There is a one-dimensional garden on the x-axis. The garden starts at the point 0 and ends at the point n. (i.e The length of the garden is n).
There are n + 1 taps located at points [0, 1, ..., n] in the garden.
Given an integer n and an integer array ranges of length n + 1 where ranges[i] (0-indexed) means the i-th tap can water the area [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]] if it was open.
Return the minimum number of taps that should be open to water the whole garden, If the garden cannot be watered return -1.
Example 1:
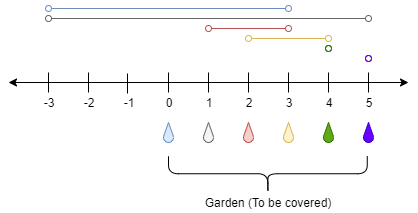
Input: n = 5, ranges = [3,4,1,1,0,0]
Output: 1
Explanation: The tap at point 0 can cover the interval [-3,3]
The tap at point 1 can cover the interval [-3,5]
The tap at point 2 can cover the interval [1,3]
The tap at point 3 can cover the interval [2,4]
The tap at point 4 can cover the interval [4,4]
The tap at point 5 can cover the interval [5,5]
Opening Only the second tap will water the whole garden [0,5]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, ranges = [0,0,0,0]
Output: -1
Explanation: Even if you activate all the four taps you cannot water the whole garden.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104ranges.length == n + 10 <= ranges[i] <= 100
这道题说是在x轴上有一个长度为n的花园,共有等距离的 n+1 喷头,现在有一个 ranges 数组,说是第i个喷头可以覆盖的范围是 [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]],问最少需要几个喷头可以覆盖整个花园。这道题跟之前那道 Video Stitching 基本上没有太大的区别,就是场景换了一下,本质都是一样的,类似的还有 Jump Game II。这道题可以使用贪婪算法 Greedy Algorithm 和动态规划 Dynamic Programming 来做,先来用贪婪算法,采用和 Jump Game II 一样的思路。
这里将题目也看成跳跃游戏的场景,从位置0开始,看是否能跳到位置n。那么就需要知道每个点的跳力,于是来构建 jumps 数组。对于每个喷头,题目说了其覆盖范围是 [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]],为了防止其越界,左边界点 left 就取 max(0, i - ranges[i]),右边界点 right 就取 min(n, i + ranges[i]),这样站在左边界点 left 上,其跳力就是 right - left,每次用这个来更新 jumps[left] 即可。有了 jumps 数组就可以开始计算最小跳跃数了,新建变量 farCanReach 表示当前最远能到达的位置,last 表示上次到达的最远位置。
然后开始遍历每个位置,若当前位置i大于 farCanReach,表示无法到达当前位置,即喷头无法覆盖整个花园,直接返回 -1。否则就用 i + jums[i] 来更新 farCanReach,因为当前的位置加上其跳力,就是其能到达的最远距离,若当前位置i等于 last 了,表示已经到达了上次跳跃的最远位置了,此时需要开始新的跳跃了,跳跃次数增1,last 更新为 farCanReach。以此类推,直到 for 循环推出后,判断若 farCanReach 大于等于n的话,表示可以到达末尾,返回结果 res,否则返回 -1 即可,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int>& ranges) {
vector<int> jumps(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
int left = max(0, i - ranges[i]);
int right = min(n, i + ranges[i]);
jumps[left] = max(jumps[left], right - left);
}
int res = 0, last = 0, farCanReach = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i > farCanReach) return -1;
farCanReach = max(farCanReach, i + jumps[i]);
if (i == last) {
++res;
last = farCanReach;
}
}
return farCanReach >= n ? res : -1;
}
};
再来看动态规划的解法,建立一个一维数组 DP,其中 dp[i] 表示覆盖范围 [0, i] 区间需要的最少喷头个数,最终结果会保存在 dp[n] 中。dp 数组长度为 n+1,每个数字初始化为 n+1,但 dp[0] 要初始化为0。接下来求状态转移方程,使用和 Video Stitching 中类似的方法,遍历 [0, n] 中的每一个喷头,然后计算其能覆盖范围的左右边界,注意还是要进行防越界处理,跟上面的解法相同。计算出喷头i的覆盖的范围 [left, right] 之后,遍历其范围内的每一个位置j,由于该区间内的每个点都是可以到达的,即相当于在 dp[left] 的基础上又增加了一个喷头,所以可以用 1 + dp[left] 来更新 dp[j],这就是状态转移方程。最终循环退出后,判断 dp[n] 是否等于初始值 n+1,是的话返回 -1,否则返回 dp[n] 即可,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int minTaps(int n, vector<int>& ranges) {
vector<int> dp(n + 1, n + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; ++i) {
int left = max(0, i - ranges[i]);
int right = min(n, i + ranges[i]);
for (int j = left; j <= right; ++j) {
dp[j] = min(dp[j], 1 + dp[left]);
}
}
return (dp[n] == n + 1) ? -1 : dp[n];
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/1326
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-number-of-taps-to-open-to-water-a-garden/
LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)
标签:Taps,1326,Garden,farCanReach,int,ranges,garden,dp,left From: https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/17046561.html