logrotate command in Linux with examples
https://linuxconfig.org/logrotate
In Linux, many applications and system services will store log files. These log files give a Linux administrator insight into how their system is performing, and are invaluable when troubleshooting issues. However, log files can get unwieldy very quickly. For example, if your web server software logs every visit to your website, and you get thousands of viewers per day, there will be way too much information to feasibly squeeze into one text file.
That’s where the logrotate command in Linux comes into play. logrotate will periodically take the current log files, rename them, optionally compress them, and generate a fresh file to which an application can continue sending its logs. The logrotate command is invoked automatically from cron, and most services have their own log rotation configuration that is implemented when they’re installed. This configuration tells logrotate what it should do with the old log files. For example, how many of them should it keep around before deleting, should it compress the files, etc.
A system administrator can use the logrotate utility for their own needs as well. For example, if a Linux admin sets up a script to run, and has that script generating logs on a regular basis, it’s possible to set up logrotate to manage the log files for us. In this tutorial, you’ll learn more about the logrotate utility as we go through an example of configuring it to rotate the logs of a service we implement.
In this tutorial you will learn:
- How to use the logrotate command on Linux
- Where the logrotate configuration files are stored
- How to set up a custom logrotate configuration
- How to test a logrotate implementation
Frequently Used Options
logrotate is a handy tool for system administrators who wish to take the
/var/logdirectory under their control. The logrotate command is called daily by the cron scheduler and it reads the following files:
- The logrotate configuration file
/etc/logrotate.conf- Files in the logrotate configuration directory
/etc/logrotate.dMost of the services (Apache webserver, postgreSQL, MySql, KDE desktop manager etc.) installed on your system create a configuration file for logrotate in
/etc/logrotate.d. For example, here are the contents of our system’s/etc/logrotate.ddirectory:
Contents of the /etc/logrotate.d directory
logrotate command in Linux Basic Example
Let’s say that we are running a service called “linuxserver” that is creating logfiles called “linux.log” within the
/var/log/linuxserverdirectory. To include “linuxserver” log files in the log rotation we need to first create a logrotate configuration file and then copy it into the/etc/logrotate.ddirectory.The logrotate configuration file would look something like this:
/var/log/linuxserver/linux.log { rotate 7 daily compress delaycompress missingok notifempty create 660 linuxuser linuxuser }This config file will run daily, create a maximum of 7 archives owned by linuxuser and linuxuser group with 660 permissions, compress all logs and exclude only yesterdays and empty log files. Here are some selected logrotate configuration keywords. For a complete tutorial, check the logrotate man page.
daily Log files are rotated every day. weekly Log files are rotated if the current weekday is less than the weekday of the last rotation or if more than a week has passed since the last rotation. This is normally the same as rotating logs on the first day of the week, but if logrotate is not being run every night a log rotation will happen at the first valid opportunity. monthly Log files are rotated the first time logrotate is run in a month (this is normally on the first day of the month). notifempty Do not rotate the log if it is empty (this overrides the ifempty option). nocompress Old versions of log files are not compressed. delaycompress Postpone compression of the previous log file to the next rotation cycle. This only has effect when used in combination with compress. It can be used when some program cannot be told to close its logfile and thus might continue writing to the previous log file for some time. compress Old versions of log files are compressed with gzip by default. mail address When a log is rotated out of existence, it is mailed to address. If no mail should be generated by a particular log, the nomail directive may be used. missingok If the log file is missing, go on to the next one without issuing an error message.
Implement logrotate configuration file
Once your config file is ready, just simply copy it into the logrotate directory and change owner and permissions:
# cp linuxserver /etc/logrotate.d/ # chmod 644 /etc/logrotate.d/linuxserver # chown root.root /etc/logrotate.d/linuxserverNOTE
You can always use the man command to read more about the logrotate command and its official documentation. Click the previous link to see how to open the manual pages for any command on a Linux system.
Viewing the logrotate configuration files for various services on a Linux system
Advanced Usage
Once your logrotate configuration has been implemented, the cron scheduler on your system will invoke the command automatically so that logrotate can do its job. Ordinarily, users will not need to execute the logrotate command manually. However, the logrotate command can still be run manually in terminal and has a few different options you can use. Mostly this just boils down to testing out the configuration that you’ve implemented. Check the examples below to see how that works.
logrotate command in Linux Advanced Examples
- You can experiment with the log rotation (outside of the usual cron job) by forcing an execution of the logrotate in the absence of any log files to rotate. To do so, use the
-foption and specify the configuration file you wish to use.# logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.d/linuxserver- If you experience any problems, and wish to debug, you can use the
-doption with logrotate. This will simulate a “test run” and not actually make any changes. Instead, it will only output debug messages to help with troubleshooting.# logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/linuxserver- Use the
-voption to turn on verbosity. This will display messages during rotation so you can see exactly what’s going on.# logrotate -v /etc/logrotate.d/linuxserver
使用 Logrotate 旋转和压缩日志文件
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/626380094
logrotate 配置文件
logrotate 作为 cron 作业每天运行,遍历各种日志文件,轮换它们,并清除配置文件中定义的旧日志文件,您需要密切关注两个主要的配置源。
(1)/etc/logrotate.conf
这是 logrotate 工具的主要配置文件,它使用 include 指令来包含位于 /etc/logrotate.d 目录中的配置,让我们看一下配置文件。
$ cat /etc/logrotate.conf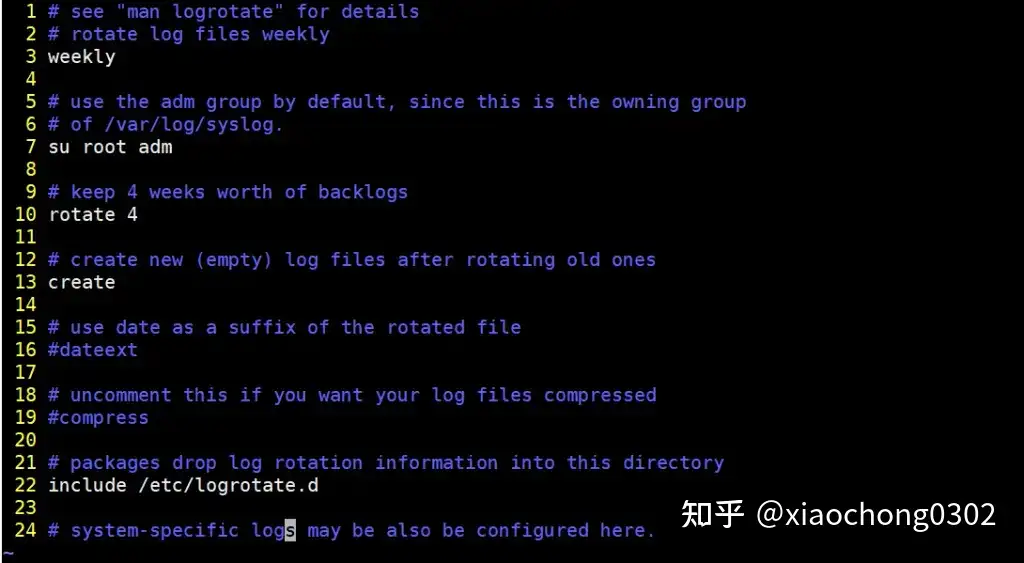
Logrotate-file-linux
(2)/etc/logrotate.d
这是一个目录,包含已安装包的日志配置,这些包的日志文件需要日志轮换。您还可能找到系统工具的配置文件,例如 apt & dpkg (用于 Debian 系统)、rsyslog、ufw 和 cups-daemon。
linuxtechi@ubuntu-server:~$ ls -l /etc/logrotate.d/ total 60 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 120 Sep 5 2019 alternatives -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 126 Dec 4 20:25 apport -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 173 Apr 9 11:21 apt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 91 Apr 1 10:49 bootlog -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 130 Jan 21 2019 btmp -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 181 Feb 17 08:19 cups-daemon -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 112 Sep 5 2019 dpkg -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 329 Feb 4 2019 nginx -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 94 Feb 8 2019 ppp -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 501 Mar 7 2019 rsyslog -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 677 Nov 29 02:08 speech-dispatcher -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 119 Mar 30 21:49 ubuntu-advantage-tools -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 178 Jan 21 22:16 ufw -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 235 Apr 13 23:37 unattended-upgrades -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 145 Feb 19 2018 wtmp linuxtechi@ubuntu-server:~$让我们看一下 dpkg 包管理器工具的配置文件
$ cat -n /etc/logrotate.d/dpkg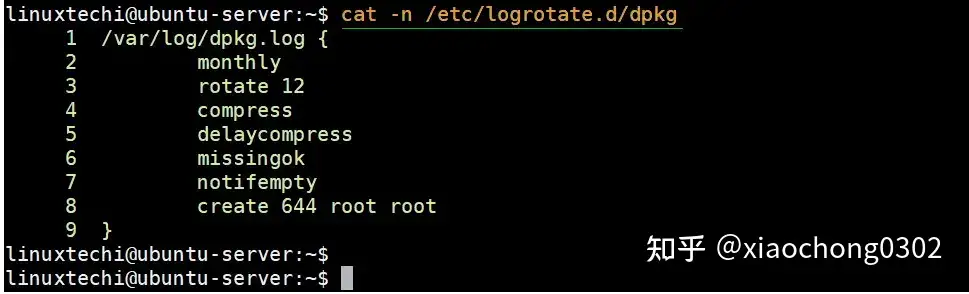
dpkg-logrotate-linux
标签:files,log,--,etc,logrotate,command,examples,root From: https://www.cnblogs.com/lightsong/p/17486701.html