1 前言
在 Android自动化测试框架uiautomator2详解 中,介绍了 uiautomator2 框架的环境配置、元素定位工具以及常用接口。
本文对 uiautomator2 框架进一步封装,用户只需要重写模板类(Template)的 first() 和 circle_body() 方法,并配置 app.cfg 文件,即可实现各种测试挂机需求。
本文使用到的主要 python 模块如下:
- uiautomator2:Android 手机 UI 自动化控制器
- aircv:图片匹配
- configparser:配置文件解析器
- subprocess:子进程管理,本文主要用于获取 adb 命令的返回结果(check_output方法)
- os:系统管理,本文主要用于创建目录(mkdir 方法)、文件路径管理(path)和执行 adb 命令(system 方法)
2 项目结构
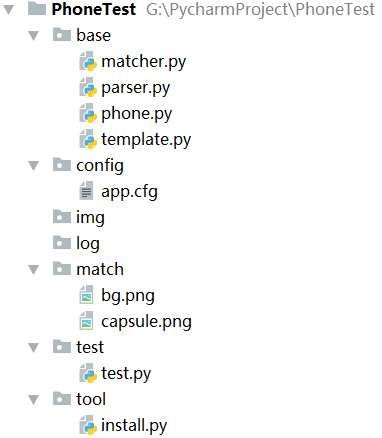

- phone.py:封装了对手机的操作,包括:连接设备、获取手机信息(分辨率、虚拟 display id)、解锁、打开应用、点击、长按、输入文本、滑动、截手机屏、截虚拟屏、旋转、点击匹配的图片等动作
- template.py:封装了一个测试模板,用户的只需要继承 Template 类,并重写 first 方法(初始状态)、circle_body 方法(循环体),即可实现各种复杂的挂机任务
- matcher:图片匹配器,在当前手机界面匹配目标图片,并返回匹配到的中心位置
- app.cfg:应用包名和控件标识(resourceId、text 等)配置
- parser:应用配置解析器,用于解析 app.cfg 文件
- img:存放用户截图
- log:存放日志
- test.py:用户挂机任务类,此类继承了 Template 类
项目路径见→Android 自动化测试项目
3 安装环境
install.py
import os
# https://pypi.douban.com/simple # 豆瓣镜像
# https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple # 清华镜像
mirror = " -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple"
os.system("python -m pip install --upgrade pip" + mirror) # 更新 pip
os.system("pip install --pre -U uiautomator2" + mirror) # 安装 uiautomator2
os.system("python -m uiautomator2 init") # 安装 atx-agent 至手机
os.system("pip install weditor" + mirror) # 安装 weditor
os.system("pip install aircv" + mirror) # 安装 aircv
os.system("pip install opencv-python" + mirror) # 安装 cv2
运行此文件,即可安装所需的模块。 若运行时报错,可以参考→Android自动化测试框架uiautomator2详解
4 自动化测试
1)手机类(Phone)
Phone 类封装了对手机的操作,包括:连接设备、解锁、打开应用、点击、长按、输入文本、滑动、截屏、旋转等动作。
phone.py
import os
import re
import shutil
import subprocess as sp
import threading
import time
from time import sleep
import uiautomator2 as u2
from base.parser import Parser
from base.matcher import Matcher
# 手机类(封装了对手机的操作)
class Phone:
# 初始化(connect:连接类型,wait_time:操作之间的等待时间, clear:是否清空 img 和 log 目录)
def __init__(self, connect_type="usb", wait_time=1, clear=False):
print("Phone 初始化...")
global d, w_time, parser, matcher, screen_shot_path, log_path
d = self.get_device(connect_type)
self.get_phone_model()
self.get_phone_size()
self.get_vs_display_id()
w_time = wait_time
parser = Parser(d, self.size)
matcher = Matcher()
screen_shot_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "\\..\\img") + "\\"
log_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "\\..\\log") + "\\"
self.clear_img_log(clear)
# 获取设备(connect_type:连接类型)
def get_device(self, connect_type="usb"):
print("获取设备...")
if connect_type == "usb":
device = self.connect_by_usb() # 通过 usb 连接设备
elif connect_type == "wifi":
device = self.connect_by_wifi() # 通过 wifi 连接设备
return device
# 通过 usb 连接设备(程序运行期间需要保持有线连接)
def connect_by_usb(self):
rst = sp.check_output('adb devices')
id = re.findall("[A-Z0-9]{16}", str(rst))[0]
print("通过 usb 连接设备,id:", id)
device = u2.connect_usb(id)
return device
# 通过 wifi 连接设备(程序启动时需要有线连接,运行后可以断开数据线)
def connect_by_wifi(self):
rst = sp.check_output('adb shell \"ip addr | grep global\"')
ip = re.findall("\d+.\d+.\d+.\d+", str(rst))[0]
print("通过 wifi 连接设备,ip:", ip)
try:
device = u2.connect(ip)
except:
device = u2.connect(ip + ":5555")
return device
# 获取手机型号
def get_phone_model(self):
rst = sp.check_output('adb shell getprop ro.product.model')
self.model = re.findall("\w+-\w+", str(rst))[0]
print("手机型号:", self.model)
# 获取手机分辨率
def get_phone_size(self):
rst = sp.check_output('adb shell wm size')
str_size = re.findall("\d+", str(rst))
x = eval(str_size[0])
y = eval(str_size[1])
self.size = (x, y)
print("手机分辨率:", self.size)
# 获取 visual display id
def get_vs_display_id(self):
rst = sp.check_output('adb shell dumpsys activity activities')
displays = re.findall("Display #\d+", str(rst))
vs_id = -1
for e in displays:
id = eval(re.findall("\d+", e)[0])
if id > 0:
vs_id = id
break
self.vs_display_id = vs_id
print("visual display id:", self.vs_display_id)
# 解锁(password:解锁密码)
def unlock(self, password=""):
print("解锁...")
d.screen_on() # 亮屏
sleep(2)
self.swipe("up") # 向上滑动
edt_password = parser.get_element("system", "edt_password")
sleep(1)
if edt_password.exists:
if not password == "":
for i in password:
key = parser.get_element_item_num("system", "key", i)
sleep(0.1)
if key.exists:
key.click()
sleep(0.3)
sleep(w_time)
# 锁屏
def lock(self):
print("锁屏...")
d.screen_off() # 息屏
# d.press("power") # 按电源键
sleep(w_time)
# 打开指定应用(app_name:应用名)
def start_app(self, app_name):
print("打开应用,app_name:", app_name, "...")
package_name = parser.get_package(app_name)
sleep(1)
d.app_start(package_name)
sleep(w_time)
# 关闭指定应用(app_name:应用名)
def stop_app(self, app_name):
print("关闭应用,app_name:", app_name, "...")
package_name = parser.get_package(app_name)
sleep(1)
d.app_stop(package_name)
sleep(w_time)
# 关闭所有应用
def stop_all_app(self):
print("关闭所有应用...")
d.app_stop_all()
sleep(w_time)
# 清除所有应用
def clear_all_app(self):
print("清除所有应用...")
d.press("recent")
sleep(w_time)
btn_clear = parser.get_element("launcher", "btn_clear")
sleep(1)
if btn_clear.exists: # 清除按钮存在
btn_clear.click() # 清除所有 app
else: # 清除按钮不存在
print("没有打开的应用")
d.press("home") # 返回桌面
sleep(w_time)
# 截手机屏(clear:是否清空 img 目录)
def screen_shot(self, clear=False):
print("截手机屏...")
time_str = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S', time.localtime()) # 获取当前时间
path = screen_shot_path + time_str + ".png"
d.screenshot(path)
sleep(w_time)
# 截虚拟屏(clear:是否清空 img 目录)
def screen_shot_vs(self, clear=False):
if self.vs_display_id > 0:
print("截虚拟屏...")
time_str = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S', time.localtime()) # 获取当前时间
path = screen_shot_path + time_str + "_vs.png"
os.system("adb shell screencap -d " + str(self.vs_display_id) + " -p /sdcard/1.png")
os.system("adb pull /sdcard/1.png " + path)
sleep(w_time)
else:
print("虚拟屏不存在")
# 转屏
def rotate(self):
orientation = d.orientation
print("转屏,当前方向:", orientation)
if orientation == "natural":
d.set_orientation("left") # 向左转为横屏(left 可以简写为 l)
elif orientation == "left":
d.set_orientation("natural") # 转为竖屏(nutural 可以简写为 n)
sleep(w_time)
# 按键 key = {"back", "home", "recent", "power", "volume_up", "volume_down", "volume_mute", "enter",...}
def press(self, key):
print("按键:" + key)
d.press(key)
sleep(w_time)
# 单击控件(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,index:同名控件中的编号,type:控件标识符的类型)
def click(self, app_name, item, index=0, type="id"):
print("单击控件,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",index:", index, ",type:", type)
element = parser.get_element(app_name, item, type)
sleep(1)
if element[index].exists:
element[index].click()
sleep(w_time)
# 通过坐标单击控件(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,relative:相对坐标)
def click_coord(self, app_name, item, relative="left_top"):
print("通过坐标单击控件,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",relative:", relative)
x, y = parser.get_coord(app_name, item, relative)
sleep(1)
d.click(x, y)
sleep(w_time)
# 通过图标单击控件(target: 目标图片, threshold: 可信阈值)
def click_icon(self, target, threshold = 0.6):
print("通过图标单击控件,target:", target, ",threshold:", threshold)
pos = matcher.get_coord(target, threshold)
if pos == None:
print("控件不存在")
else:
sleep(1)
d.click(pos[0], pos[1])
sleep(w_time)
# 长按控件(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,index:同名控件中的编号,type:控件标识符的类型)
def long_click(self, app_name, item, index=0, type="id"):
print("长按控件,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item + ",index:", index, ",type:", type)
element = parser.get_element(app_name, item, type)
sleep(1)
if element.exists:
element[index].long_click()
sleep(w_time)
# 输入文本(text:待输入的文本)
def set_text(self, text):
print("输入文本,text:", text)
d.set_fastinput_ime(True) # 打开输入法
d.send_keys(text)
d.set_fastinput_ime(False) # 关闭输入法
sleep(w_time)
# 输入文本(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,text:待输入的文本,type:控件标识符的类型)
def set_text(self, app_name, item, text, type="id"):
print("输入文本,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",text:", text, ",type:", type)
element = parser.get_element(app_name, item, type)
sleep(1)
if element.exists:
element.set_text(text)
sleep(w_time)
# 获取文本(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,type:控件标识符的类型)
def get_text(self, app_name, item, type):
print("获取文本,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",type:", type)
element = parser.get_element(app_name, item, type)
sleep(1)
text = ""
if element.exists:
text = element.get_text()
return text
# 清空文本(app_name:应用名,item:控件名,type:控件标识符的类型)
def clear_text(self, app_name, item, type):
print("获取文本,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",type:", type)
element = parser.get_element(app_name, item, type)
sleep(1)
if element.exists:
element.clear_text()
sleep(w_time)
# 滑动屏幕
def swipe(self, direction):
print("滑动屏幕,direction:" + direction)
(width, hight) = d.window_size()
width_d = width / 6
hight_d = hight / 6
if direction == "up": # 上滑
d.swipe(width / 2, hight - hight_d, width / 2, hight_d)
elif direction == "down": # 下滑
d.swipe(width / 2, hight_d, width / 2, hight - hight_d)
elif direction == "left": # 左滑
d.swipe(width - width_d, hight / 2, width_d, hight / 2)
else: # 右滑
d.swipe(width_d, hight / 2, width - width_d, hight / 2)
sleep(w_time)
# 将 pc 端文件 push 到 phone 端指定文件夹,若此文件夹不存在,会自动创建
def push(self, pc_file_path, phone_dir_path="/sdcard/000/"):
# pc_file_path = "..\\img\\" + pc_file_path
print("push,pc_file_path:", pc_file_path, ",phone_dir_path", phone_dir_path)
d.push(pc_file_path, phone_dir_path)
sleep(w_time)
# 将 phone 端的文件 pull 到 pc 端指定文件夹,若此文件夹不存在,会自动创建
def pull(self, phone_file_path, pc_dir_path="..\\img\\"):
print("pull,phone_file_path:", phone_file_path, ",pc_dir_path", pc_dir_path)
if not os.path.exists(pc_dir_path):
os.mkdir(pc_dir_path)
pc_dir_path += phone_file_path.split("/")[-1]
d.pull(phone_file_path, pc_dir_path)
sleep(w_time)
# 打印日志
def log(self):
time_str = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d__%H-%M-%S', time.localtime()) # 获取当前时间
print("记录日志,结束时间:", time_str)
path = log_path + time_str + ".txt"
threading.Thread(target=self.log_temp(path)).start()
def log_temp(self, path):
os.system("adb logcat > " + path)
# 清空 img 和 log 目录
def clear_img_log(self, clear):
if clear and os.path.exists(screen_shot_path):
shutil.rmtree(screen_shot_path) # 清空 img 目录
if not os.path.exists(screen_shot_path):
os.mkdir(screen_shot_path) # 创建 img 目录
if clear and os.path.exists(log_path):
shutil.rmtree(log_path) # 清空 log 目录
if not os.path.exists(log_path):
os.mkdir(log_path) # 创建 log 目录
2)配置文件
app.cfg
# app 配置文件
# 系统控件
[system]
package = "com.android.systemui"
edt_password = "com.android.systemui:id/fixedPinEntry" # 输入密码框
key = "com.android.systemui:id/key"
pos_capsule = (100, 16)
# 启动控件
[launcher]
package = "com.huawei.android.launcher"
btn_clear = "com.huawei.android.launcher:id/clear_all_recents_image_button" # 清除所有应用按钮
# 备忘录
[note]
package = "com.huawei.notepad"
btn_new = "com.huawei.notepad:id/fab_add" # 新建按钮
edt_text = "com.huawei.notepad:id/editor_view" # 编辑框
# 图库
[photos]
package = "com.android.gallery3d"
# QQ
[qq]
package = "com.tencent.mobileqq"
btn_login = "com.tencent.mobileqq:id/login" # 登录按钮
img_icon = "com.tencent.mobileqq:id/icon" # 最近联系人头像
edt_input = "com.tencent.mobileqq:id/input" # 消息编辑框
btn_send = "com.tencent.mobileqq:id/fun_btn" # 发送按钮
btn_send_my = "com.tencent.mobileqq:id/imy" # “我的电脑”中发送按钮
# 微信
[wechat]
package = "com.tencent.mm"
# 腾讯视频
[tencent_video]
package = "com.tencent.qqlive"
注意:QQ 中“我的电脑”界面【发送】按钮的 id(imy)与联系人聊天界面的【发送】按钮的 id(fun_btn)不一样。
3)应用配置解析器(Parser)
Parser 类用于根据 app.cfg 文件中的 key 值,获取其 value 值,并定位到控件(获取控件句柄)。
parser.py
from configparser import ConfigParser
import os
# 应用解析器
class Parser:
# 初始化(device 为设备句柄, size 为手机分辨率)
def __init__(self, device, size):
print("应用解析器初始化...")
global d, conf, phone_size
d = device
phone_size = size
conf = ConfigParser()
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "\\..\\config\\app.cfg")
conf.read(path, encoding='utf-8')
# 解析包名(app_name:应用名)
def get_package(self, app_name):
print("解析包名,app_name:", app_name)
conf_value = conf.get(app_name, "package")
package_name = eval(conf_value)
if package_name == "":
print("应用不存在,app_name:", app_name)
return package_name
# 解析元素(app_name:应用名,item:控件标识,type:控件标识类型)
def get_element(self, app_name, item, type="id"):
print("解析元素,app_name:", app_name, ",item:", item, ",type:", type)
conf_value = conf.get(app_name, item)
value = eval(conf_value)
element = d(resourceId="None")
if type == "id":
element = d(resourceId=value)
elif type == "text":
element = d(text=value)
if not element.exists:
print("元素不存在,item:", item)
return element
# 解析同类元素(app_name:应用名,item + num:控件标识,type:控件标识类型)
def get_element_item_num(self, app_name, item, num, type="id"):
print("解析元素,app_name:", app_name, ",item_num:", item + num, ",type:", type)
conf_value = conf.get(app_name, item)
value = eval(conf_value) + num
if type == "id":
element = d(resourceId=value)
elif type == "text":
element = d(text=value)
if not element.exists:
print("元素不存在,item:", item)
return element
# 解析元素(app_name:应用名,item + num:控件标识,type:控件标识类型)
def get_coord(self, app_name, item, relative = "left_top"):
print("解析元素坐标,app_name:", app_name, ",item_num:", item, ",relative:", relative)
conf_value = conf.get(app_name, item)
rela_x, rela_y = eval(conf_value)
print("相对坐标:(", rela_x, ", ", rela_y, ")")
abs_x = rela_x
abs_y = rela_y
if relative == "left_top":
abs_x = rela_x
abs_y = rela_y
elif relative == "right_top":
abs_x = phone_size[0] + rela_x
abs_y = rela_y
elif relative == "left_bottom":
abs_x = rela_x
abs_y = phone_size[1] + rela_y
elif relative == "right_bottom":
abs_x = phone_size[0] + rela_x
abs_y = phone_size[1] + rela_y
print("绝对坐标:(", abs_x, ", ", abs_y, ")")
return abs_x, abs_y
4)图片匹配器(Matcher)
图片匹配器(Matcher)用于在当前手机界面匹配目标图片,并返回匹配到的中心位置。
matcher.py
import aircv as ac
import os
# 图片匹配器
class Matcher:
# 初始化
def __init__(self):
print("图片匹配器初始化...")
global path
path = os.path.abspath(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) + "\\..\\match") + "\\"
# 获取控件坐标(target: 目标图片, threshold: 可信阈值)
def get_coord(self, target, threshold = 0.6):
os.system("adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/bg.png")
os.system("adb pull /sdcard/bg.png " + path)
imsrc = ac.imread(path + "bg.png")
imobj = ac.imread(path + target + ".png")
res = ac.find_template(imsrc, imobj, threshold = threshold)
if res == None:
print("图片匹配失败")
return None
else:
pos_f = res['result']
pos = (int(pos_f[0]), int(pos_f[1]))
print("图片匹配成功,res:", res)
return pos
5)模板类(Template)
模板类(Template)为测试类(MyTest)提供模板,所有测试类都继承模板类,测试类只需重写 first 和 circle_body 方法,即可实现各种复杂的挂机任务。
template.py
from base.phone import Phone
from time import sleep
# 模板类(为测试类提供模板,所有测试类都继承此类,测试类只需重写 first 和 circle_body 方法)
class Template:
def __init__(self, connect_type="usb", wait_time=1, log=False):
print("Template 初始化...")
self.phone = Phone(connect_type, wait_time)
self.log = log
# 设置测试初始状态
def first(self):
print("设置测试初始状态...")
# 设置循环体
def circle_body(self):
print("设置循环体...")
# 开始循环
def loop(self, max_times=1000000000):
print("开始循环...")
i = 1;
while i <= max_times:
print("********************", i, "********************")
# try:
self.circle_body()
# except BaseException:
# if self.log:
# self.phone.log()
# raise Exception("循环异常...")
i = i + 1
sleep(3)
# 主调用方法
def main(self):
self.first()
self.loop()
6)测试类(MyTest)
用户需要挂机的具体任务,可以写在此类中,每个任务建一个测试文件,如 qq_test.py(QQ测试任务)、notepad_test.py(备忘录测试任务),各个测试类中都继承了 Template 类,并重写其 first() 方法和 circle_body() 方法。
test.py
from base.template import Template
# 测试类(类名不要以 Test 开头)
class MyTest(Template):
def __init__(self):
print("Test 初始化...")
super().__init__(connect_type="usb", wait_time=2, log=True)
self.phone.unlock("123456") # 解锁
# 设置测试初始状态
def first(self):
print("执行测试初始状态...")
self.phone.start_app("note") # 打开备忘录
self.phone.start_app("photos") # 打开图库
self.phone.clear_all_app() # 清除所有打开的应用
# 设置循环体
def circle_body(self):
print("执行循环体...")
self.phone.start_app("qq") # 打开 QQ
self.phone.click("qq", "img_icon", 0) # 点击最近联系人中第1个
self.phone.set_text("qq", "edt_input", "我正在做自动化测试,请忽略此消息") # 编辑消息
self.phone.click("qq", "btn_send_my") # 点击发送,这里是给【我的电脑】发送,请将【我的电脑】置顶
self.phone.stop_app("qq") # 关闭 QQ
if __name__ == '__main__':
test = MyTest()
test.main()
 声明:本文转自Android 自动化测试项目
声明:本文转自Android 自动化测试项目