一、string概念 之前介绍过通过字符数组保存字符串,然后对字符数组中的字符串做各种操作;为了更加简单方便,在C++中,又增加了 string 来处理字符串。
char str[20] = "hello world";string s1;
string s2 = "abc";string s1;//创建空字符串
string s2 = "abc";//创建字符串#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2 = "hello world";
cout << "s1:" << s1 << endl; //s1:
cout << "s2:" << s2 << endl; //s2:hello world
return 0;
}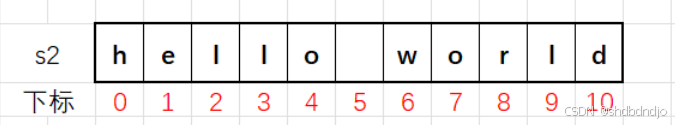 上面这个图,仅仅是字符串s2的示意图,实际上
string
类型的字符串比这个要复杂的多,我们可以大概这样去理解,更多的知识需要学习C++的类和对象的知识才能明白。
当然C++中的
string
创建的字符串和
char
类型的数组所表示的字符串还有一个区别,
string 类型的字符串对象可以直接赋值,比如:
上面这个图,仅仅是字符串s2的示意图,实际上
string
类型的字符串比这个要复杂的多,我们可以大概这样去理解,更多的知识需要学习C++的类和对象的知识才能明白。
当然C++中的
string
创建的字符串和
char
类型的数组所表示的字符串还有一个区别,
string 类型的字符串对象可以直接赋值,比如:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hehe");
s2 = s1;
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}除了以上创建字符串的写法外,C++中还有一些其他的创建字符串方式。如:
string s("hello world"); //等同于string s1 = "hello world";
string s1 = s; //⽤⼀个现成的字符串s,初始化另外⼀个字符串s1#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
//输入
cin >> s;
//输出
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);getline(cin, string str)
//cin -- 表⽰从输⼊流中读取信息
//str 是存放读取到的信息的字符串#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string name;
getline (cin, name);
cout << name << endl;
return 0;
}getline(cin, string str, char delim)
//cin -- 表⽰从输⼊流中读取信息
//str 是存放读取到的信息的字符串
//delim 是⾃定义的结束标志#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
string name;
getline (cin, name, 'q');
cout << name << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = "hello world";
string s3 = "12ab!~ ";
cout << "s:" << s.size() << endl;
cout << "s1:" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s2:" << s2.size() << endl;
cout << "s3:" << s3.size() << endl;
return 0;
}#incldue <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
int i = 0;
for(i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}4.迭代器(iterator)
迭代器是一种对象,它可以用来遍历容器(比如 string )中的元素,迭代器的作用类似于指针,或者数组下标。访问迭代器指向的值,需要解引用(*)。 C++ 中的 string 提供了多种迭代器,用于遍历和操作字符串中的内容。这里给大家介绍一种最常 用的迭代器。 begin() 和 end() begin() :返回指向字符串第一个字符的迭代器,需要一个迭代器的变量来接收。 end() :返回指向字符串最后一个字符的下一个位置的迭代器(该位置不属于字符串)。 string 中 begin() 和 end() 返回的迭代器的类型是 string::iterator 。 迭代器是可以进行大小比较,也可以进行 + 或者 - 整数运算的。 比如: it++ ,就是让迭代器前进一步, it-- 就是让迭代器退后一步。 同一个容器的两个迭代器也可以相减,相减结果的绝对值,是两个迭代器中间元素的个数。#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
string::iterator it1 = s.begin();
string::iterator it2 = s.end();
cout << (it1 < it2) << endl;
cout << it1 - it2 << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
//auto it 是让编译器⾃动推到it的类型
for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
//string::iterator 是正向迭代器类型
//string::iterator it,是直接创建迭代器,it是针对字符串的迭代器
for (string::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
for (string::iterator it = s.end() - 1; it >= s.begin(); --it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "abcdef";
cout << str << endl;
for (string::iterator it = str.begin(); it != str.end(); ++it)
{
*it = 'x';
}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//向空字符串中尾插字符
string s;
s.push_back('h');
s.push_back('e');
s.push_back('l');
s.push_back('l');
s.push_back('o');
cout << s << endl;
//向⾮空字符串中尾插字符
string s1 = "hello ";
s1.push_back('w');
s1.push_back('o');
s1.push_back('r');
s1.push_back('l');
s1.push_back('d');
cout << s1 << endl;
//批量插⼊字符
string s2;
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'f'; c++)
{
s2.push_back(c);
}
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello";
s += " world"; //字符串⽤双引号,等价于 s = s + " world"
cout << s << endl;
//除了+=操作,也可以使⽤'+'灵活进⾏字符串拼接
//1.尾部拼接
string s1 = "hello";
cout << s1 + " world" << endl; //s1仍然是"hello"
s1 = s1 + " world";
cout << s1 << endl; //s1是"hello world"
//2.头部拼接
string s2 = "hello";
s2 = "world " + s2 ;
cout << s2 << endl; //s2为:"world hello"
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello";
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
//尾删
s.pop_back();
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
//尾删
s.pop_back();
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
s.pop_back();
return 0;
} 在DevC++上,程序最终崩溃了。
为避免循环删除导致对空字符串进行尾删,可以将删除全部字符的代码写成:
在DevC++上,程序最终崩溃了。
为避免循环删除导致对空字符串进行尾删,可以将删除全部字符的代码写成:
#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abc";
while(s.size() > 0) //通过size()函数来控制字符串的⻓度
{
s.pop_back();
}
return 0;
}string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str); //pos位置前⾯插⼊⼀个string字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s); //pos位置前⾯插⼊⼀个C⻛格的字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c);//pos位置前⾯插⼊n个字符c#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdefghi";
string str = "xxx";
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(3, str);
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdefghi";
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(3, "xxx");
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdefghi";
cout << s << endl;
s.insert(3, 3, 'x');
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
//查找string类型的字符串str,默认是从头开始查找,pos可以指定位置开始
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//查找C⻛格的字符串s,默认是从头开始查找,pos可以指定位置开始
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
//在字符串的pos这个位置开始查找C⻛格的字符串s中的前n个字符,
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
//查找字符c,默认是从头开始,pos可以指定位置开始//代码1
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string str = "llo";
//查找string类型的字符串
size_t n = s.find(str);//省略第二个参数,默认为0,从头开始
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find(str, n + 1); //从n+1这个指定位置开始查找
cout << n << endl;
//查找C⻛格的字符串
n = s.find("llo");//省略第二个参数,默认为0,从头开始
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find("llo", n + 1); //从n+1这个指定位置开始查找
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}
//代码2
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
//在s中,0这个指定位置开始查找"word"中的前3个字符
size_t n = s.find("word", 0, 3);
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find("everyday", n+1, 5);
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}
//代码3
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
size_t n = s.find('o');
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find('o', n + 1);
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}
//查找不到的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string str = "bit";
size_t n = s.find(str);
cout << n << endl;
if(n != string::npos)
cout << "找到了,位置是:" << n << endl;
else
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
return 0;
}static const size_t npos = -1;#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//注意:npos是string中定义的,使⽤npos需要带上string::指明是string类中的
cout << "npos:" << string::npos << endl;
//npos:18446744073709551615
return 0;
}string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
//pos 的默认值是0,也就是从下标为0的位置开始截取
//len 的默认值是npos,意思是⼀直截取到字符串的末尾#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string s1 = s.substr(7);
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2 = s.substr(7, 6);
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头⽂件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
size_t n = s.find("world");
string s2 = s.substr(n, 10);
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "abcd";
char s3[] = "abcdef"; //C⻛格的字符串
(1) s1 == s2
bool operator== (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 == s2
bool operator== (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 == s1
bool operator== (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 == s3
(2) s1 != s2
bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 != s2
bool operator!= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 != s1
bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 != s3
(3) s1 < s2
bool operator< (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 < s2
bool operator< (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 < s1
bool operator< (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 < s3
(4) s1 <= s2
bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 <= s2
bool operator<= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 <= s1
bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 <= s3
(5) s1 > s2
bool operator> (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 > s2
bool operator> (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 > s1
bool operator> (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 > s3
(6) s1 >= s2
bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 >= s2
bool operator>= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s3 >= s1
bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使⽤⽅式:s1 >= s3"abc" < "aq" //'b'的ascii码值是⼩于'q'的
"abcdef" < "ff" //'a'的ASCII码值是⼩于'f'的
"100" < "9" //'1'的ASCII码值是⼩于'9'的#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string s2 = "hello";
if (s1 == (s2 + " world"))
{
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "abcd";
string s2 = "abbcdef";
char s3[] = "bbc";
if (s1 > s2)
cout << "s1 > s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 <= s2" << endl;
if (s1 == s2)
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
if (s1 <= s3)
cout << "s1 <= s3" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 > s3" << endl;
return 0;
}int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);
long stol (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
size_t pos = 0;
string s1 = "11x34";
int ret1 = stoi(s1, &pos, 16);
cout << ret1 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
string s2 = "11x34";
int ret2 = stoi(s2, &pos, 2);
cout << ret2 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
string s3 = "0x11x34";
int ret3 = stoi(s3, &pos, 0);
cout << ret3 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
return 0;
}double stod (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);
float stof (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "3.14x456";
double ret = stod(s, NULL);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}string to_string (int val);
string to_string (long val);
string to_string (long long val);
string to_string (unsigned val);
string to_string (unsigned long val);
string to_string (unsigned long long val);
string to_string (float val);
string to_string (double val);
string to_string (long double val);#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string pi = "pi is " + to_string(3.14159);
cout << pi << endl;
return 0;
}