版权声明:本文为本文为博主原创文章,未经同意,禁止转载。如有错误,欢迎指正,博客地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wsg1100/
目录问题概述
3年前,在文章【原创】xenomai内核解析--双核系统调用(一) 中我们提出了两个问题:
- 双核共存时,如何区分应用程序发起的系统调用是xenomai内核调用还是linux内核调用?
- 一个xenomai实时任务既可以调用xenomai内核服务,也可以调用linux内核服务,这是如何做到的?
本文通过分析源代码为你解答问题1,对于问题2,涉及双核间的调度,本文暂不涉及,后面的文章揭晓答案。
当时解答了问题1,本文将继续探讨双核间的调度问题,重点分析pthread_creta()接口的底层实现。我们知道,一个xenomai任务既可以在cobalt内核中运行,也可以在linux内核中运行,这就要求两个内核都有对应的调度实体来管理这个任务。那么,pthread_creta()接口是如何创建这样一个双重身份的任务的呢?让我们一起来揭开它的神秘面纱吧。
注意:本文是几年前基于源代码的分析记录,质量可能会略差,因为它是源代码分析时的流水记录,没有经过精心的整理和修改,所以可能存在一些不足之处。如果你只想看结论,可以直接跳到文章的最后部分。希望本文能对你有所启发。
下面是与本文有上下文联系的文章,看完后应该会对xenomai任务管理有整体的认识:
【原创】xenomai内核解析--双核系统调用(一) 该文章以X86处理器为例,解析了一个应用程序发起内核系统调用时,xenomai内核调用的流程。
【原创】xenomai内核解析--双核系统调用(二)--应用如何区分xenomai/linux系统调用或服务该文分析了应用程序发起内核系统调用后,是如何区分一个接口是该linux提供服务还是xenomai提供服务。
1 libCobalt中调用非实时POSIX接口
xenomai通过标准POSIX API创建的实时任务来衍生自己的实时线程,因此,xenomai线程继承了Linux任务在非关键时间模式下调用常规Linux服务的能力。
当升级到实时应用程序时,Linux任务将附加到称为实时shadow的特殊xenomai扩展。一个实时shadow允许xenomai协同内核在实时模式下运行时,配置已配对的Linux任务。
拿POSIX标准函数来说,pthread_creta()不是一个系统调用,由NPTL(Native POSIX Threads Library)实现(NPTL是Linux 线程实现的现代版,由UlrichDrepper 和Ingo Molnar 开发,以取代LinuxThreads),NPTL负责一个用户线程的用户空间栈创建、内存分配、初始化等工作,与linux内核配合完成线程的创建。每一线程映射一个单独的内核调度实体(KSE,Kernel Scheduling Entity)。内核分别对每个线程做调度处理。线程同步操作通过内核系统调用实现。
xenomai coblat作为实时任务的调度器,每个实时线程需要对应到 coblat调度实体,如果创建实时线程需要像linux那样NPTL与linux 内核深度结合,那么coblat与libcoblat实现将会变得很复杂,在这里,xenomai使用了一种方式,由NPTL方式去完成实时线程实体的创建,在普通线程的基础上附加一些属性,对应到内核实体时能被实时内核调度。所以libcoblat库中的实时线程创建函数pthread_creta最后还是需要使用 NPTL的pthread_creta函数,xenomai只是去扩展NPTL pthread_creta创建的线程,使这个线程在实时内核调度。
创建一个实时线程的时候,应用程序调用libcobalt实现的pthread_creta函数,做一些初始工作,libcobalt最后会去调用NPTL的pthread_creta来创建线程,同一个函数pthread_creta,三者之间是怎样区分的?下面一一解析
以pthread_creta函数开始解析cobalt内核线程创建流程。pthread_creta在pthread.h文件中定义如下:
COBALT_DECL(int, pthread_create(pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *),
void *arg));
COBALT_DECL宏在wrappers.h中如下,展开上面宏,会为pthread_create生成三个类型函数:
#define __WRAP(call) __wrap_ ## call
#define __STD(call) __real_ ## call
#define __COBALT(call) __cobalt_ ## call
#define __RT(call) __COBALT(call)
#define COBALT_DECL(T, P) \
__typeof__(T) __RT(P); \
__typeof__(T) __STD(P); \
__typeof__(T) __WRAP(P)
int __cobalt_pthread_create(pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *),
void *arg);
int __wrap_pthread_create(pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *),
void *arg);
int __real_pthread_create(pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *),
void *arg);
这三种类型的pthread_create函数为:
__RT(P):__cobalt_pthread_create 表示Cobalt实现的POSIX函数
__STD(P):__real_pthread_create表示原始的POSIX函数(glibc实现),cobalt库内部用来调用原始的POSIX函数(glibc NPTL)
__WRAP(P):__wrap_pthread_create是__cobalt_pthread_create 的弱别名,可以被覆盖
最后一种,外部库应提供其自己的__wrap_pthread_create()实现,来覆盖Cobalt实现的pthread_create ()版本。 原始的Cobalt实现仍可以引用为__COBALT(pthread_create )。由宏COBALT_IMPL来定义别名:
#define COBALT_IMPL(T, I, A) \ __typeof__(T) __wrap_ ## I A __attribute__((alias("__cobalt_" __stringify(I)), weak)); \ __typeof__(T) __cobalt_ ## I A
最后cobalt库函数pthread_create主体为(xenomai3.0.8\lib\cobalt\thread.c):
COBALT_IMPL(int, pthread_create, (pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *), void *arg))
{
pthread_attr_ex_t attr_ex;
......
return pthread_create_ex(ptid_r, &attr_ex, start, arg);
}
COBALT_IMPL定义了__cobalt_pthread_create 函数及该函数的一个弱别名__wrap_pthread_create,调用这两个函数执行的是同一个函数体。
对于 NPTL函数pthread_create,在Cobalt库里被定义为__real_pthread_create,其实只是NPTL pthread_create的封装,__real_pthread_create直接调用 NPTL pthread_create,在lib\cobalt\wrappers.c实现如下:
__weak
int __real_pthread_create(pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t * attr,
void *(*start) (void *), void *arg)
{
return pthread_create(ptid_r, attr, start, arg);
}
libcobalt调用NPTL的pthread_create完成线程创建时,使用_STD宏就可以,如下:
ret = __STD(pthread_create(&lptid, &attr, cobalt_thread_trampoline, &iargs));
if (ret) {
__STD(sem_destroy(&iargs.sync));
return ret;
}
2 阶段1 linux线程创建
pthread_create 不是一个系统调用,是实时线程库libcobalt的一个函数,为方便区分,对于一个POSIX函数 func,libCobalt实现的POSIX函数用__RT(func)表示,libc中的实现使用__STD(func)表示(xenomai3.0.8\lib\cobalt\thread.c):
COBALT_IMPL(int, pthread_create, (pthread_t *ptid_r,
const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start) (void *), void *arg))
{
pthread_attr_ex_t attr_ex;
struct sched_param param;
int policy;
if (attr == NULL)
attr = &default_attr_ex.std;
memcpy(&attr_ex.std, attr, sizeof(*attr));
pthread_attr_getschedpolicy(attr, &policy);
attr_ex.nonstd.sched_policy = policy;
pthread_attr_getschedparam(attr, ¶m);
attr_ex.nonstd.sched_param.sched_priority = param.sched_priority;
attr_ex.nonstd.personality = 0; /* Default: use Cobalt. */
return pthread_create_ex(ptid_r, &attr_ex, start, arg);
}
首先处理的是线程的属性参数attr。如果没有传入线程属性,就取默认值。
attr_ex表示Cobalt线程的属性,是pthread_attr_t 的扩展.
typedef struct pthread_attr_ex { pthread_attr_t std; struct { int personality; int sched_policy; struct sched_param_ex sched_param; } nonstd; } pthread_attr_ex_t;
根据线程属性attr获取Cobalt中对应的非标准policy。对调度参数也是同样。保存在attr_ex.nonstd中.attr_ex.nonstd.personality设置为0表示Cobalt.
根据attr获取到扩展的attr_ex后,调用pthread_create_ex进一步处理,从这里开始使用的都是attr_ex。那个标准的pthread_attr_t保存在attr_ex.std中,用户空间线程的创建还需要调用NTPL的pthread_create去完成,attr还需要用到。
为方便下面解析,说一下xenomai如何通过__STD(pthread_create)达到创建由Cobalt调度的线程的:首先通过__STD(pthread_create)创建一个普通线程,但其线程函数不是调用__RT(pthread_create)时传入的start函数,而是xenomai的设计的cobalt_thread_trampoline,当__STD(pthread_create)结合linux创建出线程后,该线程得到运行时就会执行cobalt_thread_trampoline,再由cobalt_thread_trampoline发起Cobalt内核系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_create,来完成Cobalt实时线程创建,并在实时内核上调度,当系统调用返回后真正从start函数开始执行。
在pthread_create_ex()中,用于给cobalt_thread_trampoline传递参数的结构体变量为struct pthread_iargs iargs。
struct pthread_iargs { struct sched_param_ex param_ex; int policy; //调度策略 int personality; // void *(*start)(void *);//线程执行函数 void *arg;//函数参数指针 int parent_prio;//父进程的优先级 sem_t sync;//线程创建完成同步信号 int ret; };
在调用__STD(pthread_create)之前主要填充iargs成员变量,首先通过系统调用去获取当前线程在Cobalt核中的扩展调度策略。
pthread_getschedparam_ex(pthread_self(), &iargs.policy, &iargs.param_ex);
int pthread_getschedparam_ex(pthread_t thread,
int *restrict policy_r,
struct sched_param_ex *restrict param_ex)
{
struct sched_param short_param;
int ret;ret = -XENOMAI_SYSCALL3(sc_cobalt_thread_getschedparam_ex,
thread, policy_r, param_ex);
if (ret == ESRCH) {
ret = __STD(pthread_getschedparam(thread, policy_r, &short_param));
if (ret == 0)
param_ex->sched_priority = short_param.sched_priority;
}return ret;
}
如果发起创建线程的已经是一个Cobalt的实时线程,那么系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_getschedparam_ex会拷贝一份该任务的调度参数,否则这个任务只是普通的linux任务,就需要通过NTPL的pthread_getschedparam来获取。
iargs.start = start;
iargs.arg = arg;
iargs.ret = EAGAIN;
__STD(sem_init(&iargs.sync, 0, 0));
ret = __STD(pthread_create(&lptid, &attr, cobalt_thread_trampoline, &iargs));/*__STD 调用标准库的函数*/
if (ret) {
__STD(sem_destroy(&iargs.sync));
return ret;
}
__STD(clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &timeout));
timeout.tv_sec += 5;
timeout.tv_nsec = 0;
for (;;) {
ret = __STD(sem_timedwait(&iargs.sync, &timeout));/*等待实时线程创建完成*/
if (ret && errno == EINTR)
continue;
if (ret == 0) {
ret = iargs.ret;
if (ret == 0)
*ptid_r = lptid;/*传出线程ID*/
break;
} else if (errno == ETIMEDOUT) {
ret = EAGAIN;
break;
}
ret = -errno;
panic("regular sem_wait() failed with %s", symerror(ret));
}
__STD(sem_destroy(&iargs.sync));/*销毁信号量*/
cobalt_thread_harden(); /* May fail if regular thread. */
return ret;
先初始化同步信号iargs.sync,当调用__STD(pthread_create)后父线程继续执行,等待实时线程创建完毕,实时线程创建完成时会释放iargs.sync信号量,并通过iargs.ret传出返回值。
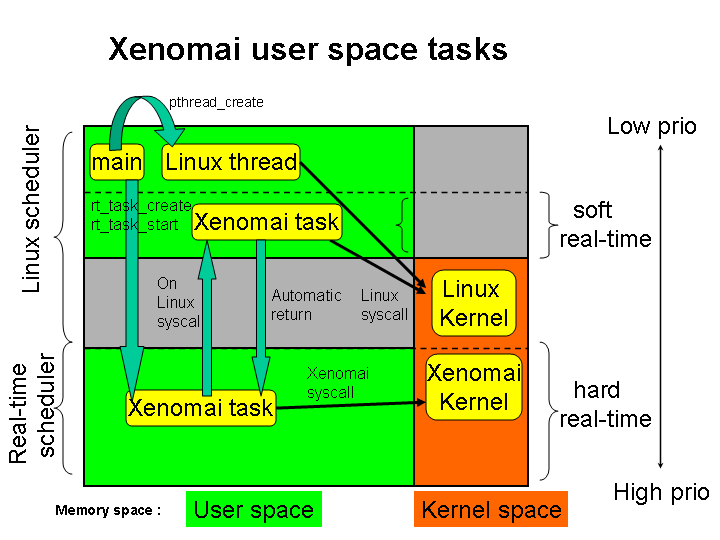
__STD(pthread_create(&lptid, &attr, cobalt_thread_trampoline, &iargs))先在用户态分配线程栈后发起linux 的clone系统调用进行内核态调度实体创建。完成创建后内核发生调度,当该线程得到运行时,开始执行cobalt_thread_trampoline函数。另linux线程与进程创建流程区别如下(下图来源于网络);

3 阶段2 Cobalt内核创建线程
I-pipe促进了实时内核细粒度的管理每线程,而不是每个进程。 由于这个原因,实时核心至少应该实现一种机制,将常规任务转换为具有扩展功能的实时线程,并将其绑定到Cobalt。
下面开始在cobalt内核创建实时线程调度实体。普通线程创建完成后,cobalt_thread_trampoline得到得到执行,根据传入的iargs,进一步发起Cobalt内核系统调用,由于从root域发起系统调用,通过ipipe 慢速系统调用入口ipipe_syscall_hook()进入,检查该系统调用的控制权限,允许非实时任务从linux域直接调用,然后执行Cobalt内核创建实时线程调度实体函数cobalt_thread ,关于系统调用7. Linux内核系统调用与实时内核系统调用
ipipe_handle_syscall()
__ipipe_notify_syscall()
ipipe_syscall_hook()
handle_head_syscall()
cobalt_search_process()/**/
ipipe_syscall_hook()
CoBaLt_thread_create()
/*
policy :调度策略
param_ex:扩展参数
struct sched_param_ex {
int sched_priority; //优先级
union {
struct __sched_ss_param ss; //SPORADIC调度类参数ss
struct __sched_rr_param rr; //调度类rr
struct __sched_tp_param tp; //调度类 tp
struct __sched_quota_param quota;//调度类quota
} sched_u;
};
personality:cobalt
*/
ret = -XENOMAI_SYSCALL5(sc_cobalt_thread_create, ptid,
policy, ¶m_ex, personality, &u_winoff);
该系统调用位于kernel\xenomai\posix\thread.c:
COBALT_SYSCALL(thread_create, init,
(unsigned long pth, int policy,
struct sched_param_ex __user *u_param,
int xid,
__u32 __user *u_winoff))
{
struct sched_param_ex param_ex;
ret = cobalt_copy_from_user(¶m_ex, u_param, sizeof(param_ex));
......
return __cobalt_thread_create(pth, policy, ¶m_ex, xid, u_winoff);
}
将调度参数从用户空间拷贝到param_ex,接着调用__cobalt_thread_create进行创建。
int __cobalt_thread_create(unsigned long pth, int policy,
struct sched_param_ex *param_ex,
int xid, __u32 __user *u_winoff)
{
struct cobalt_thread *thread = NULL;
struct task_struct *p = current;
struct cobalt_local_hkey hkey;
int ret;
/*
* We have been passed the pthread_t identifier the user-space
* Cobalt library has assigned to our caller; we'll index our
* internal pthread_t descriptor in kernel space on it.
*/
hkey.u_pth = pth;
hkey.mm = p->mm;
ret = pthread_create(&thread, policy, param_ex, p);/*创建线程*/
......
ret = cobalt_map_user(&thread->threadbase, u_winoff);/*在用户任务上创建影子线程上下文。*/
......
if (!thread_hash(&hkey, thread, task_pid_vnr(p))) {
goto fail;
}
thread->hkey = hkey;
if (xid > 0 && cobalt_push_personality(xid) == NULL) {
goto fail;
}
return xnthread_harden();
fail:
xnthread_cancel(&thread->threadbase);
return ret;
}
系统调用由该线程发起,所以内核中current指向该线程的task_struct。首先用hkey来保存该线程的用户空间线程ID pthread_t、该线程的内存管理结构current->mm,线程ID时整个系统中唯一不能重复的;
struct cobalt_local_hkey { /** pthread_t from userland. */ unsigned long u_pth; /** kernel mm context.*/ struct mm_struct *mm; };
hkey是用来做hash查找的,用hkey来快速查找对应的实时线程实体cobalt_thread 。举个例子,有个简单的需求,一个实时线程正运行在实时内核上,现需要修改线程的name,如果调用非实时的
thread_setname来修改,发起系统调用时ipipe发现这是一个linux的系统调用,需要调用linux的服务,就会触发双核间迁移,先迁移到linux内核,然后通过linux实现的thread_setname服务修改task_struct中的comm,修改完后再迁移到实时内核,整个过程代价就非常大。
避免这样的事发生,实时内核实现了内核调用
sc_cobalt_thread_setname,及libcobalt的__RT(thread_setname),libcobalt会先获取线程ID作为第一个参数来发起系统调用sc_cobalt_thread_setname,系统调用前后都是实时上下文,无需内核间切换,实时内核直接根据hkey快速得到实时内核的调度实体cobalt_thread,再得到host_task,接着修改host_task的comm成员。
//xenomai3.0.8\lib\cobalt\thread.c COBALT_IMPL(int, pthread_setname_np, (pthread_t thread, const char *name)) { return -XENOMAI_SYSCALL2(sc_cobalt_thread_setname, thread, name); }
COBALT_SYSCALL(thread_setname, current, (unsigned long pth, const char __user *u_name)) { struct cobalt_local_hkey hkey; struct cobalt_thread *thread; char name[XNOBJECT_NAME_LEN]; struct task_struct *p; ...... if (cobalt_strncpy_from_user(name, u_name, sizeof(name) - 1) < 0) ...... name[sizeof(name) - 1] = '\0'; hkey.u_pth = pth; hkey.mm = current->mm; ...... thread = thread_lookup(&hkey); ...... p = xnthread_host_task(&thread->threadbase); ...... knamecpy(p->comm, name); ...... return 0; }
3.1 初始化cobalt_thread->threadbase
接下来调用pthread_create(&thread, policy, param_ex, p)进行实时内核调度实体cobalt_thread 的创建。
static int pthread_create(struct cobalt_thread **thread_p,
int policy,
const struct sched_param_ex *param_ex,
struct task_struct *task)
{
struct xnsched_class *sched_class;
union xnsched_policy_param param;
struct xnthread_init_attr iattr;
struct cobalt_thread *thread;
xnticks_t tslice;
int ret, n;
spl_t s;
thread = xnmalloc(sizeof(*thread));
......
tslice = cobalt_time_slice; /*1000us *1000 */
sched_class = cobalt_sched_policy_param(¶m, policy,
param_ex, &tslice);/*根据参数获取调度类,设置调度参数*/
......
iattr.name = task->comm;
iattr.flags = XNUSER|XNFPU;
iattr.personality = &cobalt_personality; /*cobalt线程*/
iattr.affinity = CPU_MASK_ALL;
ret = xnthread_init(&thread->threadbase, &iattr, sched_class, ¶m);/*初始化xnthread*/
thread->magic = COBALT_THREAD_MAGIC;
xnsynch_init(&thread->monitor_synch, XNSYNCH_FIFO, NULL);
xnsynch_init(&thread->sigwait, XNSYNCH_FIFO, NULL);
sigemptyset(&thread->sigpending);
for (n = 0; n < _NSIG; n++)
INIT_LIST_HEAD(thread->sigqueues + n);
xnthread_set_slice(&thread->threadbase, tslice);/*设置线程时间切片信息*/
cobalt_set_extref(&thread->extref, NULL, NULL);
/*
* We need an anonymous registry entry to obtain a handle for
* fast mutex locking.
*/
ret = xnthread_register(&thread->threadbase, "");
xnlock_get_irqsave(&nklock, s);
list_add_tail(&thread->next, &cobalt_thread_list);/*添加到链表 cobalt_thread_list*/
xnlock_put_irqrestore(&nklock, s);
thread->hkey.u_pth = 0;
thread->hkey.mm = NULL;
*thread_p = thread;
return 0;
}
首先分配一个cobalt_thread,分配是从cobalt_heap中分配,cobalt_heap时Cobalt内核管理的一片内存空间。xenomai初始化时从linux分配而来。关于cobalt_heap,后面解析。
接下来根据用户设定的优先级,来决定调度类,默认只有xnsched_class_rt。其余调度类需内核编译时配置,详见11.2 调度策略与调度类小节。
21-24行iattr 先设置线程的属性attr;
struct xnthread_init_attr { struct xnthread_personality *personality; cpumask_t affinity; int flags; const char *name; };
该结构的成员定义如下:
-
name:代表线程符号名称的ASCII字符串。 。
-
flags:影响操作的一组创建标志。以下标志可以是此位掩码的一部分:
-
XNSUSP创建处于挂起状态的线程。在这种情况下,除了为它调用xnthread_start()之外,还应使用xnthread_resume()服务显式恢复该线程开始执行。调用xnthread_start()作为启动模式时,也可以指定此标志。
-
XNUSER 如果线程将映射到现有的用户空间任务,则应设置XNUSER。否则,将创建一个新的内核任务。
-
XNFPU(启用FPU)告诉Cobalt新线程可能使用浮点单元。即使未设置,也会隐式假设用户空间线程使用XNFPU。
-
-
affinity:此线程的处理器亲和性。传递CPU_MASK_ALL意味着允许内核将其分配到任意CPU上执行。传递空集无效。
xnthread_init->__xnthread_init()主要初始化结构体cobalt_thread各成员变量。
int __xnthread_init(struct xnthread *thread,
const struct xnthread_init_attr *attr,
struct xnsched *sched,
struct xnsched_class *sched_class,
const union xnsched_policy_param *sched_param)
{
int flags = attr->flags, ret, gravity;
......
thread->personality = attr->personality;/* xenomai_personality */
cpumask_and(&thread->affinity, &attr->affinity, &cobalt_cpu_affinity);
thread->sched = sched;
thread->state = flags;/*(XNROOT | XNFPU)*//*XNUSER|XNFPU*/
thread->info = 0;
thread->local_info = 0;
thread->lock_count = 0;
thread->rrperiod = XN_INFINITE;//0
thread->wchan = NULL;
thread->wwake = NULL;
thread->wcontext = NULL;
thread->res_count = 0;
thread->handle = XN_NO_HANDLE;
memset(&thread->stat, 0, sizeof(thread->stat));
thread->selector = NULL;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&thread->claimq);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&thread->glink);
/* These will be filled by xnthread_start() */
thread->entry = NULL;
thread->cookie = NULL;
init_completion(&thread->exited);
memset(xnthread_archtcb(thread), 0, sizeof(struct xnarchtcb));
/*初始化sched->rootc中xnthread里的定时器b*/
gravity = flags & XNUSER ? XNTIMER_UGRAVITY : XNTIMER_KGRAVITY;
xntimer_init(&thread->rtimer, &nkclock, timeout_handler,
sched, gravity); /*创建线程定时器*/
xntimer_set_name(&thread->rtimer, thread->name);
xntimer_set_priority(&thread->rtimer, XNTIMER_HIPRIO);
xntimer_init(&thread->ptimer, &nkclock, periodic_handler,
sched, gravity); /*创建线程周期定时器*/
xntimer_set_name(&thread->ptimer, thread->name);
xntimer_set_priority(&thread->ptimer, XNTIMER_HIPRIO);/*设置定时器优先级*/
thread->base_class = NULL; /* xnsched_set_policy() will set it. */
ret = xnsched_init_thread(thread);/**/
if (ret)
goto err_out;
初始化sched为当前cpu的xnsched,affinity为attr->affinity,flags为XNUSER|XNFPU;以及两个xntimer 。接下来进行调度相关初始化。
ret = xnsched_set_policy(thread, sched_class, sched_param);
/* Must be called with nklock locked, interrupts off. */
int xnsched_set_policy(struct xnthread *thread,
struct xnsched_class *sched_class,
const union xnsched_policy_param *p)
{
int ret;
/*
* Declaring a thread to a new scheduling class may fail, so
* we do that early, while the thread is still a member of the
* previous class. However, this also means that the
* declaration callback shall not do anything that might
* affect the previous class (such as touching thread->rlink
* for instance).
*/
if (sched_class != thread->base_class) {
ret = xnsched_declare(sched_class, thread, p);
......
}
/*
* As a special case, we may be called from __xnthread_init()
* with no previous scheduling class at all.
*/
if (likely(thread->base_class != NULL)) {
if (xnthread_test_state(thread, XNREADY))
xnsched_dequeue(thread);
if (sched_class != thread->base_class)
xnsched_forget(thread);
}
thread->sched_class = sched_class;
thread->base_class = sched_class;
xnsched_setparam(thread, p);
thread->bprio = thread->cprio;
thread->wprio = thread->cprio + sched_class->weight;
if (xnthread_test_state(thread, XNREADY))
xnsched_enqueue(thread);
if (!xnthread_test_state(thread, XNDORMANT))
xnsched_set_resched(thread->sched);
return 0;
}
如果将设置的sched_class与base_class不相同,则将该线程放到新的sched_class上。接下来如果已经属于某个调度类也就是base_classs不为空,而且处于就绪状态,则把该线程从base_classs的就绪队列中取下;接着如果sched_class与base_class不相同调用base_class的xnsched_forget将thread从调度类中删除。 从base_classs删除后,32-33行就可以设置新的sched_class了。
34行根据新的sched_class 设置该thread新的优先级及加权优先级,并将thead的状体位添加XNWEAK。
static inline void xnsched_setparam(struct xnthread *thread, const union xnsched_policy_param *p) { struct xnsched_class *sched_class = thread->sched_class; if (sched_class != &xnsched_class_idle) __xnsched_rt_setparam(thread, p); else __xnsched_idle_setparam(thread, p); thread->wprio = thread->cprio + sched_class->weight; } static inline void __xnsched_rt_setparam(struct xnthread *thread, const union xnsched_policy_param *p) { thread->cprio = p->rt.prio; if (!xnthread_test_state(thread, XNBOOST)) { if (thread->cprio) xnthread_clear_state(thread, XNWEAK); else xnthread_set_state(thread, XNWEAK); } }
初始化完成后,42行设置thread所属的那个xnsched重新调度标志XNRESCHED。
回到pthread_create()函数,接着初始化cobalt_thread信号相关成员sigpending和sigwait,同步资源xnsynch monitor_synch,关于同步资源13 xenomai线程间同步详细分析,设置默认时间片并启动循环定时器rrbtimer。
将cobalt_thread添加到全局链表cobalt_thread_list。
3.2 用户任务shadow线程上下文创建。
通过内核的pthread_create函数已经基本将实时调度实体初始化完毕,但还没有与linux的调度实体联系起来,也就是说虽然在实时内核已经创建了调度实体但是具体的实时程序的用户代码在哪实时内核一无所知。并且当该实时任务在实时内核运行时,需要将该任务的运行状态反映到linux空间。这样用户才能查询到实时任务的运行状态。
Cobalt中调度的实体称为linux空间的一个影子(show),cobalt_map_user函数将Xenomai线程映射到在用户空间中运行的常规Linux任务。底层Linux任务的优先级和调度类不受影响。
int cobalt_map_user(struct xnthread *thread, __u32 __user *u_winoff)
该函数接收两个参数,thread表示要映射到current的新影子线程的描述符地址,也就是xnthread,thread必须先前已通过调用xnthread_init()进行初始化。u_winoff是与thread关联的“u_window”结构在全局内存池(cobalt_kernel_ppd.umm.heap)中的与内存池起始地址的偏移量(关于xenomai xnheap详见14 xenomai内存池管理),libcobalt会将内核中cobalt_kernel_ppd.umm.heap起始地址映射到用户空间的cobalt_umm_shared,用户空间通过cobalt_umm_shared + u_winoff就可以访问该线程内核中的“u_window”结构 。从用户空间可见的线程状态信息通过此“u_window”结构通过共享内存方式获取。
if (!xnthread_test_state(thread, XNUSER))
return -EINVAL;
if (xnthread_current() || xnthread_test_state(thread, XNMAPPED))
return -EBUSY;
if (!access_wok(u_winoff, sizeof(*u_winoff)))
return -EFAULT;
首先判读该线程是不是用户线程,如果不是则报错。接着判断thread是否已经映射到一个线程任务,不能重复映射。接着判断用户空间地址u_winoff是否正常,否则发生错误。
umm = &cobalt_kernel_ppd.umm;
u_window = cobalt_umm_alloc(umm, sizeof(*u_window));
if (u_window == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
thread->u_window = u_window;
__xn_put_user(cobalt_umm_offset(umm, u_window), u_winoff);
从cobalt_kernel_ppd管理的一片与用户空间共享的内存umm里分配u_window结构,将该结构地址给thread->u_window,并且算出改地址到umm的基地址的偏移,将偏移值保存到用户空间地址u_winoff处。接下来处理task_struct。
xnthread_init_shadow_tcb(thread);
xnthread_init_shadow_tcb(thread),将linux管理的task_struct相关变量保存到thread->tcb,tcb结构如下
struct xntcb { struct task_struct *host_task; /*指向linux 管理task_struct*/ struct thread_struct *tsp; /*task_struct->thread线程切换时需要切换的寄存器*/ struct mm_struct *mm; /*用户空间任务内存管理 task_struct->mm*/ struct mm_struct *active_mm; struct thread_struct ts; #ifdef CONFIG_XENO_ARCH_WANT_TIP struct thread_info *tip; /*thread_info*/ #endif #ifdef CONFIG_XENO_ARCH_FPU struct task_struct *user_fpu_owner;/*浮点上下文*/ #endif }; struct xnarchtcb { struct xntcb core; #if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(4,8,0) unsigned long sp; unsigned long *spp; unsigned long ip; unsigned long *ipp; #endif #ifdef IPIPE_X86_FPU_EAGER struct fpu *kfpu; #else x86_fpustate *fpup; unsigned int root_used_math: 1; x86_fpustate *kfpu_state; #endif unsigned int root_kfpu: 1; struct { unsigned long ip; unsigned long ax; } mayday; };
在 task_struct 里面,有一个成员变量 thread。这里面保留了要切换进程的时候需要修改的寄存器。core.host_task指向task_struct,core.tsp指向task_struct里的thread,core.active_mm与core.mm都指向task_struct里的mm,core.tip指向task_struct中的thread_info.
xnthread_suspend(thread, XNRELAX, XN_INFINITE, XN_RELATIVE, NULL);
init_uthread_info(thread);
xnthread_set_state(thread, XNMAPPED);/*XNMAPPED 线程是映射到linux的任务 */
xnthread_run_handler(thread, map_thread);/*cobalt_thread_map*/
ipipe_enable_notifier(current);/*thread_info ->flags置位 TIP_NOTIFY*/
thread_info ->flags置位 TIP_NOTIFY.
下面启动启动线程,调用 xnthread_start(thread, &attr)启动线程.
int xnthread_start(struct xnthread *thread,
const struct xnthread_start_attr *attr)
{
spl_t s;
....
thread->entry = attr->entry;
thread->cookie = attr->cookie;
.......
if (xnthread_test_state(thread, XNUSER))
enlist_new_thread(thread);/*添加到链表 nkthreadq */
xnthread_resume(thread, XNDORMANT);
xnsched_run();
return 0;
}
设置线程入口entry与参数cookie,将thre添加到全局队列nkthreadq,接下来调用xnthread_resume()和xnsched_run(),根据标志位,均未进行任何操作。
返回到__cobalt_thread_create()函数接着处理。
3.3 绑定到Cobalt 内核
if (!thread_hash(&hkey, thread, task_pid_vnr(p))) {
ret = -EAGAIN;
goto fail;
}
thread->hkey = hkey;/*内核mm*/
return xnthread_harden();
将hkey加入local_thread_hash与global_thread_hash,并将该hkey保存到cobalt_thread->hkey。
到此全都初始化完毕,可以在xenomai域调度,由于是实时线程,优先级比linux高,创建完成应该先跑起来,调用xnthread_harden()迁移到head域运行,,在12 双核间任务迁移详细分析。
xnthread_harden()返回后,返回用户空间libCobalt中的函数cobalt_thread_trampoline继续运行执行。
ret = -XENOMAI_SYSCALL5(sc_cobalt_thread_create, ptid,
policy, ¶m_ex, personality, &u_winoff);
if (ret == 0)
cobalt_set_tsd(u_winoff);
/*
* We must access anything we'll need from *iargs before
* posting the sync semaphore, since our released parent could
* unwind the stack space onto which the iargs struct is laid
* on before we actually get the CPU back.
*/
sync_with_creator:
iargs->ret = ret;
__STD(sem_post(&iargs->sync));
if (ret)
return (void *)ret;
/*
* If the parent thread runs with the same priority as we do,
* then we should yield the CPU to it, to preserve the
* scheduling order.
*/
if (param_ex.sched_priority == parent_prio)
__STD(sched_yield());
cobalt_thread_harden();
retval = start(arg);/*开始执行真正的用户线程函数*/
pthread_setmode_np(PTHREAD_WARNSW, 0, NULL);
return retval;
}
系统调用返回0表示实时线程创建成功,cobalt_set_tsd设置线程数据tsd(TSD: Thread-Specific Data)
在单线程的程序里,有两种基本的数据:全局变量和局部变量。但在多线程程序里,还有第三种数据类型:线程数据(TSD: Thread-Specific Data)。它和全局变量很象,在线程内部,各个函数可以象使用全局变量一样调用它,但它对线程外部的其它线程是不可见的。例如我们常见的变量 errno,它返回标准的出错信息。它显然不能是一个局部变量,几乎每个函数都应该可以调用它;
cobalt_set_tsd使用系统调用sc_cobalt_get_current获取内核中的xnthread.handle结合u_winoff来设置,具体流程不展开。注意此时该线程处于head域。
接着调用glibc中的sem_post,发起linux系统调用,释放iargs->sync信号让阻塞的父线程继续执行。调用linux系统服务会发生head->root迁移,执行,后从Linux调用返回,此时线程处于root域。
由于处于root域,所以接着调用cobalt_thread_harden();发起Cobalt内核sc_cobalt_migrate系统调用(实时核心公开的专用系统调用),将线程切换至Cobalt调度(绑定到cobalt内核),到此该线程创建完毕,待cobalt调度后得到运行,返回用户空间以Cobalt线程的身份开始执行用户指定的线程函数start(arg)。
用户代码中会可能调用linux服务,这样还会发生很多次head>root->head的迁移。
4 总结
到此整个cobalt线程创建主流程如下:

- 先通过标准
pthread_creta()创建linux任务,任务执行入口为cobalt_thread_trampoline(); cobalt_thread_trampoline()中发起cobalt内核系统调用,创建cobalt调度任务实体;- 通过
cobalt_thread_harden()迁移到cobalt内核调度; - 执行真正的用户任务入口
start()函数。