目录
1.前言
2.设计与分析
3.踩坑心得
4.改进建议
5.总结
1.前言
题目集4: (训练自我学习能力,例如treeset与hashset用法,了解一些类中的方法)
菜单计价程序-3
有重复的数据
有重复的数据
单词统计与排序
面向对象编程(封装性)
GPS测绘中度分秒转换
判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
题目集5: (熟练正则表达式,并初步了解聚合)
正则表达式训练-QQ号校验
字符串训练-字符排序
正则表达式训练-验证码校验
正则表达式训练-学号校验
日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
题目集6: (题目集4的迭代)
菜单计价程序-4
第四次题目集,听到同学说需要使用hashset与treeset时,我不知所措,后来在csdn查它们的用法,发现会用即可,不需要了解它们的底层代码。在最后一道题我才发现其实老师提醒我们需要自学一些,初步了解了日期中有许多好用的类,为后面题目集4第一题与题目集6第一题提供了求日期的思路。
第五次题目集,主要看到前几题是属于正则表达式的,我去看了一下慕课,发现并没有主要交我们代码格式,我是通过b站自主学习,慢慢了解了方法,做了笔记,出的这些题目没有拐弯抹角,直接输出即可。主要的boss是2道聚合题,但我写时,最后还时有些瑕疵。
第六次题目集,是题目集4第一题的迭代,难度直线飙升,我开始做了4天,但都是错的,根本第一个样例都实现不了,听到老师说要写1600行代码加上好多同学都没做,直接摆烂了。
2.设计与分析
7-3 去掉重复的数据在一大堆数据中找出重复的是一件经常要做的事情。现在,我们要处理许多整数,在这些整数中,可能存在重复的数据。
你要写一个程序来做这件事情,读入数据,检查是否有重复的数据。如果有,去掉所有重复的数字。最后按照输入顺序输出没有重复数字的数据。所有重复的数字只保留第一次出现的那份。
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int a,c=0;
a= in.nextInt();
int[] b=new int[a];
int i;
for(i=0;i<=a-1;i++)
{
b[i]=in.nextInt();
}
LinkedHashSet<Integer> list =new LinkedHashSet<>();
for(i=0;i<b.length;i++)
{
list.add(b[i]);
}
boolean flag = true;
for(Integer number:list)
{
if(flag){
System.out.print(number);
flag = false;
}
else
System.out.print(" "+number);
}
}
}
这道题刚好满足hashset的基本算法用途,所以不需要在写自己的构造器,不像下一题,不满足treeset的基本算法,所以要自己写构造器来满足题目的排序要求。
7-4 单词统计与排序 从键盘录入一段英文文本(句子之间的标点符号只包括“,”或“.”,单词之间、单词与标点之间都以" "分割。
要求:按照每个单词的长度由高到低输出各个单词(重复单词只输出一次),如果单词长度相同,则按照单词的首字母顺序(不区分大小写,首字母相同的比较第二个字母,以此类推)升序输出。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = in.nextLine();
String[] strr = str.split(",|\\ |\\.");
TreeSet<String> ts=new TreeSet<String>(new MyCompartor());
int i;
for(i = 0;i < strr.length;i++){
if(strr[i] != null&&strr[i].length() != 0)
ts.add(strr[i]);
//System.out.printf(String.valueOf(ts));
}
//System.out.printf(String.valueOf(ts));
//System.out.println();
for (Iterator itr = ts.iterator(); itr.hasNext();)
System.out.println(itr.next());
}
}
class MyCompartor implements Comparator<String>{
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
if(o1.length() > o2.length())
return -1;
else if (o1.length() == o2.length()){
return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2);
}
else
return 1;
}
}
这里需要查一下treeset的基本原理(先按照字典来排大写字母,再按照字典来排小写字母,不满足题目要求,所以要自己写构造器来满足题目的排序要求),写这个构造器时,ideal直接给了一些代码,自己填空即可,不是很难、
面向对象编程(封装性) 太简单,不讲。
GPS测绘中度分秒转换太简单,不讲。
判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
从键盘输入两个日期,格式如:2022-06-18。判断两个日期的先后,并输出它们之间间隔的天数、周数(不足一周按0计算)。
预备知识:通过查询Java API文档,了解Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String date1= in.nextLine();
String date2= in.nextLine();
String[] split = date1.split("-",4);
String[] split1 = date2.split("-",4);
int i;
int[] a = new int[3];
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++){
a[i] = Integer.parseInt(split[i]);
//System.out.print(a[i]);
}
int[] b = new int[3];
for(i = 0;i < 3;i++){
b[i] = Integer.parseInt(split1[i]);
//System.out.print(b[i]);
}
int year,year1,month,month1,day,day1;
year = a[0];
year1 = b[0];
month = a[1];
month1 = b[1];
day = a[2];
day1 = b[2];
LocalDate date3 = LocalDate.of(year,month,day);
LocalDate date4 = LocalDate.of(year1,month1,day1);
if(date3.isBefore(date4) == true)
System.out.printf("第一个日期比第二个日期更早\n");
if(date3.isBefore(date4) == false)
System.out.printf("第一个日期比第二个日期更晚\n");
long date5 = 0,date6 = 0;
date5 = date3.until(date4,ChronoUnit.DAYS);
date6 = date3.until(date4,ChronoUnit.WEEKS);
//System.out.print(date5);
System.out.printf("两个日期间隔%d天\n",Math.abs(date5));
System.out.printf("两个日期间隔%d周\n",Math.abs(date6));
}
}
这里了解了split用法,可以把数组切开,组成新的大数组,为判断时间做了更好的安排
Integer类中parseInt()的用法,把字符串转化为整形,便于数组判断。
LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()直接使用,直接判断出差值与日期排序,特别方便。
LocalDate类中until()与ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS直接判断两日期之间相差多少天与多少周。
这道题主要体现自学,只要自学了,这道题非常方便解决。
题目集5的一些正则表达式,太简单了,我直接给出答案。
1.正则表达式训练-QQ号校验校验键盘输入的 QQ 号是否合格,判定合格的条件如下:
- 要求必须是 5-15 位;
- 0 不能开头;
- 必须都是数字;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); String a = in.next(); if (a.matches("^[1-9][0-9]{4,14}")) { System.out.print("你输入的QQ号验证成功"); } else { System.out.print("你输入的QQ号验证失败"); } } }
2.
字符串训练-字符排序对输入的字符串中的字符进行排序并输出。
输入格式:
在一行内输入一个字符串。
输出格式:
对该字符串内的字符进行排序后(按ASCII码进行升序排序)输出。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = in.next();
int l = a.length();
char[] n = new char[l];
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
n[i] = a.charAt(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < l - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < l; j++) {
if (n[i] > n[j]) {
char t = n[i];
n[i] = n[j];
n[j] = t;
}
}
}
System.out.print(n);
}
}
3.
正则表达式训练-验证码校验接受给定的字符串,判断该字符串是否属于验证码。验证码是由四位数字或者字母(包含大小写)组成的字符串。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = in.next();
if (a.matches("[0-9a-zA-Z]{4}")) {
System.out.print(a + "属于验证码");
} else {
System.out.print(a + "不属于验证码");
}
}
}
正则表达式训练-学号校验
对软件学院2020级同学学号进行校验,学号共八位,规则如下:
- 1、2位:入学年份后两位,例如20年
- 3、4位:学院代码,软件学院代码为20
- 5位:方向代码,例如1为软件工程,7为物联网
- 6位:班级序号
- 7、8位:学号(序号)
要求如下:
- 只针对2020级
- 其中软件工程专业班级分别为:202011~17、61,物联网工程专业班级为202071~202073,数据科学与大数据专业班级为202081~82
- 每个班级学号后两位为01~40
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String a = in.next();
if (a.matches("^2020(61|1[1-7]|7[1-3]|8[1-2])([1-3][0-9]|40|0[1-9])$")) {
System.out.print("正确");
} else {
System.out.print("错误");
}
}
}
接下来我重点叙述2个聚合与2个菜单
日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
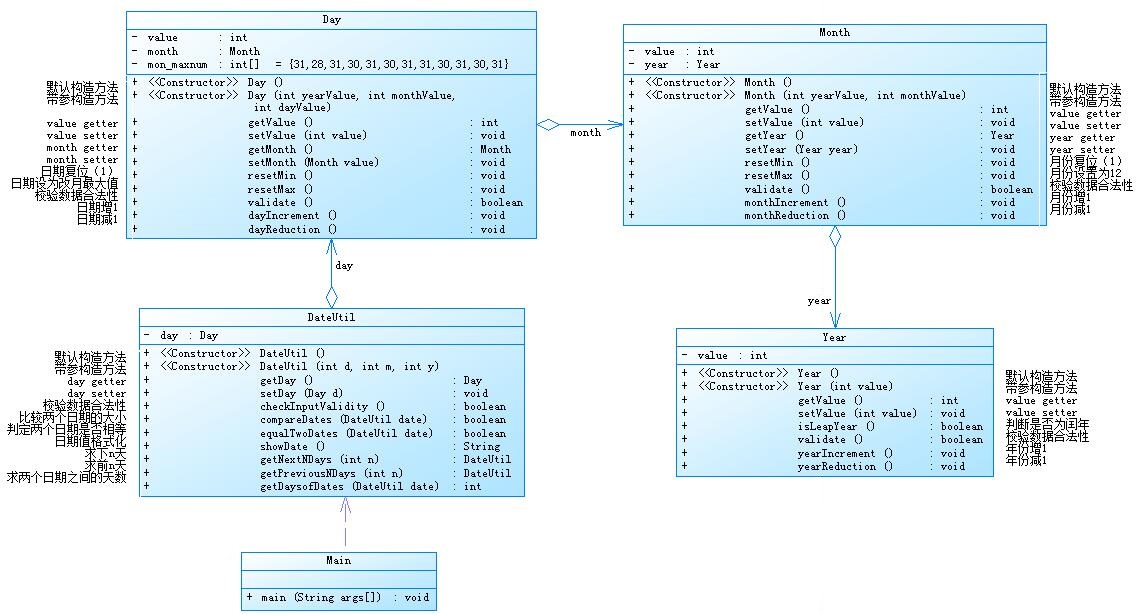
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=in.nextInt();
if(x==1) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil date =new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(date.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
date.getNextNDays(n);
date.showDate();
}
}
if(x==2) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil date=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
if(date.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
else {
date.getPrviousNDays(n);
date.showDate();
}
}
if(x==0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
if(x==3) {
int year=in.nextInt();
int month=in.nextInt();
int day=in.nextInt();
int year2=in.nextInt();
int month2=in.nextInt();
int day2=in.nextInt();
DateUtil date1=new DateUtil(day,month,year);
DateUtil date2=new DateUtil(day2,month2,year2);
if(date1.checkInputValidity()==false||date2.checkInputValidity()==false) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
if(year==year2&&month==month2&day==day2) {
System.out.println(0);
}
else {
System.out.println(date1.getDaysofDates(date2));
}
}
}
}
class Year
{
private int value;
Year(){
}
Year(int value){
this.value=value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear() {
if((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 !=0 )||(value % 400 == 0)) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value<1900||value>2050) {
return false;
}
else
return true;
}
public void yearIncrement() {
value=value+1;
}
public void yearReduction() {
value=value-1;
}
}
class Month
{
private int value;
private Year year;
Month(){
}
Month(int yearValue,int monthValue){
this.value=monthValue;
this.year=new Year(yearValue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
value=12;
}
public boolean validate() {
if(value>12||value<1) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public int monthget(){
int x;
if(value==1||value==3||value==5||value==7||value==8||value==10||value==12) {
x=31;
return x;
}
else if(value==4||value==6||value==9||value==11) {
x=30;
return x;
}
else if(value==2) {
if(year.isLeapYear()==true) {
x=29;
return 29;
}
else {
x=28;
return x;
}
}
return 0;
}
public void monthIncrement() {
if(value<12) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1; //Month 变成 1。
year.yearIncrement(); //year 加1,
}
}
public void monthReduction() {
if(value>1) {
value--;
}
else {
value=12;
year.yearReduction();
}
}
}
class Day {
private int value;
private Month month;
int []monmaxnum= {31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
Day(){
}
Day(int yearvalue,int monthvalue,int dayvalue){
this.value=dayvalue;
this.month=new Month(yearvalue,monthvalue);
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void resetMin() {
value=1;
}
public void resetMax() {
int i;
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
monmaxnum[1]=29;
}
else {
monmaxnum[1]=28;
}
value=monmaxnum[month.getValue()-1];
}
public boolean validate() {
if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12){
if(value<1||value>31) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getValue()==4||month.getValue()==6||month.getValue()==9||month.getValue()==11) {
if(value<1||value>30) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==true) {
if(value<1||value>29) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
else if(month.getYear().isLeapYear()==false) {
if(value<1||value>28) {
return false;
}
}
else {
return true;
}
return true;
}
public void DayIncrement() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value<days) {
value++;
}
else {
value=1;
month.monthIncrement();
}
}
public void DayReduction() {
int days=month.monthget();
if(value>=2) {
value--;
}
else {
month.monthReduction();
value=month.monthget();
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private Day day;
DateUtil(){
}
DateUtil(int d,int m,int y){
this.day=new Day(y,m,d);
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
if(day.getMonth().getYear().validate()==false||day.getMonth().validate()==false||day.validate()==false) {
return false;
}
else {
return true;
}
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()>day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()<day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()>day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()<day.getMonth().getValue()) {
return false;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()>day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()<day.getValue()) {
return false;
}
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) {
if(date.day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()==day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()&&date.day.getMonth().getValue()==day.getMonth().getValue()&&date.day.getValue()==day.getValue()) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
public void showDate() {
System.out.println(day.getMonth().getYear().getValue()+"-"+day.getMonth().getValue()+"-"+day.getValue());
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
day.DayIncrement();
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public DateUtil getPrviousNDays(int n) {
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++) {
day.DayReduction();
}
return new DateUtil(day.getValue(),day.getMonth().getValue(),day.getMonth().getYear().getValue());
}
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) {
int a=0;
if(compareDates(date)==true) {
while(compareDates(date)==true) {
day.DayIncrement();
a++;
}
return a;
}
if(compareDates(date)==false) {
while(compareDates(date)==false) {
date.day.DayIncrement();
a++;
if(equalTwoDates(date)==true) {
break;
}
}
return a;
}
else
return 0;
}
}
我的类图

我的类图基本满足老师给的类图,从图中我们直接看出它们的耦合性太强,操作性不强
我的思路与之前的一样,先管下n天与前n天的算法


我先写了这两个功能,但是它又是出现了月份越界与天数越界,因为我用的是累加,使得我最后的数值可能会超过int的边界值,起初我都没在意,接着写求2天的差的功能,代码一交,它直接让我所有测试点都过了,搞的我一脸懵,但是还是开心的。


最终这道题还是稳稳拿下,主要还是老师给了类图且注释了该方法的具体作用,我们只需要搭建框架写功能即可。整体难度不高,这道题让我们初步了解聚合的使用。
日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二)
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
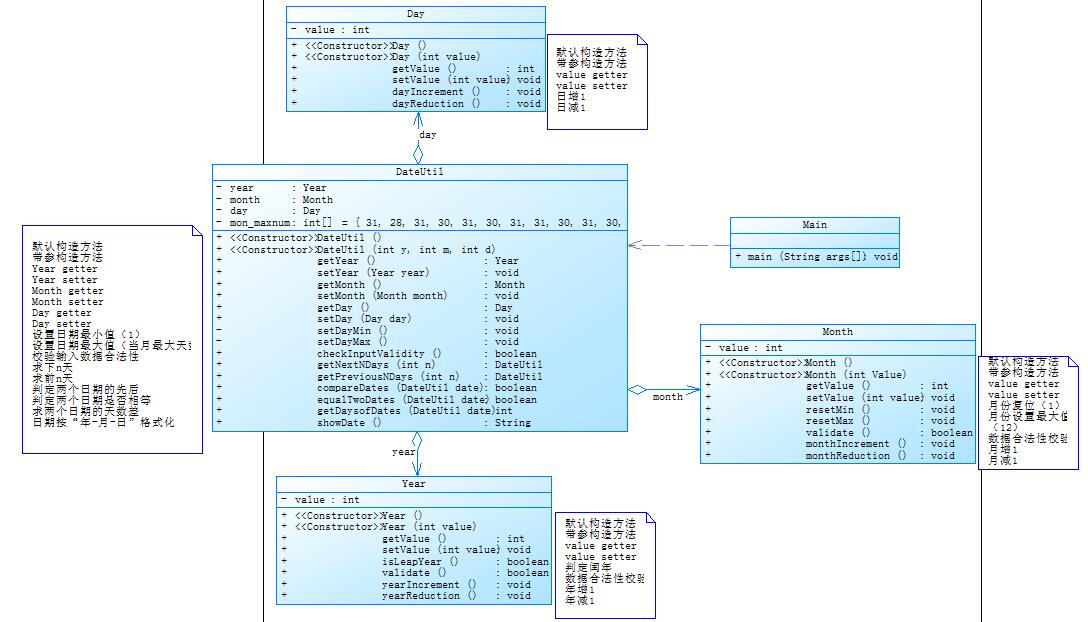
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = in.nextInt();
if(x == 1) {
Year year = new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month = new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day = new Day(in.nextInt());
int n = in.nextInt();
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(date.checkInputValidity() == false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d next %d days is:",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue(),n);
date.getNextNDays(n);
}
}
if(x == 2){
Year year = new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month = new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day = new Day(in.nextInt());
int n = in.nextInt();
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(date.checkInputValidity() == false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d previous %d days is:",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue(),n);
date.getPreviousNDays(n);
}
}
if(x == 3){
Year year=new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month=new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day=new Day(in.nextInt());
Year year2=new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month2=new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day2=new Day(in.nextInt());
DateUtil date1=new DateUtil(year,month,day);
DateUtil date2=new DateUtil(year2,month2,day2);
if((date1.checkInputValidity() == false)||(date2.checkInputValidity() == false))
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}//对两次输入的年月日都做合法性检验
else
date1.getDaysofDates(year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue(),year2.getValue(),month2.getValue(),day2.getValue());
}
if(x == 0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
public Month() {
}
public Month(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void resetMin(){
value = 1;
}
public void resetMax(){
value = 12;
}
public boolean validate(){
if(value>=1&&value<=12)
return true;
else return false;
}
public void monthIncrement(){
value += 1;
}
public void monthReduction(){
value -= 1;
}
}
class Year{
private int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(){
if(value%400==0||(value%4==0&&value%100!=0))
return true;
else return false;
}
public boolean validate(){
if(value>=1820&&value<=2020)
return true;
else return false;
}
public void dayIncrement(){
value += 1;
}
public void yearReduction(){
value -= 1;
}
}
class Day{
private int value;
public Day() {
}
public Day(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void dayIncrement(){
value += 1;
}
public void dayReduction(){
value -= 1;
}
}
class DateUtil{
private Year year;
private Month month;
private Day day;
private int []monmaxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil() {
}
public DateUtil(Year year, Month month, Day day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
public void setDayMin(){
day.setValue(1);
}
public void setDayMax(){
if(year.isLeapYear()==true) {
if (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)
day.setValue(31);
else if (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)
day.setValue(30);
else
day.setValue(29);
}
else
{
if (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)
day.setValue(31);
else if (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)
day.setValue(30);
else
day.setValue(28);
}
}
public boolean checkInputValidity() {
boolean p=false;
if(year.getValue()<1820||year.getValue()>2020)
{
return false;
}
if(month.getValue()<1||month.getValue()>12)
{
return false;
}
else if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12) {
if (day.getValue() <= 31) {
p = true;
} else {
p = false;
}
}
else if(month.getValue()==2) {
if(year.getValue()%400==0||(year.getValue()%4==0&&year.getValue()%100!=0)) {
if(day.getValue()<=29) {
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
else {
if(day.getValue()<=28){
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
}
else {
if(day.getValue()<=30){
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
return p;
}
public void getNextNDays(int n){
int a[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
day.setValue(day.getValue()+n);
if(isLeapYear(year.getValue()))
a[2] = 29;
else
a[2] = 28;
while (day.getValue()>a[month.getValue()]) {
day.setValue(day.getValue()-a[month.getValue()]);
month.setValue(month.getValue() + 1);
if (month.getValue() == 13)
{
month.setValue(month.getValue() - 12);
year.setValue(year.getValue() + 1);
}
if(isLeapYear(year.getValue()))
a[2] = 29;
else
a[2] = 28;
}
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue());
}
public void getPreviousNDays(int n){
int a[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
day.setValue(day.getValue()-n);
if(isLeapYear( year.getValue()))
a[2] = 29;
else
a[2] = 28;
while (day.getValue()<=0)
{
month.setValue(month.getValue()-1);
if (month.getValue()==0){
month.setValue(month.getValue() + 12);
year.setValue(year.getValue() - 1);
}
day.setValue(day.getValue()+a[month.getValue()]);
if(isLeapYear( year.getValue()))
a[2] = 29;
else
a[2] = 28;
}
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d", year.getValue(), month.getValue(),day.getValue());
}
public void getDaysofDates(int year, int month, int day, int year2, int month2, int day2) { //这里我试了一个暴力方法,直接算日期所拥有的时间。
int startday=0;
int endday=0;
int i ;
int []aa = new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
for(i = 1;i < year;i++){
if(i%4 == 0&&i%100 != 0||i%400 == 0) {
startday += 366;
}
else
startday+=365;
}
if((year % 4 == 0 && year% 100 !=0 )||year% 400 == 0)
aa[2]=29;
for(i = 1;i<month;i++){
startday += aa[
else
endday+=365;
}
if(( year2 % 4 == 0 && year2% 100 !=0 )||year2 % 400 == 0)
aa[2]=29;
for(i = 1;i<month2;i++){
endday += aa[i];}
endday += day2;
System.out.printf("The days between %d-%d-%d and %d-%d-%d are:%d",year,month,day,year2,month2,day2,Math.abs(startday-endday));//这里用了绝对值,这样我们不需要判断两日期的前后顺序与大小。
}
public boolean isLeapYeari];
}
startday = startday + day;
for(i = 1;i < year2;i++){
if(i%4 == 0&&i%100 != 0||i%400 == 0) {
endday+=366;
}(int year) {
return (year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) ? true : false;
}
}

我的思路与之前的一样,先管下n天与前n天的算法

我看到这里我就知道,这道题应该稳了,只是数据越界问题,我以为我写完完整代码,也会直接过
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int x=in.nextInt();
if(x==1) {
Year year=new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month=new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day=new Day(in.nextInt());
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil date=new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(date.checkInputValidity()==false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d next %d days is:",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue(),n);
date.getNextNDays(n);
}
}
if(x == 2){
Year year=new Year(in.nextInt());
Month month=new Month(in.nextInt());
Day day=new Day(in.nextInt());
int n=in.nextInt();
DateUtil date=new DateUtil(year,month,day);
if(date.checkInputValidity()==false)
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else {
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d previous %d days is:",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue(),n);
date.getPreviousNDays(n);
}
}
if(x == 0){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Month{
private int value;
public Month() {
}
public Month(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
void resetMin(){
value=1;
}
void resetMax(){
value=12;
}
boolean validate(){
if(value>=1&&value<=12)
return true;
else return false;
}
void monthIncrement(){
value+=1;
}
void monthReduction(){
value-=1;
}
}
class Year{
private int value;
public Year() {
}
public Year(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
boolean isLeapYear(){
if(value%400==0||(value%4==0&&value%100!=0))
return true;
else return false;
}
boolean validate(){
if(value>=1820&&value<=2020)
return true;
else return false;
}
void dayIncrement(){
value+=1;
}
void yearReduction(){
value-=1;
}
}
class Day{
private int value;
public Day() {
}
public Day(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
void dayIncrement(){
value+=1;
}
void dayReduction(){
value-=1;
}
}
class DateUtil{
private Year year;
private Month month;
private Day day;
private int []monmaxnum={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public DateUtil() {
}
public DateUtil(Year year, Month month, Day day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public Year getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Year year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Month getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Month month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Day getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Day day) {
this.day = day;
}
void setDayMin(){
day.setValue(1);
}
void setDayMax(){
if(year.isLeapYear()==true) {
if (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)
day.setValue(31);
else if (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)
day.setValue(30);
else
day.setValue(29);
}
else
{
if (month.getValue() == 1 || month.getValue() == 3 || month.getValue() == 5 || month.getValue() == 7 || month.getValue() == 8 || month.getValue() == 10 || month.getValue() == 12)
day.setValue(31);
else if (month.getValue() == 4 || month.getValue() == 6 || month.getValue() == 9 || month.getValue() == 11)
day.setValue(30);
else
day.setValue(28);
}
}
boolean checkInputValidity() {
boolean p=false;
if(year.getValue()<1820||year.getValue()>2020)
{
return false;
}
if(month.getValue()<1||month.getValue()>12)
{
return false;
}
else if(month.getValue()==1||month.getValue()==3||month.getValue()==5||month.getValue()==7||month.getValue()==8||month.getValue()==10||month.getValue()==12) {
if (day.getValue() <= 31) {
p = true;
} else {
p = false;
}
}
else if(month.getValue()==2) {
if(year.getValue()%400==0||(year.getValue()%4==0&&year.getValue()%100!=0)) {
if(day.getValue()<=29) {
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
else {
if(day.getValue()<=28){
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
}
else {
if(day.getValue()<=30){
p=true;
}
else {
p=false;
}
}
return p;
}
void getNextNDays(int n){
int a[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
day.setValue(day.getValue()+n);
if(isLeapYear(year.getValue()))
a[2]=29;
else
a[2]=28;
while (day.getValue()>a[month.getValue()]) {
day.setValue(day.getValue()-a[month.getValue()]);
month.setValue(month.getValue()+1);
if (month.getValue()==13)
{
month.setValue(month.getValue()-12);
year.setValue(year.getValue()+1);
}
if(isLeapYear(year.getValue()))
a[2]=29;
else
a[2]=28;
}
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d",year.getValue(),month.getValue(),day.getValue());
}
void getPreviousNDays(int n){
int a[]= {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
day.setValue(day.getValue()-n);
if(isLeapYear( year.getValue()))
a[2]=29;
else
a[2]=28;
while (day.getValue()<=0)
{
month.setValue(month.getValue()-1);
if (month.getValue()==0){
month.setValue(month.getValue()+12);
year.setValue(year.getValue()-1);
}
day.setValue(day.getValue()+a[month.getValue()]);
if(isLeapYear( year.getValue()))
a[2]=29;
else
a[2]=28;
}
System.out.printf("%d-%d-%d", year.getValue(), month.getValue(),day.getValue());
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year) {
return (year % 4 == 0) && (year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) ? true : false;
}
}
这是我一开始的算法,满足了2个功能。
然后我听到我同学,说用暴力算法计算2日期的差值,我试了一下,但我这算法中没有判断2日期的前后,是否相等。
我采用的是直接算日期的所拥有的天数,再二者相减,再取绝对值,再输出这个绝对值即可。结果如下。

从思路上,感觉是没问题的,还简单好多,但是这时就不会出现我上次的情况,没有满分,因为我没有判断的方法,估计就是我代码问题。因为时间不够,我做到这里就直接结束了,但是我觉得按照上面代码思路应该能做到满分。
下面是菜单问题
第一次菜单问题,
菜单计价程序-3 分数 30 作者 蔡轲 单位 南昌航空大学设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish\[\] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\\
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record\[\] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
### 输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
### 输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Menu mu = new Menu();
Table[] tablemes = new Table[10];
int j = 0;//菜单数
int l = 0;//订单数
int k = 0;//代点菜数
Dish tt;
//int sum = 0;
int cntTable = 0;//桌号
int count;
String[] temp;
int a1,a2,a3,a4,a5;
while (true) {
String st = sc.nextLine();
temp = st.split(" ");
if(st.equals("end"))
break;
count = temp.length;
if (count == 2) {//一个空格
//String[] temp1 = st.split(" ");
if (temp[1].equals("delete")) {//第二个为delete
a1 = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
int c = tablemes[cntTable].odt.delARecordByOrderNum(a1);
tablemes[cntTable].sum-=c;
} else {//菜单添加
a2 = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
mu.dishs[j] = mu.addDish(temp[0], a2);
j++;
}
//continue;
}
else if (count == 4) {//三个空格
//String[] temp2 = st.split(" ");
if (temp[0].equals("table")) {//桌号
cntTable++;//跳过0;
l = 0;
tablemes[cntTable] = new Table();
//tablemes[cntTable].tableDtime = st;
tablemes[cntTable].AheadProcess(st);
System.out.println("table " + cntTable + ": ");
} else {//增加订单的情况;
a3 =Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
a4 = Integer.parseInt(temp[2]);
a5=Integer.parseInt(temp[3]);
tablemes[cntTable].odt.addARecord(a3, temp[1],a4 , a5);
tt = mu.searthDish(temp[1]);
if (tt != null) {
tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].d = tt;
int a = tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].getPrice();
System.out.println(tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].orderNum + " " + tt.name + " " +a );
tablemes[cntTable].sum +=a;
}
l++;
}
//continue;
}
else if (count == 5) {//代点菜
//String[] temp3 = st.split(" ");
a1 = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
a2 = Integer.parseInt(temp[3]);
a3 = Integer.parseInt(temp[4]);
tablemes[cntTable].odt.addARecord( a1, temp[2], a2, a3);
tt = mu.searthDish(temp[2]);
if (tt != null) {
tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].d.unit_price = tt.unit_price;
int b = tablemes[cntTable].odt.records[l].getPrice();
System.out.println(temp[1] + " table " + tablemes[cntTable].tableNum + " pay for table " + temp[0] + " " + b);
tablemes[cntTable].sum += b;
}
l++;
}
//st = sc.nextLine();
}
for (int i = 1; i < cntTable + 1; i++) {
tablemes[i].Gettottalprice();
}
}
}
class Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
//int num;
int getPrice(int portion) {
int peic = 0;
if (portion == 1) {
peic = unit_price ;
} else if (portion == 2) {
peic = Math.round((float) (unit_price * 1.5)) ;
} else if (portion == 3) {
peic = (unit_price * 2) ;
}
return peic;//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份)
}
}
class Menu {
Dish[] dishs = new Dish[10];//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
int count = 0;
Dish searthDish(String dishName){
Dish temd = null;
for(int i=count-1;i>=0;i--){
if(dishName.equals(dishs[i].name)){
temd = dishs[i];
break;
}
}
if(temd==null){
System.out.println(dishName+" does not exist");
}
return temd;
}//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price){
Dish dh = new Dish();
dh.name = dishName;
dh.unit_price = unit_price;
count++;
return dh;
}//添加一道菜品信息
}
class Order {
Record[] records = new Record[10];//保存订单上每一道的记录
int count = 0;//订单数量
void addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num){
records[count] = new Record();
records[count].d.name = dishName;
records[count].orderNum = orderNum;
records[count].portion = portion;
records[count].num = num;
count++;
}//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
int delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum){
if(orderNum>count||orderNum<=0){
System.out.println("delete error;");
return 0;
}else {
return records[orderNum - 1].getPrice();
}
}//根据序号删除一条记录
}
public class Record {
int orderNum;//序号\
//int AntherOrderNum;
Dish d = new Dish();//菜品\
int num = 0;
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\
//int exist = 1;
int getPrice(){
return d.getPrice(portion)*num;
}//计价,计算本条记录的价格\
}
public class Table {
int tableNum;
String tableDtime;
int year,month,day,week,hh,mm,ss;
int sum = 0;//一桌价格 ;
Order odt = new Order();
double discnt = -1;
void Gettottalprice(){
if(discnt>0){
sum = (int) Math.round(sum*discnt);
System.out.println("table " + tableNum + ": " + sum);
}else {
System.out.println("table " + tableNum + " out of opening hours");
}
}
void AheadProcess(String tableDtime){
this.tableDtime = tableDtime;
processTime();
discount();
}
void processTime(){//处理时间
String[] temp = tableDtime.split(" ");
tableNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
String[] temp1 = temp[2].split("/");
String[] temp2 = temp[3].split("/");
year = Integer.parseInt(temp1[0]);
month = Integer.parseInt(temp1[1]);
day = Integer.parseInt(temp1[2]);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(year, (month-1), day);
week = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
if(week==1)
week = 7;
else
week--;
hh = Integer.parseInt(temp2[0]);
mm = Integer.parseInt(temp2[1]);
ss = Integer.parseInt(temp2[2]);
}
void discount(){
if(week>=1&&week<=5)
{
if(hh>=17&&hh<20)
discnt=0.8;
else if(hh==20&&mm<30)
discnt=0.8;
else if(hh==20&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt=0.8;
else if(hh>=11&&hh<=13||hh==10&&mm>=30)
discnt=0.6;
else if(hh==14&&mm<30)
discnt=0.6;
else if(hh==14&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt=0.6;
}
else
{
if(hh>=10&&hh<=20)
discnt= 1.0;
else if(hh==9&&mm>=30)
discnt= 1.0;
else if(hh==21&&mm<30||hh==21&&mm==30&&ss==0)
discnt= 1.0;
}
}
}
这段代码是我在题目集6中写出的代码,题目集4第一次菜单我没写,但在第二次菜单中我先写出正常情况下的点餐,未考虑一些异常情况。但是我写出来的代码发现连第一次的全部情况都没满足,只满足了一些情况。
如图


满足了一些情况,但是我没写出算总价的情况。
第二次题目集太难了,不像聚合一样,老师给了类图,我只需填空即可。这两到题没有一点提示,全靠自己的思路。我思路是先满足正常点餐,在考虑异常点餐。但我发现我花了4天写出的代码连正常点餐都做不到,我就直接放弃写第二次点餐程序了。但是我发现我写的代码满足第一次正常点餐程序的大部分情况,感觉还是有点成就的。
类图如下

很可惜我这两道题没得一分。但我了解了一些道理,只要你写了,并且有了一定成果,那就不算白干,这2次程序,至少我满足了一些情况,放在第一次点餐题中,我的代码应该能拿到一些分数。
3.踩坑心得
一开始写题目集4时,我还在使用循环算法,后面听人说用hashset与treeset会更好,后面同学给我推了个问题软件,后面可以提供思路。
写题目集5时,我一开始用的是慕课中算法,发现不太完全懂,后面看了b站视频,发现直接判断输出即可。有时候真的要多去学习。
写这2道聚合题,我个人觉得,不是很难,也尝试了新方法(虽然有些瑕疵,但是是可行的),多跟同学交流思维是最重要的。
而且我懂了那个月份超限与日期超限的原因与解决办法。(具体对比我2次代码的方法使用即可退出)
关于2道菜单题,后面花了时间才勉强完成第一次菜单题的一些要求,根本还没碰到第二次异常情况的处理。但我看到了这2次题目集都有人得到了分数,个人觉得要去和他们交流,获取一些方法。例如室友就告诉我写这两题用一些split方法和用正则表达式相比我最初的代码会更清楚一些。
4.改进建议:
1.我缺乏迎难而上精神,我看到大部分人没写加上题目要写好多行,我就几乎要放弃了。这个需要慢慢来培养。
2.关于那些大题,我写的代码大部分是根据老师给的类图写的,一步一步来的。一碰到大题(且没给提示),我直接就不知道从哪里下手,这次也是第1次体会到我写代码的思路问题很大,这个要多练。
3.学会的东西就要想着怎样去用它,这是个很大的问题,写日期需求,我用了一些方法,但是配对菜名时,我没有想到用正则表达式,思路没打开。以后要多想想自己掌握的方法。
5.总结:
一、对Bug的小感悟
bug通常来自三种原因:
1.对题面理解的疏忽(有时题目给的时中文符号)
2.对自己代码架构细节出现问题(使用错误方法)
3.知识的缺乏(例如超时,超限)
二、学到的东西
1对正则表达式的使用
2.熟悉理解了类的设计与使用
3.能够熟练对代码进行调试,查找调试过程中代码的各类数据的变化等
4.写代码真的不像之前一样,写的只是一些简单问题,我们写代码是要完成一些系统功能,难度是绝对有的,要有这个觉悟
5.不能像之前一样,要有迎难而上的精神
标签:总结性,题目,int,value,month,Blog,public,getValue,day From: https://www.cnblogs.com/fengyufeng/p/17360191.html