2023-05-19:汽车从起点出发驶向目的地,该目的地位于出发位置东面 target 英里处。
沿途有加油站,每个 station[i] 代表一个加油站,
它位于出发位置东面 station[i][0] 英里处,并且有 station[i][1] 升汽油。
假设汽车油箱的容量是无限的,其中最初有 startFuel 升燃料。
它每行驶 1 英里就会用掉 1 升汽油。
当汽车到达加油站时,它可能停下来加油,将所有汽油从加油站转移到汽车中。
为了到达目的地,汽车所必要的最低加油次数是多少?如果无法到达目的地,则返回 -1 。
注意:如果汽车到达加油站时剩余燃料为 0,它仍然可以在那里加油。
如果汽车到达目的地时剩余燃料为 0,仍然认为它已经到达目的地。
输入:target = 100, startFuel = 10, stations = [[10,60],[20,30],[30,30],[60,40]]。
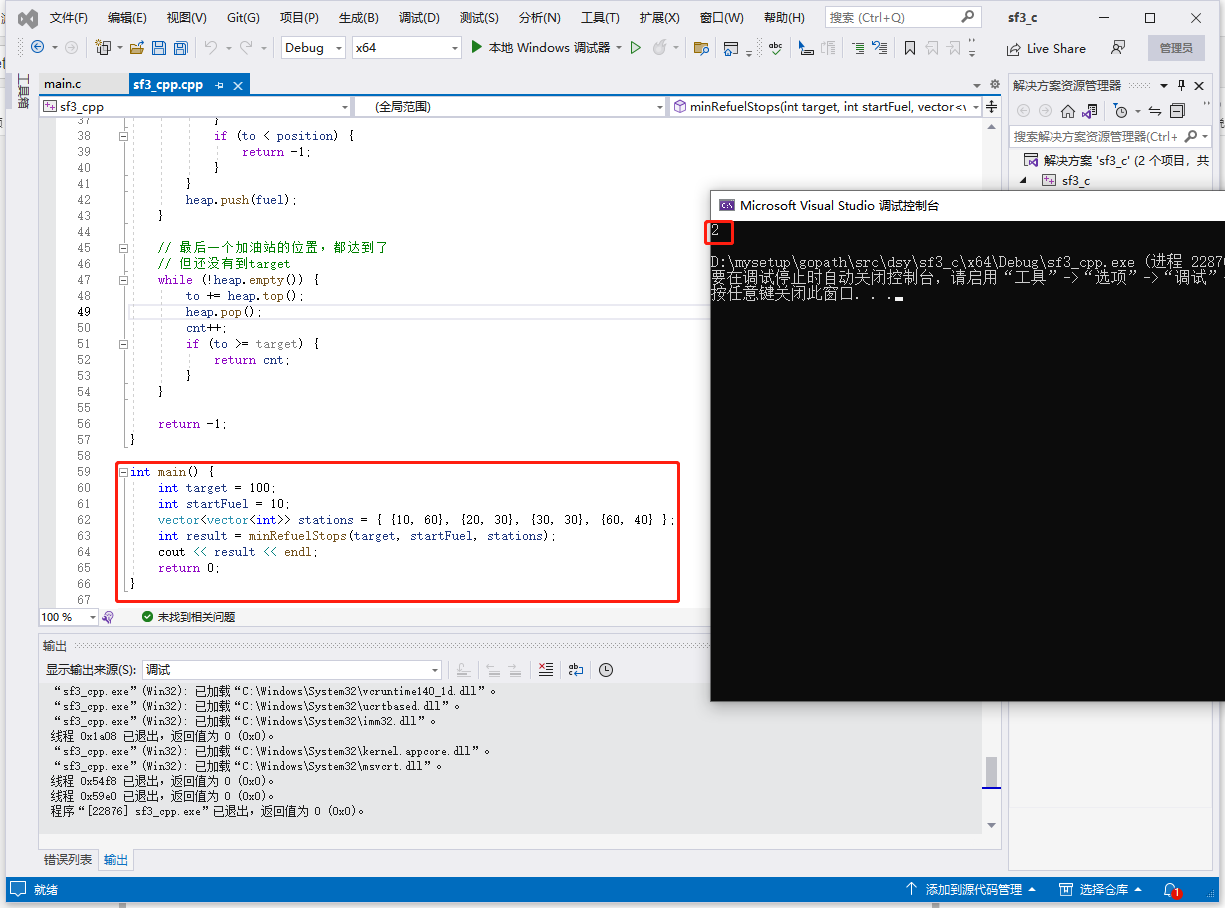
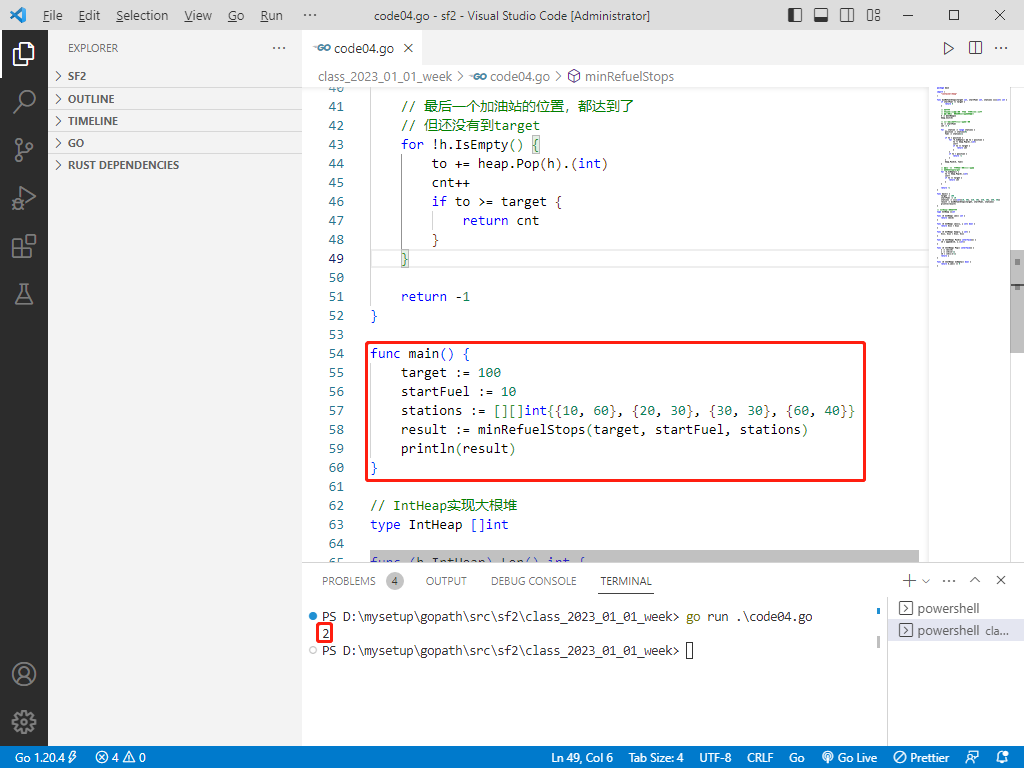
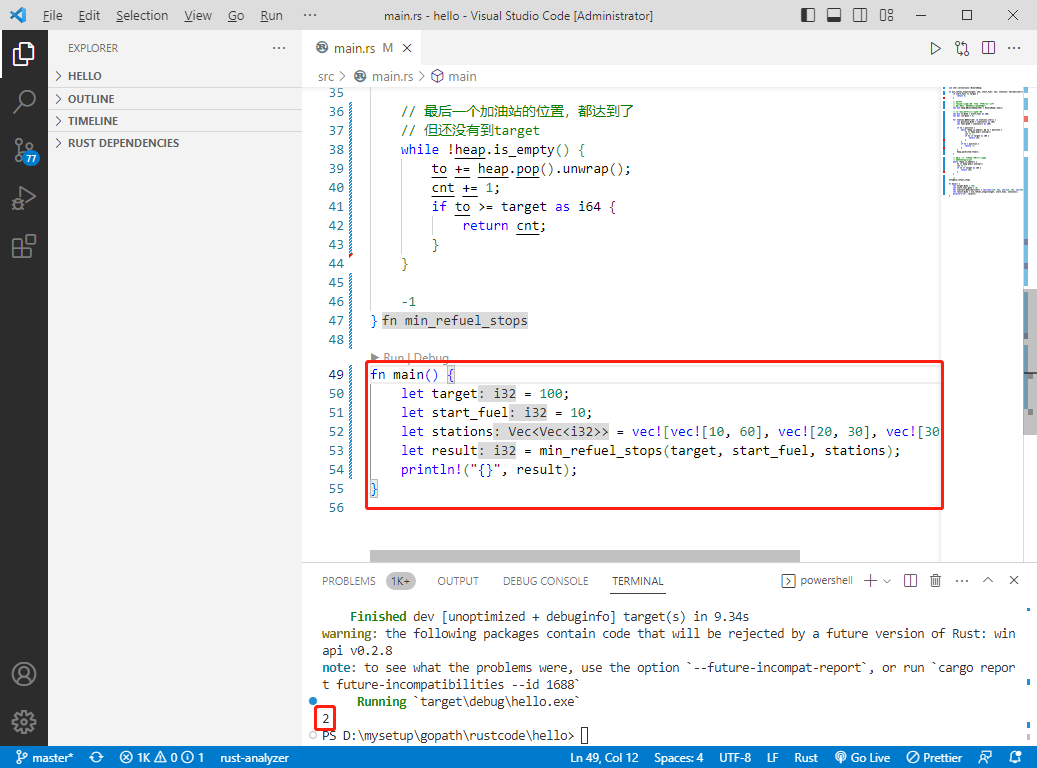
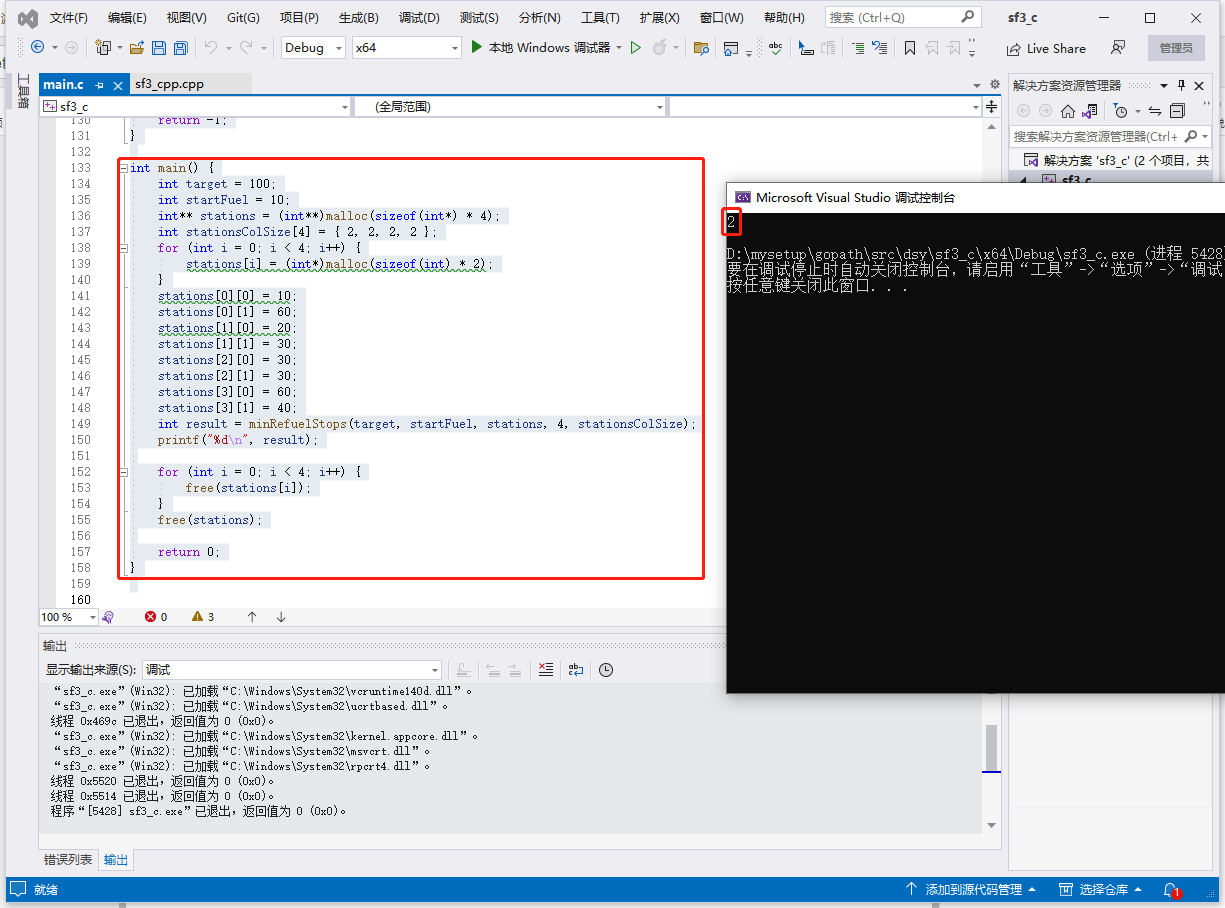
输出:2。
答案2023-05-19:
具体步骤如下:
1.初始化车内油量 to 和已经加得次数 cnt。
2.遍历所有加油站,对于每个加油站,判断能否到达。如果不能到达,就从大根堆中不断取出油量添加到车内,直至可以到达该加油站或无法再添加油量为止。如果无法到达该加油站,则无法到达目标位置,返回-1。
3.如果能够到达该加油站,则将该加油站的油量添加到大根堆中,并继续向前移动。
4.如果无法到达目标位置,则不断从大根堆中取出油量,直至能够到达目标位置或者大根堆为空为止。
5.返回已经加油的次数。
时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中n为加油站的数量。主要是因为该算法使用了堆来维护加油站的油量,每次需要考虑哪个加油站的油量最多,以便优先选择加油量最大的加油站。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中n为加油站的数量。主要是因为该算法使用了堆存储加油站的油量,所以需要额外的空间存储堆中的元素。
go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
)
func minRefuelStops(target int, startFuel int, stations [][]int) int {
if startFuel >= target {
return 0
}
// 大根堆
// 维持的是:最值得加油的加油站,有多少油
// 最值得:加得次数少,跑的还最远
h := &IntHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
// 当前车里的油,能达到的位置
to := startFuel
cnt := 0
for _, station := range stations {
position := station[0]
fuel := station[1]
if to < position {
for !h.IsEmpty() && to < position {
to += heap.Pop(h).(int)
cnt++
if to >= target {
return cnt
}
}
if to < position {
return -1
}
}
heap.Push(h, fuel)
}
// 最后一个加油站的位置,都达到了
// 但还没有到target
for !h.IsEmpty() {
to += heap.Pop(h).(int)
cnt++
if to >= target {
return cnt
}
}
return -1
}
func main() {
target := 100
startFuel := 10
stations := [][]int{{10, 60}, {20, 30}, {30, 30}, {60, 40}}
result := minRefuelStops(target, startFuel, stations)
println(result)
}
// IntHeap实现大根堆
type IntHeap []int
func (h IntHeap) Len() int {
return len(h)
}
func (h IntHeap) Less(i, j int) bool {
return h[i] > h[j]
}
func (h IntHeap) Swap(i, j int) {
h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i]
}
func (h *IntHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, x.(int))
}
func (h *IntHeap) Pop() interface{} {
n := len(*h)
x := (*h)[n-1]
*h = (*h)[:n-1]
return x
}
func (h *IntHeap) IsEmpty() bool {
return h.Len() == 0
}
rust完整代码如下:
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
fn min_refuel_stops(target: i32, start_fuel: i32, stations: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
if start_fuel >= target {
return 0;
}
// 大根堆
// 维持的是:最值得加油的加油站,有多少油
// 最值得:加得次数少,跑的还最远
let mut heap = BinaryHeap::new();
// 当前车里的油,能达到的位置
let mut to = start_fuel as i64;
let mut cnt = 0;
for station in stations.iter() {
let position = station[0] as i64;
let fuel = station[1] as i64;
if to < position {
while !heap.is_empty() && to < position {
to += heap.pop().unwrap();
cnt += 1;
if to >= target as i64 {
return cnt;
}
}
if to < position {
return -1;
}
}
heap.push(fuel);
}
// 最后一个加油站的位置,都达到了
// 但还没有到target
while !heap.is_empty() {
to += heap.pop().unwrap();
cnt += 1;
if to >= target as i64 {
return cnt;
}
}
-1
}
fn main() {
let target = 100;
let start_fuel = 10;
let stations = vec![vec![10, 60], vec![20, 30], vec![30, 30], vec![60, 40]];
let result = min_refuel_stops(target, start_fuel, stations);
println!("{}", result);
}
c语言完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// IntHeap实现大根堆,这里用函数指针代替仿函数
int cmp(int a, int b) {
return a < b;
}
// 交换两个数的值
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
typedef struct IntHeap {
int (*cmp)(int, int);
void (*swap)(int*, int*);
int* data;
int size;
int capacity;
}IntHeap;
// 初始化大根堆
void initHeap(IntHeap* heap, int (*cmp)(int, int)) {
heap->cmp = cmp;
heap->swap = &swap;
heap->data = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 128);
heap->size = 0;
heap->capacity = 128;
}
// 扩容
void resize(IntHeap* heap) {
int newCapacity = heap->capacity * 2;
int* newData = (int*)realloc(heap->data, sizeof(int) * newCapacity);
heap->data = newData;
heap->capacity = newCapacity;
}
// 堆化
void down(IntHeap* heap, int i) {
while (i * 2 + 1 < heap->size) {
int left = i * 2 + 1;
int right = i * 2 + 2;
int j = left;
if (right < heap->size && heap->cmp(heap->data[right], heap->data[left])) {
j = right;
}
if (heap->cmp(heap->data[i], heap->data[j])) {
break;
}
heap->swap(&heap->data[i], &heap->data[j]);
i = j;
}
}
// 入堆
void pushHeap(IntHeap* heap, int val) {
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
resize(heap);
}
heap->data[heap->size++] = val;
int i = heap->size - 1;
while (i > 0) {
int p = (i - 1) / 2;
if (heap->cmp(heap->data[p], heap->data[i])) {
break;
}
heap->swap(&heap->data[p], &heap->data[i]);
i = p;
}
}
// 弹出堆顶元素
int popHeap(IntHeap* heap) {
int top = heap->data[0];
heap->data[0] = heap->data[--heap->size];
down(heap, 0);
return top;
}
int minRefuelStops(int target, int startFuel, int** stations, int stationsSize, int* stationsColSize) {
if (startFuel >= target) {
return 0;
}
// 大根堆
// 维持的是:最值得加油的加油站,有多少油
// 最值得:加得次数少,跑的还最远
IntHeap heap;
initHeap(&heap, &cmp);
// 当前车里的油,能达到的位置
long long to = startFuel;
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < stationsSize; i++) {
int position = stations[i][0];
int fuel = stations[i][1];
if (to < position) {
while (heap.size && to < position) {
to += popHeap(&heap);
cnt++;
if (to >= target) {
return cnt;
}
}
if (to < position) {
return -1;
}
}
pushHeap(&heap, fuel);
}
// 最后一个加油站的位置,都达到了
// 但还没有到 target
while (heap.size) {
to += popHeap(&heap);
cnt++;
if (to >= target) {
return cnt;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int target = 100;
int startFuel = 10;
int** stations = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * 4);
int stationsColSize[4] = { 2, 2, 2, 2 };
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
stations[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
}
stations[0][0] = 10;
stations[0][1] = 60;
stations[1][0] = 20;
stations[1][1] = 30;
stations[2][0] = 30;
stations[2][1] = 30;
stations[3][0] = 60;
stations[3][1] = 40;
int result = minRefuelStops(target, startFuel, stations, 4, stationsColSize);
printf("%d\n", result);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
free(stations[i]);
}
free(stations);
return 0;
}
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// IntHeap实现大根堆
struct IntHeap {
bool operator()(int a, int b) { return a < b; }
};
int minRefuelStops(int target, int startFuel, vector<vector<int>>& stations) {
if (startFuel >= target) {
return 0;
}
// 大根堆
// 维持的是:最值得加油的加油站,有多少油
// 最值得:加得次数少,跑的还最远
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, IntHeap> heap;
// 当前车里的油,能达到的位置
long long to = startFuel;
int cnt = 0;
for (auto station : stations) {
int position = station[0];
int fuel = station[1];
if (to < position) {
while (!heap.empty() && to < position) {
to += heap.top();
heap.pop();
cnt++;
if (to >= target) {
return cnt;
}
}
if (to < position) {
return -1;
}
}
heap.push(fuel);
}
// 最后一个加油站的位置,都达到了
// 但还没有到target
while (!heap.empty()) {
to += heap.top();
heap.pop();
cnt++;
if (to >= target) {
return cnt;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
int target = 100;
int startFuel = 10;
vector<vector<int>> stations = { {10, 60}, {20, 30}, {30, 30}, {60, 40} };
int result = minRefuelStops(target, startFuel, stations);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}