {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GuavaLimitAop.class);
@Before("execution(@RateConfigAnno * *(..))")
public void limit(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//1、获取当前的调用方法
Method currentMethod = getCurrentMethod(joinPoint);
if (Objects.isNull(currentMethod)) {
return;
}
//2、从方法注解定义上获取限流的类型
String limitType = currentMethod.getAnnotation(RateConfigAnno.class).limitType();
double limitCount = currentMethod.getAnnotation(RateConfigAnno.class).limitCount();
//使用guava的令牌桶算法获取一个令牌,获取不到先等待
RateLimiter rateLimiter = RateLimitHelper.getRateLimiter(limitType, limitCount);
boolean b = rateLimiter.tryAcquire();
if (b) {
System.out.println("获取到令牌");
}else {
HttpServletResponse resp = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getResponse();
JSONObject jsonObject=new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("success",false);
jsonObject.put("msg","限流中");
try {
output(resp, jsonObject.toJSONString());
}catch (Exception e){
logger.error("error,e:{}",e);
}
}
}
private Method getCurrentMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Method[] methods = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getMethods();
Method target = null;
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(joinPoint.getSignature().getName())) {
target = method;
break;
}
}
//或者使用如下方式获取method对象
//MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
//Method method = signature.getMethod();
return target;
}
public void output(HttpServletResponse response, String msg) throws IOException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
ServletOutputStream outputStream = null;
try {
outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(msg.getBytes("UTF-8"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
}
}
}
其中限流的核心API即为RateLimiter这个对象,涉及到的RateLimitHelper类如下
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.RateLimiter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class RateLimitHelper {
private RateLimitHelper(){}
private static Map<String,RateLimiter> rateMap = new HashMap<>();
public static RateLimiter getRateLimiter(String limitType,double limitCount ){
RateLimiter rateLimiter = rateMap.get(limitType);
if(rateLimiter == null){
rateLimiter = RateLimiter.create(limitCount);
rateMap.put(limitType,rateLimiter);
}
return rateLimiter;
}
}
1.3.4 测试接口
下面添加一个测试接口,测试一下上面的代码是否生效
@RestController
public class OrderController {
//localhost:8081/save
@GetMapping("/save")
@RateConfigAnno(limitType = "saveOrder",limitCount = 1)
public String save(){
return "success";
}
}
在接口中为了模拟出效果,我们将参数设置的非常小,即QPS为1,可以预想当每秒请求超过1时将会出现被限流的提示,启动工程并验证接口,每秒1次的请求,可以正常得到结果,如果快速刷接口,将会报错
1.4 基于sentinel限流实现
在不少人的意识中,sentinel通常是需要结合springcloud-alibaba框架一起实用的,而且与框架集成之后,可以配合控制台一起使用达到更好的效果,实际上,sentinel官方也提供了相对原生的SDK可供使用,接下来就以这种方式进行整合。
1.4.1 引入sentinel核心依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
1.4.2 自定义限流注解
可以根据需要,添加更多的属性
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SentinelLimitAnnotation {
String resourceName();
int limitCount() default 5;
}
1.4.3 自定义AOP类实现限流
该类的实现思路与上述使用guava类似,不同的是,这里使用的是sentinel原生的限流相关的API
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Entry;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.SphU;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.Tracer;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.BlockException;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.RuleConstant;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
@Aspect
@Component
public class SentinelMethodLimitAop {
private static void initFlowRule(String resourceName,int limitCount) {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
//设置受保护的资源
rule.setResource(resourceName);
//设置流控规则 QPS
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
//设置受保护的资源阈值
rule.setCount(limitCount);
rules.add(rule);
//加载配置好的规则
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.congge.sentinel.SentinelLimitAnnotation)")
public void rateLimit() {
}
@Around("rateLimit()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
//1、获取当前的调用方法
Method currentMethod = getCurrentMethod(joinPoint);
if (Objects.isNull(currentMethod)) {
return null;
}
//2、从方法注解定义上获取限流的类型
String resourceName = currentMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelLimitAnnotation.class).resourceName();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(resourceName)){
throw new RuntimeException("资源名称为空");
}
int limitCount = currentMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelLimitAnnotation.class).limitCount();
initFlowRule(resourceName,limitCount);
Entry entry = null;
Object result = null;
try {
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName);
try {
result = joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (BlockException ex) {
// 资源访问阻止,被限流或被降级
// 在此处进行相应的处理操作
System.out.println("blocked");
return "被限流了";
} catch (Exception e) {
Tracer.traceEntry(e, entry);
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
return result;
}
private Method getCurrentMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Method[] methods = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getMethods();
Method target = null;
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(joinPoint.getSignature().getName())) {
target = method;
break;
}
}
//或者使用如下方式获取method对象
//MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
//Method method = signature.getMethod();
return target;
}
}
1.4.4 自定义测试接口
为了模拟效果,这里将QPS的数量设置为1
//localhost:8081/limit
@GetMapping("/limit")
@SentinelLimitAnnotation(limitCount = 1,resourceName = "sentinelLimit")
public String sentinelLimit(){
return "sentinelLimit";
}
启动工程之后,浏览器调用接口测试一下,每秒一个请求,可以正常通过
快速刷接口,超过每秒1次时报错
1.5 基于redis+lua限流实现
1.5.1 简介
redis是线程安全的,天然具有线程安全的特性,支持原子性操作,限流服务不仅需要承接超高QPS,还要保证限流逻辑的执行层面具备线程安全的特性,利用Redis这些特性做限流,既能保证线程安全,也能保证性能。基于redis的限流实现完整流程如下图:
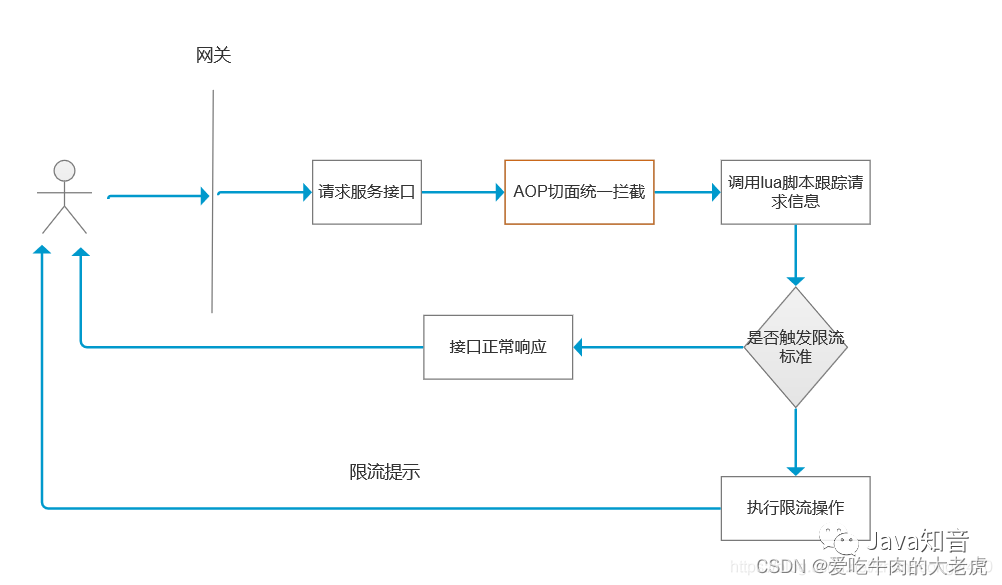
1.5.2 引入redis依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.5.3 自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface RedisLimitAnnotation {
/**
* key
*/
String key() default "";
/**
* Key的前缀
*/
String prefix() default "";
/**
* 一定时间内最多访问次数
*/
int count();
/**
* 给定的时间范围 单位(秒)
*/
int period();
}
1.5.4 自定义redis配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Component
public class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
public DefaultRedisScript<Number> redisluaScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Number> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptSource(new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("limit.lua")));
redisScript.setResultType(Number.class);
return redisScript;
}
@Bean("redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//设置value的序列化方式为JSOn
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//设置key的序列化方式为String
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
1.5.5 自定义限流AOP类
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
@Aspect
@Configuration
public class LimitRestAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LimitRestAspect.class);
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private DefaultRedisScript<Number> redisluaScript;
@Pointcut(value = "@annotation(com.congge.config.limit.RedisLimitAnnotation)")
public void rateLimit() {
}
@Around("rateLimit()")
public Object interceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
Class<?> targetClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
RedisLimitAnnotation rateLimit = method.getAnnotation(RedisLimitAnnotation.class);
if (rateLimit != null) {
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
String ipAddress = getIpAddr(request);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
stringBuffer.append(ipAddress).append("-")
.append(targetClass.getName()).append("- ")
.append(method.getName()).append("-")
.append(rateLimit.key());
List<String> keys = Collections.singletonList(stringBuffer.toString());
//调用lua脚本,获取返回结果,这里即为请求的次数
Number number = redisTemplate.execute(
redisluaScript,
keys,
rateLimit.count(),
rateLimit.period()
);
if (number != null && number.intValue() != 0 && number.intValue() <= rateLimit.count()) {
logger.info("限流时间段内访问了第:{} 次", number.toString());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
} else {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
throw new RuntimeException("访问频率过快,被限流了");
}
/**
* 获取请求的IP方法
* @param request
* @return
*/
private static String getIpAddr(HttpServletRequest request) {
String ipAddress = null;
try {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP");
}
if (ipAddress == null || ipAddress.length() == 0 || "unknown".equalsIgnoreCase(ipAddress)) {
ipAddress = request.getRemoteAddr();
}
// 对于通过多个代理的情况,第一个IP为客户端真实IP,多个IP按照','分割
if (ipAddress != null && ipAddress.length() > 15) {
if (ipAddress.indexOf(",") > 0) {
ipAddress = ipAddress.substring(0, ipAddress.indexOf(","));
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
ipAddress = "";
}
return ipAddress;
}
}
该类要做的事情和上面的两种限流措施类似,不过在这里核心的限流是通过读取lua脚步,通过参数传递给lua脚步实现的。
1.5.6 自定义lua脚本
在工程的 resources 目录下,添加如下的lua脚本
local key = "rate.limit:" .. KEYS[1]
local limit = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local current = tonumber(redis.call('get', key) or "0")
if current + 1 > limit then
return 0
else
-- 没有超阈值,将当前访问数量+1,并设置2秒过期(可根据自己的业务情况调整)
redis.call("INCRBY", key,"1")
redis.call("expire", key,"2")
return current + 1
end
redis中验证 lua脚本的两种方式:
- 登录
redis后执行eval命令:EVAL script numkeys key [key ...] arg [arg ...]
例如:EVAL "local key = KEYS[1]\nlocal value = ARGV[1]\nredis.call('SET', key, value)" 1 mykey myvaluescript:是要执行的Lua脚本numkeys:是脚本中用到的键的数量key [key ...]:是脚本中用到的键的名称arg [arg ...]:是脚本中用到的参数
- 不登录执行
--eval命令,如果lua脚本较长,可以使用redis-cli --eval的方式,新建lua.lua文件,在文件中输入:return KEYS[1]..ARGV[1]
在linux中执行:redis-cli --eval 文件路径 keys , argvs
key和参数间需要使用逗号(,)隔开,并且逗号前后需要占用空格
1.5.7 添加测试接口
@RestController
public class RedisController {
//localhost:8081/redis/limit
@GetMapping("/redis/limit")
@RedisLimitAnnotation(key = "queryFromRedis",period = 1, count = 1)
public String queryFromRedis(){
return "success";
}
}
为了模拟效果,这里将QPS设置为1 ,启动工程后(提前启动redis服务),调用一下接口,正常的效果如下,如果快速刷接口,超过每秒1次的请求时报错
标签:lang,方案,SpringBoot,redis,限流,import,org,public From: https://www.cnblogs.com/jingzh/p/17533526.html