前言
嗨喽~大家好呀,这里是魔王呐 !

环境介绍:
-
python 3.6
-
pycharm
爬虫部分使用模块:
-
csv
-
requests >>> pip install requests
-
parsel
如何安装python第三方模块:
- win + R 输入 cmd 点击确定, 输入安装命令 pip install 模块名 (pip install requests) 回车
- 在pycharm中点击Terminal(终端) 输入安装命令

数据可视化使用模块:
-
pyecharts
-
pandas
本节课程的案例流程思路:
一. 网站数据来源查询:
-
确定一下目标需求: 爬取猫咪交易网站数据 做一个数据可视化图
-
去网站 : 地区 ...
-
如果想要在网页上抓包 找一些数据来源 都是要通过开发者工具 F12/ 鼠标右键点击检查
- 可以直接复制想要数据内容在开发者工具进行搜索

二. 代码实现步骤
-
请求 http://www.maomijiaoyi.com/index.php?/chanpinliebiao_c_2.html 获取 猫咪的详情页url地址以及地区
-
请求 猫咪的详情页url地址 获取猫咪详情信息数据
-
保存数据 到CSV文件
-
数据可视化

采集代码
获取源码链接点击
import requests # 第三方模块 需要 pip install requests 发送请求
import parsel # 解析模块 pip install parsel
import csv # 内置模块 不需要大家安装
f = open('猫咪.csv', mode='a', encoding='utf-8', newline='')
csv_writer = csv.DictWriter(f, fieldnames=['地区', '店名', '标题', '价格', '浏览次数', '卖家承诺', '在售只数',
'年龄', '品种', '预防', '联系人', '联系方式', '异地运费', '是否纯种',
'猫咪性别', '驱虫情况', '能否视频', '详情页'])
# 写入表头
csv_writer.writeheader()
for page in range(1, 21):
print(f'===========================正在爬取第{page}页的数据内容==================================')

请求头: 把python代码伪装成 浏览器对服务器发送请求
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/89.0.4389.114 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
获取网页的文本数据 response.text json() 获取json字典数据
# print(response.text)
# 解析数据 获取 猫咪的详情页url地址以及地区
# 要把 网页文本数据转换成 parsel 解析的 对象
selector = parsel.Selector(response.text)
href = selector.css('div.content:nth-child(1) a::attr(href)').getall()
areas = selector.css('div.content:nth-child(1) .area .color_333::text').getall()
# 列表推导式
areas = [i.strip() for i in areas]
# 需要把两个列表合成一个列表 遍历循环提取每一个元素
zip_data = zip(href, areas)
for index in zip_data:
css选择器: 根据标签提取数据内容
getall() 返回的是列表
get() 是返回的字符串

response_1 = requests.get(url=index_url, headers=headers)
selector_1 = parsel.Selector(response_1.text)
area = index[1]
# get() 取一个 返回是字符串 strip() 字符串的方法
title = selector_1.css('.detail_text .title::text').get().strip() # 标题
shop = selector_1.css('.dinming::text').get().strip() # 店名
price = selector_1.css('.info1 div:nth-child(1) span.red.size_24::text').get() # 价格
views = selector_1.css('.info1 div:nth-child(1) span:nth-child(4)::text').get() # 浏览次数
# replace() 替换
promise = selector_1.css('.info1 div:nth-child(2) span::text').get().replace('卖家承诺: ', '') # 浏览次数
num = selector_1.css('.info2 div:nth-child(1) div.red::text').get() # 在售只数
age = selector_1.css('.info2 div:nth-child(2) div.red::text').get() # 年龄
kind = selector_1.css('.info2 div:nth-child(3) div.red::text').get() # 品种
prevention = selector_1.css('.info2 div:nth-child(4) div.red::text').get() # 预防
person = selector_1.css('div.detail_text .user_info div:nth-child(1) .c333::text').get() # 联系人
phone = selector_1.css('div.detail_text .user_info div:nth-child(2) .c333::text').get() # 联系方式
postage = selector_1.css('div.detail_text .user_info div:nth-child(3) .c333::text').get().strip() # 包邮
purebred = selector_1.css('.xinxi_neirong div:nth-child(1) .item_neirong div:nth-child(1) .c333::text').get().strip() # 是否纯种
sex = selector_1.css('.xinxi_neirong div:nth-child(1) .item_neirong div:nth-child(4) .c333::text').get().strip() # 猫咪性别
video = selector_1.css('.xinxi_neirong div:nth-child(2) .item_neirong div:nth-child(4) .c333::text').get().strip() # 能否视频
worming = selector_1.css('.xinxi_neirong div:nth-child(2) .item_neirong div:nth-child(2) .c333::text').get().strip() # 是否驱虫
dit = {
'地区': area,
'店名': shop,
'标题': title,
'价格': price,
'浏览次数': views,
'卖家承诺': promise,
'在售只数': num,
'年龄': age,
'品种': kind,
'预防': prevention,
'联系人': person,
'联系方式': phone,
'异地运费': postage,
'是否纯种': purebred,
'猫咪性别': sex,
'驱虫情况': worming,
'能否视频': video,
}
csv_writer.writerow(dit)
print(title, area, shop, price, views, promise, num, age,
kind, prevention, person, phone, postage, purebred, sex, video, worming, index_url, sep=' | ')

可视化代码
获取源码链接点击
import pandas as pd
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None)
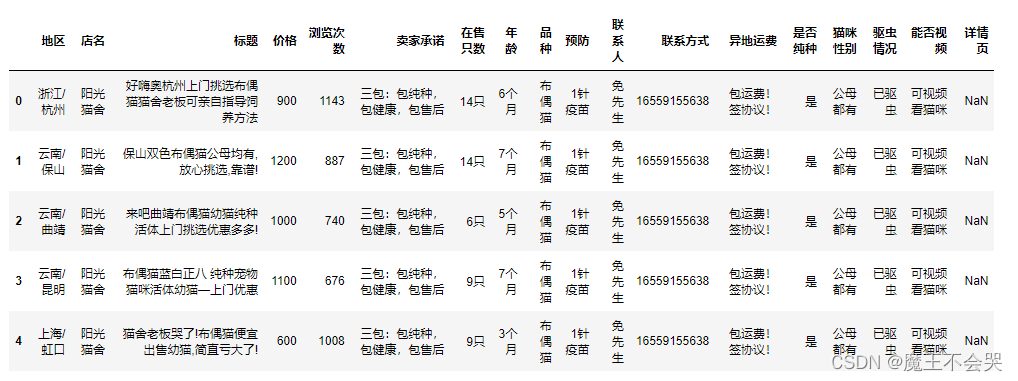
cat_info = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\青灯教育\Desktop\猫咪.csv', encoding='utf-8', engine='python')
cat_info.head(5)
cat_info['地区'] = cat_info['地区'].astype(str)
cat_info['province'] = cat_info['地区'].map(lambda s: s.split('/')[0])
pv = cat_info['province'].value_counts().reset_index()
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Map
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
c = (
Map(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
.add("", [list(z) for z in zip(list(pv['index']), list(pv['province']))], "china")
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="猫猫售卖省份分布"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(max_=16500, is_piecewise=True),
)
)
c.render_notebook()
# 交易品种占比树状图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import TreeMap
pingzhong = cat_info['品种'].value_counts().reset_index()
data = [{'value':i[1],'name':i[0]} for i in zip(list(pingzhong['index']),list(pingzhong['品种']))]
c = (
TreeMap(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
.add("", data)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title=""))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position="inside"))
)
c.render_notebook()

#
price = cat_info.groupby('品种').mean()['价格'].reset_index()
price['价格'] = round(price['价格'],0)
price = price.sort_values(by='价格')
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import PictorialBar
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
location = list(price['品种'])
values = list(price['价格'])
c = (
PictorialBar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
.add_xaxis(location)
.add_yaxis(
"",
values,
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
symbol_size=18,
symbol_repeat="fixed",
symbol_offset=[0, 0],
is_symbol_clip=True,
symbol=SymbolType.ROUND_RECT,
)
.reversal_axis()
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="均价排名"),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(is_show=False),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
axistick_opts=opts.AxisTickOpts(is_show=False),
axisline_opts=opts.AxisLineOpts(
linestyle_opts=opts.LineStyleOpts(opacity=0),
),
),
)
.set_series_opts(
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(position='insideRight')
)
)
c.render_notebook()

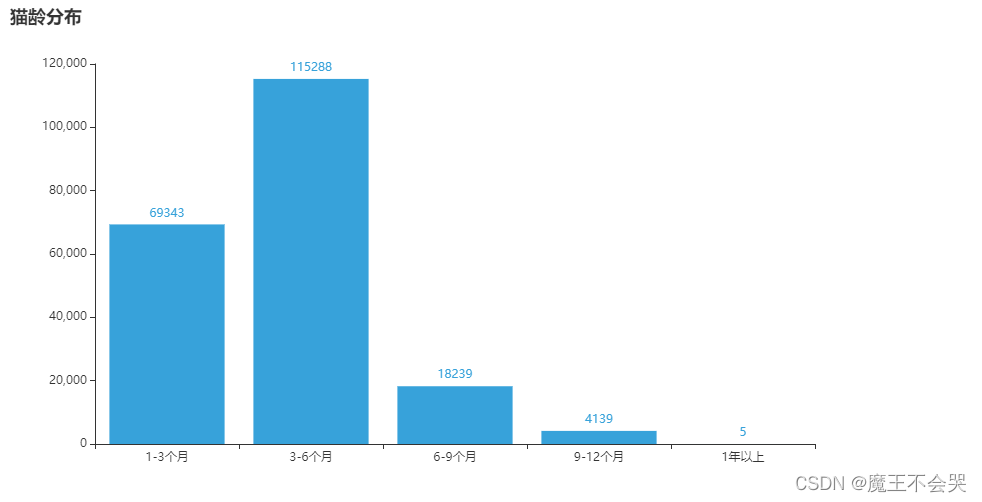
# 年龄分布,柱状图
cat_info['年龄'] = cat_info['年龄'].astype(str)
age = cat_info['年龄'].map(lambda x: x.replace('个月','')).reset_index()
def ages(s):
if s == 'nan':
return s
s = int(s)
if 1 <= s < 3:
return '1-3个月'
if 3 <= s < 6:
return '3-6个月'
if 6 <= s < 9:
return '6-9个月'
if 9 <= s < 12 :
return '9-12个月'
if s >= 12:
return '1年以上'
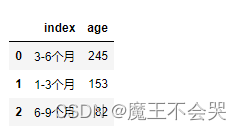
age['age'] = age['年龄'].map(ages)
age = age['age'].value_counts().reset_index()
age = age[age['index'] != 'nan']
age
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.faker import Faker
x = ['1-3个月','3-6个月','6-9个月','9-12个月','1年以上']
y = [69343,115288,18239,4139,5]
c = (
Bar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
.add_xaxis(x)
.add_yaxis('', y)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="猫龄分布"))
)
c.render_notebook()
## 浏览次数是否跟价格成正比,散点图
view = cat_info['浏览次数']
money = cat_info['价格']
import pyecharts.options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Scatter
x_data = list(view)[:1000]
y_data = list(money)[:1000]
c = (
Scatter(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
.add_xaxis(xaxis_data=x_data)
.add_yaxis(
series_name="",
y_axis=y_data,
symbol_size=20,
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False),
)
.set_series_opts()
.set_global_opts(
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
type_="value",
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True),
name='浏览次数'
),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(
type_="value",
axistick_opts=opts.AxisTickOpts(is_show=True),
splitline_opts=opts.SplitLineOpts(is_show=True),
name='价格'
),
tooltip_opts=opts.TooltipOpts(is_show=False),
)
)
c.render_notebook()

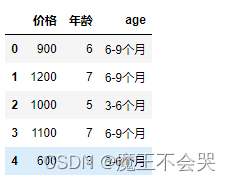
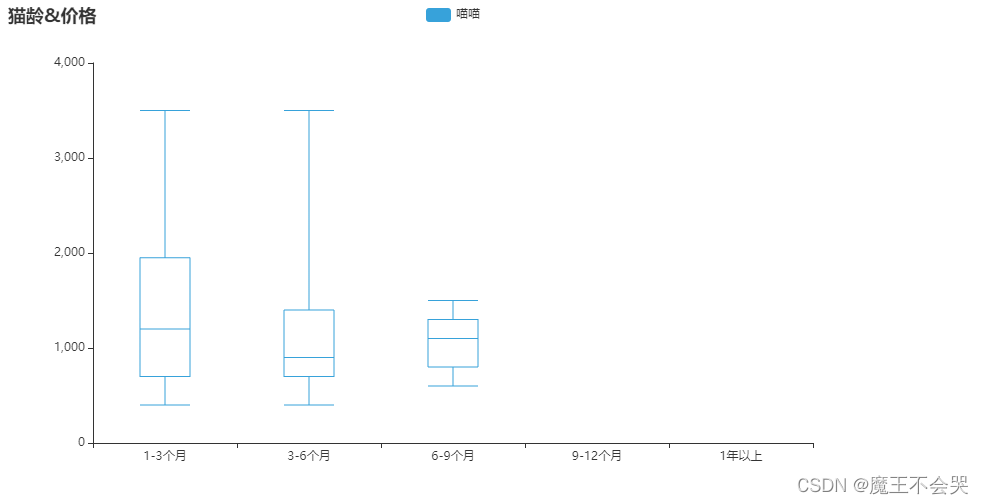
# 价格是否与年龄有关,箱型图
a_p = cat_info[['价格','年龄']]
a_p['年龄'] = a_p['年龄'].map(lambda x: x.replace('个月',''))
def ages(s):
if s == 'nan':
return s
s = int(s)
if 1 <= s < 3:
return '1-3个月'
if 3 <= s < 6:
return '3-6个月'
if 6 <= s < 9:
return '6-9个月'
if 9 <= s < 12 :
return '9-12个月'
if s >= 12:
return '1年以上'
a_p['age'] = a_p['年龄'].map(ages)
a_p.head()
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Boxplot
v1 = [
list(a_p[a_p['age'] == '1-3个月']['价格']),
list(a_p[a_p['age'] == '3-6个月']['价格']),
list(a_p[a_p['age'] == '6-9个月']['价格']),
list(a_p[a_p['age'] == '9-12个月']['价格']),
list(a_p[a_p['age'] == '1年以上']['价格'])
]
c = Boxplot(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(theme=ThemeType.LIGHT))
c.add_xaxis(["1-3个月", "3-6个月",'6-9个月','9-12个月','1年以上'])
c.add_yaxis("喵喵", c.prepare_data(v1))
c.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="猫龄&价格"))
c.render_notebook()

尾语
没有太晚的开始,不如就从今天行动。
总有一天,那个一点一点可见的未来,
会在你心里,也在你的脚下慢慢清透。
生活,从不亏待每一个努力向上的人。
—— 心灵鸡汤
本文章到这里就结束啦~感兴趣的小伙伴可以复制代码去试试哦
标签:python,猫咪,child,selector,nth,可视化,text,div,opts From: https://www.cnblogs.com/Qqun261823976/p/16757971.html