props,混入mixin,插件,elementui使用(重点),vuex,vue Router, localStorage系列
props
1.方式一:使用数组
props:['msg']
2.方式二:使用对象
props:[msg:String]
3.方式三:使用对象,默认值和必填
props:{
msg:{
type:String, // 类型
required:true, // 必要性
default:'老张' // 默认值
}
}
混入mixin
可以把多个组件共同的配置提取成一个混入对象
使用方法:
第一步定义混入:
export const xiao = {
data(){
return{
age:19
}
},
methods:{
showName(){
alert(this.name);
}
},
mounted(){
console.log('那好,挂载正在执行')
}
}
第二步:使用混入(全局)
<template>
<div class="home">
<h3>混入的使用</h3>
<button @click="showName">看名字</button>
<h3>{{age}}</h3>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {xiao} from '@/mixin'
export default {
name: "index",
data(){
return{
name:'张昕'
}
},
mixins:[xiao]
}
</script>
全局混入:
在main.js中写入
import {hunhe} from "@/mixin";
Vue.mixin(hunhe)
第三步:使用混入(局部)
<template>
<div class="home">
<h1>混入的使用</h1>
<button @click="showName">点我,看名字</button>
<h2>{{age}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 导入混入对象
import {lqz} from '@/mixin'
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
data() {
return {
name: '张昕'
}
},
mixins: [lqz]
}
</script>
局部混入:
1.新建一个文件夹mixin
2.在mixin里新建一个index.js文件(使用index这个名字的话就是在导入的时候只需要导入到文件夹就可以了)
3.里面可以放一些公用的东西
4.export const hunhe = {
methods:{
handlePrintName(){
alert(this.name)
}
},
}
5.在需要使用的地方只需要写入:
import {hunhe} from "@/mixin";
mixins:[hunhe,] // 列表可以写多个
插件
功能:用于增强vue
本质:包含install方法的一个对象,install的第一个参数是Vue,第二个以后的参数是插件使用者传递的数据
import Vue from "vue";
import axios from "axios";
export default {
install(vue,name) {
console.log(name)
console.log('执行了插件', vue)
// 可以做的事
// 1 了解,自定义指令(不了解没关系)
Vue.directive("fbind", {
//指令与元素成功绑定时(一上来)
bind(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
},
//指令所在元素被插入页面时
inserted(element, binding) {
element.focus();
},
//指令所在的模板被重新解析时
update(element, binding) {
element.value = binding.value;
},
})
// 2 定义全局变量,以后在任何组件中都可以使用到,借助于Vue.prototype往里放 ,以后所有组件只要this.$ajax 就是axios对象
Vue.prototype.$name = '彭于晏'
Vue.prototype.$add = (a, b) => {
return a + b
}
Vue.prototype.$ajax=axios
// 3 使用全局混入
Vue.mixin({
data() {
return {
name: '彭于晏',
age: 19,
};
},
});
// 4 自定义全局组件
// Vue.component('child',{
//
// })
}
}
elementui使用(重点)
vue样式组件库:
vant ,element ,mintui ,materia vue ui,ant ui,iconic,iconfont.cn火箭
-elementui 做网页端 样式用的多 vue2的 饿了吗团队开发的
-elementui-plus 第三方团队继续基于vue3写的
-vant 做app的样式
-iview pc端用www.iviewui.com
# 移动端用 vant,pc端用 elementui
elementui快速上手指南:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45525630/article/details/119383414


Vuex 的使用
在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
在Vue中实现集中式状态(数据)管理的一个Vue插件,对vue应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信
Vuex的使用流程
-status:存数据的地方,菜
-actions:中转站,服务员
-mutations:真正改state数据的地方,厨师

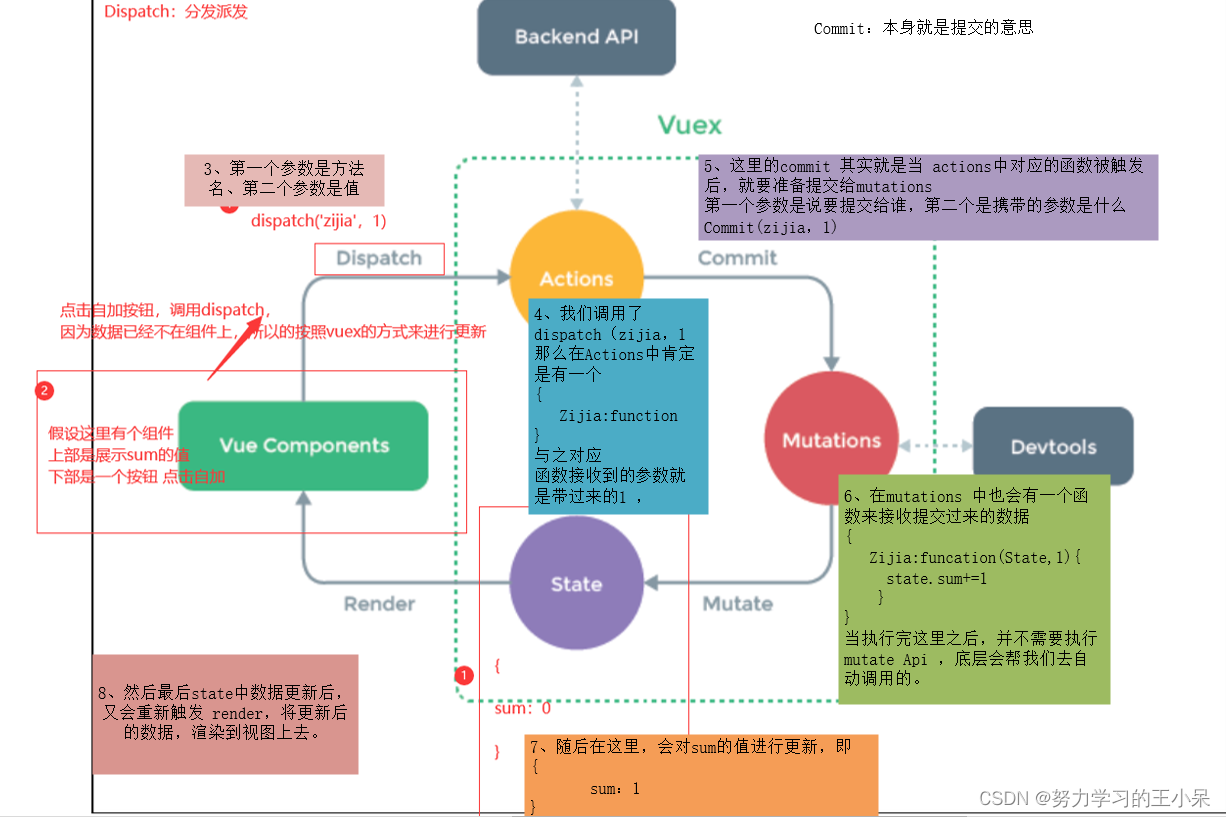
1 在state中定义变量
2 在组件中通过this.$store.dispatch('actions中定义的函数'),触发actions中得函数执行
3 在actions中得函数中,调用 context.commit('mutations中定义的函数')
4 在mutations中定义的函数实现真正的修改state中得数据
5 页面中只要使用$store.state.变量,变量变化,页面就变化 实现了组件间通信
6 注意:
-在组件中可以直接调用commit触发【mutations中定义的函数】
-在组件中可以直接修改state中定义变量
Vue-router的使用
官方提供的用来实现SPA 的vue 插件:有了它以后,我们可以写很多页面组件,通过地址栏不同的路径显示不同的页面组件
https://router.vuejs.org/zh/index.html
基本使用
1 新建router/index.js
const routes = [配置路由1,配置路由2]
2 main.js中使用:之前已经写好了
import router from './router'
new Vue({
...
router,
...
}).$mount('#app')
3 只需要写页面组件,配置路由即可
4 在App.vue中加入
<router-view> // 用来显示当前路由组件界面
</router-view>
5 在浏览器访问const routes中配置的路径,就能看到对应的页面组件了
路由的跳转
在html中使用
<router-link :to="path">去登录</router-link>
在js中使用
this.$router.push('goods')
路由跳转携带参数
# 两种情况
-带在请求地址中以 ?name=lqz&age=19
-在地址中类似于django的分组 /goods/1/
# 情况1:请求地址中
-<router-link to="/login/?name=lqz&age=19">去登录</router-link>
-组件中接受:this.$route.query.取
# 情况2:地址中
<router-link to="/login/lyf">去登录</router-link>
-组件中接受:this.$route.params.取
区分this.$route this.$router
this.$router # new VueRouter对象,实例,可以实现路由的跳转
this.$route # 是当前路由对象,内部有传入的参数
路由嵌套
1 router/index.js 相应的路由中
{
path: '/goods',
name: 'goods',
component: Goods,
children: [
{
path: 'list',
component: GoodList
},
{
path: 'detail',
component: GoodDetail
}
]
},
2 必须要在Goods组件中,写<router-view></router-view>
3 使用router-link标签跳转
4 只会变更Goods下router-view包裹的位置
相关API
this.$router.push(path): 相当于点击路由链接(可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.replace(path): 用新路由替换当前路由(不可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.back(): 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(-1): 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(1): 请求下一个记录路由
路由守卫
作用:对路由进行权限控制
# 前置路由守卫
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
console.log('前置路由守卫', to, from)
if (to.name == 'shoppingcart') {
let name = localStorage.getItem('name')
if (name) {
next()
} else {
alert('不好意思没有权限')
}
} else {
next()
}
})
# 后置路由守卫
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log('后置路由守卫',to,from)
document.title = to.name
})
全局守卫
// 该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
//引入组件
import About from '../pages/About'
import Home from '../pages/Home'
import News from '../pages/News'
import Message from '../pages/Message'
import Detail from '../pages/Detail'
//创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:About,
meta:{title:'关于'}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
component:Home,
meta:{title:'主页'},
children:[
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'新闻'}
},
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'消息'},
children:[
{
name:'xiangqing',
path:'detail',
component:Detail,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'详情'},
//props的第一种写法,值为对象,该对象中的所有key-value都会以props的形式传给Detail组件。
// props:{a:1,b:'hello'}
//props的第二种写法,值为布尔值,若布尔值为真,就会把该路由组件收到的所有params参数,以props的形式传给Detail组件。
// props:true
//props的第三种写法,值为函数
props($route){
return {
id:$route.query.id,
title:$route.query.title,
a:1,
b:'hello'
}
}
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
//全局前置路由守卫————初始化的时候被调用、每次路由切换之前被调用
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
console.log('前置路由守卫',to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){ //判断是否需要鉴权
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='lqz'){
next()
}else{
alert('名不对,无权限查看!')
}
}else{
next()
}
})
//全局后置路由守卫————初始化的时候被调用、每次路由切换之后被调用
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log('后置路由守卫',to,from)
document.title = to.meta.title || 'lqz系统'
})
export default router
localStorage系列
localStorage和sessionStorage和cookies
window 浏览器对象有的东西,如果想在浏览器中存储数据,永久存储,关闭页面数据就没了(临时存储),设定一个时间,到时候就过期
永久存储:localStorage 不登录加购物车,关闭浏览器,购物车里面的东西依然在
临时存储:sessionStorage 关闭页面数据就没有了
设定一个时间,到时间就过期:cookies
localStorage
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>localStorage操作</h1>
<button @click="saveStorage">点我向localStorage放数据</button>
<button @click="getStorage">点我获取localStorage数据</button>
<button @click="removeStorage">点我删除localStorage放数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import cookies from 'vue-cookies'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
saveStorage() {
var person = {
name: '彭于晏',
age: 38
}
localStorage.setItem('userinfo', JSON.stringify(person))
},
getStorage() {
let userinfo = localStorage.getItem('userinfo')
console.log(userinfo)
console.log(typeof userinfo)
},
removeStorage() {
// localStorage.clear()
localStorage.removeItem('userinfo')
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
sessionStorage
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>sessionStorage操作</h1>
<button @click="saveSessionStorage">点我向localStorage放数据</button>
<button @click="getSessionStorage">点我获取localStorage数据</button>
<button @click="removeSessionStorage">点我删除localStorage放数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import cookies from 'vue-cookies'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
saveSessionStorage() {
var person = {
name: '彭于晏',
age: 38
}
sessionStorage.setItem('userinfo', JSON.stringify(person))
},
getSessionStorage() {
let userinfo = sessionStorage.getItem('userinfo')
console.log(userinfo)
console.log(typeof userinfo)
},
removeSessionStorage() {
// localStorage.clear()
sessionStorage.removeItem('userinfo')
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
cookies
npm install vue-cookies
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>cookie操作</h1>
<button @click="saveCookie">点我向cookie放数据</button>
<button @click="getCookie">点我获取cookie数据</button>
<button @click="removeCookie">点我删除cookie放数据</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import cookies from 'vue-cookies'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
saveCookie() {
cookies.set('name','zxr','7d') // 按秒计
},
getCookie() {
console.log(cookies.get('name'))
},
removeCookie() {
cookies.remove('name')
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
h1 {
background-color: aqua;
}
</style>
HBuilderX
HBuilder是DCloud(数字天堂)推出的一款支持HTML5的Web开发IDE。HBuilder的编写用到了Java、C、Web和Ruby。HBuilder本身主体是由Java编写。快,是HBuilder的最大优势,通过完整的语法提示和代码输入法、代码块等,大幅提升HTML、js、css的开发效率。
