问题描述
你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中
heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0
开始编号)。你每次可以往 上, 下, 左, 右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费
体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例 1:
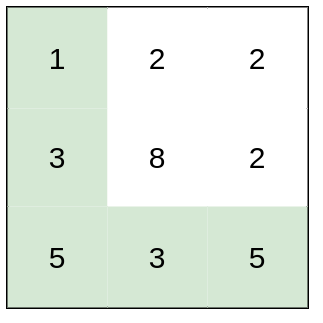
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
输出:2
解释:路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 连续格子的差值绝对值最大为 2 。
这条路径比路径 [1,2,2,2,5] 更优,因为另一条路径差值最大值为 3 。
示例 2:
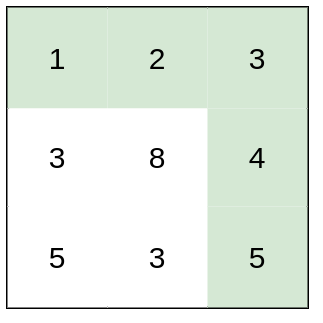
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
输出:1
解释:路径 [1,2,3,4,5] 的相邻格子差值绝对值最大为 1 ,比路径 [1,3,5,3,5] 更优。
示例 3:
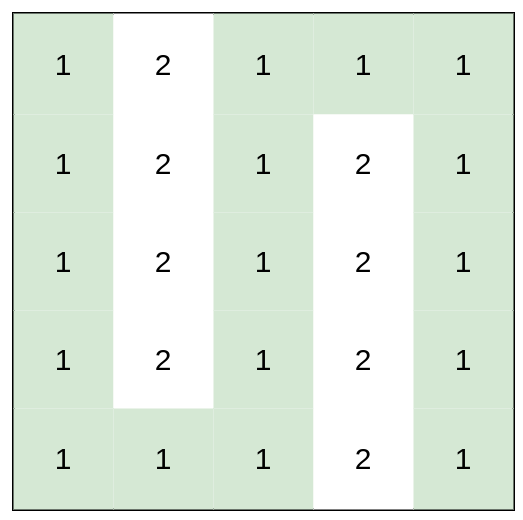
输入:heights =
[[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]]
输出:0
解释:上图所示路径不需要消耗任何体力。
提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 10⁶
解题思路
Dijkstra算法
可以使用Dijkstra算法来求解,使用小顶堆。
常规的的Dijkstra算法,一般是pq.push({idx, len + len[idx]}),这里则是pq.push({idx, std::max(len, len[idx])})。
二分
二分答案+广度优先搜索
代码
Dijkstra算法
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>> &heights) {
int m = heights.size(), n = heights[0].size();
// Dijkstra
auto cmp = [&](vector<int> &v1, vector<int> &v2) {
return v1[2] > v2[2];
};
priority_queue<vector<int>, vector<vector<int>>, decltype(cmp)> pq(cmp);
vector<vector<int>> dis(m, vector<int>(n, -1));
vector<vector<int>> move{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
pq.push({0, 0, 0});
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto vec = pq.top();
pq.pop();
int x = vec[0], y = vec[1], cost = vec[2];
if (dis[x][y] != -1) {
continue;
}
dis[x][y] = cost;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int new_x = x + move[i][0];
int new_y = y + move[i][1];
if (new_x >= 0 && new_x < m && new_y >= 0 && new_y < n) {
if (dis[new_x][new_y] == -1) {
pq.push({new_x, new_y, std::max(cost, abs(heights[x][y] - heights[new_x][new_y]))});
}
}
}
}
return dis[m - 1][n - 1];
}
};