API Hooking revealed part 3 and 4 - Thread Deadlock Detector
Introduction
This is the third, fourth (and the last) part for building a thread deadlock detector. Please see the first and second articles to understand what is going on, at A (working) implementation of API hooking (Part II).
In fact, I've added a small library called SetThreadName which allows you to set the thread name and to get meaningful names for the synchronization object. The library does nothing in Release build, you don't even need it.
Remarks: This software will work even without this DLL, you don't have to recompile anything, unless you want to have your thread and object named.
The thread naming trick allows the thread name to be supported in Visual debugger (under Debug\Thread menu, real names instead of 0x0000C340), so it is of 100% benefit if you use it, even if you are not using my software. For the automatic object naming, the following algorithm is used :
- The first is the process clock value, so that a function creating the object will still create different object names.
- The second is the process ID, so that you can run your application multiple times, it will still have a unique name.
- The third string is the object type. (Mutex, Event, Semaphore, etc.)
- The fourth string is the file name where the object was created.
- The fifth number is the line where the object was created.
Part III : The thread deadlock detector
The background
If you've followed my previous articles, then you should know what is API hooking, and how to use it to spy what is going on in any application (Part I). You should also know what are we interested in for a thread deadlock detector, and what are the tricks to get all the required information (Part II).
The idea
Now that we can get every call to any synchronization and thread function, we face a problem. How can we know when a target application is deadlocked or not? The algorithm I'm using here is quite simple. Here is an example of a deadlock:
Let's take 2 threads (A and B), and 2 objects (o0 and o1).
Thread B locks o0, and then locks o1.
In parallel, Thread A locks o1, and then locks o0.
If o0 and o1 are free (ready to be locked), then they are 4 possibles cases:
1) Thread B is executed, and not interrupted, then thread A is executed.
2) Thread A is executed, and not interrupted, then thread B is executed.
3) Thread B is executed, but gets interrupted before locking o1, then thread A
is executed, and waits for o0. Thread B is then executed, and waits for o1.
4) Thread A is executed, but gets interrupted before locking o0, then thread B
is executed, locks o0 and waits for o1. Thread A is then executed,
and waits for o0.
It is clear that case 1 and 2 are okay. However, when reaching case 3 or 4, the application goes to deadlock. To avoid this, the server (deadlock detector) monitors each object and thread using its CSyncObject and CThread classes. Then, each object keeps a track on who owns it (a thread list). Similarly, each thread has an object waiting list and locked list. Now let's see how the algorithm finds the deadlock:
Case 3:
Time
0 Thread B locks o0 (o0 now has Thread B in its list
and Thread B have o0 in its Locked list)
1 Thread B is interrupted
2 Thread A locks o1 (o1 now has Thread A in its list
and Thread A have o1 in its Locked list)
3 Thread A tries to lock o0
(as o0 is already locked, we look inside it to find who got it.
we find Thread B, so then we check if thread B is waiting for
any object current thread (thread A) may have. In that case,
the waiting list of thread B is empty, so we add o0 to our
waiting list)
4 Thread A is interrupted
5 Thread B tries to lock o1
(as o1 is already locked, we look inside it to find who'got it.
we find Thread A, so then we check if thread A is waiting for
any object current thread (thread B) may have. Thread A is
waiting for o0 but o0 is in our locked list => deadlock)
The algorithm is quite simple but works out of the box.
The implementation
We need a server called ThreadDLD (what a wonderful name, isn't it?). Its purpose is to:
- Launch the debuggee (can be any application with or without source code).
- Inject the spying DLL in it, and make it infect the debuggee.
- Receive the thread monitoring function.
- Receive any API sniffing from the client.
- Parse the sniff, and display them as log.
- Analyze the sniff and spot errors (deadlocks).
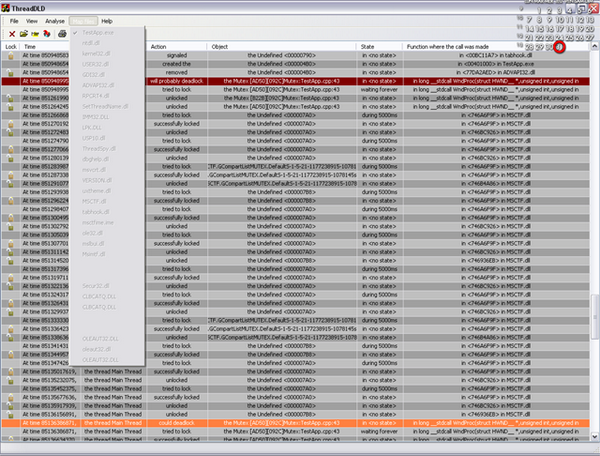
The debuggee is launched in CMainFrame::OnFileOpen in suspended state. The spying DLL ThreadSpy.DLL is then injected using the usual CreateRemoteThread trick. Then the debuggee is resumed, and the server waits for any message from it. The debuggee then sends the StartMeUp command with the thread monitoring function address, and sends any hooked command to the server (with stack trace and timestamp). The server waits for any CommunicationObject from the debuggee in its CThreadDLDView::ReceivedMessage. The server then parses the message and logs it accordingly. There are four logging modes, from the simple mode to the Analysis mode. Each of them reports the same information but from a different point of view.
-
Log mode
In this mode the received messages are shown un-factored, and is not intelligent. However, this is the fastest reporting mode, and should be used while reproducing the deadlock in the debuggee.
-
Thread life
In this mode the received messages are shown from the thread point of view. No deadlock detection is done in this mode. However, this mode is perfect to check each thread behavior.
-
Object life
In this mode the received messages are shown from the object point of view. No deadlock detection is done in this mode. However, this mode is perfect to check what happens to any object you are monitoring.
-
Analysis
In this mode the received messages are analyzed and the deadlock detection is performed on the fly. This is the slowest mode. However, this is the only mode that will outline thread deadlocks and errors. The algorithm described above is defined in
CThread::CheckLockmethod. The objects are declared in SyncObject.h.
Part IV : The bonus track
Each CommunicationObject sent between the debuggee and the server contains the stack trace in the debuggee. This stack trace is useful to spot where the deadlock has occurred. The problem with stack traces, is mainly due to their lack of meaning (when an error occurs at 0x00401345, I'm almost sure it doesn't tell you much). The idea, is to use a map file (if available), to map the address from the stack trace to real functions. I've included a MapFileParser to reverse the addresses into undecorated function names. It will not give you the line number, but anyway it is better than nothing. (Map file can be built in Release build too without any risks, as they are separate files). The map file parser finds the function that is just before the given address. This will not work for DLLs, as it is really not possible to know where the DLL will be mapped (except if you specify it by yourself like Google says "Mark Pietrek").
To conclude
I looked around to find such a tool for about a month, and because none of them where available, here is mine. It is obvious that this is not a "professional" software. For example, it cannot detect potential deadlock like tools that cover code statically, it will only detect real deadlock. I'm sure I can add the functionality for the same, because I have all the needed data. This project is made with ATL and WTL, so I would rather encourage you to learn those tools. I've implemented an owner drawn CListViewCtrl as I didn't find any good one around. The implementation is in CThreadDLDView. It is not possible to save the log, or read it. I've kept the print icon, but there is no print code. If you want to upgrade/add functionalities please post a line or two below:
What I would like to see is:
- function::line number in the map field (it is possible to generate a map file with line numbers too, but then the
MapFileParserwill be more complex). - Reply to the debuggee to prevent it from deadlocking (as we know the situation before it really happens in the debuggee process). This could be done without thread and delay by using shared memory area.
Update
- April 1st, 2005
- Added mapping of imported DLL too (so now, you should be able to locate deadlock even a in DLL).
- You can use the software to see what modules are loaded in a target process.
- Analyze mode can now detect possible deadlocks (yes, even those that deadlock only in client site).
- Can pass parameters to the program being analyzed.
- Can save the analysis to a file (yes, and can be imported in Excel too).
- Feb - 2005
- Initial release.