一、一维数组
构造类型之一,存放的数据地址连续
1.定义
使用格式:【存储类型】 数据类型 标识符 [下标]
2.初始化
3.元素引用
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define M 3
int main()
{
int i;
// /*auto*/int arr[M] = {1,2,3} //数组初始化
//arr = {1,2,3}; //这种表述是错误的,违背了常量的概念
int arr[M];
//数组所占内存大小
printf("this array's size is %d\n",sizeof(arr));
//显示arr的首地址
printf("arr address is %p\n",&arr);
//手动输入数组数据
printf("请输入数值:\n");
for(i = 0; i < M;i++)
scanf("%d",&arr[i]); //scanf中不能包含其他字符否则会无法执行。
//循环输出数组各个元素在内存中的位置
for(i = 0; i < M;i++)
printf("%p --> %d\n",&arr[i],arr[i]);
exit(0);
}
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./arr1
this array's size is 12
arr adress is 0x7ffeaabdc4dc
请输入数值:
12
23
56
0x7ffeaabdc4dc --> 12
0x7ffeaabdc4e0 --> 23
0x7ffeaabdc4e4 --> 56
4.数组名
数组名是表示数组的常量,其所在的地址也表示该数组的起始地址。
5.数组越界
指的是一个数组所含有的元素数量超过了其容量,该错误只能人为地去发现,编译器并不会报错。
//在上述代码中,arr[M] = {1 ,2, 3},即arr[0]=1,arr[1]=2,arr[2]=3.
arr[3]=10
//打印输出该值时仍会正常显示,不会报错。
printf("arr[3] = %d\n",arr[3]);
出现该问题的原因是:c指针偏移导致的。
指针的使用:arr[i] = *arr[arr + i],第i个元素的地址就是arr的地址加上i * 元素所占内存大小.*表示读取存放在该地址处的元素值。因此定义arr[3]后,其地址也根据公式随之确定,也就可以读取该地址存放的数据。
6.Quizs
-
求fibonacci数列前十项,并逆序排列该数组。
fibonacci数列:n > 2时,任意元素值等于前两个元素值之和。
代码:
int main()
{
int fab[10] = { 1,1 }; //初始化数组前两个值
int i, j, temp;
//求解这十个数
for(i = 2; i < 10; i++) //change to : for(i = 2; i < sizeof(fab) / sizeof(fab[0]))
fab[i] = fab[i - 1] + fab[i - 2];
//输出这十个数
for(j = 0; j < 10; j++)
printf("%d,", fab[j]);
printf("\n");
//print in Reverse order
i = 0;
j = sizeof(fab) / sizeof(fab[0]) - 1;
while (i < j)
{
temp = fab[i];
fab[i] = fab[j];
fab[j] = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
for (i = 0; i < sizeof(fab) / sizeof(fab[0]); i++)
printf("%d ", fab[i]);
printf("\n");
exit(0);
}
输出结果:
1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,
55 34 21 13 8 5 3 2 1 1
-
排序:冒泡排序、选择排序、快速排序
1)冒泡排序
逻辑所在:比较相邻的两个元素值,若第一个比第二个大,则两者交换位置。对所有的元素进行操作,从开始的第一对到最后一对。
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define M 10
//function: 对输入的数据进行排序
static void bubble_sort(void)
{
int sort[M];
int i,j,tmp;
printf("请输入十个数值:\n");
for(i = 0; i < M;i++) //输入数值
scanf("%d",&sort[i]);
for(i = 0;i < M;i++) //输出显示的数值
printf("%d ",sort[i]);
printf("\n");
//冒泡排序
for(i = 0;i < M - 1; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < M - 1 - i;j++)
{
if(sort[j] > sort[j + 1])
{
tmp = sort[j];
sort[j] = sort[j + 1];
sort[j + 1] = tmp;
}
}
}
for(i = 0;i < M;i++)
printf("%d ",sort[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
bubble_sort();
exit(0);
}
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./bubble_order
请输入十个数值:
1
5
6
3
2
4
7
9
8
10
1 5 6 3 2 4 7 9 8 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
2)选择排序
逻辑所在:
- 遍历每一行数据,寻找出最小(大)值,将最小(大)值存放在排序序列的首位。
- 再从剩余未排序序列中选择最小值,放在已排序序列的后面。
- 重复上一个步骤,直至所有元素均排序完毕。
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 10
static void selection_sort(void)
{
int i,j,min,tmp;
int sort[N];
printf("请输入数组的值:\n");
for(i = 0;i < sizeof(sort) / sizeof(sort[0]);i++)
scanf("%d",&sort[i]);
for(i = 0;i < sizeof(sort) / sizeof(sort[0]);i++)
printf("%d ",sort[i]);
printf("\n");
for(i = 0;i < sizeof(sort) / sizeof(sort[0])-1;i++)
{
//确定该组数值最小值的下标
min = i;
for(j = i + 1;j < sizeof(sort) / sizeof(sort[0]);j++)
{
if(sort[j] < sort[min])
{
min = j;
}
}
if(min != i)
{
tmp = sort[i];
sort[i] = sort[min];
sort[min] = tmp;
}
}
for(i = 0;i < sizeof(sort) / sizeof(sort[0]);i++)
printf("%d ",sort[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
selection_sort();
exit(0);
}
运行结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./select_order
请输入数组的值:
78
79
74
75
76
71
72
14
15
56
78 79 74 75 76 71 72 14 15 56
14 15 56 71 72 74 75 76 78 79
拓展:给定一组数值,输出其最大值与最小值:
法一:
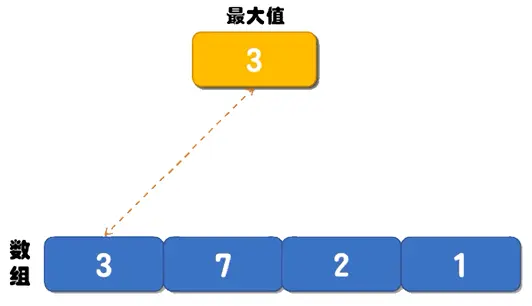
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 #define N 10
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 int i;
9 int min,max;
10 int arr[N] = {12,22,33,43,55,72,95,19,56,59};
11 min = arr[0];
12 max = arr[0];
13
14 for(i = 1; i < N; i++) //从第二个数开始遍历
15 {
16 if(max < arr[i]) //如果遍历的值大于max,则更新max的值
17 {
18 max = arr[i];
19 }
20 if(min > arr[i]) //如果遍历的值小于min,则更新min的值
21 {
22 min = arr[i];
23 }
24 }
25 printf("max = %d,min = %d\n",max,min);
26
27 exit(0);
28 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/pointer$ ./max
max = 95,min = 12
法二:
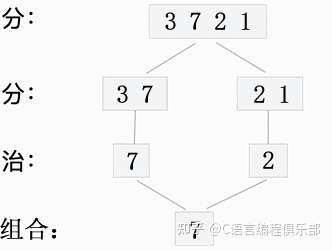
#include <stdio.h>
//自定义函数,其中 [left,right] 表示 arr 数组中查找最大值的范围
int get_max(int* arr, int left, int right) {
int max_left = 0, max_right = 0, middle = 0;
//如果数组不存在
if (arr == NULL) {
return -1;
}
//如果查找范围中仅有一个数字
if (right - left == 0) {
return arr[left];
}
//如果查找范围中有 2 个数字,直接比较即可
if (right - left <= 1) {
if (arr[left] >= arr[right]) {
return arr[left];
}
return arr[right];
}
//等量划分成 2 个区域
middle = (right - left) / 2 + left;
//得到左侧区域中的最大值
max_left = get_max(arr, left, middle);
//得到右侧区域中的最大值
max_right = get_max(arr, middle + 1, right);
//比较左、右两侧的最大值,找到 [left,right] 整个区域的最大值
if (max_left >= max_right) {
return max_left;
}
else {
return max_right;
}
}
int main() {
int arr[4] = { 3,7,2,1 };
int max = get_max(arr, 0, 3);
printf("最大值:%d\n", max);
return 0;
}
3)进制转换
对输入的数值进行二进制、八进制、十六进进制转换。
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int a[128]; //store the converted value
int num,base;
int i = 0;
printf("Please Input value: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
printf("Please Input base: ");
scanf("%d",&base);
do
{
a[i] = num % base;
num = num / base; //update num
i++;
}while(num != 0);
for(i--;i >= 0;i--)
{
if(a[i] > 10)
{
printf("%c",a[i] - 10 + 'A');
}
else
{
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
exit(0);
}
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./base_convert
Please Input value: 245
Please Input base: 16
F5
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./base_convert
Please Input value: 245
Please Input base: 2
11110101
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./base_convert
Please Input value: 245
Please Input base: 8
365
4)删除法求质数
逻辑所在:从i = 2开始遍历所有数据,之后在循环将i的倍数标记为-1,最后输出角标为0的所有值即为质数。
示例代码
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 int main()
5 {
6 //primers in 0~1000
7 int primer[1001] ={0}; //initiallize array 部分初始化后,其他元素也随之被初始化。另外static直接定义数组也可以实现这样的功能。
8 int i,j;
9
10 for(i = 2;i < 1001;i++)
11 {
12 if(primer[i] == 0)
13 {
14 for(j = i * 2;j < 1001;j += i)
15 {
16 primer[j] = -1;
17 }
18 }
19 }
20 for(i = 2;i < 1001;i++) //1既不是质数也不是合数。
21 if(primer[i] == 0 )
22 printf("%d ",i);
23
24 printf("\n");
25 exit(0);
26 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./primer
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19 23 29 31 37 41 43 47 53 59 61 67 71 73 79 83 89 97 101 103 107 109 113 127 131 137 139 149 151 157 163 167 173 179 181 191 193 197 199 211 223 227 229 233 239 241 251 257 263 269 271 277 281 283 293 307 311 313 317 331 337 347 349 353 359 367 373 379 383 389 397 401 409 419 421 431 433 439 443 449 457 461 463 467 479 487 491 499 503 509 521 523 541 547 557 563 569 571 577 587 593 599 601 607 613 617 619 631 641 643 647 653 659 661 673 677 683 691 701 709 719 727 733 739 743 751 757 761 769 773 787 797 809 811 821 823 827 829 839 853 857 859 863 877 881 883 887 907 911 919 929 937 941 947 953 967 971 977 983 991 997
二、二维数组
1.定义,初始化
【存储类型】 数据类型 标识符 [行下标] [列下标]
与一维数组类似部分初始化后其他元素也会初始化,另外在初始化前提下,行号可以省略,列号不可以省略:
//比如m行n列的二维数组 a[2][3] = {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}} //标准形式初始化 a[2][3] = {{1,2},{3}} //未涉及直接初始化的值为0 > 1 2 0 > 3 0 0 a[][3] = {{1,2},{3}} //省略行号的初始化结果与上面相同 a[2][3] = {1,2,3,4} 初始化结果为: > 1 2 3 > 4 0 0 //原因是虽然是二维数组但是在内存中的存储形式还是按行进行连续存储的,与一维数组的存储形式类似。二维数组的大小指定后,每个数值的存储形式也就确定了。
示例代码
//要求打印输出二维数组,并输出每个值对应的内存地址。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//定义数组大小
#define M 2
#define N 3
int main()
{
int a[M][N];
int i,j;
for(i = 0; i < M;i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < N;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i = 0; i < M;i++))
{
for(j = 0; j < N;j++)
{
printf("%p --> %d\n",&a[i][j],a[i][j]);
}
//printf("\n");
}
exit(0);
}
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./2d_array
1
2
3
4
5
6
0x7ffe8bcb78d0 --> 1
0x7ffe8bcb78d4 --> 2
0x7ffe8bcb78d8 --> 3
0x7ffe8bcb78dc --> 4
0x7ffe8bcb78e0 --> 5
0x7ffe8bcb78e4 --> 6
2.元素引用
数组名 [行标] [下标]
3.存储形式
顺序存储、按行存储
4.Quizs
1)行列互换
示例代码:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 #define M 2
5 #define N 3
6
7 static void matrix_trans(void)
8 {
9 int a[M][N] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
10 int b[N][M];
11 int i,j;
12
13 //print values
14 printf("matrix a :\n");
15 for(i = 0;i < M;i++)
16 {
17 for(j = 0; j < N;j++)
18 {
19 printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
20 b[j][i] = a[i][j];
21 }
22 printf("\n");
23 }
24
25 printf("matrix b :\n");
26 for(i = 0;i < N;i++ )
27 {
28 for(j = 0;j < M;j++)
29 {
30 printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
31 }
32 printf("\n");
33 }
34 }
35
36 int main()
37 {
38 matrix_trans();
39
40 exit(0);
41 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./matrix_transpose
matrix a :
1 2 3
4 5 6
matrix b :
1 4
2 5
3 6
2)求最大值及其所在位置
示例代码:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 #define M 2
5 #define N 3
6
7 static void matrix_max(void)
8 {
9 int i,j,row,colum;
10 int a[M][N] = {{14,12,45},{56,89,78}};
11 int max = a[0][0];
12 printf("this matrix is :\n");
13
14 for(i = 0;i < M;i++ )
15 {
16 for(j = 0;j < N;j++)
17 {
18 printf("%d ",a[i][j]);
19 }
20 printf("\n");
21 }
22 for(i = 0;i < M;i++ )
23 {
24 for(j = 0;j < N;j++)
25 {
26 if(max < a[i][j])
27 {
28 max = a[i][j];
29 row = i + 1 ;
30 colum = j + 1;
31 }
32
33 }
34 }
35 printf("max value is : %d\n",max);
36 printf("it is located in :row = %d,colum = %d\n",row,colum);
37
38 }
39
40 int main()
41 {
42 matrix_max();
43
44 exit(0);
45 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./matrix_max
this matrix is :
14 12 45
56 89 78
max value is : 89
it is located in :row = 2,colum = 2
3)求各行与各列的和
示例代码:
40 static void matrix_sum(void)
41 {
42 int i,j;
43 int a[5][6] = {{1,2,5,6,8},{56,89,45,5,2},{4,5,9,56,8},{4,52,32,58,62}}; //4 row and 5 colum
44
45
46 for(i = 0;i < 4;i++)
47 {
48 for(j = 0;j < 5;j++)
49 {
50 a[4][5] += a[i][j];
51 a[4][j] += a[i][j]; //sum of colum
52 a[i][5] += a[i][j]; //sum of row
53 }
54 }
55
56 for(i = 0;i < 5;i++)
57 {
58 for(j = 0;j < 6;j++)
59 {
60 printf("%8d ",a[i][j]);
61 }
62 printf("\n");
63 }
64
65
66 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./matrix_max
1 2 5 6 8 22
56 89 45 5 2 197
4 5 9 56 8 82
4 52 32 58 62 208
65 148 91 125 80 509
4)矩阵乘积运算
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 #define M 3
5 #define N 2
6 #define K 3
7
8 static void matrix_multi(void)
9 {
10 int a[M][N] ={{3,4},{2,2},{2,2}}; //row = 3,colume = 2
11 int b[N][K] = {{1,2,5},{3,4,7}}; //row = 2,colume = 3
12 static int c[M][K];
13 int i,j,k;
14
15 for(i = 0;i < M;i++)
16 {
17 for(j = 0;j < K;j++)
18 {
19 for(k = 0;k < N;k++)
20 {
21 c[i][j] += a[i][k] * b[k][j];
22 }
23 }
24
25 }
26
27 for(i = 0;i < M;i++)
28 {
29 for(j = 0;j < K;j++)
30 {
31 printf("%d ",c[i][j]);
32 }
33 printf("\n");
34 }
35 }
36
37 int main()
38 {
39 matrix_multi();
40
41 exit(0);
42 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./matrix_multi
15 22 43
8 12 24
8 12 24
5.深入理解二维数组
二维数组其实就是由一维数组构成的连续存储空间。
示例代码:
//分别输出一维数组,二维数组标识符 + 1的地址
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 //定义数组大小
5 #define M 2
6 #define N 3
7
8 int main()
9 {
10 int a[M][N] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
11 int b[N] = {1,2,3};
12 int i,j,k;
13
14 printf("二维数组a地址是:%p\n",a);
15 printf("二维数组a+1地址是:%p\n",a+1);
16
17 printf("一维数组b地址是:%p\n",b);
18 printf("一维数组b+1地址是:%p\n",b+1);
19
20 for(i = 0; i < M;i++)
21 {
22 for(j = 0; j < N;j++)
23 {
24 printf("%p --> %d\n",&a[i][j],a[i][j]);
25 }
26 }
27 printf("\n");
28
29 for(k = 0;k < N;k++)
30 {
31 printf("%p --> %d\n",&b[k],b[k]);
32 }
33 printf("\n");
34
35 exit(0);
36 }
输出结果:
xs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./arr_pointer
二维数组a地址是: 0x7ffe7f24a4b0
二维数组a+1地址是:0x7ffe7f24a4bc //行跳跃
一维数组b地址是: 0x7ffe7f24a4a4
一维数组b+1地址是:0x7ffe7f24a4a8
0x7ffe7f24a4b0 --> 1
0x7ffe7f24a4b4 --> 2
0x7ffe7f24a4b8 --> 3
0x7ffe7f24a4bc --> 4
0x7ffe7f24a4c0 --> 5
0x7ffe7f24a4c4 --> 6
0x7ffe7f24a4a4 --> 1
0x7ffe7f24a4a8 --> 2
0x7ffe7f24a4ac --> 3
三、字符数组
1.定义,初始化,存储特点
【存储类型】 数据类型 标识符 [下标]
字符数组初始化方式:单个字符初始化以及用字符串常量初始化
str[3] = {'a','v','f'}; //单个字符初始化 str[3] = "a" //字符串常量初始化 //字符数组在存储字符串时,在字符串的结尾处会有一个尾0作为结尾;即 \0
2.输入输出
字符数组的输入输出会以TAB,Space,Enter键为终端结束输出命令.
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3
4 #define N 32
5
6 int main()
7 {
8 char str[N],str1[N],str2[N];
9
10 scanf("%s%s%s",str,str1,str2); //字符串常量是地址常量,因此不需要加取址符
11 printf("%s\n%s\n%s\n",str,str1,str2);
12
13 exit(0);
14 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./str_func
hello world hhaha
hello
world
hhaha
3.常用函数
1).strlen & sizeof
示例代码:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4
5 /*Compare with
6 *strlen & sizeof //strlen指字符串的长度,并且以尾0(\0)作为结束标记; sizeof表示字符串实际占用的字节数;
7 *strcpy & strncpy
8 *strcat & strncat
9 *strcmp & strncmp
10 * */
11
12 #define N 32
13
14 int main()
15 {
16 //strlen: caculate the length of string
17 char str[] = "hello";
18 char str1[] = "hello\0";
19 char str2[] = "hello\0world"; //strlen函数使用时,尾0(null byte)之后的内容就不计入字符串长度
20
21 printf("\"hello\" length is :%ld\n",strlen(str));
22 printf("the size of this 'hello' is :%ld\n\n",sizeof(str));
23
24 printf("'hello\\0' length is :%ld\n",strlen(str1));
25 printf("the size of this 'hello\\0' is :%ld\n\n",sizeof(str1));
26
27 printf("\"hello\\0world\" length is :%ld\n",strlen(str2));
28 printf("the size of this 'hello\\0world' is :%ld\n\n",sizeof(str2));
29
30 exit(0);
31 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./str_func
"hello" length is :5
the size of this 'hello' is :6
'hello\0' length is :5
the size of this 'hello\0' is :7
"hello\0world" length is :5
the size of this 'hello\0world' is :12
2).strcpy & strncpy
defination:
strcpy, strncpy:复制一个字符串
usage:#include <string.h> char *strcpy(char *dest(目标数组), const char *src(待拷贝的字符串)); char *strncpy(char *dest(目标数组), const char *src(待拷贝的字符串), size_t n(限制拷贝到目标字符数组的字符串长度,防止overrun!));
示例代码:
32 char str[STRSIZE];
33 // strcpy(str,"hello\ world");
34 strncpy(str,"hello world",STRSIZE); //限制copy的字符串长度
35
36 puts(str);
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./str_func
hello world
3).strcat & strncat
- defination:
strcat, strncat- concatenate(连接) two strings- usage:
#include <string.h> char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src); char *strncat(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n);
strcat(str,"hello"): 表示将"hello"字符串附加到字符数组str中,覆盖 >str结尾处中的\0,之后再增加一个\0;附加的字符串或许不会重叠(覆盖相同的空> 间),但是str必须要有足够的空间来容纳附加的字符串;strncat(str,"hello",STRSIZE):前两个说明与上述相同;STRSIZE表示从hello中至多取用STRSIZEbyte。如果hello占用的字节数大于或等于STRSIZE,则strncat()会写进str中n+1个字节(n + \0)。因此,str的空间(sizeof)至少为strlen(str) + n + 1.
示例代码:
41 char str[STRSIZE] = "I "; //STRSIZE = 32
42 strcat(str,"Love ");
43 strncat(str,"You are",4);
44 strncat(str,"Yansang",8);
输出结果:
I Love You Yansang
这里如果
strncat(str,"Yansang",7);的话,会有错误提示:str_func.c: In function ‘main’: str_func.c:44:5: warning: ‘strncat’ specified bound 7 equals source length > [-Wstringop-overflow=] 44 | strncat(str,"Yansang",7); | ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~原因在于:
strcat指定的字符约束值为7等于要附加到str的字符串长度(7),此时Yansang只剩下\0,可以小于7大于7但不能等于7。
4).strcmp & strncmp
- defination:
strcmp, strncmp- 比较两个字符串的 ASCII码值。- usages:
#include <string.h> int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2); int strncmp(const char *s1, const char *s2, size_t n);比较两个字符串,使用无符号字符数据类型来完成的。
strcmp返回int类型数据来表示比较结果:
- 如果前者同于后者,返回值为0 值;
- 如果前者小于后者,返回值为负值;
- 如果前者大于后者,返回值为正值;
strncmp与上述类似,唯一的不同点在于,strnmp只比较前n个(at most)字符串是否相同.
示例代码:
49 char str1[STRSIZE] = "hella",str[STRSIZE] = "hello";
50
51 printf("%d\n",strcmp(str1,str));
52 printf("%d\n",strncmp(str1,str,4));
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./str_func
-14 //只对首字符进行ASCII进行比较
0
Note:按字符串自左向右进行ANSCII码值进行比较,直到出现不同的字符或者
\0为止:1."A"<"B" 2."A"<"AB" 3."Apple"<"Banana" 4."A"<"a" 5."compare"<"computer"只能比较字符串常量或者字符数组,不能比较数字以及其它形式的参数,ANSI 标准规定,返回值为正数,负数,0 。而确切数值是依赖不同的C实现的。当两个字符串不相等时,C 标准没有规定返回值会是 1 或 -1,只规定了正数和负数。有些会把两个字符的 ASCII 码之差作为比较结果由函数值返回。但无论如何不能以此条依据作为程序中的流程逻辑。
-
Quizs
-
单词计数
分析:自定义输入一连串字符,判断字符串的个数,需要排除空格、TAB键计算字符串个数。
示例代码:
1 #include <stdio.h>
2 #include <stdlib.h>
3 #include <string.h>
4
5 //such as : avd fadff sdfasf sfaf
6
7 int main()
8 {
9 int i,count,flag;
10 char str[128];
11 gets(str);
12
13 for(i = 0;str[i] != '\0';i++)
14 {
15 if(str[i] == ' ' || str[i] == '\t') //如果遇到空格或者TAB键令flag = 0;
16 flag = 0;
17
18 else //如果不是空格,并且上一个字符是空格(flag = 0);
19 {
20 if(flag == 0)
21 {
22 count++; //发现字符串
23 flag = 1; //flag = 1;
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 printf("%d\n",count);
28
29 exit(0);
30 }
输出结果:
jxs@jxs-ubuntu:~/Desktop/c language/array$ ./cacu_abc
anf afann afnanfnnan fnafnanfnnanfn f nannfnnannn n nfannfna
8
三、多维数组
示例图: