2023-05-05:给定一个无向、连通的树
树中有 n 个标记为 0...n-1 的节点以及 n-1 条边 。
给定整数 n 和数组 edges ,
edges[i] = [ai, bi]表示树中的节点 ai 和 bi 之间有一条边。
返回长度为 n 的数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] :
树中第 i 个节点与所有其他节点之间的距离之和。
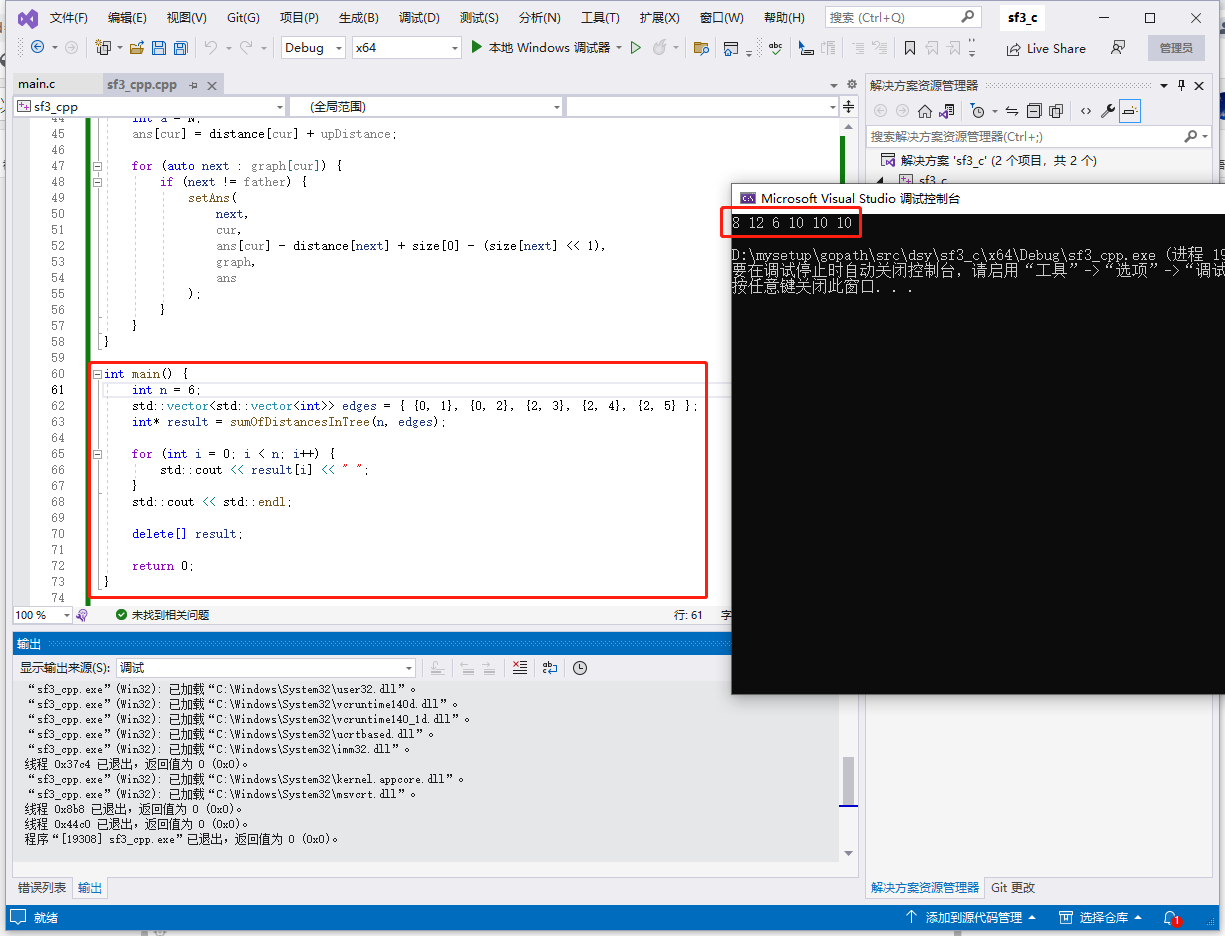
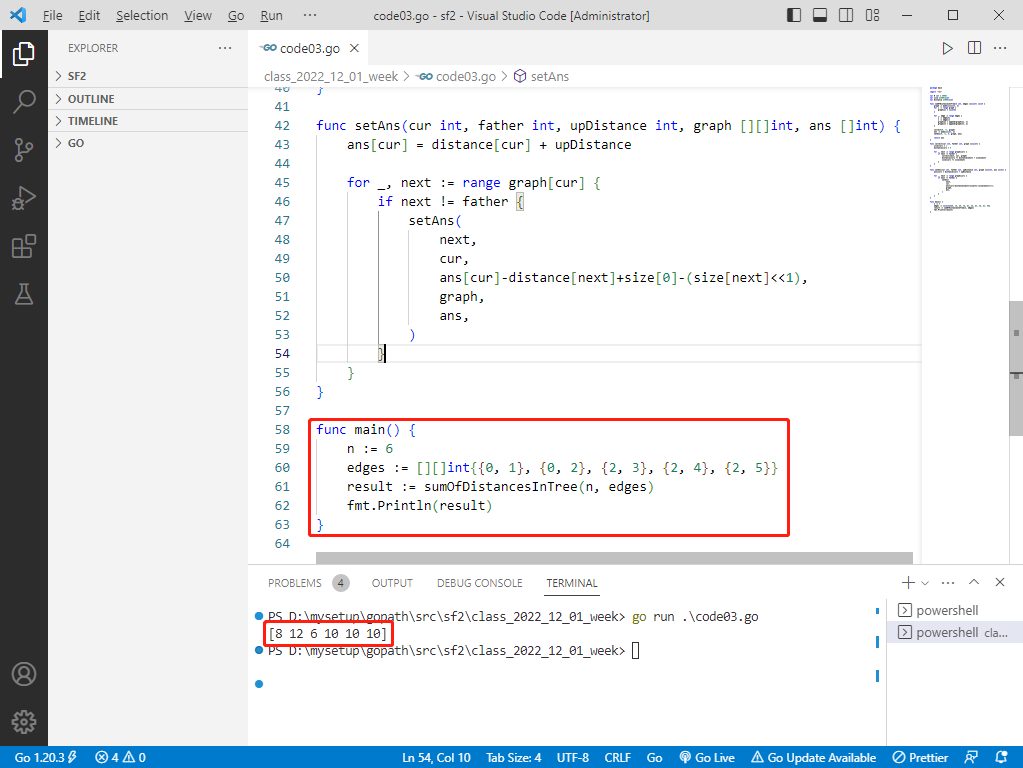
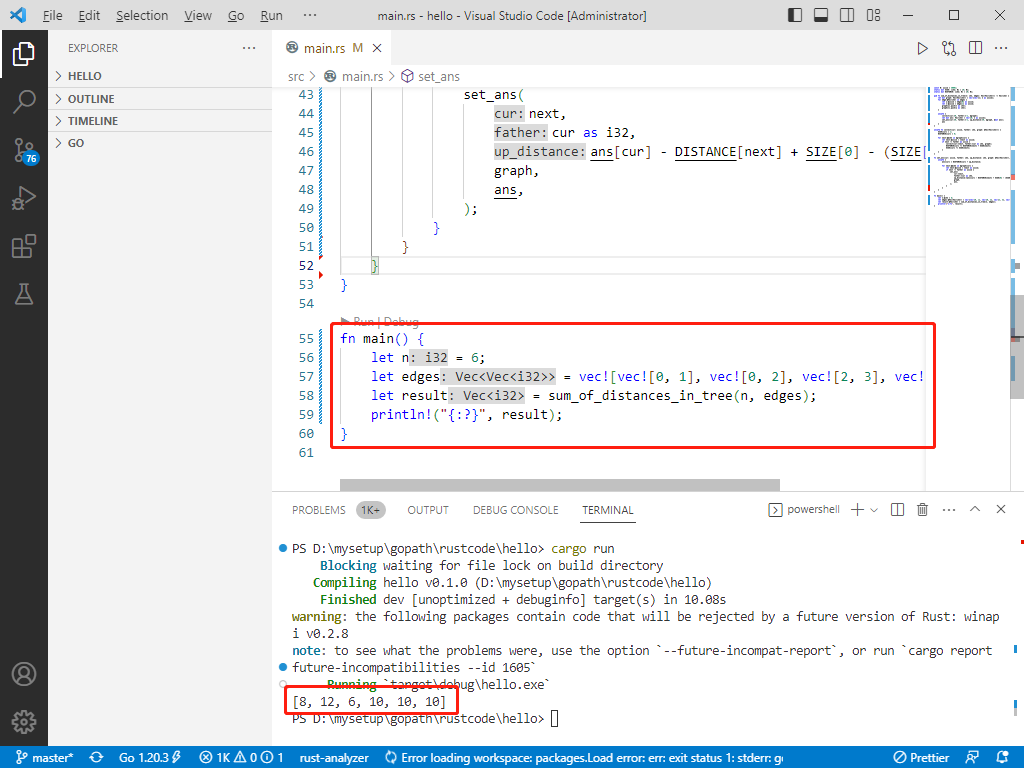
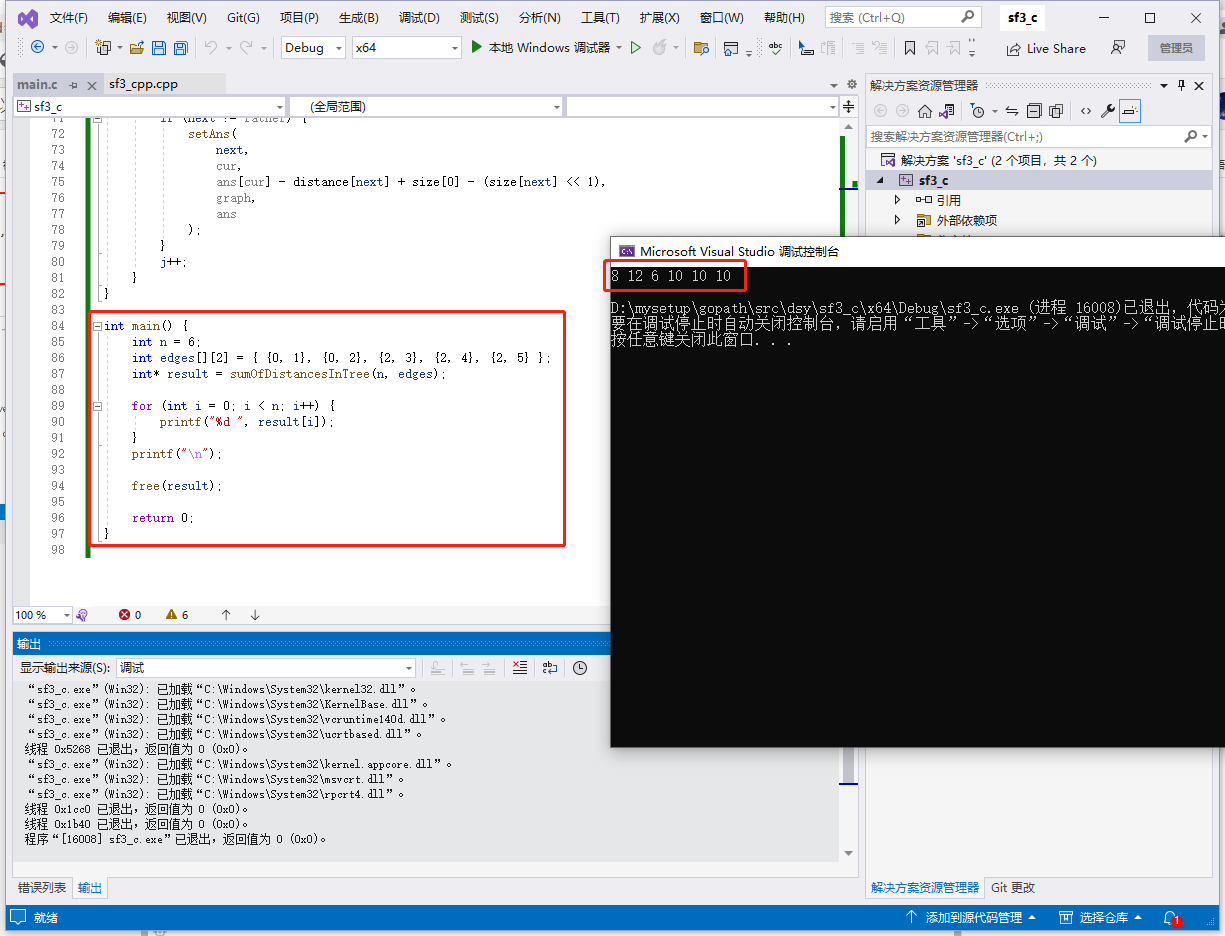
输入: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]]。
输出: [8,12,6,10,10,10]。
答案2023-05-05:
思路:
给定一棵无向、连通的树,要求计算每个节点到其他所有节点的距离之和。
可以通过遍历树,对于每个节点分别计算它到其他节点的距离之和。对于每个节点,利用它的子节点信息来更新它到其他节点的距离之和,然后递归地更新它的子节点。最终得到所有节点的距离之和。
具体实现如下:
1.构造图
通过给定的 edges 数组构造无向图。
2.遍历树,计算每个节点到其他节点的距离之和
从根节点开始递归遍历树,对于每个节点,首先初始化它到其他节点的距离之和为 0,然后递归地处理它的子节点。处理完所有子节点之后,计算该节点到其他节点的距离之和,并将该节点的大小(即包括自身在内的节点数)保存下来。
3.递归更新节点到其他节点的距离之和
从根节点开始递归遍历树,对于每个节点,首先计算它到其他节点的距离之和,并将其保存在 ans 数组中。然后递归地处理它的子节点,将它们对应的距离之和更新到 upDistance 中,并计算每个子节点到其他节点的距离之和。
总时间复杂度:O(n)
总空间复杂度:O(n)
go完整代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
var N int = 30001
var size [30001]int
var distance [30001]int
func sumOfDistancesInTree(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
graph := make([][]int, n)
for i := range graph {
graph[i] = []int{}
}
for _, edge := range edges {
u := edge[0]
v := edge[1]
graph[u] = append(graph[u], v)
graph[v] = append(graph[v], u)
}
collect(0, -1, graph)
ans := make([]int, n)
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans)
return ans
}
func collect(cur int, father int, graph [][]int) {
size[cur] = 1
distance[cur] = 0
for _, next := range graph[cur] {
if next != father {
collect(next, cur, graph)
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next]
size[cur] += size[next]
}
}
}
func setAns(cur int, father int, upDistance int, graph [][]int, ans []int) {
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance
for _, next := range graph[cur] {
if next != father {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur]-distance[next]+size[0]-(size[next]<<1),
graph,
ans,
)
}
}
}
func main() {
n := 6
edges := [][]int{{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5}}
result := sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges)
fmt.Println(result)
}
rust完整代码如下:
const N: usize = 30001;
static mut SIZE: [i32; N] = [0; N];
static mut DISTANCE: [i32; N] = [0; N];
pub fn sum_of_distances_in_tree(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut graph: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![vec![]; n as usize];
for edge in edges {
let u = edge[0] as usize;
let v = edge[1] as usize;
graph[u].push(v as i32);
graph[v].push(u as i32);
}
unsafe {
collect(0, -1, &graph);
let mut ans: Vec<i32> = vec![0; n as usize];
set_ans(0, -1, 0, &graph, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
unsafe fn collect(cur: usize, father: i32, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
SIZE[cur] = 1;
DISTANCE[cur] = 0;
for next in &graph[cur] {
let next = *next as usize;
if next != father as usize {
collect(next, cur as i32, graph);
DISTANCE[cur] += DISTANCE[next] + SIZE[next];
SIZE[cur] += SIZE[next];
}
}
}
fn set_ans(cur: usize, father: i32, up_distance: i32, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, ans: &mut Vec<i32>) {
unsafe {
ans[cur] = DISTANCE[cur] + up_distance;
for next in &graph[cur] {
let next = *next as usize;
if next != father as usize {
set_ans(
next,
cur as i32,
ans[cur] - DISTANCE[next] + SIZE[0] - (SIZE[next] << 1),
graph,
ans,
);
}
}
}
}
fn main() {
let n = 6;
let edges = vec![vec![0, 1], vec![0, 2], vec![2, 3], vec![2, 4], vec![2, 5]];
let result = sum_of_distances_in_tree(n, edges);
println!("{:?}", result);
}
c完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 30001
int size[N];
int distance[N];
void collect(int cur, int father, int** graph, int n);
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, int** graph, int* ans);
int* sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, int edges[][2]) {
int** graph = malloc(n * sizeof(*graph));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = malloc((n + 1) * sizeof(**graph));
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
graph[i][j] = -1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
if (graph[u][0] == -1) {
graph[u][0] = 0;
}
if (graph[v][0] == -1) {
graph[v][0] = 0;
}
int j = 0;
while (graph[u][++j] != -1);
graph[u][j] = v;
j = 0;
while (graph[v][++j] != -1);
graph[v][j] = u;
}
collect(0, -1, graph, n);
int* ans = malloc(n * sizeof(int));
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
free(graph[i]);
}
free(graph);
return ans;
}
void collect(int cur, int father, int** graph, int n) {
size[cur] = 1;
distance[cur] = 0;
int j = 1;
while (graph[cur][j] != -1) {
int next = graph[cur][j];
if (next != father) {
collect(next, cur, graph, n);
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next];
size[cur] += size[next];
}
j++;
}
}
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, int** graph, int* ans) {
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance;
int j = 1;
while (graph[cur][j] != -1) {
int next = graph[cur][j];
if (next != father) {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur] - distance[next] + size[0] - (size[next] << 1),
graph,
ans
);
}
j++;
}
}
int main() {
int n = 6;
int edges[][2] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5} };
int* result = sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", result[i]);
}
printf("\n");
free(result);
return 0;
}
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
//using namespace std;
const int N = 30001;
static int size[N];
static int distance[N];
void collect(int cur, int father, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph);
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph, int* ans);
int* sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& edges) {
std::vector<std::vector<int>> graph(n);
for (auto edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
collect(0, -1, graph);
int* ans = new int[n];
setAns(0, -1, 0, graph, ans);
return ans;
}
void collect(int cur, int father, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph) {
size[cur] = 1;
distance[cur] = 0;
for (auto next : graph[cur]) {
if (next != father) {
collect(next, cur, graph);
distance[cur] += distance[next] + size[next];
size[cur] += size[next];
}
}
}
void setAns(int cur, int father, int upDistance, std::vector<std::vector<int>>& graph, int* ans) {
int a = N;
ans[cur] = distance[cur] + upDistance;
for (auto next : graph[cur]) {
if (next != father) {
setAns(
next,
cur,
ans[cur] - distance[next] + size[0] - (size[next] << 1),
graph,
ans
);
}
}
}
int main() {
int n = 6;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> edges = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {2, 3}, {2, 4}, {2, 5} };
int* result = sumOfDistancesInTree(n, edges);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
std::cout << result[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
delete[] result;
return 0;
}